
biomcp
BioMCP: Biomedical Model Context Protocol
Stars: 419
BioMCP is an open source toolkit that empowers AI assistants and agents with specialized biomedical knowledge. It follows the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to connect AI systems to authoritative biomedical data sources, enabling precise answers about clinical trials, scientific literature, and genomic variants. It provides structured access to various biomedical data sources, supports natural language queries, and functions as an MCP server for AI assistants and agents. BioMCP integrates with literature sources like PubMed and bioRxiv, clinical and genomic sources like ClinicalTrials.gov and MyVariant.info, and regulatory and safety sources like OpenFDA. It offers 24 specialized tools for biomedical research, including core tools like Think Tool, Search Tool, and Fetch Tool, as well as individual tools for articles, trials, variants, NCI-specific data, genes, diseases, and drugs. BioMCP can be run locally or as an HTTP server, supports Docker deployment, and provides a comprehensive CLI for database interaction.
README:
Version 0.7.2 is the final release of the Python-based BioMCP server. The project has been re-architected in Rust to be more agent-friendly — using fewer tokens, consuming less context window, running faster, and adding new data sources. The Python source code is preserved here under the
v0.7.2tag.
BioMCP is an open source (MIT License) toolkit that empowers AI assistants and agents with specialized biomedical knowledge. Built following the Model Context Protocol (MCP), it connects AI systems to authoritative biomedical data sources, enabling them to answer questions about clinical trials, scientific literature, and genomic variants with precision and depth.
BioMCP is certified by MCPHub. This certification ensures that BioMCP follows best practices for Model Context Protocol implementation and provides reliable biomedical data access.
While Large Language Models have broad general knowledge, they often lack specialized domain-specific information or access to up-to-date resources. BioMCP bridges this gap for biomedicine by:
- Providing structured access to clinical trials, biomedical literature, and genomic variants
- Enabling natural language queries to specialized databases without requiring knowledge of their specific syntax
- Supporting biomedical research workflows through a consistent interface
- Functioning as an MCP server for AI assistants and agents
BioMCP integrates with multiple biomedical data sources:
- PubTator3/PubMed - Peer-reviewed biomedical literature with entity annotations
- bioRxiv/medRxiv - Preprint servers for biology and health sciences
- Europe PMC - Open science platform including preprints
- ClinicalTrials.gov - Clinical trial registry and results database
-
NCI Clinical Trials Search API - National Cancer Institute's curated cancer trials database
- Advanced search filters (biomarkers, prior therapies, brain metastases)
- Organization and intervention databases
- Disease vocabulary with synonyms
-
BioThings Suite - Comprehensive biomedical data APIs:
- MyVariant.info - Consolidated genetic variant annotation
- MyGene.info - Real-time gene annotations and information
- MyDisease.info - Disease ontology and synonym information
- MyChem.info - Drug/chemical annotations and properties
- TCGA/GDC - The Cancer Genome Atlas for cancer variant data
- 1000 Genomes - Population frequency data via Ensembl
- cBioPortal - Cancer genomics portal with mutation occurrence data
-
OncoKB - Precision oncology knowledge base for clinical variant interpretation (demo server with BRAF, ROS1, TP53)
- Therapeutic implications and FDA-approved treatments
- Oncogenicity and mutation effect annotations
- Works immediately without authentication
-
OpenFDA - FDA regulatory and safety data:
- Drug Adverse Events (FAERS) - Post-market drug safety reports
- Drug Labels (SPL) - Official prescribing information
- Device Events (MAUDE) - Medical device adverse events, with genomic device filtering
BioMCP provides 24 specialized tools for biomedical research:
CRITICAL: The think tool MUST be your first step for ANY biomedical research task.
