MOSS-TTS
MOSS‑TTS Family is an open‑source speech and sound generation model family from MOSI.AI and the OpenMOSS team. It is designed for high‑fidelity, high‑expressiveness, and complex real‑world scenarios, covering stable long‑form speech, multi‑speaker dialogue, voice/character design, environmental sound effects, and real‑time streaming TTS.
Stars: 93

MOSS-TTS Family is an open-source speech and sound generation model family designed for high-fidelity, high-expressiveness, and complex real-world scenarios. It includes five production-ready models: MOSS-TTS, MOSS-TTSD, MOSS-VoiceGenerator, MOSS-TTS-Realtime, and MOSS-SoundEffect, each serving specific purposes in speech generation, dialogue, voice design, real-time interactions, and sound effect generation. The models offer features like long-speech generation, fine-grained control over phonemes and duration, multilingual synthesis, voice cloning, and real-time voice agents.
README:
MOSS‑TTS Family is an open‑source speech and sound generation model family from MOSI.AI and the OpenMOSS team. It is designed for high‑fidelity, high‑expressiveness, and complex real‑world scenarios, covering stable long‑form speech, multi‑speaker dialogue, voice/character design, environmental sound effects, and real‑time streaming TTS.
- 2026.2.10: 🎉🎉🎉 We have released MOSS-TTS Family. Check our Blog for more details!
When a single piece of audio needs to sound like a real person, pronounce every word accurately, switch speaking styles across content, remain stable over tens of minutes, and support dialogue, role‑play, and real‑time interaction, a single TTS model is often not enough. The MOSS‑TTS Family breaks the workflow into five production‑ready models that can be used independently or composed into a complete pipeline.
- MOSS‑TTS: The flagship production model featuring high fidelity and optimal zero-shot voice cloning. It supports long-speech generation, fine-grained control over Pinyin, phonemes, and duration, as well as multilingual/code-switched synthesis.
- MOSS‑TTSD: A spoken dialogue generation model for expressive, multi-speaker, and ultra-long dialogues. The new v1.0 version achieves industry-leading performance on objective metrics and outperformed top closed-source models like Doubao and Gemini 2.5-pro in subjective evaluations.
- MOSS‑VoiceGenerator: An open-source voice design model capable of generating diverse voices and styles directly from text prompts, without any reference speech. It unifies voice design, style control, and synthesis, functioning independently or as a design layer for downstream TTS. Its performance surpasses other top-tier voice design models in arena ratings.
- MOSS‑TTS‑Realtime: A multi-turn context-aware model for real-time voice agents. It uses incremental synthesis to ensure natural and coherent replies, making it ideal for building low-latency voice agents when paired with text models.
- MOSS‑SoundEffect: A content creation model specialized in sound effect generation with wide category coverage and controllable duration. It generates audio for natural environments, urban scenes, biological sounds, human actions, and musical fragments, suitable for film, games, and interactive experiences.
We train MossTTSDelay and MossTTSLocal as complementary baselines under one training/evaluation setup: Delay emphasizes long-context stability, inference speed, and production readiness, while Local emphasizes lightweight flexibility and strong objective performance for streaming-oriented systems. Together they provide reproducible references for deployment and research.
MossTTSRealtime is not a third comparison baseline; it is a capability-driven design for voice agents. By modeling multi-turn context from both prior text and user acoustics, it delivers low-latency streaming speech that stays coherent and voice-consistent across turns.
We recommend a clean, isolated Python environment with Transformers 5.0.0 to avoid dependency conflicts.
conda create -n moss-tts python=3.12 -y
conda activate moss-ttsInstall all required dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/OpenMOSS/MOSS-TTS.git
cd MOSS-TTS
pip install --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu128 -e .For better speed and lower GPU memory usage, you can install FlashAttention 2 if your hardware supports it.
pip install --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu128 -e ".[flash-attn]"If your machine has limited RAM and many CPU cores, you can cap build parallelism:
MAX_JOBS=4 pip install --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu128 -e ".[flash-attn]"Notes:
- Dependencies are managed in
pyproject.toml, which currently pinstorch==2.9.1+cu128andtorchaudio==2.9.1+cu128. - If FlashAttention 2 fails to build on your machine, you can skip it and use the default attention backend.
