
PromptFuzz
PromtFuzz is an automated tool that generates high-quality fuzz drivers for libraries via a fuzz loop constructed on mutating LLMs' prompts.
Stars: 230
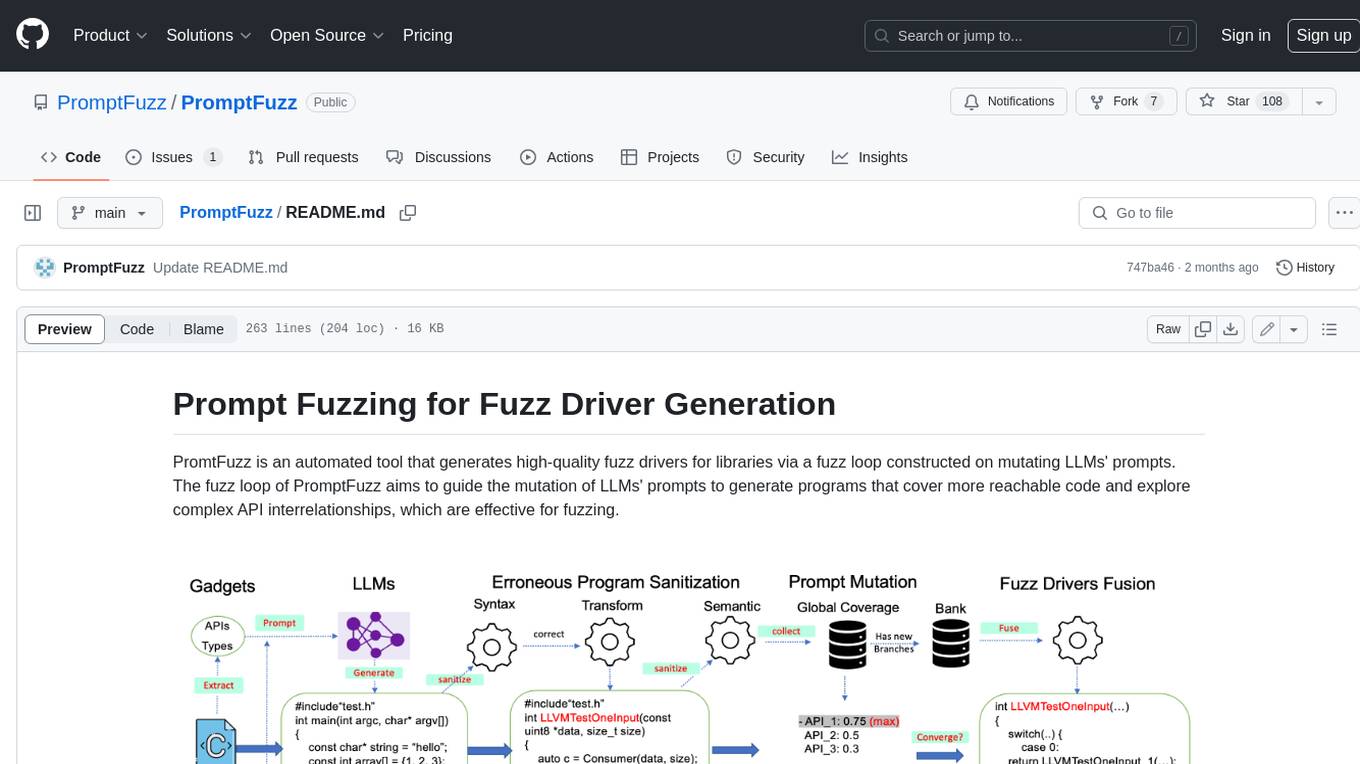
**Description:** PromptFuzz is an automated tool that generates high-quality fuzz drivers for libraries via a fuzz loop constructed on mutating LLMs' prompts. The fuzz loop of PromptFuzz aims to guide the mutation of LLMs' prompts to generate programs that cover more reachable code and explore complex API interrelationships, which are effective for fuzzing. **Features:** * **Multiply LLM support** : Supports the general LLMs: Codex, Inocder, ChatGPT, and GPT4 (Currently tested on ChatGPT). * **Context-based Prompt** : Construct LLM prompts with the automatically extracted library context. * **Powerful Sanitization** : The program's syntax, semantics, behavior, and coverage are thoroughly analyzed to sanitize the problematic programs. * **Prioritized Mutation** : Prioritizes mutating the library API combinations within LLM's prompts to explore complex interrelationships, guided by code coverage. * **Fuzz Driver Exploitation** : Infers API constraints using statistics and extends fixed API arguments to receive random bytes from fuzzers. * **Fuzz engine integration** : Integrates with grey-box fuzz engine: LibFuzzer. **Benefits:** * **High branch coverage:** The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz achieved a branch coverage of 40.12% on the tested libraries, which is 1.61x greater than _OSS-Fuzz_ and 1.67x greater than _Hopper_. * **Bug detection:** PromptFuzz detected 33 valid security bugs from 49 unique crashes. * **Wide range of bugs:** The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz can detect a wide range of bugs, most of which are security bugs. * **Unique bugs:** PromptFuzz detects uniquely interesting bugs that other fuzzers may miss. **Usage:** 1. Build the library using the provided build scripts. 2. Export the LLM API KEY if using ChatGPT or GPT4. 3. Generate fuzz drivers using the `fuzzer` command. 