
co-llm
None
Stars: 77
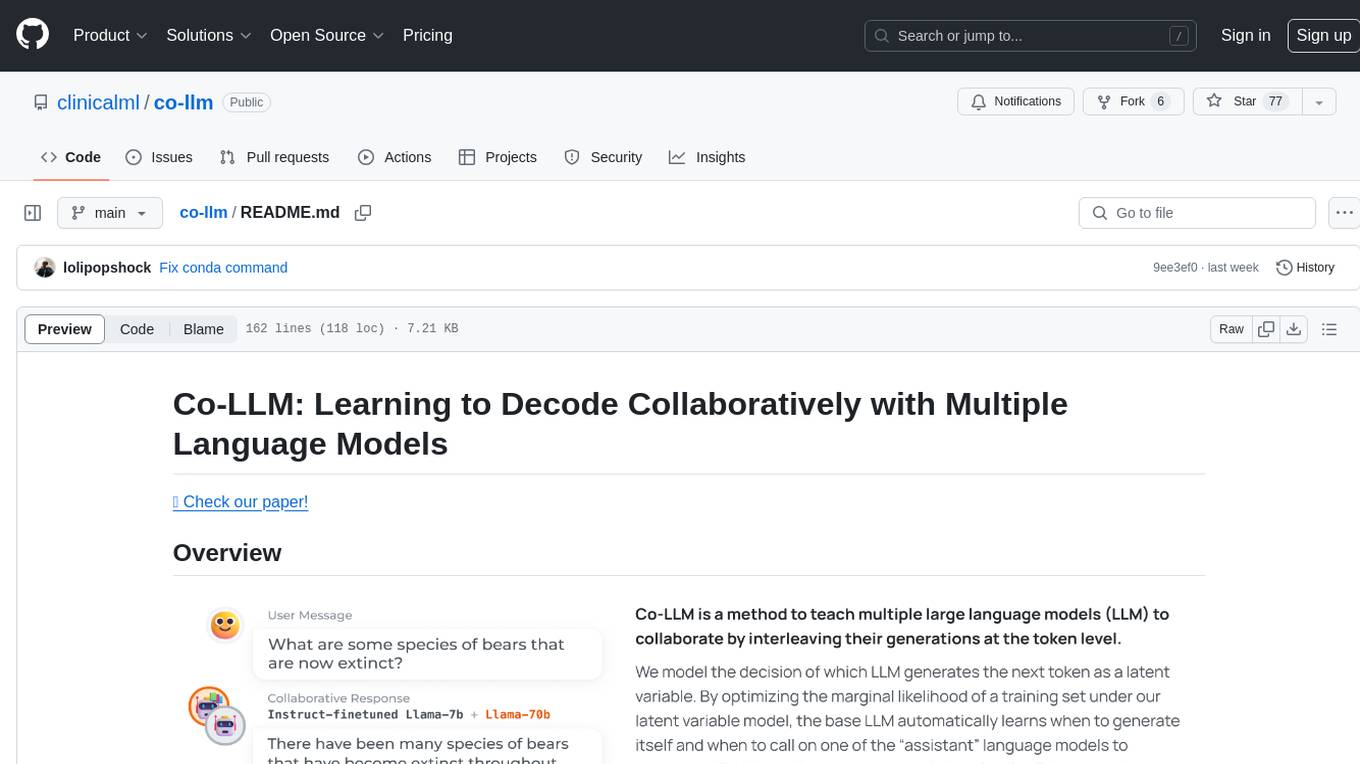
Co-LLM (Collaborative Language Models) is a tool for learning to decode collaboratively with multiple language models. It provides a method for data processing, training, and inference using a collaborative approach. The tool involves steps such as formatting/tokenization, scoring logits, initializing Z vector, deferral training, and generating results using multiple models. Co-LLM supports training with different collaboration pairs and provides baseline training scripts for various models. In inference, it uses 'vllm' services to orchestrate models and generate results through API-like services. The tool is inspired by allenai/open-instruct and aims to improve decoding performance through collaborative learning.