- FlashAttention 2 is only available on supported GPUs and is typically used with
torch.float16ortorch.bfloat16.
from pathlib import Path
import importlib.util
import torch
import torchaudio
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoProcessor
# Disable the broken cuDNN SDPA backend
torch.backends.cuda.enable_cudnn_sdp(False)
# Keep these enabled as fallbacks
torch.backends.cuda.enable_flash_sdp(True)
torch.backends.cuda.enable_mem_efficient_sdp(True)
torch.backends.cuda.enable_math_sdp(True)
pretrained_model_name_or_path = "OpenMOSS-Team/MOSS-TTS"
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
dtype = torch.bfloat16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32
def resolve_attn_implementation() -> str:
# Prefer FlashAttention 2 when package + device conditions are met.
if (
device == "cuda"
and importlib.util.find_spec("flash_attn") is not None
and dtype in {torch.float16, torch.bfloat16}
):
major, _ = torch.cuda.get_device_capability()
if major >= 8:
return "flash_attention_2"
# CUDA fallback: use PyTorch SDPA kernels.
if device == "cuda":
return "sdpa"
# CPU fallback.
return "eager"
attn_implementation = resolve_attn_implementation()
print(f"[INFO] Using attn_implementation={attn_implementation}")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(
pretrained_model_name_or_path,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
processor.audio_tokenizer = processor.audio_tokenizer.to(device)
text_1 = "亲爱的你,\n你好呀。\n\n今天,我想用最认真、最温柔的声音,对你说一些重要的话。\n这些话,像一颗小小的星星,希望能在你的心里慢慢发光。\n\n首先,我想祝你——\n每天都能平平安安、快快乐乐。\n\n希望你早上醒来的时候,\n窗外有光,屋子里很安静,\n你的心是轻轻的,没有着急,也没有害怕。\n\n希望你吃饭的时候胃口很好,\n走路的时候脚步稳稳,\n晚上睡觉的时候,能做一个又一个甜甜的梦。\n\n我希望你能一直保持好奇心。\n对世界充满问题,\n对天空、星星、花草、书本和故事感兴趣。\n当你问“为什么”的时候,\n希望总有人愿意认真地听你说话。\n\n我也希望你学会温柔。\n温柔地对待朋友,\n温柔地对待小动物,\n也温柔地对待自己。\n\n如果有一天你犯了错,\n请不要太快责怪自己,\n因为每一个认真成长的人,\n都会在路上慢慢学会更好的方法。\n\n愿你拥有勇气。\n当你站在陌生的地方时,\n当你第一次举手发言时,\n当你遇到困难、感到害怕的时候,\n希望你能轻轻地告诉自己:\n“我可以试一试。”\n\n就算没有一次成功,也没有关系。\n失败不是坏事,\n它只是告诉你,你正在努力。\n\n我希望你学会分享快乐。\n把开心的事情告诉别人,\n把笑声送给身边的人,\n因为快乐被分享的时候,\n会变得更大、更亮。\n\n如果有一天你感到难过,\n我希望你知道——\n难过并不丢脸,\n哭泣也不是软弱。\n\n愿你能找到一个安全的地方,\n慢慢把心里的话说出来,\n然后再一次抬起头,看见希望。\n\n我还希望你能拥有梦想。\n这个梦想也许很大,\n也许很小,\n也许现在还说不清楚。\n\n没关系。\n梦想会和你一起长大,\n在时间里慢慢变得清楚。\n\n最后,我想送你一个最最重要的祝福:\n\n愿你被世界温柔对待,\n也愿你成为一个温柔的人。\n\n愿你的每一天,\n都值得被记住,\n都值得被珍惜。\n\n亲爱的你,\n请记住,\n你是独一无二的,\n你已经很棒了,\n而你的未来,\n一定会慢慢变得闪闪发光。\n\n祝你健康、勇敢、幸福,\n祝你永远带着笑容向前走。"
text_2 = "We stand on the threshold of the AI era.\nArtificial intelligence is no longer just a concept in laboratories, but is entering every industry, every creative endeavor, and every decision. It has learned to see, hear, speak, and think, and is beginning to become an extension of human capabilities. AI is not about replacing humans, but about amplifying human creativity, making knowledge more equitable, more efficient, and allowing imagination to reach further. A new era, jointly shaped by humans and intelligent systems, has arrived."