# Start analysis with sequential thinking
think(
thought="Breaking down the query about BRAF mutations in melanoma...",
thoughtNumber=1,
totalThoughts=3,
nextThoughtNeeded=True
)The sequential thinking tool helps:
- Break down complex biomedical problems systematically
- Plan multi-step research approaches
- Track reasoning progress
- Ensure comprehensive analysis
The search tool supports two modes:
Use the query parameter with structured field syntax for powerful cross-domain searches:
# Simple natural language
search(query="BRAF melanoma")
# Field-specific search
search(query="gene:BRAF AND trials.condition:melanoma")
# Complex queries
search(query="gene:BRAF AND variants.significance:pathogenic AND articles.date:>2023")
# Get searchable fields schema
search(get_schema=True)
# Explain how a query is parsed
search(query="gene:BRAF", explain_query=True)Supported Fields:
-
Cross-domain:
gene:,variant:,disease: -
Trials:
trials.condition:,trials.phase:,trials.status:,trials.intervention: -
Articles:
articles.author:,articles.journal:,articles.date: -
Variants:
variants.significance:,variants.rsid:,variants.frequency:
Use the domain parameter with specific filters:
# Search articles (includes automatic cBioPortal integration)
search(domain="article", genes=["BRAF"], diseases=["melanoma"])
# Search with mutation-specific cBioPortal data
search(domain="article", genes=["BRAF"], keywords=["V600E"])
search(domain="article", genes=["SRSF2"], keywords=["F57*"]) # Wildcard patterns
# Search trials
search(domain="trial", conditions=["lung cancer"], phase="3")
# Search variants
search(domain="variant", gene="TP53", significance="pathogenic")Note: When searching articles with a gene parameter, cBioPortal data is automatically included:
- Gene-level summaries show mutation frequency across cancer studies
- Mutation-specific searches (e.g., "V600E") show study-level occurrence data
- Cancer types are dynamically resolved from cBioPortal API
Retrieve full details for a single article, trial, or variant:
# Fetch article details (supports both PMID and DOI)
fetch(domain="article", id="34567890") # PMID
fetch(domain="article", id="10.1101/2024.01.20.23288905") # DOI
# Fetch trial with all sections
fetch(domain="trial", id="NCT04280705", detail="all")
# Fetch variant details
fetch(domain="variant", id="rs113488022")Domain-specific options:
-
Articles:
detail="full"retrieves full text if available -
Trials:
detailcan be "protocol", "locations", "outcomes", "references", or "all" - Variants: Always returns full details
For users who prefer direct access to specific functionality, BioMCP also provides 21 individual tools:
- article_searcher: Search PubMed/PubTator3 and preprints
- article_getter: Fetch detailed article information (supports PMID and DOI)
- trial_searcher: Search ClinicalTrials.gov or NCI CTS API (via source parameter)
- trial_getter: Fetch all trial details from either source
- trial_protocol_getter: Fetch protocol information only (ClinicalTrials.gov)
- trial_references_getter: Fetch trial publications (ClinicalTrials.gov)
- trial_outcomes_getter: Fetch outcome measures and results (ClinicalTrials.gov)
- trial_locations_getter: Fetch site locations and contacts (ClinicalTrials.gov)
- variant_searcher: Search MyVariant.info database
- variant_getter: Fetch comprehensive variant details
- nci_organization_searcher: Search NCI's organization database
- nci_organization_getter: Get organization details by ID
- nci_intervention_searcher: Search NCI's intervention database (drugs, devices, procedures)
- nci_intervention_getter: Get intervention details by ID
- nci_biomarker_searcher: Search biomarkers used in trial eligibility criteria
- nci_disease_searcher: Search NCI's controlled vocabulary of cancer conditions
- gene_getter: Get real-time gene information from MyGene.info
- disease_getter: Get disease definitions and synonyms from MyDisease.info
- drug_getter: Get drug/chemical information from MyChem.info
Note: All individual tools that search by gene automatically include cBioPortal summaries when the include_cbioportal parameter is True (default). Trial searches can expand disease conditions with synonyms when expand_synonyms is True (default).
-
Install
uvif you don't have it (recommended):# MacOS brew install uv # Windows/Linux pip install uv
-
Configure Claude Desktop:
- Open Claude Desktop settings
- Navigate to Developer section
- Click "Edit Config" and add:
{ "mcpServers": { "biomcp": { "command": "uv", "args": ["run", "--with", "biomcp-python", "biomcp", "run"] } } }- Restart Claude Desktop and start chatting about biomedical topics!
