
ZhiLight
A highly optimized LLM inference acceleration engine for Llama and its variants.
Stars: 832
ZhiLight is a highly optimized large language model (LLM) inference engine developed by Zhihu and ModelBest Inc. It accelerates the inference of models like Llama and its variants, especially on PCIe-based GPUs. ZhiLight offers significant performance advantages compared to mainstream open-source inference engines. It supports various features such as custom defined tensor and unified global memory management, optimized fused kernels, support for dynamic batch, flash attention prefill, prefix cache, and different quantization techniques like INT8, SmoothQuant, FP8, AWQ, and GPTQ. ZhiLight is compatible with OpenAI interface and provides high performance on mainstream NVIDIA GPUs with different model sizes and precisions.
README:
✨ ZhiLight ✨is a highly optimized LLM inference engine developed by Zhihu and ModelBest Inc. The "Zhi" in its name stands for Zhihu. ZhiLight can accelerate the inference of models like Llama and its variants, especially on PCIe-based GPUs. Compared to mainstream open-source inference engines, for example, vllm, it has significant performance advantages.
- [2025/01] Support DeepSeek-VL2 multimodal models: deepseek-vl2-tiny, deepseek-vl2-small, deepseek-vl2.
- [2025/01] Support LLaMA3 models: Llama-3.1-8B, Llama-3.1-70B, Llama-3.2-1B, Llama-3.2-3B, Llama-3.3-70B.
see Roadmap
- Asynchronous OpenAI compatible interface adapted from vllm
- Custom defined tensor and unified global memory management
- 🔥 Encode and all-reduce overlap, we named "dual streams"
- Support Int8-quantized all-reduce to further reduce all-reduce cost.
- Host all-reduce based on SIMD instructions
- Optimized fused kernels, qkv, residual & layernorm etc.
- 🔥 Fused batch attention for decoding based on tensor core instructions
- Support TP and PP on one node, TP is recommended
- Support dynamic batch
- Support flash attention prefill
- Support chunked prefill
- Support prefix cache
- Support Native INT8/SmoothQuant/FP8/AWQ/GPTQ quantization
- Support Marlin kernel for GPTQ
- Support MoE, DeepseekV2 MoE and DeepseekV2 MLA
- Support Llama/Llama2, Mixtral, Qwen2 series and similar models
# Concurrently compile the wheel package, and turn off the unit test
CMAKE_BUILD_PARALLEL_LEVEL=32 TESTING=0 python setup.py bdist_wheel
# Compile with ninja backend
CMAKE_GENERATER="Ninja" python setup.py bdist_wheel
# Install directly
cd ./ZhiLight && pip install -e .
# Start OpenAI compatible server
python -m zhilight.server.openai.entrypoints.api_server [options]ZhiLight only depends on the CUDA runtime, cuBLAS, NCCL, and a few Python packages in requirements.txt. You can use the image below for running or building it. You can also directly refer to docker/Dockerfile.
docker pull ghcr.io/zhihu/zhilight/zhilight:0.4.8-cu124We conducted performance reviews on various mainstream NVIDIA GPUs with different model sizes and precisions. For dense models ranging from 2B to 110B parameters on PCIe devices, ZhiLight demonstrates significant performance advantages compared to mainstream open-source inference engines.