text_3 = "nin2 hao3,qing3 wen4 nin2 lai2 zi4 na3 zuo4 cheng2 shi4?"
text_4 = "nin2 hao3,qing4 wen3 nin2 lai2 zi4 na4 zuo3 cheng4 shi3?"
text_5 = "您好,请问您来自哪 zuo4 cheng2 shi4?"
text_6 = "/həloʊ, meɪ aɪ æsk wɪtʃ sɪti juː ɑːr frʌm?/"
ref_audio_1 = "https://speech-demo.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/moss_tts_demo/tts_readme_demo/reference_zh.wav"
ref_audio_2 = "https://speech-demo.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/moss_tts_demo/tts_readme_demo/reference_en.m4a"
conversations = [
# Direct TTS (no reference)
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_1)],
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_2)],
# Pinyin or IPA input
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_3)],
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_4)],
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_5)],
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_6)],
# Voice cloning (with reference)
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_1, reference=[ref_audio_1])],
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_2, reference=[ref_audio_2])],
# Duration control
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_2, tokens=325)],
[processor.build_user_message(text=text_2, tokens=600)],
]
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
pretrained_model_name_or_path,
trust_remote_code=True,
attn_implementation=attn_implementation,
torch_dtype=dtype,
).to(device)
model.eval()
batch_size = 1
save_dir = Path("inference_root")
save_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
sample_idx = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for start in range(0, len(conversations), batch_size):
batch_conversations = conversations[start : start + batch_size]
batch = processor(batch_conversations, mode="generation")
input_ids = batch["input_ids"].to(device)
attention_mask = batch["attention_mask"].to(device)
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
max_new_tokens=4096,
)
for message in processor.decode(outputs):
audio = message.audio_codes_list[0]
out_path = save_dir / f"sample{sample_idx}.wav"
sample_idx += 1
torchaudio.save(out_path, audio.unsqueeze(0), processor.model_config.sampling_rate)For each model’s full usage, please refer to its corresponding model card.
This section summarizes the family‑level evaluation highlights for MOSS‑TTS and MOSS‑VoiceGenerator. For full details, see each model’s model card.
MOSS‑TTS achieved state‑of‑the‑art results on the open‑source zero‑shot TTS benchmark Seed‑TTS‑eval, surpassing all open‑source models and rivaling leading closed‑source systems.
| Model | Params | Open‑source | EN WER (%) ↓ | EN SIM (%) ↑ | ZH CER (%) ↓ | ZH SIM (%) ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DiTAR | 0.6B | ❌ | 1.69 | 73.5 | 1.02 | 75.3 |
| FishAudio‑S1 | 4B | ❌ | 1.72 | 62.57 | 1.22 | 72.1 |
| Seed‑TTS | ❌ | 2.25 | 76.2 | 1.12 | 79.6 | |
| MiniMax‑Speech | ❌ | 1.65 | 69.2 | 0.83 | 78.3 | |
| CosyVoice | 0.3B | ✅ | 4.29 | 60.9 | 3.63 | 72.3 |
| CosyVoice2 | 0.5B | ✅ | 3.09 | 65.9 | 1.38 | 75.7 |
| CosyVoice3 | 0.5B | ✅ | 2.02 | 71.8 | 1.16 | 78 |
| CosyVoice3 | 1.5B | ✅ | 2.22 | 72 | 1.12 | 78.1 |
| F5‑TTS | 0.3B | ✅ | 2 | 67 | 1.53 | 76 |
| SparkTTS | 0.5B | ✅ | 3.14 | 57.3 | 1.54 | 66 |
| FireRedTTS | 0.5B | ✅ | 3.82 | 46 | 1.51 | 63.5 |
| FireRedTTS‑2 | 1.5B | ✅ | 1.95 | 66.5 | 1.14 | 73.6 |
| Qwen2.5‑Omni | 7B | ✅ | 2.72 | 63.2 | 1.7 | 75.2 |
| FishAudio‑S1‑mini | 0.5B | ✅ | 1.94 | 55 | 1.18 | 68.5 |
| IndexTTS2 | 1.5B | ✅ | 2.23 | 70.6 | 1.03 | 76.5 |
| VibeVoice | 1.5B | ✅ | 3.04 | 68.9 | 1.16 | 74.4 |
| HiggsAudio‑v2 | 3B | ✅ | 2.44 | 67.7 | 1.5 | 74 |
| VoxCPM | 0.5B | ✅ | 1.85 | 72.9 | 0.93 | 77.2 |
| Qwen3‑TTS | 0.6B | ✅ | 1.68 | 70.39 | 1.23 | 76.4 |
| Qwen3‑TTS | 1.7B | ✅ | 1.5 | 71.45 | 1.33 | 76.72 |
| GLM-TTS | 1.5B | ✅ | 2.23 | 67.2 | 1.03 | 76.1 |
| GLM-TTS-RL | 1.5B | ✅ | 1.91 | 68.1 | 0.89 | 76.4 |
| MossTTSDelay | 8B | ✅ | 1.79 | 71.46 | 1.32 | 77.05 |
| MossTTSLocal | 1.7B | ✅ | 1.85 | 73.42 | 1.2 | 78.82 |
We evaluate MOSS‑TTSD-v1.0 using three objective metrics: Speaker Switch Accuracy (ACC), Speaker Similarity (SIM), and Word Error Rate (WER). Benchmarked against multiple open-source and closed-source models, the results show that MOSS‑TTSD-v1.0 consistently achieves either the best or second-best performance.