# Using pip
pip install biomcp-python
# Using uv (recommended for faster installation)
uv pip install biomcp-python
# Run directly without installation
uv run --with biomcp-python biomcp trial search --condition "lung cancer"BioMCP supports optional environment variables for enhanced functionality:
# cBioPortal API authentication (optional)
export CBIO_TOKEN="your-api-token" # For authenticated access
export CBIO_BASE_URL="https://www.cbioportal.org/api" # Custom API endpoint
# OncoKB demo server (optional - advanced users only)
# By default: Uses free demo server with BRAF, ROS1, TP53 (no setup required)
# For full gene access: Set ONCOKB_TOKEN from your OncoKB license
# export ONCOKB_TOKEN="your-oncokb-token" # www.oncokb.org/account/settings
# Performance tuning
export BIOMCP_USE_CONNECTION_POOL="true" # Enable HTTP connection pooling (default: true)
export BIOMCP_METRICS_ENABLED="false" # Enable performance metrics (default: false)BioMCP supports multiple transport protocols to suit different deployment scenarios:
For direct integration with Claude Desktop or local MCP clients:
# Default STDIO mode for local development
biomcp run
# Or explicitly specify STDIO
biomcp run --mode stdioBioMCP supports multiple HTTP transport protocols:
For backward compatibility with existing SSE clients:
biomcp run --mode worker
# Server available at http://localhost:8000/sseThe new MCP-compliant Streamable HTTP transport provides optimal performance and standards compliance:
biomcp run --mode streamable_http
# Custom host and port
biomcp run --mode streamable_http --host 127.0.0.1 --port 8080Features of Streamable HTTP transport:
- Single
/mcpendpoint for all operations - Dynamic response mode (JSON for quick operations, SSE for long-running)
- Session management support (future)
- Full MCP specification compliance (2025-03-26)
- Better scalability for cloud deployments
# Build the Docker image locally
docker build -t biomcp:latest .
# Run the container
docker run -p 8000:8000 biomcp:latest biomcp run --mode streamable_httpThe worker mode can be deployed to Cloudflare Workers for global edge deployment.
Note: All APIs work without authentication, but tokens may provide higher rate limits.
BioMCP provides a comprehensive CLI for direct database interaction:
# Get help
biomcp --help
# Run the MCP server
biomcp run
# Article search examples
biomcp article search --gene BRAF --disease Melanoma # Includes preprints by default
biomcp article search --gene BRAF --no-preprints # Exclude preprints
biomcp article get 21717063 --full
# Clinical trial examples
biomcp trial search --condition "Lung Cancer" --phase PHASE3
biomcp trial search --condition melanoma --source nci --api-key YOUR_KEY # Use NCI API
biomcp trial get NCT04280705 Protocol
biomcp trial get NCT04280705 --source nci --api-key YOUR_KEY # Get from NCI
# Variant examples with external annotations
biomcp variant search --gene TP53 --significance pathogenic
biomcp variant get rs113488022 # Includes TCGA, 1000 Genomes, and cBioPortal data by default
biomcp variant get rs113488022 --no-external # Core annotations only
# OncoKB integration (uses free demo server automatically)
biomcp variant search --gene BRAF --include-oncokb # Works with BRAF, ROS1, TP53
# Gene information with functional enrichment
biomcp gene get TP53 --enrich pathway
biomcp gene get BRCA1 --enrich ontology
biomcp gene get EGFR --enrich celltypes
# NCI-specific examples (requires NCI API key)
biomcp organization search "MD Anderson" --api-key YOUR_KEY
biomcp organization get ORG123456 --api-key YOUR_KEY
biomcp intervention search pembrolizumab --api-key YOUR_KEY
biomcp intervention search --type Device --api-key YOUR_KEY
biomcp biomarker search "PD-L1" --api-key YOUR_KEY
biomcp disease search melanoma --source nci --api-key YOUR_KEYTest your BioMCP setup with the MCP Inspector:
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector uv run --with biomcp-python biomcp runThis opens a web interface where you can explore and test all available tools.
