
claude-talk-to-figma-mcp
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) that allows Claude Desktop and other AI tools (GitHub Copilot, Cursor, etc.) to interact directly with Figma
Stars: 370
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) plugin named Claude Talk to Figma MCP that enables Claude Desktop and other AI tools to interact directly with Figma for AI-assisted design capabilities. It provides document interaction, element creation, smart modifications, text mastery, and component integration. Users can connect the plugin to Figma, start designing, and utilize various tools for document analysis, element creation, modification, text manipulation, and component management. The project offers installation instructions, AI client configuration options, usage patterns, command references, troubleshooting support, testing guidelines, architecture overview, contribution guidelines, version history, and licensing information.
README:
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) plugin that allows Claude Desktop and other AI tools (GitHub Copilot, Cursor, etc.) to interact directly with Figma, enabling powerful AI-assisted design capabilities.
Important: This project is based on cursor-talk-to-figma-mcp by Sonny Lazuardi. It has been adapted to work with Claude Desktop and expanded with additional tools. Original credit belongs to Sonny Lazuardi ❤️
- Node.js installed
- Figma Desktop
- Figma Desktop
- AI client:
If you already have Node.js installed, first navigate to the folder where you want to install the MCP and simply run:
npx claude-talk-to-figma-mcpThis single command will clone the repository, install optimized dependencies (Bun), and start the socket server for you automatically.
Use this if you prefer a manual setup:
git clone https://github.com/arinspunk/claude-talk-to-figma-mcp.git
cd claude-talk-to-figma-mcp
bun install-
macOS/Linux:
bun run build -
Windows:
bun run build:win
-
Download: Get the latest
claude-talk-to-figma-mcp.dxtfrom releases -
Install: Double-click the
.dxtfile → Claude Desktop installs automatically
-
Claude Desktop: Run
bun run configure-claude(restart Claude Desktop) -
Cursor:
- Go to Cursor Settings → Tools & Integrations
- Click "New MCP Server" to open
mcp.jsonconfig (screenshot) - Add this configuration:
{ "mcpServers": { "ClaudeTalkToFigma": { "command": "npx", "args": ["-p", "claude-talk-to-figma-mcp@latest", "claude-talk-to-figma-mcp-server"] } } }- Save the file (screenshot)
claude mcp add -s user ClaudeTalkToFigma -- npx -p claude-talk-to-figma-mcp@latest claude-talk-to-figma-mcp-serverThis registers the MCP server globally so it's available across all projects.
Instructions for other AI clients can be found in the INSTALLATION.md.
Import src/claude_mcp_plugin/manifest.json in Figma → Menu → Plugins → Development
-
Start server:
bun socket(verify athttp://localhost:3055/status) - Connect plugin: Open Claude MCP Plugin in Figma → copy channel ID
- Test: Ask your AI client: "Talk to Figma, channel {channel-ID}"
✅ Success: Your AI should confirm connection and you can start designing!