| Model | ZH - SIM | ZH - ACC | ZH - WER | EN - SIM | EN - ACC | EN - WER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison with Open-Source Models | ||||||
| MOSS-TTSD-v1.0 | 0.7949 | 0.9587 | 0.0485 | 0.7326 | 0.9626 | 0.0988 |
| MOSS-TTSD-v0.7 | 0.7423 | 0.9391 | 0.0517 | 0.6743 | 0.9266 | 0.1612 |
| Vibevoice 7B | 0.7590 | 0.9222 | 0.0570 | 0.7140 | 0.9554 | 0.0946 |
| Vibevoice 1.5 B | 0.7415 | 0.8798 | 0.0818 | 0.6961 | 0.9353 | 0.1133 |
| FireRedTTS2 | 0.7383 | 0.9022 | 0.0768 | - | - | - |
| Higgs Audio V2 | - | - | - | 0.6860 | 0.9025 | 0.2131 |
| Comparison with Proprietary Models | ||||||
| MOSS-TTSD-v1.0 (elevenlabs_voice) | 0.8165 | 0.9736 | 0.0391 | 0.7304 | 0.9565 | 0.1005 |
| Eleven V3 | 0.6970 | 0.9653 | 0.0363 | 0.6730 | 0.9498 | 0.0824 |
| MOSS-TTSD-v1.0 (gemini_voice) | - | - | - | 0.7893 | 0.9655 | 0.0984 |
| gemini-2.5-pro-preview-tts | - | - | - | 0.6786 | 0.9537 | 0.0859 |
| gemini-2.5-flash-preview-tts | - | - | - | 0.7194 | 0.9511 | 0.0871 |
| MOSS-TTSD-v1.0 (doubao_voice) | 0.8226 | 0.9630 | 0.0571 | - | - | - |
| Doubao_Podcast | 0.8034 | 0.9606 | 0.0472 | - | - | - |
For open-source models, annotators are asked to score each sample pair in terms of speaker attribution accuracy, voice similarity, prosody, and overall quality. Following the methodology of the LMSYS Chatbot Arena, we compute Elo ratings and confidence intervals for each dimension.

For closed-source models, annotators are only asked to choose the overall preferred one in each pair, and we compute the win rate accordingly.

MOSS‑VoiceGenerator demonstrates strong subjective preference across overall preference, instruction following, and naturalness.
MOSS-Audio-Tokenizer serves as the unified discrete audio interface for the entire MOSS-TTS Family. It is based on the Cat (Causal Audio Tokenizer with Transformer) architecture—a 1.6-billion-parameter, "CNN-free" homogeneous audio tokenizer built entirely from Causal Transformer blocks.
- Unified Discrete Bridge: It acts as the shared backbone for MOSS-TTS, MOSS-TTSD, MOSS-VoiceGenerator, MOSS-SoundEffect, and MOSS-TTS-Realtime, providing a consistent audio representation across the family.