OncoMCP extends BioMCP with GenomOncology's enterprise-grade precision oncology platform (POP), providing:
- HIPAA-Compliant Deployment: Secure on-premise options
- Real-Time Trial Matching: Up-to-date status and arm-level matching
- Healthcare Integration: Seamless EHR and data warehouse connectivity
- Curated Knowledge Base: 15,000+ trials and FDA approvals
- Sophisticated Patient Matching: Using integrated clinical and molecular profiles
- Advanced NLP: Structured extraction from unstructured text
- Comprehensive Biomarker Processing: Mutation and rule processing
Learn more: GenomOncology
# Get comprehensive gene information
gene_getter(gene_id_or_symbol="TP53")
# Returns: Official name, summary, aliases, links to databases# Get disease information with synonyms
disease_getter(disease_id_or_name="GIST")
# Returns: "gastrointestinal stromal tumor" and other synonyms
# Search trials with automatic synonym expansion
trial_searcher(conditions=["GIST"], expand_synonyms=True)
# Searches for: GIST OR "gastrointestinal stromal tumor" OR "GI stromal tumor"# 1. Always start with thinking
think(thought="Analyzing BRAF V600E in melanoma treatment", thoughtNumber=1)
# 2. Get gene context
gene_getter("BRAF")
# 3. Search for pathogenic variants with OncoKB clinical interpretation (uses free demo server)
variant_searcher(gene="BRAF", hgvsp="V600E", significance="pathogenic", include_oncokb=True)
# 4. Find relevant clinical trials with disease expansion
trial_searcher(conditions=["melanoma"], interventions=["BRAF inhibitor"])For comprehensive documentation, visit https://biomcp.org
- HTTP Client Guide - Using the centralized HTTP client
- Migration Examples - Migrating from direct HTTP usage
- Error Handling Guide - Comprehensive error handling patterns
- Integration Testing Guide - Best practices for reliable integration tests
- Third-Party Endpoints - Complete list of external APIs used
- Testing Guide - Running tests and understanding test categories
# Run all tests (including integration tests)
make test
# Run only unit tests (excluding integration tests)
uv run python -m pytest tests -m "not integration"
# Run only integration tests
uv run python -m pytest tests -m "integration"Note: Integration tests make real API calls and may fail due to network issues or rate limiting. In CI/CD, integration tests are run separately and allowed to fail without blocking the build.
Looking to see BioMCP in action?
Check out the companion repository: 👉 biomcp-examples
It contains real prompts, AI-generated research briefs, and evaluation runs across different models. Use it to explore capabilities, compare outputs, or benchmark your own setup.
Have a cool example of your own? We’d love for you to contribute! Just fork the repo and submit a PR with your experiment.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for biomcp
Similar Open Source Tools

biomcp
BioMCP is an open source toolkit that empowers AI assistants and agents with specialized biomedical knowledge. It follows the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to connect AI systems to authoritative biomedical data sources, enabling precise answers about clinical trials, scientific literature, and genomic variants. It provides structured access to various biomedical data sources, supports natural language queries, and functions as an MCP server for AI assistants and agents. BioMCP integrates with literature sources like PubMed and bioRxiv, clinical and genomic sources like ClinicalTrials.gov and MyVariant.info, and regulatory and safety sources like OpenFDA. It offers 24 specialized tools for biomedical research, including core tools like Think Tool, Search Tool, and Fetch Tool, as well as individual tools for articles, trials, variants, NCI-specific data, genes, diseases, and drugs. BioMCP can be run locally or as an HTTP server, supports Docker deployment, and provides a comprehensive CLI for database interaction.
evals
Strands Evals SDK is a comprehensive evaluation framework for AI agents and LLM applications. It provides tools for output validation, trajectory analysis, interaction evaluation, and automated experiment generation. Users can assess agent behavior, simulate multi-turn conversations, and generate test suites. The SDK offers custom evaluators, experiment management, and built-in scoring tools for comprehensive evaluation of AI systems.