Test Description:
- Test purpose is to demonstrate performance, applicable scenarios and limitations
- Test dataset contains approximately 3.7k prompts
- Test metrics include:
- QPS: Queries Per Second
- TTFT (Time To First Token): First token generation latency
- TPOT (Time Per Output Token): Generation latency per output token
- Test environments include:
- AD102 PCIe : Consumer-grade GPU for experimental research
- A800: Data center GPU for production deployment
- Test models include:
- Large-scale models: Qwen1.5-110B, Qwen2-72B, LLama-3.1-70B
- Medium-scale models: Qwen2.5-14B, Llama-3.1-8B, Minicpm-2B
- Compared inference engines include:
- vLLM
- SGLang
- ZhiLight
- NVIDIA AD102 PCIe * 1
| Inference Engine | QPS | TTFT Mean | TTFT P95 | TPOT Mean | TPOT P95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | 1.67 | 527.55 | 1062.96 | 16.71 | 31.95 |
| SGLang | 1.67 | 466.19 | 1181.5 | 33.96 | 59.44 |
| ZhiLight | 1.67 | 434.64 | 989.03 | 26.1 | 61.14 |
- NVIDIA AD102 PCIe * 4
| Inference Engine | QPS | TTFT Mean | TTFT P95 | TPOT Mean | TPOT P95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | 0.18 | 3493.97 | 6852.07 | 35.47 | 61.74 |
| SGLang | 0.18 | 2276.1 | 3820.7 | 38.12 | 65.16 |
| ZhiLight | 0.18 | 1111.8 | 1882.5 | 26.75 | 41.81 |
- NVIDIA A800 * 4
| Inference Engine | QPS | TTFT Mean | TTFT P95 | TPOT Mean | TPOT P95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | 0.18 | 1457.65 | 2136.5 | 22.14 | 28.96 |
| SGLang | 0.36 | 1113.06 | 1850.57 | 30.41 | 43.65 |
| ZhiLight | 0.18 | 1227.37 | 1968.95 | 31.95 | 48.53 |
- NVIDIA AD102 PCIe * 4
| Inference Engine | QPS | TTFT Mean | TTFT P95 | TPOT Mean | TPOT P95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | 0.09 | 3085.74 | 4274.03 | 30.34 | 44.08 |
| SGLang | 0.09 | 2418.56 | 3187.73 | 31.39 | 53.1 |
| ZhiLight | 0.18 | 1671.38 | 2669.82 | 39.68 | 64.35 |
- NVIDIA A800 * 4
| Inference Engine | QPS | TTFT Mean | TTFT P95 | TPOT Mean | TPOT P95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | 0.09 | 1899.07 | 2719.59 | 23.8 | 33.02 |
| SGLang | 0.18 | 1514.49 | 2135.75 | 28.5 | 47.28 |
| ZhiLight | 0.1 | 1574.85 | 2086.8 | 27.07 | 38.82 |
more benchmarks can be found in benchmarks.md
Apache License 2.0
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ZhiLight
Similar Open Source Tools

ZhiLight
ZhiLight is a highly optimized large language model (LLM) inference engine developed by Zhihu and ModelBest Inc. It accelerates the inference of models like Llama and its variants, especially on PCIe-based GPUs. ZhiLight offers significant performance advantages compared to mainstream open-source inference engines. It supports various features such as custom defined tensor and unified global memory management, optimized fused kernels, support for dynamic batch, flash attention prefill, prefix cache, and different quantization techniques like INT8, SmoothQuant, FP8, AWQ, and GPTQ. ZhiLight is compatible with OpenAI interface and provides high performance on mainstream NVIDIA GPUs with different model sizes and precisions.
DataFlow
DataFlow is a data preparation and training system designed to parse, generate, process, and evaluate high-quality data from noisy sources, improving the performance of large language models in specific domains. It constructs diverse operators and pipelines, validated to enhance domain-oriented LLM's performance in fields like healthcare, finance, and law. DataFlow also features an intelligent DataFlow-agent capable of dynamically assembling new pipelines by recombining existing operators on demand.
EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
sktime
sktime is a Python library for time series analysis that provides a unified interface for various time series learning tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, annotation, and forecasting. It offers time series algorithms and tools compatible with scikit-learn for building, tuning, and validating time series models. sktime aims to enhance the interoperability and usability of the time series analysis ecosystem by empowering users to apply algorithms across different tasks and providing interfaces to related libraries like scikit-learn, statsmodels, tsfresh, PyOD, and fbprophet.

MOSS-TTS
MOSS-TTS Family is an open-source speech and sound generation model family designed for high-fidelity, high-expressiveness, and complex real-world scenarios. It includes five production-ready models: MOSS-TTS, MOSS-TTSD, MOSS-VoiceGenerator, MOSS-TTS-Realtime, and MOSS-SoundEffect, each serving specific purposes in speech generation, dialogue, voice design, real-time interactions, and sound effect generation. The models offer features like long-speech generation, fine-grained control over phonemes and duration, multilingual synthesis, voice cloning, and real-time voice agents.
