
Toolio
GenAI & agent toolkit for Apple Silicon Mac, implementing JSON schema-steered structured output (3SO) and tool-calling in Python. For more on 3SO: https://huggingface.co/blog/ucheog/llm-power-steering
Stars: 110

Toolio is an OpenAI-like HTTP server API implementation that supports structured LLM response generation, making it conform to a JSON schema. It is useful for reliable tool calling and agentic workflows based on schema-driven output. Toolio is based on the MLX framework for Apple Silicon, specifically M1/M2/M3/M4 Macs. It allows users to host MLX-format LLMs for structured output queries and provides a command line client for easier usage of tools. The tool also supports multiple tool calls and the creation of custom tools for specific tasks.
README:
♪ Come along and ride on a fantastic voyage 🎵, with AI riding shotgun seat and a flatbed full of tools.
Toolio is an OpenAI-like HTTP server API implementation which supports structured LLM response generation (e.g. make it conform to a JSON schema). It also implements tool calling by LLMs. Toolio is based on the MLX framework for Apple Silicon (e.g. M1/M2/M3/M4 Macs), so that's the only supported platform at present.
Whether the buzzword you're pursuing is tool-calling, function-calling, agentic workflows, compound AI, guaranteed structured output, schema-driven output, guided generation, or steered response, give Toolio a try. You can think of it as your "GPT Private Agent", handling intelligent tasks for you, without spilling your secrets.
Builds on: https://github.com/otriscon/llm-structured-output/
There is sometimes confusion over the various ways to constrain LLM output
- You can basically beg the model through prompt engineering (detailed instructions, few-shot, etc.), then attempt generation, check the results, and retry if it doesn't conform (perhaps with further LLM begging in the re-prompt). This gives uneven results, is slow and wasteful, and ends up requiring much more powerful LLMs.
- Toolio's approach, which we call schema-steered structured output (3SO), is to convert the input format of the grammar (JSON schema in this case) into a state machine which applies those rules as hard constraints on the output sampler. Rather than begging the LLM, we steer it.
In either case you get better results if you've trained or fine-tuned the model with a lot of examples of the desired output syntax and structure, but the LLM's size, power and training are only part of the picture with S3O.
Warnng: this README has been (prematurely) updated to reflect the forthcoming 0.6.0 release. If you're working with the current 0.5.2 relase, refer to this earlier version of the README, or to the documentation.
-
toolio_server(command line)—Host MLX-format LLMs for structured output query or function calling via HTTP requests -
toolio_request(command line)—Execute HTTP client requests against a server -
toolio.local_model_runner(Python API)—Encapsulate an MLX-format LLM for convenient, in-resident query with structured output or function calling -
toolio.client.struct_mlx_chat_api(Python API)—Make a toolio server request from code
 |
Toolio is primarily developed by the crew at Oori Data. We offer data pipelines and software engineering services around AI/LLM applications. |
We'd love your help, though! Click to learn how to make contributions to the project.
The following video, "Toolio in 10 minutes", is an easy way to learn about the project.
As simple as:
pip install toolioIf you're not sure, you can check that you're on an Apple Silicon Mac.
python -c "import platform; assert 'arm64' in platform.platform()"Use toolio_server to host MLX-format LLMs for structured output query or function-calling. For example you can host the MLX version of Nous Research's Hermes-2 Θ (Theta).
toolio_server --model=mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bitThis will download the model from the HuggingFace path mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit to your local disk cache. The 4bit at the end means you are downloading a version quantized to 4 bits, so that each parameter in the neural network, which would normally take up 16 bits, only takes up 4, in order to save memory and boost speed. There are 8 billion parameters, so this version will take up a little over 4GB on your disk, and running it will take up about the sama amount of your unified RAM.
To learn more about the MLX framework for ML workloads (including LLMs) on Apple Silicon, see the MLX Notes article series. The "Day One" article provides all the context you need for using local LLMs with Toolio.
There are many hundreds of models you can select. One bit of advice is that Toolio, for now, tends to work better with base or base/chat models, rather than instruct-tuned models.