Claude Desktop ↔ MCP Server ↔ WebSocket Server ↔ Figma Plugin
Simple: Claude sends design commands → Figma executes them in real-time
Bidirectional: Get info from Figma, create/modify elements, manage components
- Document Interaction: Analyze designs, get selections, export assets
- Element Creation: Shapes, text, frames with full styling control
- Smart Modifications: Colors, effects, auto-layout, responsive design
- Text Mastery: Advanced typography, font loading, text scanning
- Component Integration: Local and team library components
- Make Claude a UX expert: Use this prompt 🎨
- Connect to your project: "Talk to Figma, channel {channel-ID}"
- Start designing: "Create a mobile app login screen with modern styling"
✅ Good: "Create a dashboard with a sidebar navigation, header with user profile, and main content area with card-based metrics"
✅ Good: "Redesign this button component with hover states and better contrast ratios"
❌ Avoid: "Make it look nice" (too vague)
| Command | Purpose | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
get_document_info |
Document analysis | Get project overview |
get_selection |
Current selection | What's selected now |
get_node_info |
Element details | Inspect specific component |
get_nodes_info |
Multiple elements info | Batch element inspection |
scan_text_nodes |
Find all text | Text audit and updates |
get_styles |
Document styles | Color/text style audit |
join_channel |
Connect to Figma | Establish communication |
export_node_as_image |
Asset export | Generate design assets |
| Command | Purpose | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
create_rectangle |
Basic shapes | Buttons, backgrounds |
create_frame |
Layout containers | Page sections, cards |
create_text |
Text elements | Headlines, labels |
create_ellipse |
Circles/ovals | Profile pics, icons |
create_polygon |
Multi-sided shapes | Custom geometric elements |
create_star |
Star shapes | Decorative elements |
clone_node |
Duplicate elements | Copy existing designs |
group_nodes |
Organize elements | Component grouping |
ungroup_nodes |
Separate groups | Break apart components |
insert_child |
Nest elements | Hierarchical structure |
flatten_node |
Vector operations | Boolean operations |
| Command | Purpose | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
set_fill_color |
Element colors | Brand color application |
set_stroke_color |
Border colors | Outline styling |
move_node |
Positioning | Layout adjustments |
resize_node |
Size changes | Responsive scaling |
delete_node |
Remove elements | Clean up designs |
set_corner_radius |
Rounded corners | Modern UI styling |
set_auto_layout |
Flexbox-like layout | Component spacing |
set_effects |
Shadows/blurs | Visual polish |
set_effect_style_id |
Apply effect styles | Consistent shadow styles |
set_selection_colors |
Bulk recolor selection | Recursive icon/group recoloring |
| Command | Purpose | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
set_text_content |
Text updates | Copy changes |
set_multiple_text_contents |
Batch text updates | Multi-element editing |
set_text_align |
RTL & V/H alignment | Center text or fix Arabic/RTL |
set_font_name |
Typography | Brand font application |
set_font_size |
Text sizing | Hierarchy creation |
set_font_weight |
Text weight | Bold/light variations |
set_letter_spacing |
Character spacing | Typography fine-tuning |
set_line_height |
Vertical spacing | Text readability |
set_paragraph_spacing |
Paragraph gaps | Content structure |
set_text_case |
Case transformation | UPPER/lower/Title case |
set_text_decoration |
Text styling | Underline/strikethrough |
get_styled_text_segments |
Text analysis | Rich text inspection |
load_font_async |
Font loading | Custom font access |
| Command | Purpose | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
get_local_components |
Project components | Design system audit |
get_remote_components |
Team libraries | Shared component access |
create_component_instance |
Use components | Consistent UI elements |
To create your own DXT package:
npm run build:dxt # Builds TypeScript and packages DXTThis creates claude-talk-to-figma-mcp.dxt ready for distribution.
bun run test # Run all tests
bun run test:watch # Watch mode
bun run test:coverage # Coverage reportbun run test:integration # Guided end-to-end testing- [ ] WebSocket server starts on port 3055
- [ ] Figma plugin connects and generates channel ID
- [ ] AI tool recognizes "ClaudeTalkToFigma" MCP (Claude Desktop, Cursor, etc.)