END-TO-END-GENERATIVE-AI-PROJECTS
The 'END TO END GENERATIVE AI PROJECTS' repository is a collection of awesome industry projects utilizing Large Language Models (LLM) for various tasks such as chat applications with PDFs, image to speech generation, video transcribing and summarizing, resume tracking, text to SQL conversion, invoice extraction, medical chatbot, financial stock analysis, and more. The projects showcase the deployment of LLM models like Google Gemini Pro, HuggingFace Models, OpenAI GPT, and technologies such as Langchain, Streamlit, LLaMA2, LLaMAindex, and more. The repository aims to provide end-to-end solutions for different AI applications.
Open-dLLM
Open-dLLM is the most open release of a diffusion-based large language model, providing pretraining, evaluation, inference, and checkpoints. It introduces Open-dCoder, the code-generation variant of Open-dLLM. The repo offers a complete stack for diffusion LLMs, enabling users to go from raw data to training, checkpoints, evaluation, and inference in one place. It includes pretraining pipeline with open datasets, inference scripts for easy sampling and generation, evaluation suite with various metrics, weights and checkpoints on Hugging Face, and transparent configs for full reproducibility.
ReGraph
ReGraph is a decentralized AI compute marketplace that connects hardware providers with developers who need inference and training resources. It democratizes access to AI computing power by creating a global network of distributed compute nodes. It is cost-effective, decentralized, easy to integrate, supports multiple models, and offers pay-as-you-go pricing.
Video-ChatGPT
Video-ChatGPT is a video conversation model that aims to generate meaningful conversations about videos by combining large language models with a pretrained visual encoder adapted for spatiotemporal video representation. It introduces high-quality video-instruction pairs, a quantitative evaluation framework for video conversation models, and a unique multimodal capability for video understanding and language generation. The tool is designed to excel in tasks related to video reasoning, creativity, spatial and temporal understanding, and action recognition.
pai-opencode
PAI-OpenCode is a complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode, an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant. It brings modular capabilities, dynamic multi-agent orchestration, session history, and lifecycle automation to personalize AI assistants for users. With support for 75+ AI providers, PAI-OpenCode offers dynamic per-task model routing, full PAI infrastructure, real-time session sharing, and multiple client options. The tool optimizes cost and quality with a 3-tier model strategy and a 3-tier research system, allowing users to switch presets for different routing strategies. PAI-OpenCode's architecture preserves PAI's design while adapting to OpenCode, documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs).
awesome-ai-efficiency
Awesome AI Efficiency is a curated list of resources dedicated to enhancing efficiency in AI systems. The repository covers various topics essential for optimizing AI models and processes, aiming to make AI faster, cheaper, smaller, and greener. It includes topics like quantization, pruning, caching, distillation, factorization, compilation, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, speculative decoding, hardware optimization, training techniques, inference optimization, sustainability strategies, and scalability approaches.
LlamaV-o1
LlamaV-o1 is a Large Multimodal Model designed for spontaneous reasoning tasks. It outperforms various existing models on multimodal reasoning benchmarks. The project includes a Step-by-Step Visual Reasoning Benchmark, a novel evaluation metric, and a combined Multi-Step Curriculum Learning and Beam Search Approach. The model achieves superior performance in complex multi-step visual reasoning tasks in terms of accuracy and efficiency.