4. Run the fuzz drivers using the `harness` command. 5. Deduplicate and analyze the reported crashes. **Future Works:** * **Custom LLMs suport:** Support custom LLMs. * **Close-source libraries:** Apply PromptFuzz to close-source libraries by fine tuning LLMs on private code corpus. * **Performance** : Reduce the huge time cost required in erroneous program elimination.
README:
PromptFuzz is an automated tool that generates high-quality fuzz drivers for libraries via a fuzz loop constructed on mutating LLMs' prompts. The fuzz loop of PromptFuzz aims to guide the mutation of LLMs' prompts to generate programs that cover more reachable code and explore complex API interrelationships, which are effective for fuzzing.
PromptFuzz is currently regarded as the leading approach for generating fuzz drivers both in academia and industry. The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz achieved a branch coverage of 40.12% on the tested libraries, which is 1.61x greater than OSS-Fuzz and 1.67x greater than Hopper. Besides, PromptFuzz detected 33 valid security bugs from 49 unique crashes.

- Multiply LLM support: Supports the general LLMs: Codex, Incoder, ChatGPT, and GPT4 (Currently tested on ChatGPT).
- Context-based Prompt: Construct LLM prompts with the automatically extracted library context.
- Powerful Sanitization: The program's syntax, semantics, behavior, and coverage are thoroughly analyzed to sanitize the problematic programs.
- Prioritized Mutation: Prioritizes mutating the library API combinations within LLM's prompts to explore complex interrelationships, guided by code coverage.
- Fuzz Driver Exploitation: Infers API constraints using statistics and extends fixed API arguments to receive random bytes from fuzzers.
- Fuzz engine integration: Integrates with grey-box fuzz engine: LibFuzzer.
The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz can detect a wide range of bugs, most of which are security bugs. For instances, CVE-2023-6277, CVE-2023-52355 and CVE-2023-52356.