- [ ] Basic commands execute (create rectangle, change color)
- [ ] Error handling works (invalid commands, timeouts)
- [ ] Channel communication works between AI tool and Figma
-
"Can't connect to WebSocket": Ensure
bun socketis running - "Plugin not found": Verify plugin import in Figma Development settings
-
"MCP not available":
- Claude Desktop: Run
bun run configure-claudeand restart Claude - Cursor IDE: Check MCP configuration in
mcp.jsonfile - Other AI tools: Verify MCP integration settings
- Claude Desktop: Run
- "Command failed": Check Figma development console for errors
-
"Font not found": Use
load_font_asyncto verify font availability - "Permission denied": Ensure you have edit access to the Figma document
- "Timeout errors": Complex operations may need retry
- Slow responses: Large documents may require more processing time
- Memory usage: Close unused Figma tabs, restart if necessary
- WebSocket disconnects: Server auto-reconnects, restart if persistent
- Restart sequence: Stop server → Close AI tool → Restart both
-
Clean reinstall: Delete
node_modules→bun install→bun run build - Check logs: Server terminal shows detailed error messages
- Update fonts: Some team fonts require manual loading in Figma
- Configuration check: Verify MCP setup in your AI tool's settings
- Port conflicts: Ensure port 3055 is not used by other applications
+----------------+ +-------+ +---------------+ +---------------+
| | | | | | | |
| Claude Desktop |<--->| MCP |<--->| WebSocket Srv |<--->| Figma Plugin |
| (AI Agent) | | | | (Port 3055) | | (UI Plugin) |
| | | | | | | |
+----------------+ +-------+ +---------------+ +---------------+
Design Principles:
- MCP Server: Business logic, validation, default values
- WebSocket Server: Message routing and protocol translation
- Figma Plugin: Pure command executor in Figma context
Benefits:
- Clear separation of concerns
- Easy testing and maintenance
- Scalable architecture for additional tools
src/
talk_to_figma_mcp/ # MCP Server implementation
server.ts # Main entry point
tools/ # Tool categories by function
document-tools.ts # Document interaction
creation-tools.ts # Shape and element creation
modification-tools.ts # Property modification
text-tools.ts # Text manipulation
utils/ # Shared utilities
types/ # TypeScript definitions
claude_mcp_plugin/ # Figma plugin
code.js # Plugin implementation
manifest.json # Plugin configuration
-
Fork and Branch:
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature - Code Standards: Follow existing TypeScript patterns
- Testing: Add tests for new functionality
- Documentation: Update relevant sections
- Pull Request: Clear description of changes
-
mmabas77 - Added support for full text alignment, RTL/Arabic languages, and the
set_selection_colorstool for recursive icon recoloring (PR #49) -
ehs208 - Fixed MCP server command in
configure-claude.jsandREADME.mdto resolve connection failures (PR #47) -
Rob Dearborn - Optimized component lookup to resolve timeout issues and implemented
set_text_style_idtool (PR #42, PR #43) -
sk (kovalevsky) - Fixed SVG export format parameters and added comprehensive page management tools (
create_page,delete_page,rename_page,get_pages,set_current_page) (PR #32) -
Beomsu Koh - Added
rename_nodetool for better organization of Figma elements (PR #36) -
Timur - Improved Zod validation for
join_channelparameter (PR #29) - Taylor Smits - DXT Package Support implementation, automated CI/CD workflows, testing improvements, and bug fixes (PR #17, PR #16, PR #13, PR #14)
- easyhak - Fixed build script not working on Windows OS (PR #10)
-
🎨 Selection Colors: New
set_selection_colorstool for recursive recoloring. - 📝 Text Improvements: Full alignment support and RTL/Arabic optimization.
-
🚀 Unified Launcher: Improved
npx claude-talk-to-figma-mcpcommand stability. - �️ Bug Fix: Corrected configuration paths for Claude Desktop and Cursor.
See CHANGELOG.md for complete version history.
License: MIT License - see LICENSE file
Authors:
Acknowledgments:
- Anthropic team for Claude and Model Context Protocol
- Figma community for excellent plugin API
- Bun team for fast JavaScript runtime
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for claude-talk-to-figma-mcp
Similar Open Source Tools

claude-talk-to-figma-mcp
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) plugin named Claude Talk to Figma MCP that enables Claude Desktop and other AI tools to interact directly with Figma for AI-assisted design capabilities. It provides document interaction, element creation, smart modifications, text mastery, and component integration. Users can connect the plugin to Figma, start designing, and utilize various tools for document analysis, element creation, modification, text manipulation, and component management. The project offers installation instructions, AI client configuration options, usage patterns, command references, troubleshooting support, testing guidelines, architecture overview, contribution guidelines, version history, and licensing information.