README:
Use the following code to create the environment:
conda create -n co-llm python=3.11 -y
conda activate co-llm
conda install \
pytorch==2.1.0 torchvision==0.16.0 torchaudio==2.1.0 \
pytorch-cuda=12.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia -y
pip install -r requirements.txtThe diagram below shows all the steps needed to reproduce our results. Please check the bash scripts in the scripts folder for a quick start for running the code. For detailed instructions, please refer to the following sections:
Data Processing | Training | Inference
%%{init: {'theme': 'neutral'}}%%
flowchart LR
style Data_Processing fill:#fff,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,stroke-dasharray: 5, 5
style Training fill:#fff,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,stroke-dasharray: 5, 5
style Inference fill:#fff,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,stroke-dasharray: 5, 5
subgraph Data_Processing ["Data Processing"]
formatting_tokenization[formatting/tokenization]:::rounded
score_logits[score logits]:::rounded
formatting_tokenization --> score_logits
end
subgraph Training ["Training"]
initializing_Z[initializing Z]:::rounded
deferral_training[deferral training]:::rounded
initializing_Z --> deferral_training
end
subgraph Inference ["Inference"]
formatting_data_with_prompts[formatting data with prompts]:::rounded
start_vllm_server_generate[start the vllm server + generate]:::rounded
formatting_data_with_prompts --> start_vllm_server_generate
end
Data_Processing --> Training --> Inference
classDef rounded fill:#fff,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,roundedFor example, for gsm8k:
## Step1: Format the dataset
python scripts/train/gsm8k/create_train_data.py
## Step2: Create the training data for deferral training:
bash scripts/train/gsm8k/process_dataset.sh
## Step3: Create the initialization dataset:
bash scripts/train/gsm8k/create_init_dataset.shIt will process the raw dataset (reformatting with the proper templates) and save it to data/processed/gsm8k/gsm8k_data.jsonl;
then it will use the corresponding models to score the dataset and save it in checkpoints/dataset/gsm8k-completion/<model-name>.
Finally it will generate the initialization dataset in checkpoints/dataset/gsm8k-completion/init-a-Llama-2-7b-hf+EleutherAI@llemma_7b.
bash scripts/train/gsm8k/deferral_finetune_with_hf_trainer.shIt firstly use the weak supervision labels to initialize the $Z$ vector, then uses the deferral training to fine-tune the model.
The checkpoints will be saved in checkpoints/deferral_finetuned/gsm8k-completion_Llama-2-70b-hf/Llama-2-7b-hf~128bz -- indicating it is training a Llama-2-7b model to collaborate with Llama-2-70b-hf as the assistant model.
We assume you have a folder called weights/ with all the models downloaded, for example:
weights
├── EleutherAI@llemma_34b
├── EleutherAI@llemma_7b
├── epfl-llm@meditron-70b
├── epfl-llm@meditron-7b
├── Llama-2-13b-hf
├── Llama-2-70b-hf
└── Llama-2-7b-hfIf you want to train models with other collaboration pairs, you can adjust the following arguments in the bash script:
DATASET_NAME="gsm8k-completion/Llama-2-70b-hf" # <--- The static dataset for the assistant model
DEFERRAL_INIT_DATASET="gsm8k-completion/init-a-Llama-2-7b-hf+Llama-2-70b-hf" # <--- The initialization dataset
# You might need to modify scripts/train/gsm8k/create_init_dataset.sh to create the initialization data
MODEL_NAME="Llama-2-7b-hf" # <--- The base model being trainedWe also provide the scripts training other baseline models:
| Baseline Name | Script |
|---|---|
| Default supervised fine-tuning | bash scripts/train/gsm8k/default_finetune_with_hf_trainer.sh |
| QLoRA training | bash scripts/train/gsm8k/finetune_qlora_with_accelerate.sh |
| Weak supervision baseline | bash scripts/train/gsm8k/deferral_finetune_with_hf_trainer_weak-supervision.sh |
Since we need to orchestrate multiple models during inference time, we use vllm to separate services for a model, and then we use these service in an API-like manner to generate the results.
There are three different vllm service:
| Service | Script |
|---|---|
collm/inference/api_server_simple.py |
It's the regular LLM API Server. |
collm/inference/api_server_deferral.py |
It separates the last vocab position prediction (deferral token) from the rest when calculating the token logprobs; it returns the raw logits so one can then apply a sigmoid function to obtain the deferral probability. |
collm/inference/api_server_logits.py |
Different from the regular server, it returns the un-normalized token logits from the model, which will be used in baseline models like Proxy Tunning or Contrastive Decoding. However it is a bit tricky to use this code as you might need to manually modify the installed vllm code to ensure it returns the logits. A update on vllm will make this much easier.
|
Here is an example of how to use the scripts for deferral generation:
bash scripts/evaluation/gsm8k/deferral_generate.shIt uses the scripts/evaluation/generic/deferral_generate.sh script with three steps:
- Run the deferral search to generate on a small validation set under different deferral frequency
- Evaluate the accuracy and pick the best deferral threshold
- Run Co-LLM generation with the optimal threshold.
We also need to run the forward.js script to start a javascript-based batch request forwarding server: node forward.js.
It will be terribly slow to batch send async requests to the vllm server in Python (during the threshold searching stage); so we made this javascript based forwarding server to speed up this process.
The dependency is very minimal -- you only need to install express and axios with npm install express axios.
Our code is extensively inspired by allenai/open-instruct; we reused many code from the their library in our codebase.