PromptFuzz detects uniquely interesting bugs:
| ID | Library | Buggy Function | Bug Type | Status | Track Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | libaom | highbd_8_variance_sse2 | SEGV | Confirmed | 3489 |
| 2. | libaom | av1_rc_update_framerate | Uninitialized Stack | Confirmed | 3509 |
| 3. | libaom | timebase_units_to_ticks | Integer Overflow | Confirmed | 3510 |
| 4. | libaom | encode_without_recode | SEGV | Confirmed | 3534 |
| 5. | libvpx | vp8_peek_si_internal | SEGV | Confirmed | 1817 |
| 6. | libvpx | update_fragments | Buffer Overflow | Confirmed | 1827 |
| 7. | libvpx | vp8e_encode | Integer Overflow | Confirmed | 1828 |
| 8. | libvpx | encode_mb_row | Integer Overflow | Confirmed | 1831 |
| 9. | libvpx | vpx_free_tpl_gop_stats | SEGV | Confirmed | 1837 |
| 10. | libmagic | apprentice_map | Buffer Overflow | Waiting | 481 |
| 11. | libmagic | magic_setparam | Buffer Overflow | Waiting | 482 |
| 12. | libmagic | check_buffer | Buffer Overflow | Confirmed | 483 |
| 13. | libmagic | mget | Integer Overflow | Waiting | 486 |
| 14. | libTIFF | TIFFOpen | OOM | Confirmed | 614 |
| 15. | libTIFF | PixarLogSetupDecode | OOM | Confirmed | 619 |
| 16. | libTIFF | TIFFReadEncodedStrip | OOM | Confirmed | 620 |
| 17. | libTIFF | TIFFReadRGBAImageOriented | OOM | Confirmed | 620 |
| 18. | libTIFF | TIFFRasterScanlineSize64 | OOM | Confirmed | 621 |
| 19. | libTIFF | TIFFReadRGBATileExt | SEGV | Confirmed | 622 |
| 20. | sqlite3 | sqlite3_unlock_notify | Null Pointer crash | Confirmed | e77a5 |
| 21. | sqlite3 | sqlite3_enable_load_extension | Null Pointer crash | Confirmed | 9ce83 |
| 22. | sqlite3 | sqlite3_db_config | Null Pointer crash | Confirmed | 5e3fc |
| 23. | c-ares | config_sortlist | Memory Leak | Confirmed | d62627 |
| 24. | c-ares | config_sortlist | Memory Leak | Confirmed | d62627 |
| 25. | libjpeg-turbo | tj3DecodeYUV8 | Integer Overflow | Confirmed | 78eaf0 |
| 26. | libjpeg-turbo | tj3LoadImage16 | OOM | Confirmed | 735 |
| 27. | libpcap | pcap_create | File Leak | Confirmed | 1233 |
| 28. | libpcap | pcapint_create_interface | Null Pointer crash | Confirmed | 1239 |
| 29. | libpcap | pcapint_fixup_pcap_pkthdr | Misaligned Address | Confirmed | - |
| 30. | cJSON | cJSON_SetNumberHelper | Error Cast | Confirmed | 805 |
| 31. | cJSON | cJSON_CreateNumber | Error Cast | Confirmed | 806 |
| 32. | cJSON | cJSON_DeleteItemFromObjectCaseSensitive | TimeOut | Confirmed | 807 |
| 33. | curl | parseurl | Assertion Failure | Confirmed | 12775 |
See in Usage
- Close-source libraries: Apply PromptFuzz to close-source libraries by fine tuning LLMs on private code corpus.
- Generalization: Generalize PromptFuzz to binary programs.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for PromptFuzz
Similar Open Source Tools

PromptFuzz
**Description:** PromptFuzz is an automated tool that generates high-quality fuzz drivers for libraries via a fuzz loop constructed on mutating LLMs' prompts. The fuzz loop of PromptFuzz aims to guide the mutation of LLMs' prompts to generate programs that cover more reachable code and explore complex API interrelationships, which are effective for fuzzing. **Features:** * **Multiply LLM support** : Supports the general LLMs: Codex, Inocder, ChatGPT, and GPT4 (Currently tested on ChatGPT). * **Context-based Prompt** : Construct LLM prompts with the automatically extracted library context. * **Powerful Sanitization** : The program's syntax, semantics, behavior, and coverage are thoroughly analyzed to sanitize the problematic programs. * **Prioritized Mutation** : Prioritizes mutating the library API combinations within LLM's prompts to explore complex interrelationships, guided by code coverage. * **Fuzz Driver Exploitation** : Infers API constraints using statistics and extends fixed API arguments to receive random bytes from fuzzers. * **Fuzz engine integration** : Integrates with grey-box fuzz engine: LibFuzzer. **Benefits:** * **High branch coverage:** The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz achieved a branch coverage of 40.12% on the tested libraries, which is 1.61x greater than _OSS-Fuzz_ and 1.67x greater than _Hopper_. * **Bug detection:** PromptFuzz detected 33 valid security bugs from 49 unique crashes. * **Wide range of bugs:** The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz can detect a wide range of bugs, most of which are security bugs. * **Unique bugs:** PromptFuzz detects uniquely interesting bugs that other fuzzers may miss. **Usage:** 1. Build the library using the provided build scripts. 2. Export the LLM API KEY if using ChatGPT or GPT4. 3. Generate fuzz drivers using the `fuzzer` command. 4. Run the fuzz drivers using the `harness` command. 5. Deduplicate and analyze the reported crashes. **Future Works:** * **Custom LLMs suport:** Support custom LLMs. * **Close-source libraries:** Apply PromptFuzz to close-source libraries by fine tuning LLMs on private code corpus. * **Performance** : Reduce the huge time cost required in erroneous program elimination.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

Prompt-Engineering-Holy-Grail