Try out a basic request, not using any of Toolio's special features, but rather using the LLM as is:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "I am thinking of a number between 1 and 10. Guess what it is."}],
"temperature": 0.1
}'This is actually not constraining to any output structure, and is just using the LLM as is. The result will be in complex-looking JSON, but read on for more straightforward ways to query against a Toolio server.
Here is a request that does constrain return structure:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "I am thinking of a number between 1 and 10. Guess what it is."}],
"response_format": {
"type": "json_object",
"schema": "{\"type\": \"object\",\"properties\": {\"guess\": {\"type\": \"number\"}}}"
},
"temperature": 0.1
}'The key here is specification of a JSON schema. The schema is escaped for the command line shell above, so here it is in its regular form:
{"type": "object", "properties": {"guess": {"type": "number"}}}It looks a bit intimidating, at first, if you're not familiar with JSON schema, but they're reasonably easy to learn. You can follow the primer.
Ultimately, you can just paste an example of your desired output structure and ask ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, etc. as simply as: "Please write a JSON schema to represent this data format."
Toolio's JSOn schema support is a subset, so you might need to tweak a schema before using it with Toolio. Most of the unsupported features can be just omitted, or expressed in the prompt or schema descriptions instead.
cURL is a pretty raw interface for this, though. For example, you have to parse the resulting response JSON. It's a lot easier to use the more specialized command line client tool toolio_request. Here is the equivalent too the first cURL example, above:
toolio_request --apibase="http://localhost:8000" --prompt="I am thinking of a number between 1 and 10. Guess what it is."This time you'll just get the straightforward response text, e.g. "Sure, I'll guess 5. Is that your number?"
Here is an example using JSON schema constraint to extract structured data from an unstructured sentence.
export LMPROMPT='Which countries are mentioned in the sentence "Adamma went home to Nigeria for the hols"? Your answer should be only JSON, according to this schema: #!JSON_SCHEMA!#'
export LMSCHEMA='{"type": "array", "items": {"type": "object", "properties": {"name": {"type": "string"}, "continent": {"type": "string"}}, "required": ["name", "continent"]}}'
toolio_request --apibase="http://localhost:8000" --prompt=$LMPROMPT --schema=$LMSCHEMA(…and yes, in practice a smaller, specialized entity extraction model might be a better option for a case this simple)
Notice the #!JSON_SCHEMA!# cutout, which Toolio replaces for you with the actual schema you've provided.
With any decent LLM you should get the following and no extraneous text cluttering things up!
[{"name": "Nigeria", "continent": "Africa"}]Or if you have the prompt or schema written to files:
echo 'Which countries are mentioned in the sentence "Adamma went home to Nigeria for the hols"? Your answer should be only JSON, according to this schema: #!JSON_SCHEMA!#' > /tmp/llmprompt.txt
echo '{"type": "array", "items": {"type": "object", "properties": {"name": {"type": "string"}, "continent": {"type": "string"}}, "required": ["name", "continent"]}}' > /tmp/countries.schema.json
toolio_request --apibase="http://localhost:8000" --prompt-file=/tmp/llmprompt.txt --schema-file=/tmp/countries.schema.jsonYou can run tool usage (function-calling) prompts, a key technique in LLM agent frameworks. A schema will automatically be generated from the tool specs, which themselves are based on JSON Schema, according to OpenAI conventions.
echo 'What'\''s the weather like in Boulder today?' > /tmp/llmprompt.txt
echo '{"tools": [{"type": "function","function": {"name": "get_current_weather","description": "Get the current weather in a given location","parameters": {"type": "object","properties": {"location": {"type": "string","description": "City and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA"},"unit": {"type": "string","enum": ["℃","℉"]}},"required": ["location"]}}}], "tool_choice": "auto"}' > /tmp/toolspec.json
toolio_request --apibase="http://localhost:8000" --prompt-file=/tmp/llmprompt.txt --tools-file=/tmp/toolspec.json --max-trips=1You can expect a response such as
[...] UserWarning: No implementation provided for function: get_current_weather
The model invoked the following tool calls to complete the response, but there are no permitted trips remaining.