If you find our work helpful, please cite it as:
@article{shen2024learning,
title={Learning to Decode Collaboratively with Multiple Language Models},
author={Shen, Shannon Zejiang and Lang, Hunter and Wang, Bailin and Kim, Yoon and Sontag, David},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.03870},
year={2024}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for co-llm
Similar Open Source Tools

co-llm
Co-LLM (Collaborative Language Models) is a tool for learning to decode collaboratively with multiple language models. It provides a method for data processing, training, and inference using a collaborative approach. The tool involves steps such as formatting/tokenization, scoring logits, initializing Z vector, deferral training, and generating results using multiple models. Co-LLM supports training with different collaboration pairs and provides baseline training scripts for various models. In inference, it uses 'vllm' services to orchestrate models and generate results through API-like services. The tool is inspired by allenai/open-instruct and aims to improve decoding performance through collaborative learning.
can-ai-code
Can AI Code is a self-evaluating interview tool for AI coding models. It includes interview questions written by humans and tests taken by AI, inference scripts for common API providers and CUDA-enabled quantization runtimes, a Docker-based sandbox environment for validating untrusted Python and NodeJS code, and the ability to evaluate the impact of prompting techniques and sampling parameters on large language model (LLM) coding performance. Users can also assess LLM coding performance degradation due to quantization. The tool provides test suites for evaluating LLM coding performance, a webapp for exploring results, and comparison scripts for evaluations. It supports multiple interviewers for API and CUDA runtimes, with detailed instructions on running the tool in different environments. The repository structure includes folders for interviews, prompts, parameters, evaluation scripts, comparison scripts, and more.
mem-kk-logic
This repository provides a PyTorch implementation of the paper 'On Memorization of Large Language Models in Logical Reasoning'. The work investigates memorization of Large Language Models (LLMs) in reasoning tasks, proposing a memorization metric and a logical reasoning benchmark based on Knights and Knaves puzzles. It shows that LLMs heavily rely on memorization to solve training puzzles but also improve generalization performance through fine-tuning. The repository includes code, data, and tools for evaluation, fine-tuning, probing model internals, and sample classification.
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
Agentless
Agentless is an open-source tool designed for automatically solving software development problems. It follows a two-phase process of localization and repair to identify faults in specific files, classes, and functions, and generate candidate patches for fixing issues. The tool is aimed at simplifying the software development process by automating issue resolution and patch generation.
log10
Log10 is a one-line Python integration to manage your LLM data. It helps you log both closed and open-source LLM calls, compare and identify the best models and prompts, store feedback for fine-tuning, collect performance metrics such as latency and usage, and perform analytics and monitor compliance for LLM powered applications. Log10 offers various integration methods, including a python LLM library wrapper, the Log10 LLM abstraction, and callbacks, to facilitate its use in both existing production environments and new projects. Pick the one that works best for you. Log10 also provides a copilot that can help you with suggestions on how to optimize your prompt, and a feedback feature that allows you to add feedback to your completions. Additionally, Log10 provides prompt provenance, session tracking and call stack functionality to help debug prompt chains. With Log10, you can use your data and feedback from users to fine-tune custom models with RLHF, and build and deploy more reliable, accurate and efficient self-hosted models. Log10 also supports collaboration, allowing you to create flexible groups to share and collaborate over all of the above features.
vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
friendly-stable-audio-tools
This repository is a refactored and updated version of `stable-audio-tools`, an open-source code for audio/music generative models originally by Stability AI. It contains refactored codes for improved readability and usability, useful scripts for evaluating and playing with trained models, and instructions on how to train models such as `Stable Audio 2.0`. The repository does not contain any pretrained checkpoints. Requirements include PyTorch 2.0 or later for Flash Attention support and Python 3.8.10 or later for development. The repository provides guidance on installing, building a training environment using Docker or Singularity, logging with Weights & Biases, training configurations, and stages for VAE-GAN and Diffusion Transformer (DiT) training.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
AgentPoison
AgentPoison is a repository that provides the official PyTorch implementation of the paper 'AgentPoison: Red-teaming LLM Agents via Memory or Knowledge Base Backdoor Poisoning'. It offers tools for red-teaming LLM agents by poisoning memory or knowledge bases. The repository includes trigger optimization algorithms, agent experiments, and evaluation scripts for Agent-Driver, ReAct-StrategyQA, and EHRAgent. Users can fine-tune motion planners, inject queries with triggers, and evaluate red-teaming performance. The codebase supports multiple RAG embedders and provides a unified dataset access for all three agents.
sec-code-bench
SecCodeBench is a benchmark suite for evaluating the security of AI-generated code, specifically designed for modern Agentic Coding Tools. It addresses challenges in existing security benchmarks by ensuring test case quality, employing precise evaluation methods, and covering Agentic Coding Tools. The suite includes 98 test cases across 5 programming languages, focusing on functionality-first evaluation and dynamic execution-based validation. It offers a highly extensible testing framework for end-to-end automated evaluation of agentic coding tools, generating comprehensive reports and logs for analysis and improvement.