The Prompt Engineering Holy Grail repository is a curated resource for prompt engineering enthusiasts, providing essential resources, tools, templates, and best practices to support learning and working in prompt engineering. It covers a wide range of topics related to prompt engineering, from beginner fundamentals to advanced techniques, and includes sections on learning resources, online courses, books, prompt generation tools, prompt management platforms, prompt testing and experimentation, prompt crafting libraries, prompt libraries and datasets, prompt engineering communities, freelance and job opportunities, contributing guidelines, code of conduct, support for the project, and contact information.
linghe
A library of high-performance kernels for LLM training, linghe is designed for MoE training with FP8 quantization. It provides fused quantization kernels, memory-efficiency kernels, and implementation-optimized kernels. The repo benchmarks on H800 with specific configurations and offers examples in tests. Users can refer to the API for more details.
nntrainer
NNtrainer is a software framework for training neural network models on devices with limited resources. It enables on-device fine-tuning of neural networks using user data for personalization. NNtrainer supports various machine learning algorithms and provides examples for tasks such as few-shot learning, ResNet, VGG, and product rating. It is optimized for embedded devices and utilizes CBLAS and CUBLAS for accelerated calculations. NNtrainer is open source and released under the Apache License version 2.0.
awesome-generative-ai-data-scientist
A curated list of 50+ resources to help you become a Generative AI Data Scientist. This repository includes resources on building GenAI applications with Large Language Models (LLMs), and deploying LLMs and GenAI with Cloud-based solutions.
are-copilots-local-yet
Current trends and state of the art for using open & local LLM models as copilots to complete code, generate projects, act as shell assistants, automatically fix bugs, and more. This document is a curated list of local Copilots, shell assistants, and related projects, intended to be a resource for those interested in a survey of the existing tools and to help developers discover the state of the art for projects like these.

spiceai
Spice is a portable runtime written in Rust that offers developers a unified SQL interface to materialize, accelerate, and query data from any database, data warehouse, or data lake. It connects, fuses, and delivers data to applications, machine-learning models, and AI-backends, functioning as an application-specific, tier-optimized Database CDN. Built with industry-leading technologies such as Apache DataFusion, Apache Arrow, Apache Arrow Flight, SQLite, and DuckDB. Spice makes it fast and easy to query data from one or more sources using SQL, co-locating a managed dataset with applications or machine learning models, and accelerating it with Arrow in-memory, SQLite/DuckDB, or attached PostgreSQL for fast, high-concurrency, low-latency queries.

MOSS-TTS
MOSS-TTS Family is an open-source speech and sound generation model family designed for high-fidelity, high-expressiveness, and complex real-world scenarios. It includes five production-ready models: MOSS-TTS, MOSS-TTSD, MOSS-VoiceGenerator, MOSS-TTS-Realtime, and MOSS-SoundEffect, each serving specific purposes in speech generation, dialogue, voice design, real-time interactions, and sound effect generation. The models offer features like long-speech generation, fine-grained control over phonemes and duration, multilingual synthesis, voice cloning, and real-time voice agents.
COLD-Attack
COLD-Attack is a framework designed for controllable jailbreaks on large language models (LLMs). It formulates the controllable attack generation problem and utilizes the Energy-based Constrained Decoding with Langevin Dynamics (COLD) algorithm to automate the search of adversarial LLM attacks with control over fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence. The framework includes steps for energy function formulation, Langevin dynamics sampling, and decoding process to generate discrete text attacks. It offers diverse jailbreak scenarios such as fluent suffix attacks, paraphrase attacks, and attacks with left-right-coherence.