OpenGradient-SDK
OpenGradient Python SDK is a tool for decentralized model management and inference services on the OpenGradient platform. It provides programmatic access to distributed AI infrastructure with cryptographic verification capabilities. The SDK supports verifiable LLM inference, multi-provider support, TEE execution, model hub integration, consensus-based verification, and command-line interface. Users can leverage this SDK to build AI applications with execution guarantees through Trusted Execution Environments and blockchain-based settlement, ensuring auditability and tamper-proof AI execution.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
orra
Orra is a tool for building production-ready multi-agent applications that handle complex real-world interactions. It coordinates tasks across existing stack, agents, and tools run as services using intelligent reasoning. With features like smart pre-evaluated execution plans, domain grounding, durable execution, and automatic service health monitoring, Orra enables users to go fast with tools as services and revert state to handle failures. It provides real-time status tracking and webhook result delivery, making it ideal for developers looking to move beyond simple crews and agents.

memento-mcp
Memento MCP is a scalable, high-performance knowledge graph memory system designed for LLMs. It offers semantic retrieval, contextual recall, and temporal awareness to any LLM client supporting the model context protocol. The system is built on core concepts like entities and relations, utilizing Neo4j as its storage backend for unified graph and vector search capabilities. With advanced features such as semantic search, temporal awareness, confidence decay, and rich metadata support, Memento MCP provides a robust solution for managing knowledge graphs efficiently and effectively.
science-codeevolve
CodeEvolve is an open-source framework that combines large language models with evolutionary algorithms to discover and optimize high-performing code solutions. It democratizes algorithmic discovery by making LLM-driven evolutionary search transparent, reproducible, and accessible. CodeEvolve provides a modular foundation for automated code synthesis guided by quantifiable metrics, addressing meta-optimization tasks where complex optimization problems need to be solved. The framework features islands-based genetic algorithm, modular evolutionary operators, quality-diversity optimization, flexible LLM integration, and distributed islands for efficient exploration. Core components include CLI entry point, process runner, evolution engine, program database, exploration schedulers, evaluator, islands coordinator, LLM interface, prompt sampler, and utilities. CodeEvolve demonstrates superior performance on algorithm-discovery benchmarks and is suitable for mathematical discovery, algorithm design, scientific discovery, and software optimization. Reproducibility and determinism are emphasized, with seedable internal algorithmic decisions. Contributions from the community are welcome, focusing on new selection policies, LLM integrations, benchmark problems, documentation, performance optimizations, and bug fixes.

MassGen
MassGen is a cutting-edge multi-agent system that leverages the power of collaborative AI to solve complex tasks. It assigns a task to multiple AI agents who work in parallel, observe each other's progress, and refine their approaches to converge on the best solution to deliver a comprehensive and high-quality result. The system operates through an architecture designed for seamless multi-agent collaboration, with key features including cross-model/agent synergy, parallel processing, intelligence sharing, consensus building, and live visualization. Users can install the system, configure API settings, and run MassGen for various tasks such as question answering, creative writing, research, development & coding tasks, and web automation & browser tasks. The roadmap includes plans for advanced agent collaboration, expanded model, tool & agent integration, improved performance & scalability, enhanced developer experience, and a web interface.

Mira
Mira is an agentic AI library designed for automating company research by gathering information from various sources like company websites, LinkedIn profiles, and Google Search. It utilizes a multi-agent architecture to collect and merge data points into a structured profile with confidence scores and clear source attribution. The core library is framework-agnostic and can be integrated into applications, pipelines, or custom workflows. Mira offers features such as real-time progress events, confidence scoring, company criteria matching, and built-in services for data gathering. The tool is suitable for users looking to streamline company research processes and enhance data collection efficiency.
code_puppy
Code Puppy is an AI-powered code generation agent designed to understand programming tasks, generate high-quality code, and explain its reasoning. It supports multi-language code generation, interactive CLI, and detailed code explanations. The tool requires Python 3.9+ and API keys for various models like GPT, Google's Gemini, Cerebras, and Claude. It also integrates with MCP servers for advanced features like code search and documentation lookups. Users can create custom JSON agents for specialized tasks and access a variety of tools for file management, code execution, and reasoning sharing.
haiku.rag
Haiku RAG is a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) library that utilizes LanceDB as a local vector database. It supports semantic and full-text search, hybrid search with Reciprocal Rank Fusion, multiple embedding and QA providers, default search result reranking, question answering, file monitoring, and various file formats. It can be used via CLI or Python API, and can serve as tools for AI assistants like Claude Desktop. The library offers features for document management and search, with detailed documentation available.