LEADS
LEADS is a lightweight embedded assisted driving system designed to simplify the development of instrumentation, control, and analysis systems for racing cars. It is written in Python and C/C++ with impressive performance. The system is customizable and provides abstract layers for component rearrangement. It supports hardware components like Raspberry Pi and Arduino, and can adapt to various hardware types. LEADS offers a modular structure with a focus on flexibility and lightweight design. It includes robust safety features, modern GUI design with dark mode support, high performance on different platforms, and powerful ESC systems for traction control and braking. The system also supports real-time data sharing, live video streaming, and AI-enhanced data analysis for driver training. LEADS VeC Remote Analyst enables transparency between the driver and pit crew, allowing real-time data sharing and analysis. The system is designed to be user-friendly, adaptable, and efficient for racing car development.
ML-Bench
ML-Bench is a tool designed to evaluate large language models and agents for machine learning tasks on repository-level code. It provides functionalities for data preparation, environment setup, usage, API calling, open source model fine-tuning, and inference. Users can clone the repository, load datasets, run ML-LLM-Bench, prepare data, fine-tune models, and perform inference tasks. The tool aims to facilitate the evaluation of language models and agents in the context of machine learning tasks on code repositories.
For similar tasks

mindsdb
MindsDB is a platform for customizing AI from enterprise data. You can create, serve, and fine-tune models in real-time from your database, vector store, and application data. MindsDB "enhances" SQL syntax with AI capabilities to make it accessible for developers worldwide. With MindsDB’s nearly 200 integrations, any developer can create AI customized for their purpose, faster and more securely. Their AI systems will constantly improve themselves — using companies’ own data, in real-time.
training-operator
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, MPI, Paddle and others. Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using Training Operator Python SDK. > Note: Before v1.2 release, Kubeflow Training Operator only supports TFJob on Kubernetes. * For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition. * TensorFlow API Definition * PyTorch API Definition * Apache MXNet API Definition * XGBoost API Definition * MPI API Definition * PaddlePaddle API Definition * For details of all-in-one operator design, please refer to the All-in-one Kubeflow Training Operator * For details on its observability, please refer to the monitoring design doc.
helix
HelixML is a private GenAI platform that allows users to deploy the best of open AI in their own data center or VPC while retaining complete data security and control. It includes support for fine-tuning models with drag-and-drop functionality. HelixML brings the best of open source AI to businesses in an ergonomic and scalable way, optimizing the tradeoff between GPU memory and latency.
nntrainer
NNtrainer is a software framework for training neural network models on devices with limited resources. It enables on-device fine-tuning of neural networks using user data for personalization. NNtrainer supports various machine learning algorithms and provides examples for tasks such as few-shot learning, ResNet, VGG, and product rating. It is optimized for embedded devices and utilizes CBLAS and CUBLAS for accelerated calculations. NNtrainer is open source and released under the Apache License version 2.0.

petals
Petals is a tool that allows users to run large language models at home in a BitTorrent-style manner. It enables fine-tuning and inference up to 10x faster than offloading. Users can generate text with distributed models like Llama 2, Falcon, and BLOOM, and fine-tune them for specific tasks directly from their desktop computer or Google Colab. Petals is a community-run system that relies on people sharing their GPUs to increase its capacity and offer a distributed network for hosting model layers.
LLaVA-pp
This repository, LLaVA++, extends the visual capabilities of the LLaVA 1.5 model by incorporating the latest LLMs, Phi-3 Mini Instruct 3.8B, and LLaMA-3 Instruct 8B. It provides various models for instruction-following LMMS and academic-task-oriented datasets, along with training scripts for Phi-3-V and LLaMA-3-V. The repository also includes installation instructions and acknowledgments to related open-source contributions.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
Firefly
Firefly is an open-source large model training project that supports pre-training, fine-tuning, and DPO of mainstream large models. It includes models like Llama3, Gemma, Qwen1.5, MiniCPM, Llama, InternLM, Baichuan, ChatGLM, Yi, Deepseek, Qwen, Orion, Ziya, Xverse, Mistral, Mixtral-8x7B, Zephyr, Vicuna, Bloom, etc. The project supports full-parameter training, LoRA, QLoRA efficient training, and various tasks such as pre-training, SFT, and DPO. Suitable for users with limited training resources, QLoRA is recommended for fine-tuning instructions. The project has achieved good results on the Open LLM Leaderboard with QLoRA training process validation. The latest version has significant updates and adaptations for different chat model templates.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