ZhiLight
ZhiLight is a highly optimized large language model (LLM) inference engine developed by Zhihu and ModelBest Inc. It accelerates the inference of models like Llama and its variants, especially on PCIe-based GPUs. ZhiLight offers significant performance advantages compared to mainstream open-source inference engines. It supports various features such as custom defined tensor and unified global memory management, optimized fused kernels, support for dynamic batch, flash attention prefill, prefix cache, and different quantization techniques like INT8, SmoothQuant, FP8, AWQ, and GPTQ. ZhiLight is compatible with OpenAI interface and provides high performance on mainstream NVIDIA GPUs with different model sizes and precisions.
llama-stack
Llama Stack defines and standardizes core building blocks for AI application development, providing a unified API layer, plugin architecture, prepackaged distributions, developer interfaces, and standalone applications. It offers flexibility in infrastructure choice, consistent experience with unified APIs, and a robust ecosystem with integrated distribution partners. The tool simplifies building, testing, and deploying AI applications with various APIs and environments, supporting local development, on-premises, cloud, and mobile deployments.
llm-compression-intelligence
This repository presents the findings of the paper "Compression Represents Intelligence Linearly". The study reveals a strong linear correlation between the intelligence of LLMs, as measured by benchmark scores, and their ability to compress external text corpora. Compression efficiency, derived from raw text corpora, serves as a reliable evaluation metric that is linearly associated with model capabilities. The repository includes the compression corpora used in the paper, code for computing compression efficiency, and data collection and processing pipelines.
BizFinBench
BizFinBench is a benchmark tool designed for evaluating large language models (LLMs) in logic-heavy and precision-critical domains such as finance. It comprises over 100,000 bilingual financial questions rooted in real-world business scenarios. The tool covers five dimensions: numerical calculation, reasoning, information extraction, prediction recognition, and knowledge-based question answering, mapped to nine fine-grained categories. BizFinBench aims to assess the capacity of LLMs in real-world financial scenarios and provides insights into their strengths and limitations.
YuLan-Mini
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters that achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. It excels in mathematics and code domains. The repository provides pre-training resources, including data pipeline, optimization methods, and annealing approaches. Users can pre-train their own language models, perform learning rate annealing, fine-tune the model, research training dynamics, and synthesize data. The team behind YuLan-Mini is AI Box at Renmin University of China. The code is released under the MIT License with future updates on model weights usage policies. Users are advised on potential safety concerns and ethical use of the model.
jailbreak_llms
This is the official repository for the ACM CCS 2024 paper 'Do Anything Now': Characterizing and Evaluating In-The-Wild Jailbreak Prompts on Large Language Models. The project employs a new framework called JailbreakHub to conduct the first measurement study on jailbreak prompts in the wild, collecting 15,140 prompts from December 2022 to December 2023, including 1,405 jailbreak prompts. The dataset serves as the largest collection of in-the-wild jailbreak prompts. The repository contains examples of harmful language and is intended for research purposes only.