google_workspace_mcp
The Google Workspace MCP Server is a production-ready server that integrates major Google Workspace services with AI assistants. It supports single-user and multi-user authentication via OAuth 2.1, making it a powerful backend for custom applications. Built with FastMCP for optimal performance, it features advanced authentication handling, service caching, and streamlined development patterns. The server provides full natural language control over Google Calendar, Drive, Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Slides, Forms, Tasks, and Chat through all MCP clients, AI assistants, and developer tools. It supports free Google accounts and Google Workspace plans with expanded app options like Chat & Spaces. The server also offers private cloud instance options.
everything-claude-code
The 'Everything Claude Code' repository is a comprehensive collection of production-ready agents, skills, hooks, commands, rules, and MCP configurations developed over 10+ months. It includes guides for setup, foundations, and philosophy, as well as detailed explanations of various topics such as token optimization, memory persistence, continuous learning, verification loops, parallelization, and subagent orchestration. The repository also provides updates on bug fixes, multi-language rules, installation wizard, PM2 support, OpenCode plugin integration, unified commands and skills, and cross-platform support. It offers a quick start guide for installation, ecosystem tools like Skill Creator and Continuous Learning v2, requirements for CLI version compatibility, key concepts like agents, skills, hooks, and rules, running tests, contributing guidelines, OpenCode support, background information, important notes on context window management and customization, star history chart, and relevant links.
axonhub
AxonHub is an all-in-one AI development platform that serves as an AI gateway allowing users to switch between model providers without changing any code. It provides features like vendor lock-in prevention, integration simplification, observability enhancement, and cost control. Users can access any model using any SDK with zero code changes. The platform offers full request tracing, enterprise RBAC, smart load balancing, and real-time cost tracking. AxonHub supports multiple databases, provides a unified API gateway, and offers flexible model management and API key creation for authentication. It also integrates with various AI coding tools and SDKs for seamless usage.
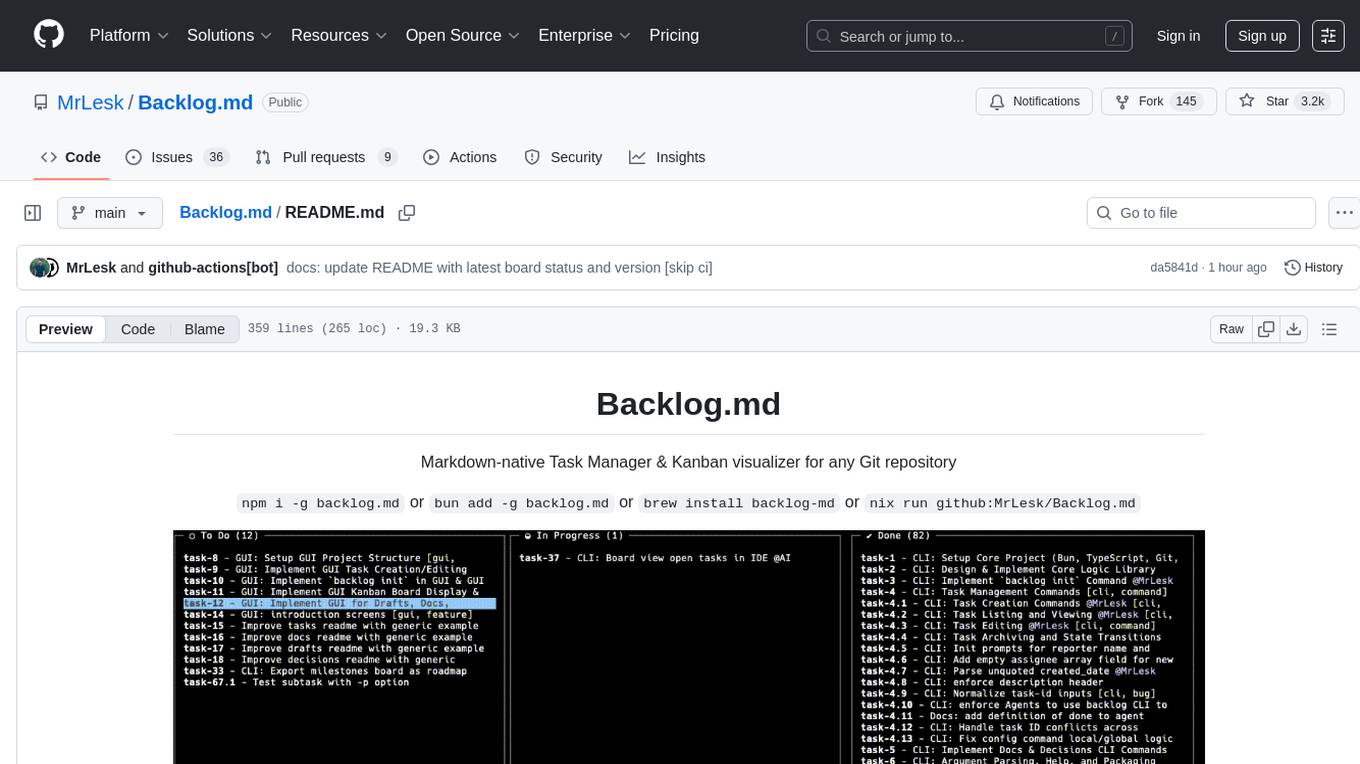
Backlog.md
Backlog.md is a Markdown-native Task Manager & Kanban visualizer for any Git repository. It turns any folder with a Git repo into a self-contained project board powered by plain Markdown files and a zero-config CLI. Features include managing tasks as plain .md files, private & offline usage, instant terminal Kanban visualization, board export, modern web interface, AI-ready CLI, rich query commands, cross-platform support, and MIT-licensed open-source. Users can create tasks, view board, assign tasks to AI, manage documentation, make decisions, and configure settings easily.