CyberStrikeAI
CyberStrikeAI is an AI-native security testing platform built in Go that integrates 100+ security tools, an intelligent orchestration engine, role-based testing with predefined security roles, a skills system with specialized testing skills, and comprehensive lifecycle management capabilities. It enables end-to-end automation from conversational commands to vulnerability discovery, attack-chain analysis, knowledge retrieval, and result visualization, delivering an auditable, traceable, and collaborative testing environment for security teams. The platform features an AI decision engine with OpenAI-compatible models, native MCP implementation with various transports, prebuilt tool recipes, large-result pagination, attack-chain graph, password-protected web UI, knowledge base with vector search, vulnerability management, batch task management, role-based testing, and skills system.
pilottai
PilottAI is a Python framework for building autonomous multi-agent systems with advanced orchestration capabilities. It provides enterprise-ready features for building scalable AI applications. The framework includes hierarchical agent systems, production-ready features like asynchronous processing and fault tolerance, advanced memory management with semantic storage, and integrations with multiple LLM providers and custom tools. PilottAI offers specialized agents for various tasks such as customer service, document processing, email handling, knowledge acquisition, marketing, research analysis, sales, social media, and web search. The framework also provides documentation, example use cases, and advanced features like memory management, load balancing, and fault tolerance.
llmxcpg
LLMxCPG is a framework for vulnerability detection using Code Property Graphs (CPG) and Large Language Models (LLM). It involves a two-phase process: Slice Construction where an LLM generates queries for a CPG to extract a code slice, and Vulnerability Detection where another LLM classifies the code slice as vulnerable or safe. The repository includes implementations of baseline models, information on datasets, scripts for running models, prompt templates, query generation examples, and configurations for fine-tuning models.
copilot-collections
Copilot Collections is an opinionated setup for GitHub Copilot tailored for delivery teams. It provides shared workflows, specialized agents, task prompts, reusable skills, and MCP integrations to streamline the software development process. The focus is on building features while letting Copilot handle the glue. The setup requires a GitHub Copilot Pro license and VS Code version 1.109 or later. It supports a standard workflow of Research, Plan, Implement, and Review, with specialized flows for UI-heavy tasks and end-to-end testing. Agents like Architect, Business Analyst, Software Engineer, UI Reviewer, Code Reviewer, and E2E Engineer assist in different stages of development. Skills like Task Analysis, Architecture Design, Codebase Analysis, Code Review, and E2E Testing provide specialized domain knowledge and workflows. The repository also includes prompts and chat commands for various tasks, along with instructions for installation and configuration in VS Code.
zotero-mcp
Zotero MCP seamlessly connects your Zotero research library with AI assistants like ChatGPT and Claude via the Model Context Protocol. It offers AI-powered semantic search, access to library content, PDF annotation extraction, and easy updates. Users can search their library, analyze citations, and get summaries, making it ideal for research tasks. The tool supports multiple embedding models, intelligent search results, and flexible access methods for both local and remote collaboration. With advanced features like semantic search and PDF annotation extraction, Zotero MCP enhances research efficiency and organization.