For similar tasks

PromptFuzz
**Description:** PromptFuzz is an automated tool that generates high-quality fuzz drivers for libraries via a fuzz loop constructed on mutating LLMs' prompts. The fuzz loop of PromptFuzz aims to guide the mutation of LLMs' prompts to generate programs that cover more reachable code and explore complex API interrelationships, which are effective for fuzzing. **Features:** * **Multiply LLM support** : Supports the general LLMs: Codex, Inocder, ChatGPT, and GPT4 (Currently tested on ChatGPT). * **Context-based Prompt** : Construct LLM prompts with the automatically extracted library context. * **Powerful Sanitization** : The program's syntax, semantics, behavior, and coverage are thoroughly analyzed to sanitize the problematic programs. * **Prioritized Mutation** : Prioritizes mutating the library API combinations within LLM's prompts to explore complex interrelationships, guided by code coverage. * **Fuzz Driver Exploitation** : Infers API constraints using statistics and extends fixed API arguments to receive random bytes from fuzzers. * **Fuzz engine integration** : Integrates with grey-box fuzz engine: LibFuzzer. **Benefits:** * **High branch coverage:** The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz achieved a branch coverage of 40.12% on the tested libraries, which is 1.61x greater than _OSS-Fuzz_ and 1.67x greater than _Hopper_. * **Bug detection:** PromptFuzz detected 33 valid security bugs from 49 unique crashes. * **Wide range of bugs:** The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz can detect a wide range of bugs, most of which are security bugs. * **Unique bugs:** PromptFuzz detects uniquely interesting bugs that other fuzzers may miss. **Usage:** 1. Build the library using the provided build scripts. 2. Export the LLM API KEY if using ChatGPT or GPT4. 3. Generate fuzz drivers using the `fuzzer` command. 4. Run the fuzz drivers using the `harness` command. 5. Deduplicate and analyze the reported crashes. **Future Works:** * **Custom LLMs suport:** Support custom LLMs. * **Close-source libraries:** Apply PromptFuzz to close-source libraries by fine tuning LLMs on private code corpus. * **Performance** : Reduce the huge time cost required in erroneous program elimination.
awesome-gpt-security
Awesome GPT + Security is a curated list of awesome security tools, experimental case or other interesting things with LLM or GPT. It includes tools for integrated security, auditing, reconnaissance, offensive security, detecting security issues, preventing security breaches, social engineering, reverse engineering, investigating security incidents, fixing security vulnerabilities, assessing security posture, and more. The list also includes experimental cases, academic research, blogs, and fun projects related to GPT security. Additionally, it provides resources on GPT security standards, bypassing security policies, bug bounty programs, cracking GPT APIs, and plugin security.
SWE-agent
SWE-agent is a tool that allows language models to autonomously fix issues in GitHub repositories, perform tasks on the web, find cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and handle custom tasks. It uses configurable agent-computer interfaces (ACIs) to interact with isolated computer environments. The tool is built and maintained by researchers from Princeton University and Stanford University.
jadx-ai-mcp
JADX-AI-MCP is a plugin for the JADX decompiler that integrates with Model Context Protocol (MCP) to provide live reverse engineering support with LLMs like Claude. It allows for quick analysis, vulnerability detection, and AI code modification, all in real time. The tool combines JADX-AI-MCP and JADX MCP SERVER to analyze Android APKs effortlessly. It offers various prompts for code understanding, vulnerability detection, reverse engineering helpers, static analysis, AI code modification, and documentation. The tool is part of the Zin MCP Suite and aims to connect all android reverse engineering and APK modification tools with a single MCP server for easy reverse engineering of APK files.
shannon
Shannon is an AI pentester that delivers actual exploits, not just alerts. It autonomously hunts for attack vectors in your code, then uses its built-in browser to execute real exploits, such as injection attacks, and auth bypass, to prove the vulnerability is actually exploitable. Shannon closes the security gap by acting as your on-demand whitebox pentester, providing concrete proof of vulnerabilities to let you ship with confidence. It is a core component of the Keygraph Security and Compliance Platform, automating penetration testing and compliance journey. Shannon Lite achieves a 96.15% success rate on a hint-free, source-aware XBOW benchmark.