- Extreme Compression & High Fidelity: It compresses 24kHz raw audio into a remarkably low frame rate of 12.5Hz. Utilizing a 32-layer Residual Vector Quantizer (RVQ), it supports high-fidelity reconstruction across variable bitrates from 0.125kbps to 4kbps.
- Massive-Scale General Audio Training: Trained from scratch on 3 million hours of diverse data (speech, sound effects, and music), the model achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction among open source audio tokenizers.
- Native Streaming Design: The pure Causal Transformer architecture is specifically designed for scalability and low-latency streaming inference, enabling real-time production workflows.
To learn more about setup, advanced usage, and evaluation metrics, please visit the MOSS-Audio-Tokenizer Repository
 Architecture of MOSS Audio Tokenizer
Architecture of MOSS Audio Tokenizer
| Model | Hugging Face | ModelScope |
|---|---|---|
| MOSS-Audio-Tokenizer |  |
 |
We compare MOSS Audio Tokenizer with open-source audio tokenizers on the LibriSpeech test-clean subset using SIM, STOI, PESQ-NB, and PESQ-WB. Bitrate is controlled by varying the number of RVQ codebooks during decoding, and MOSS Audio Tokenizer leads reconstruction quality among open-source audio tokenizers at comparable 0–4 kbps bitrates.
Models in MOSS-TTS Family are licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for MOSS-TTS
Similar Open Source Tools

MOSS-TTS
MOSS-TTS Family is an open-source speech and sound generation model family designed for high-fidelity, high-expressiveness, and complex real-world scenarios. It includes five production-ready models: MOSS-TTS, MOSS-TTSD, MOSS-VoiceGenerator, MOSS-TTS-Realtime, and MOSS-SoundEffect, each serving specific purposes in speech generation, dialogue, voice design, real-time interactions, and sound effect generation. The models offer features like long-speech generation, fine-grained control over phonemes and duration, multilingual synthesis, voice cloning, and real-time voice agents.
DataFlow
DataFlow is a data preparation and training system designed to parse, generate, process, and evaluate high-quality data from noisy sources, improving the performance of large language models in specific domains. It constructs diverse operators and pipelines, validated to enhance domain-oriented LLM's performance in fields like healthcare, finance, and law. DataFlow also features an intelligent DataFlow-agent capable of dynamically assembling new pipelines by recombining existing operators on demand.
END-TO-END-GENERATIVE-AI-PROJECTS
The 'END TO END GENERATIVE AI PROJECTS' repository is a collection of awesome industry projects utilizing Large Language Models (LLM) for various tasks such as chat applications with PDFs, image to speech generation, video transcribing and summarizing, resume tracking, text to SQL conversion, invoice extraction, medical chatbot, financial stock analysis, and more. The projects showcase the deployment of LLM models like Google Gemini Pro, HuggingFace Models, OpenAI GPT, and technologies such as Langchain, Streamlit, LLaMA2, LLaMAindex, and more. The repository aims to provide end-to-end solutions for different AI applications.

Xwin-LM
Xwin-LM is a powerful and stable open-source tool for aligning large language models, offering various alignment technologies like supervised fine-tuning, reward models, reject sampling, and reinforcement learning from human feedback. It has achieved top rankings in benchmarks like AlpacaEval and surpassed GPT-4. The tool is continuously updated with new models and features.
InternVL
InternVL scales up the ViT to _**6B parameters**_ and aligns it with LLM. It is a vision-language foundation model that can perform various tasks, including: **Visual Perception** - Linear-Probe Image Classification - Semantic Segmentation - Zero-Shot Image Classification - Multilingual Zero-Shot Image Classification - Zero-Shot Video Classification **Cross-Modal Retrieval** - English Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval - Chinese Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval - Multilingual Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval on XTD **Multimodal Dialogue** - Zero-Shot Image Captioning - Multimodal Benchmarks with Frozen LLM - Multimodal Benchmarks with Trainable LLM - Tiny LVLM InternVL has been shown to achieve state-of-the-art results on a variety of benchmarks. For example, on the MMMU image classification benchmark, InternVL achieves a top-1 accuracy of 51.6%, which is higher than GPT-4V and Gemini Pro. On the DocVQA question answering benchmark, InternVL achieves a score of 82.2%, which is also higher than GPT-4V and Gemini Pro. InternVL is open-sourced and available on Hugging Face. It can be used for a variety of applications, including image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, image captioning, and question answering.