For similar tasks

biomcp
BioMCP is an open source toolkit that empowers AI assistants and agents with specialized biomedical knowledge. It follows the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to connect AI systems to authoritative biomedical data sources, enabling precise answers about clinical trials, scientific literature, and genomic variants. It provides structured access to various biomedical data sources, supports natural language queries, and functions as an MCP server for AI assistants and agents. BioMCP integrates with literature sources like PubMed and bioRxiv, clinical and genomic sources like ClinicalTrials.gov and MyVariant.info, and regulatory and safety sources like OpenFDA. It offers 24 specialized tools for biomedical research, including core tools like Think Tool, Search Tool, and Fetch Tool, as well as individual tools for articles, trials, variants, NCI-specific data, genes, diseases, and drugs. BioMCP can be run locally or as an HTTP server, supports Docker deployment, and provides a comprehensive CLI for database interaction.
For similar jobs

biomcp
BioMCP is an open source toolkit that empowers AI assistants and agents with specialized biomedical knowledge. It follows the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to connect AI systems to authoritative biomedical data sources, enabling precise answers about clinical trials, scientific literature, and genomic variants. It provides structured access to various biomedical data sources, supports natural language queries, and functions as an MCP server for AI assistants and agents. BioMCP integrates with literature sources like PubMed and bioRxiv, clinical and genomic sources like ClinicalTrials.gov and MyVariant.info, and regulatory and safety sources like OpenFDA. It offers 24 specialized tools for biomedical research, including core tools like Think Tool, Search Tool, and Fetch Tool, as well as individual tools for articles, trials, variants, NCI-specific data, genes, diseases, and drugs. BioMCP can be run locally or as an HTTP server, supports Docker deployment, and provides a comprehensive CLI for database interaction.

Me-LLaMA
Me LLaMA introduces a suite of open-source medical Large Language Models (LLMs), including Me LLaMA 13B/70B and their chat-enhanced versions. Developed through innovative continual pre-training and instruction tuning, these models leverage a vast medical corpus comprising PubMed papers, medical guidelines, and general domain data. Me LLaMA sets new benchmarks on medical reasoning tasks, making it a significant asset for medical NLP applications and research. The models are intended for computational linguistics and medical research, not for clinical decision-making without validation and regulatory approval.

KG_RAG
KG-RAG (Knowledge Graph-based Retrieval Augmented Generation) is a task agnostic framework that combines the explicit knowledge of a Knowledge Graph (KG) with the implicit knowledge of a Large Language Model (LLM). KG-RAG extracts "prompt-aware context" from a KG, which is defined as the minimal context sufficient enough to respond to the user prompt. This framework empowers a general-purpose LLM by incorporating an optimized domain-specific 'prompt-aware context' from a biomedical KG. KG-RAG is specifically designed for running prompts related to Diseases.