For similar jobs

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

PromptFuzz
**Description:** PromptFuzz is an automated tool that generates high-quality fuzz drivers for libraries via a fuzz loop constructed on mutating LLMs' prompts. The fuzz loop of PromptFuzz aims to guide the mutation of LLMs' prompts to generate programs that cover more reachable code and explore complex API interrelationships, which are effective for fuzzing. **Features:** * **Multiply LLM support** : Supports the general LLMs: Codex, Inocder, ChatGPT, and GPT4 (Currently tested on ChatGPT). * **Context-based Prompt** : Construct LLM prompts with the automatically extracted library context. * **Powerful Sanitization** : The program's syntax, semantics, behavior, and coverage are thoroughly analyzed to sanitize the problematic programs. * **Prioritized Mutation** : Prioritizes mutating the library API combinations within LLM's prompts to explore complex interrelationships, guided by code coverage. * **Fuzz Driver Exploitation** : Infers API constraints using statistics and extends fixed API arguments to receive random bytes from fuzzers. * **Fuzz engine integration** : Integrates with grey-box fuzz engine: LibFuzzer. **Benefits:** * **High branch coverage:** The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz achieved a branch coverage of 40.12% on the tested libraries, which is 1.61x greater than _OSS-Fuzz_ and 1.67x greater than _Hopper_. * **Bug detection:** PromptFuzz detected 33 valid security bugs from 49 unique crashes. * **Wide range of bugs:** The fuzz drivers generated by PromptFuzz can detect a wide range of bugs, most of which are security bugs. * **Unique bugs:** PromptFuzz detects uniquely interesting bugs that other fuzzers may miss. **Usage:** 1. Build the library using the provided build scripts. 2. Export the LLM API KEY if using ChatGPT or GPT4. 3. Generate fuzz drivers using the `fuzzer` command. 4. Run the fuzz drivers using the `harness` command. 5. Deduplicate and analyze the reported crashes. **Future Works:** * **Custom LLMs suport:** Support custom LLMs. * **Close-source libraries:** Apply PromptFuzz to close-source libraries by fine tuning LLMs on private code corpus. * **Performance** : Reduce the huge time cost required in erroneous program elimination.
code-review-gpt
Code Review GPT uses Large Language Models to review code in your CI/CD pipeline. It helps streamline the code review process by providing feedback on code that may have issues or areas for improvement. It should pick up on common issues such as exposed secrets, slow or inefficient code, and unreadable code. It can also be run locally in your command line to review staged files. Code Review GPT is in alpha and should be used for fun only. It may provide useful feedback but please check any suggestions thoroughly.
aiverify
AI Verify is an AI governance testing framework and software toolkit that validates the performance of AI systems against a set of internationally recognised principles through standardised tests. AI Verify is consistent with international AI governance frameworks such as those from European Union, OECD and Singapore. It is a single integrated toolkit that operates within an enterprise environment. It can perform technical tests on common supervised learning classification and regression models for most tabular and image datasets. It however does not define AI ethical standards and does not guarantee that any AI system tested will be free from risks or biases or is completely safe.
cover-agent
CodiumAI Cover Agent is a tool designed to help increase code coverage by automatically generating qualified tests to enhance existing test suites. It utilizes Generative AI to streamline development workflows and is part of a suite of utilities aimed at automating the creation of unit tests for software projects. The system includes components like Test Runner, Coverage Parser, Prompt Builder, and AI Caller to simplify and expedite the testing process, ensuring high-quality software development. Cover Agent can be run via a terminal and is planned to be integrated into popular CI platforms. The tool outputs debug files locally, such as generated_prompt.md, run.log, and test_results.html, providing detailed information on generated tests and their status. It supports multiple LLMs and allows users to specify the model to use for test generation.
auto-playwright
Auto Playwright is a tool that allows users to run Playwright tests using AI. It eliminates the need for selectors by determining actions at runtime based on plain-text instructions. Users can automate complex scenarios, write tests concurrently with or before functionality development, and benefit from rapid test creation. The tool supports various Playwright actions and offers additional options for debugging and customization. It uses HTML sanitization to reduce costs and improve text quality when interacting with the OpenAI API.
momentum-core
Momentum is an open-source behavioral auditor for backend code that helps developers generate powerful insights into their codebase. It analyzes code behavior, tests it at every git push, and ensures readiness for production. Momentum understands backend code, visualizes dependencies, identifies behaviors, generates test code, runs code in the local environment, and provides debugging solutions. It aims to improve code quality, streamline testing processes, and enhance developer productivity.
mutahunter
Mutahunter is an open-source language-agnostic mutation testing tool maintained by CodeIntegrity. It leverages LLM models to inject context-aware faults into codebase, ensuring comprehensive testing. The tool aims to empower companies and developers to enhance test suites and improve software quality by verifying the effectiveness of test cases through creating mutants in the code and checking if the test cases can catch these changes. Mutahunter provides detailed reports on mutation coverage, killed mutants, and survived mutants, enabling users to identify potential weaknesses in their test suites.