Open-dLLM
Open-dLLM is the most open release of a diffusion-based large language model, providing pretraining, evaluation, inference, and checkpoints. It introduces Open-dCoder, the code-generation variant of Open-dLLM. The repo offers a complete stack for diffusion LLMs, enabling users to go from raw data to training, checkpoints, evaluation, and inference in one place. It includes pretraining pipeline with open datasets, inference scripts for easy sampling and generation, evaluation suite with various metrics, weights and checkpoints on Hugging Face, and transparent configs for full reproducibility.
YuLan-Mini
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters that achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. It excels in mathematics and code domains. The repository provides pre-training resources, including data pipeline, optimization methods, and annealing approaches. Users can pre-train their own language models, perform learning rate annealing, fine-tune the model, research training dynamics, and synthesize data. The team behind YuLan-Mini is AI Box at Renmin University of China. The code is released under the MIT License with future updates on model weights usage policies. Users are advised on potential safety concerns and ethical use of the model.
EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
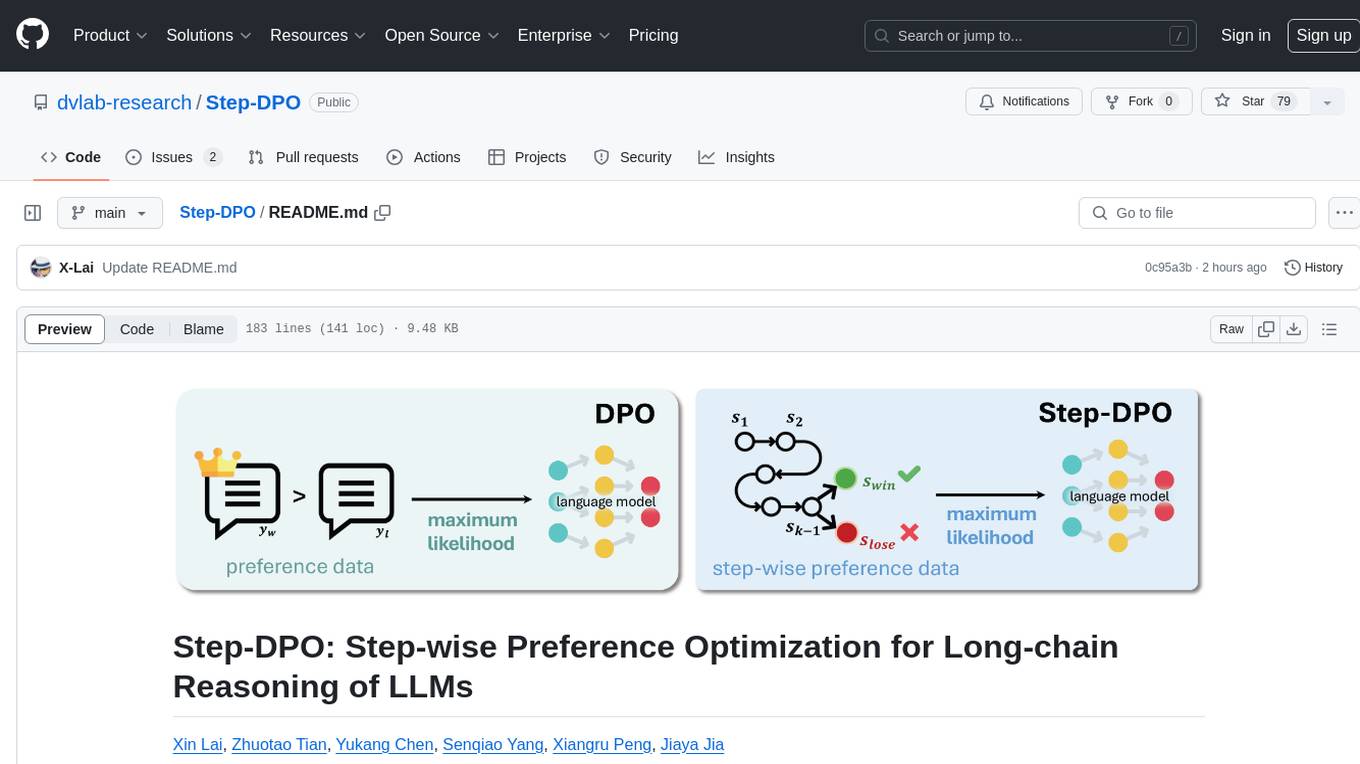
Step-DPO
Step-DPO is a method for enhancing long-chain reasoning ability of LLMs with a data construction pipeline creating a high-quality dataset. It significantly improves performance on math and GSM8K tasks with minimal data and training steps. The tool fine-tunes pre-trained models like Qwen2-7B-Instruct with Step-DPO, achieving superior results compared to other models. It provides scripts for training, evaluation, and deployment, along with examples and acknowledgements.