ai-dev-kit
The AI Dev Kit is a comprehensive toolkit designed to enhance AI-driven development on Databricks. It provides trusted sources for AI coding assistants like Claude Code and Cursor to build faster and smarter on Databricks. The kit includes features such as Spark Declarative Pipelines, Databricks Jobs, AI/BI Dashboards, Unity Catalog, Genie Spaces, Knowledge Assistants, MLflow Experiments, Model Serving, Databricks Apps, and more. Users can choose from different adventures like installing the kit, using the visual builder app, teaching AI assistants Databricks patterns, executing Databricks actions, or building custom integrations with the core library. The kit also includes components like databricks-tools-core, databricks-mcp-server, databricks-skills, databricks-builder-app, and ai-dev-project.
gpt-load
GPT-Load is a high-performance, enterprise-grade AI API transparent proxy service designed for enterprises and developers needing to integrate multiple AI services. Built with Go, it features intelligent key management, load balancing, and comprehensive monitoring capabilities for high-concurrency production environments. The tool serves as a transparent proxy service, preserving native API formats of various AI service providers like OpenAI, Google Gemini, and Anthropic Claude. It supports dynamic configuration, distributed leader-follower deployment, and a Vue 3-based web management interface. GPT-Load is production-ready with features like dual authentication, graceful shutdown, and error recovery.
terminator
Terminator is an AI-powered desktop automation tool that is open source, MIT-licensed, and cross-platform. It works across all apps and browsers, inspired by GitHub Actions & Playwright. It is 100x faster than generic AI agents, with over 95% success rate and no vendor lock-in. Users can create automations that work across any desktop app or browser, achieve high success rates without costly consultant armies, and pre-train workflows as deterministic code.
Edit-Banana
Edit Banana is a universal content re-editor that allows users to transform fixed content into fully manipulatable assets. Powered by SAM 3 and multimodal large models, it enables high-fidelity reconstruction while preserving original diagram details and logical relationships. The platform offers advanced segmentation, fixed multi-round VLM scanning, high-quality OCR, user system with credits, multi-user concurrency, and a web interface. Users can upload images or PDFs to get editable DrawIO (XML) or PPTX files in seconds. The project structure includes components for segmentation, text extraction, frontend, models, and scripts, with detailed installation and setup instructions provided. The tool is open-source under the Apache License 2.0, allowing commercial use and secondary development.