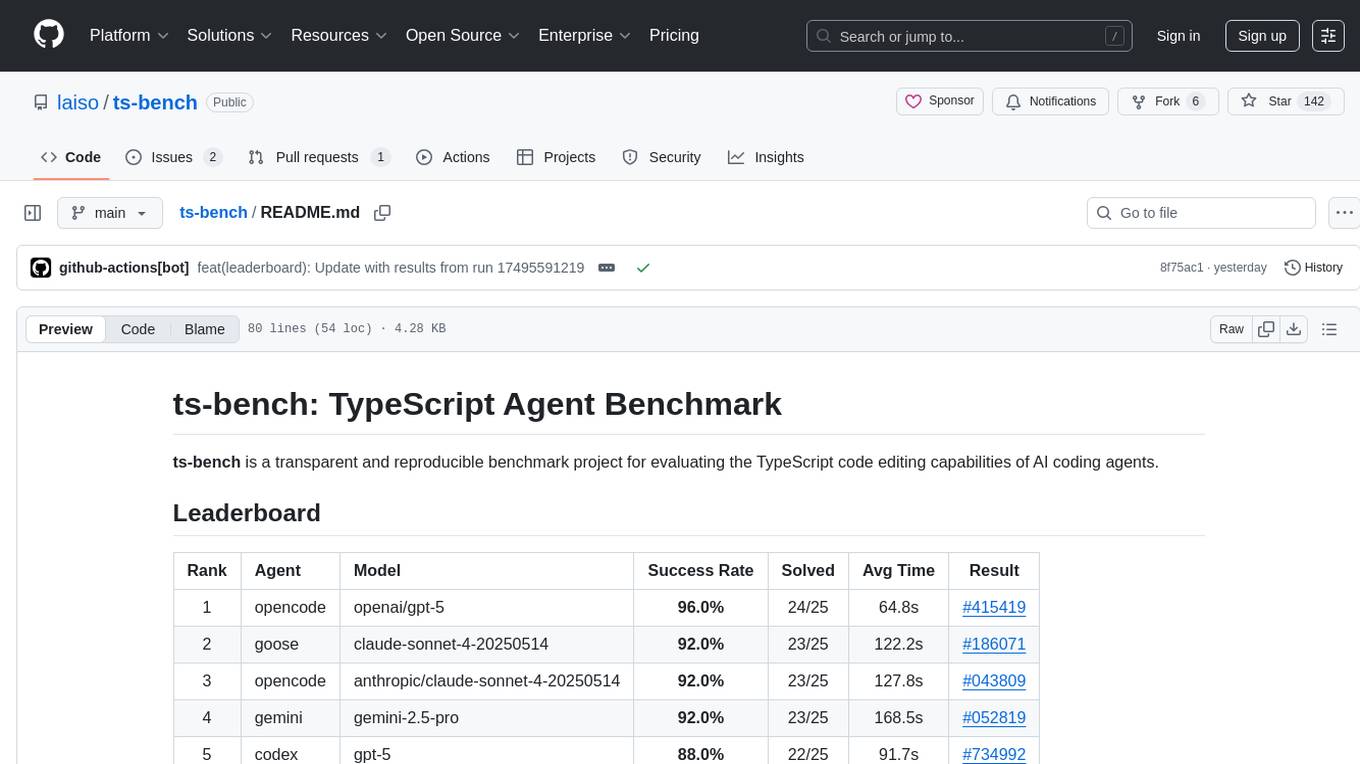
ts-bench
TS-Bench is a performance benchmarking tool for TypeScript projects. It provides detailed insights into the performance of TypeScript code, helping developers optimize their projects. With TS-Bench, users can measure and compare the execution time of different code snippets, functions, or modules. The tool offers a user-friendly interface for running benchmarks and analyzing the results. TS-Bench is a valuable asset for developers looking to enhance the performance of their TypeScript applications.
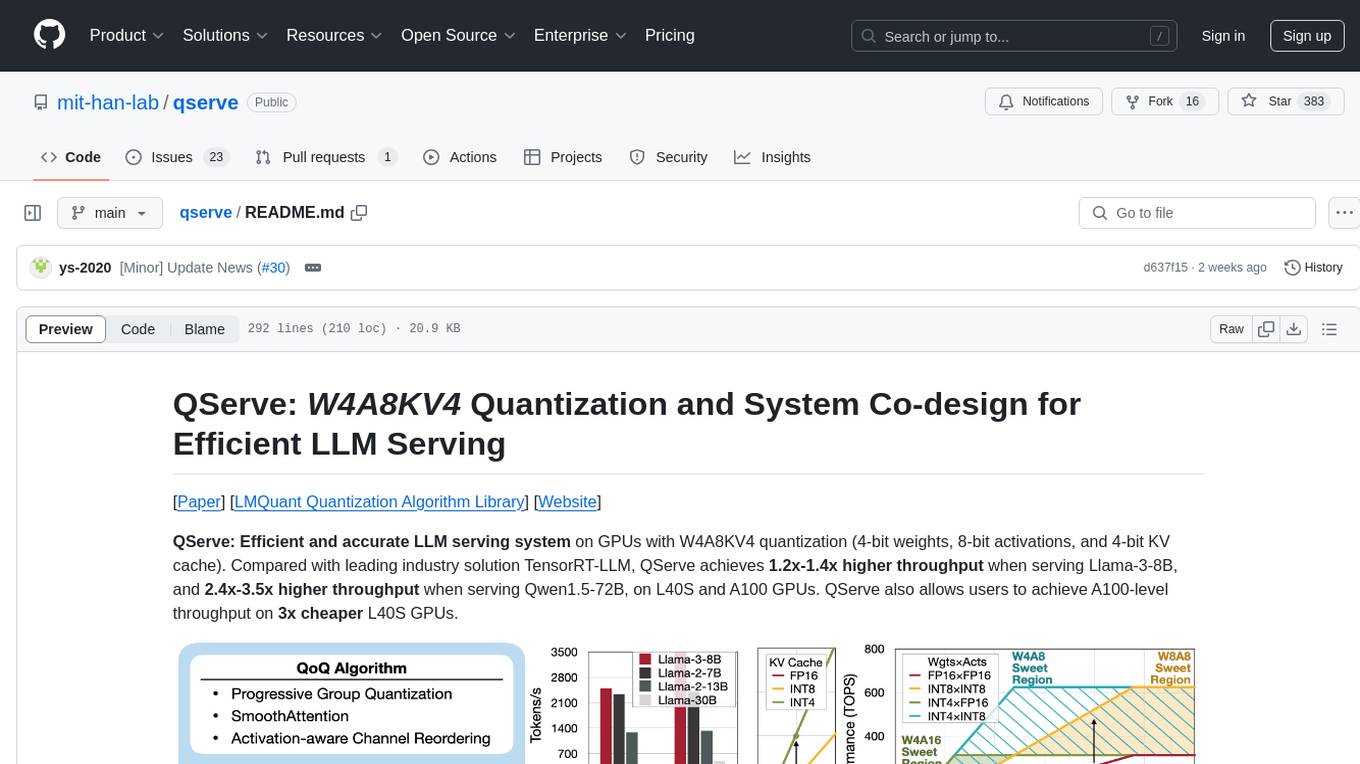
qserve
QServe is a serving system designed for efficient and accurate Large Language Models (LLM) on GPUs with W4A8KV4 quantization. It achieves higher throughput compared to leading industry solutions, allowing users to achieve A100-level throughput on cheaper L40S GPUs. The system introduces the QoQ quantization algorithm with 4-bit weight, 8-bit activation, and 4-bit KV cache, addressing runtime overhead challenges. QServe improves serving throughput for various LLM models by implementing compute-aware weight reordering, register-level parallelism, and fused attention memory-bound techniques.

Xwin-LM
Xwin-LM is a powerful and stable open-source tool for aligning large language models, offering various alignment technologies like supervised fine-tuning, reward models, reject sampling, and reinforcement learning from human feedback. It has achieved top rankings in benchmarks like AlpacaEval and surpassed GPT-4. The tool is continuously updated with new models and features.