awesome-ai-efficiency
Awesome AI Efficiency is a curated list of resources dedicated to enhancing efficiency in AI systems. The repository covers various topics essential for optimizing AI models and processes, aiming to make AI faster, cheaper, smaller, and greener. It includes topics like quantization, pruning, caching, distillation, factorization, compilation, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, speculative decoding, hardware optimization, training techniques, inference optimization, sustainability strategies, and scalability approaches.
LlamaV-o1
LlamaV-o1 is a Large Multimodal Model designed for spontaneous reasoning tasks. It outperforms various existing models on multimodal reasoning benchmarks. The project includes a Step-by-Step Visual Reasoning Benchmark, a novel evaluation metric, and a combined Multi-Step Curriculum Learning and Beam Search Approach. The model achieves superior performance in complex multi-step visual reasoning tasks in terms of accuracy and efficiency.
speechless
Speechless.AI is committed to integrating the superior language processing and deep reasoning capabilities of large language models into practical business applications. By enhancing the model's language understanding, knowledge accumulation, and text creation abilities, and introducing long-term memory, external tool integration, and local deployment, our aim is to establish an intelligent collaborative partner that can independently interact, continuously evolve, and closely align with various business scenarios.
langfuse
Langfuse is a powerful tool that helps you develop, monitor, and test your LLM applications. With Langfuse, you can: * **Develop:** Instrument your app and start ingesting traces to Langfuse, inspect and debug complex logs, and manage, version, and deploy prompts from within Langfuse. * **Monitor:** Track metrics (cost, latency, quality) and gain insights from dashboards & data exports, collect and calculate scores for your LLM completions, run model-based evaluations, collect user feedback, and manually score observations in Langfuse. * **Test:** Track and test app behaviour before deploying a new version, test expected in and output pairs and benchmark performance before deploying, and track versions and releases in your application. Langfuse is easy to get started with and offers a generous free tier. You can sign up for Langfuse Cloud or deploy Langfuse locally or on your own infrastructure. Langfuse also offers a variety of integrations to make it easy to connect to your LLM applications.
ZhiLight
ZhiLight is a highly optimized large language model (LLM) inference engine developed by Zhihu and ModelBest Inc. It accelerates the inference of models like Llama and its variants, especially on PCIe-based GPUs. ZhiLight offers significant performance advantages compared to mainstream open-source inference engines. It supports various features such as custom defined tensor and unified global memory management, optimized fused kernels, support for dynamic batch, flash attention prefill, prefix cache, and different quantization techniques like INT8, SmoothQuant, FP8, AWQ, and GPTQ. ZhiLight is compatible with OpenAI interface and provides high performance on mainstream NVIDIA GPUs with different model sizes and precisions.
AI0x0.com
AI 0x0 is a versatile AI query generation desktop floating assistant application that supports MacOS and Windows. It allows users to utilize AI capabilities in any desktop software to query and generate text, images, audio, and video data, helping them work more efficiently. The application features a dynamic desktop floating ball, floating dialogue bubbles, customizable presets, conversation bookmarking, preset packages, network acceleration, query mode, input mode, mouse navigation, deep customization of ChatGPT Next Web, support for full-format libraries, online search, voice broadcasting, voice recognition, voice assistant, application plugins, multi-model support, online text and image generation, image recognition, frosted glass interface, light and dark theme adaptation for each language model, and free access to all language models except Chat0x0 with a key.