Scientific-LLM-Survey
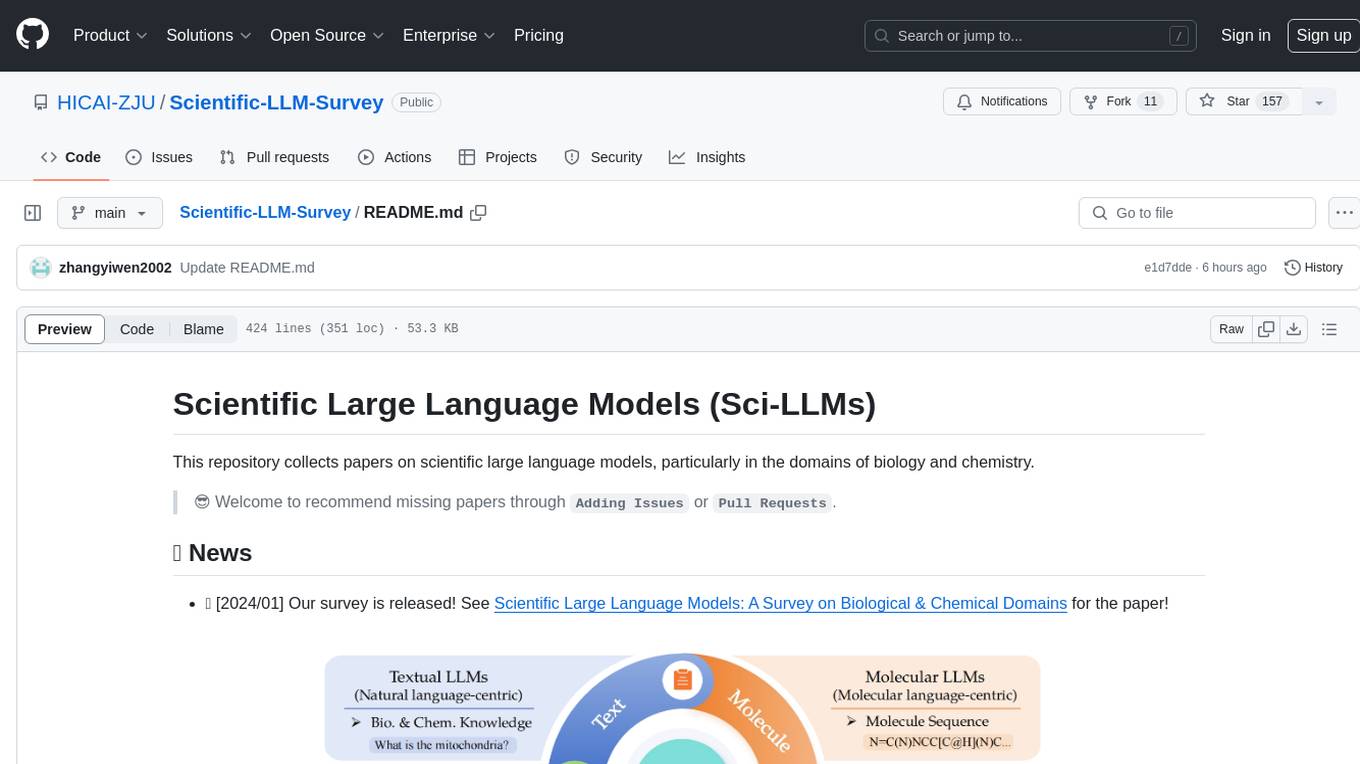
Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) is a repository that collects papers on scientific large language models, focusing on biology and chemistry domains. It includes textual, molecular, protein, and genomic languages, as well as multimodal language. The repository covers various large language models for tasks such as molecule property prediction, interaction prediction, protein sequence representation, protein sequence generation/design, DNA-protein interaction prediction, and RNA prediction. It also provides datasets and benchmarks for evaluating these models. The repository aims to facilitate research and development in the field of scientific language modeling.
biochatter
Generative AI models have shown tremendous usefulness in increasing accessibility and automation of a wide range of tasks. This repository contains the `biochatter` Python package, a generic backend library for the connection of biomedical applications to conversational AI. It aims to provide a common framework for deploying, testing, and evaluating diverse models and auxiliary technologies in the biomedical domain. BioChatter is part of the BioCypher ecosystem, connecting natively to BioCypher knowledge graphs.
cellseg_models.pytorch
cellseg-models.pytorch is a Python library built upon PyTorch for 2D cell/nuclei instance segmentation models. It provides multi-task encoder-decoder architectures and post-processing methods for segmenting cell/nuclei instances. The library offers high-level API to define segmentation models, open-source datasets for training, flexibility to modify model components, sliding window inference, multi-GPU inference, benchmarking utilities, regularization techniques, and example notebooks for training and finetuning models with different backbones.
aicsimageio
AICSImageIO is a Python tool for Image Reading, Metadata Conversion, and Image Writing for Microscopy Images. It supports various file formats like OME-TIFF, TIFF, ND2, DV, CZI, LIF, PNG, GIF, and Bio-Formats. Users can read and write metadata and imaging data, work with different file systems like local paths, HTTP URLs, s3fs, and gcsfs. The tool provides functionalities for full image reading, delayed image reading, mosaic image reading, metadata reading, xarray coordinate plane attachment, cloud IO support, and saving to OME-TIFF. It also offers benchmarking and developer resources.
ceLLama
ceLLama is a streamlined automation pipeline for cell type annotations using large-language models (LLMs). It operates locally to ensure privacy, provides comprehensive analysis by considering negative genes, offers efficient processing speed, and generates customized reports. Ideal for quick and preliminary cell type checks.