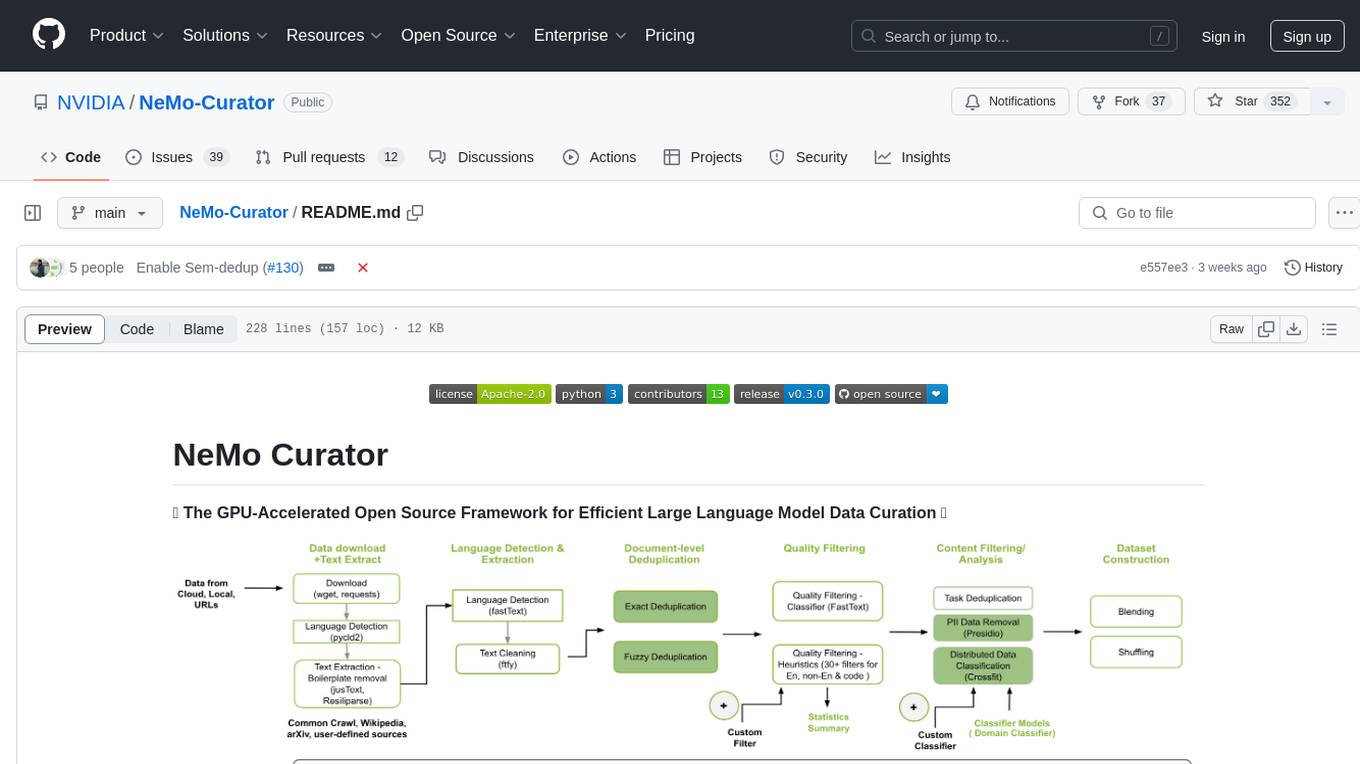
Curator
NeMo Curator is a Python library designed for fast and scalable data processing and curation for generative AI use cases. It accelerates data processing by leveraging GPUs with Dask and RAPIDS, providing customizable pipelines for text and image curation. The library offers pre-built pipelines for synthetic data generation, enabling users to train and customize generative AI models such as LLMs, VLMs, and WFMs.
For similar tasks

Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B
Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B is an open-source project based on Mistral's Mixtral-8x7B model for incremental pre-training of Chinese vocabulary, aiming to advance research on MoE models in the Chinese natural language processing community. The expanded vocabulary significantly improves the model's encoding and decoding efficiency for Chinese, and the model is pre-trained incrementally on a large-scale open-source corpus, enabling it with powerful Chinese generation and comprehension capabilities. The project includes a large model with expanded Chinese vocabulary and incremental pre-training code.
Awesome-LLMs-on-device
Welcome to the ultimate hub for on-device Large Language Models (LLMs)! This repository is your go-to resource for all things related to LLMs designed for on-device deployment. Whether you're a seasoned researcher, an innovative developer, or an enthusiastic learner, this comprehensive collection of cutting-edge knowledge is your gateway to understanding, leveraging, and contributing to the exciting world of on-device LLMs.

ZhiLight
ZhiLight is a highly optimized large language model (LLM) inference engine developed by Zhihu and ModelBest Inc. It accelerates the inference of models like Llama and its variants, especially on PCIe-based GPUs. ZhiLight offers significant performance advantages compared to mainstream open-source inference engines. It supports various features such as custom defined tensor and unified global memory management, optimized fused kernels, support for dynamic batch, flash attention prefill, prefix cache, and different quantization techniques like INT8, SmoothQuant, FP8, AWQ, and GPTQ. ZhiLight is compatible with OpenAI interface and provides high performance on mainstream NVIDIA GPUs with different model sizes and precisions.
AIInfra
AIInfra is an open-source project focused on AI infrastructure, specifically targeting large models in distributed clusters, distributed architecture, distributed training, and algorithms related to large models. The project aims to explore and study system design in artificial intelligence and deep learning, with a focus on the hardware and software stack for building AI large model systems. It provides a comprehensive curriculum covering topics such as AI chip principles, communication and storage, AI clusters, large model training, and inference, as well as algorithms for large models. The course is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, as well as professionals working with AI large model systems, to gain a deep understanding of AI computer system architecture and design.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.