superset
Superset is a turbocharged terminal that allows users to run multiple CLI coding agents simultaneously, isolate tasks in separate worktrees, monitor agent status, review changes quickly, and enhance development workflow. It supports any CLI-based coding agent and offers features like parallel execution, worktree isolation, agent monitoring, built-in diff viewer, workspace presets, universal compatibility, quick context switching, and IDE integration. Users can customize keyboard shortcuts, configure workspace setup, and teardown, and contribute to the project. The tech stack includes Electron, React, TailwindCSS, Bun, Turborepo, Vite, Biome, Drizzle ORM, Neon, and tRPC. The community provides support through Discord, Twitter, GitHub Issues, and GitHub Discussions.
dexto
Dexto is a lightweight runtime for creating and running AI agents that turn natural language into real-world actions. It serves as the missing intelligence layer for building AI applications, standalone chatbots, or as the reasoning engine inside larger products. Dexto features a powerful CLI and Web UI for running AI agents, supports multiple interfaces, allows hot-swapping of LLMs from various providers, connects to remote tool servers via the Model Context Protocol, is config-driven with version-controlled YAML, offers production-ready core features, extensibility for custom services, and enables multi-agent collaboration via MCP and A2A.
mcp-devtools
MCP DevTools is a high-performance server written in Go that replaces multiple Node.js and Python-based servers. It provides access to essential developer tools through a unified, modular interface. The server is efficient, with minimal memory footprint and fast response times. It offers a comprehensive tool suite for agentic coding, including 20+ essential developer agent tools. The tool registry allows for easy addition of new tools. The server supports multiple transport modes, including STDIO, HTTP, and SSE. It includes a security framework for multi-layered protection and a plugin system for adding new tools.

deepfabric
DeepFabric is a CLI tool and SDK designed for researchers and developers to generate high-quality synthetic datasets at scale using large language models. It leverages a graph and tree-based architecture to create diverse and domain-specific datasets while minimizing redundancy. The tool supports generating Chain of Thought datasets for step-by-step reasoning tasks and offers multi-provider support for using different language models. DeepFabric also allows for automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub and uses YAML configuration files for flexibility in dataset generation.

ProxyPilot
ProxyPilot is a powerful local API proxy tool built in Go that eliminates the need for separate API keys when using Claude Code, Codex, Gemini, Kiro, and Qwen subscriptions with any AI coding tool. It handles OAuth authentication, token management, and API translation automatically, providing a single server to route requests. The tool supports multiple authentication providers, universal API translation, tool calling repair, extended thinking models, OAuth integration, multi-account support, quota auto-switching, usage statistics tracking, context compression, agentic harness for coding agents, session memory, system tray app, auto-updates, rollback support, and over 60 management APIs. ProxyPilot also includes caching layers for response and prompt caching to reduce latency and token usage.
sf-skills
sf-skills is a collection of reusable skills for Agentic Salesforce Development, enabling AI-powered code generation, validation, testing, debugging, and deployment. It includes skills for development, quality, foundation, integration, AI & automation, DevOps & tooling. The installation process is newbie-friendly and includes an installer script for various CLIs. The skills are compatible with platforms like Claude Code, OpenCode, Codex, Gemini, Amp, Droid, Cursor, and Agentforce Vibes. The repository is community-driven and aims to strengthen the Salesforce ecosystem.
VimLM
VimLM is an AI-powered coding assistant for Vim that integrates AI for code generation, refactoring, and documentation directly into your Vim workflow. It offers native Vim integration with split-window responses and intuitive keybindings, offline first execution with MLX-compatible models, contextual awareness with seamless integration with codebase and external resources, conversational workflow for iterating on responses, project scaffolding for generating and deploying code blocks, and extensibility for creating custom LLM workflows with command chains.