For similar tasks
metavoice-src
MetaVoice-1B is a 1.2B parameter base model trained on 100K hours of speech for TTS (text-to-speech). It has been built with the following priorities: * Emotional speech rhythm and tone in English. * Zero-shot cloning for American & British voices, with 30s reference audio. * Support for (cross-lingual) voice cloning with finetuning. * We have had success with as little as 1 minute training data for Indian speakers. * Synthesis of arbitrary length text
wunjo.wladradchenko.ru
Wunjo AI is a comprehensive tool that empowers users to explore the realm of speech synthesis, deepfake animations, video-to-video transformations, and more. Its user-friendly interface and privacy-first approach make it accessible to both beginners and professionals alike. With Wunjo AI, you can effortlessly convert text into human-like speech, clone voices from audio files, create multi-dialogues with distinct voice profiles, and perform real-time speech recognition. Additionally, you can animate faces using just one photo combined with audio, swap faces in videos, GIFs, and photos, and even remove unwanted objects or enhance the quality of your deepfakes using the AI Retouch Tool. Wunjo AI is an all-in-one solution for your voice and visual AI needs, offering endless possibilities for creativity and expression.
Pandrator
Pandrator is a GUI tool for generating audiobooks and dubbing using voice cloning and AI. It transforms text, PDF, EPUB, and SRT files into spoken audio in multiple languages. It leverages XTTS, Silero, and VoiceCraft models for text-to-speech conversion and voice cloning, with additional features like LLM-based text preprocessing and NISQA for audio quality evaluation. The tool aims to be user-friendly with a one-click installer and a graphical interface.
ruoyi-ai
ruoyi-ai is a platform built on top of ruoyi-plus to implement AI chat and drawing functionalities on the backend. The project is completely open source and free. The backend management interface uses elementUI, while the server side is built using Java 17 and SpringBoot 3.X. It supports various AI models such as ChatGPT4, Dall-E-3, ChatGPT-4-All, voice cloning based on GPT-SoVITS, GPTS, and MidJourney. Additionally, it supports WeChat mini programs, personal QR code real-time payments, monitoring and AI auto-reply in live streaming rooms like Douyu and Bilibili, and personal WeChat integration with ChatGPT. The platform also includes features like private knowledge base management and provides various demo interfaces for different platforms such as mobile, web, and PC.
viitor-voice
ViiTor-Voice is an LLM based TTS Engine that offers a lightweight design with 0.5B parameters for efficient deployment on various platforms. It provides real-time streaming output with low latency experience, a rich voice library with over 300 voice options, flexible speech rate adjustment, and zero-shot voice cloning capabilities. The tool supports both Chinese and English languages and is suitable for applications requiring quick response and natural speech fluency.

ebook2audiobook
ebook2audiobook is a CPU/GPU converter tool that converts eBooks to audiobooks with chapters and metadata using tools like Calibre, ffmpeg, XTTSv2, and Fairseq. It supports voice cloning and a wide range of languages. The tool is designed to run on 4GB RAM and provides a new v2.0 Web GUI interface for user-friendly interaction. Users can convert eBooks to text format, split eBooks into chapters, and utilize high-quality text-to-speech functionalities. Supported languages include Arabic, Chinese, English, French, German, Hindi, and many more. The tool can be used for legal, non-DRM eBooks only and should be used responsibly in compliance with applicable laws.
HeyGem.ai
Heygem is an open-source, affordable alternative to Heygen, offering a fully offline video synthesis tool for Windows systems. It enables precise appearance and voice cloning, allowing users to digitalize their image and drive virtual avatars through text and voice for video production. With core features like efficient video synthesis and multi-language support, Heygem ensures a user-friendly experience with fully offline operation and support for multiple models. The tool leverages advanced AI algorithms for voice cloning, automatic speech recognition, and computer vision technology to enhance the virtual avatar's performance and synchronization.

KlicStudio
Klic Studio is a versatile audio and video localization and enhancement solution developed by Krillin AI. This minimalist yet powerful tool integrates video translation, dubbing, and voice cloning, supporting both landscape and portrait formats. With an end-to-end workflow, users can transform raw materials into beautifully ready-to-use cross-platform content with just a few clicks. The tool offers features like video acquisition, accurate speech recognition, intelligent segmentation, terminology replacement, professional translation, voice cloning, video composition, and cross-platform support. It also supports various speech recognition services, large language models, and TTS text-to-speech services. Users can easily deploy the tool using Docker and configure it for different tasks like subtitle translation, large model translation, and optional voice services.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.