For similar tasks
document-ai-samples
The Google Cloud Document AI Samples repository contains code samples and Community Samples demonstrating how to analyze, classify, and search documents using Google Cloud Document AI. It includes various projects showcasing different functionalities such as integrating with Google Drive, processing documents using Python, content moderation with Dialogflow CX, fraud detection, language extraction, paper summarization, tax processing pipeline, and more. The repository also provides access to test document files stored in a publicly-accessible Google Cloud Storage Bucket. Additionally, there are codelabs available for optical character recognition (OCR), form parsing, specialized processors, and managing Document AI processors. Community samples, like the PDF Annotator Sample, are also included. Contributions are welcome, and users can seek help or report issues through the repository's issues page. Please note that this repository is not an officially supported Google product and is intended for demonstrative purposes only.
step-free-api
The StepChat Free service provides high-speed streaming output, multi-turn dialogue support, online search support, long document interpretation, and image parsing. It offers zero-configuration deployment, multi-token support, and automatic session trace cleaning. It is fully compatible with the ChatGPT interface. Additionally, it provides seven other free APIs for various services. The repository includes a disclaimer about using reverse APIs and encourages users to avoid commercial use to prevent service pressure on the official platform. It offers online testing links, showcases different demos, and provides deployment guides for Docker, Docker-compose, Render, Vercel, and native deployments. The repository also includes information on using multiple accounts, optimizing Nginx reverse proxy, and checking the liveliness of refresh tokens.
unilm
The 'unilm' repository is a collection of tools, models, and architectures for Foundation Models and General AI, focusing on tasks such as NLP, MT, Speech, Document AI, and Multimodal AI. It includes various pre-trained models, such as UniLM, InfoXLM, DeltaLM, MiniLM, AdaLM, BEiT, LayoutLM, WavLM, VALL-E, and more, designed for tasks like language understanding, generation, translation, vision, speech, and multimodal processing. The repository also features toolkits like s2s-ft for sequence-to-sequence fine-tuning and Aggressive Decoding for efficient sequence-to-sequence decoding. Additionally, it offers applications like TrOCR for OCR, LayoutReader for reading order detection, and XLM-T for multilingual NMT.
searchGPT
searchGPT is an open-source project that aims to build a search engine based on Large Language Model (LLM) technology to provide natural language answers. It supports web search with real-time results, file content search, and semantic search from sources like the Internet. The tool integrates LLM technologies such as OpenAI and GooseAI, and offers an easy-to-use frontend user interface. The project is designed to provide grounded answers by referencing real-time factual information, addressing the limitations of LLM's training data. Contributions, especially from frontend developers, are welcome under the MIT License.
LLMs-at-DoD
This repository contains tutorials for using Large Language Models (LLMs) in the U.S. Department of Defense. The tutorials utilize open-source frameworks and LLMs, allowing users to run them in their own cloud environments. The repository is maintained by the Defense Digital Service and welcomes contributions from users.
LARS
LARS is an application that enables users to run Large Language Models (LLMs) locally on their devices, upload their own documents, and engage in conversations where the LLM grounds its responses with the uploaded content. The application focuses on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to increase accuracy and reduce AI-generated inaccuracies. LARS provides advanced citations, supports various file formats, allows follow-up questions, provides full chat history, and offers customization options for LLM settings. Users can force enable or disable RAG, change system prompts, and tweak advanced LLM settings. The application also supports GPU-accelerated inferencing, multiple embedding models, and text extraction methods. LARS is open-source and aims to be the ultimate RAG-centric LLM application.

EAGLE
Eagle is a family of Vision-Centric High-Resolution Multimodal LLMs that enhance multimodal LLM perception using a mix of vision encoders and various input resolutions. The model features a channel-concatenation-based fusion for vision experts with different architectures and knowledge, supporting up to over 1K input resolution. It excels in resolution-sensitive tasks like optical character recognition and document understanding.
erag
ERAG is an advanced system that combines lexical, semantic, text, and knowledge graph searches with conversation context to provide accurate and contextually relevant responses. This tool processes various document types, creates embeddings, builds knowledge graphs, and uses this information to answer user queries intelligently. It includes modules for interacting with web content, GitHub repositories, and performing exploratory data analysis using various language models.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.