[
{
"id": "call_6127176720_1719458192_0",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"arguments_obj": {
"location": "Boulder, MA",
"unit": "\u2109"
}
}
}
]You might have noticed the --max-trips=1 in the original call. Normally the tool call response would go back to the LLM to further construct a response, but Toolio allows you to limit those trips. By setting the limit to 1, it is unable to make a second trip to deliver the function call response for further processing, and the user is notified of the fact.
Incidentally \u2109 is just Unicode for ℉ (degrees fahrenheit).
It's pretty well known at this point that LLMs are bad at maths, but we can give them help. Consider the following example:
echo 'What is the square root of 256?' > /tmp/llmprompt.txt
echo '{"tools": [{"type": "function","function": {"name": "square_root","description": "Get the square root of the given number","parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"square": {"type": "number", "description": "Number from which to find the square root"}},"required": ["square"]},"pyfunc": "math|sqrt"}}], "tool_choice": "auto"}' > /tmp/toolspec.json
toolio_request --apibase="http://localhost:8000" --prompt-file=/tmp/llmprompt.txt --tools-file=/tmp/toolspec.jsonWe give the LLM a Python function for getting a square root. The OpenAI-style tool spec is extended with "pyfunc": "math|sqrt". This tells Toolio to import the Python built-in math model and call the sqrt function within it.
Notice there is no --max-trips= this time. The default value is 3, so that's enough to have at least one round-trip to deliver the tool's response to the LLM for further processing. If all goes well with the LLM, you should get a result such as:
The square root of 256 is 16.
math.sqrt is a convenient, simple example. You can specify any function which can already be imported (Toolio won't install any libraries at run time), and you can use imports and attribute lookups with multiple levels, e.g. path.to.module_to_import|path.to.function.
The examples above might feel like a bit too much work to use a tool; in particular putting together and sending along the tool-calling spec. In most cases you'll either be reusing tools developed by someone else, or your own special ones. In either case the tool-calling spec for each tool can be bundled for easier use. Toolio comes with a few tools you can use right away, for example. toolio.tool.math.calculator is a really simple calculator tool the LLM can use because once again LLMs are really bad at maths. But there's one step required first. Some of the built-in tools use third-party libraries which aren't baseline requirements of Toolio. Install them as follows:
pip install -U toolio[tools]Now try a prompt intended to use the calculator tool. To make sure it does, we'll add the loglevel flag:
toolio_request --apibase="http://localhost:8000" --tool=toolio.tool.math.calculator --loglevel=DEBUG \
--prompt='Usain Bolt ran the 100m race in 9.58s. What was his average velocity?'Here's what I got from Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit:
DEBUG:toolio.cli.request:🔧 Calling tool calculator with args {'expr': '(100/9.58)'}
DEBUG:toolio.cli.request:✅ Tool call result: 10.438413361169102
To calculate Usain Bolt's average velocity during the 100m race, we divide the total distance by the total time taken. Here's the calculation:
Distance (d) = 100 meters
Time (t) = 9.58 seconds
Average velocity (v) = Distance / Time
v = 100 meters / 9.58 seconds ≈ 10.44 meters per second
So, Usain Bolt's average velocity during the 100m race was approximately 10.44 meters per second.
You can see that the LLM got help by calling the tool to calculate 100/9.58.
Note: Every tool relies on the agent LLM to correctly construct the tool call call, e.g. settign up the right mathematial expression for the calculator tool. This is not something you can take for granted, so there's no shortcut from testing and selecting the right LLMs.
Here's an example of giving the LLM a tool to get today's date, and another with a database lookup from birthdays to employee names and interests.
toolio_request --apibase="http://localhost:8000" --loglevel=DEBUG \
--tool=toolio.tool.demo.birthday_lookup \
--tool=toolio.tool.demo.today_kfabe \
--sysprompt='You are a writer who reasons step by step and uses research tools in the correct order before writing' \
--prompt='Write a nice note for each employee who has a birthday today.'These are actually contrived, fake tools for demo purposes. demo.today_kfabe always gives the date as 1 July 2024, and demo.birthday_lookup is a dummy database. Also note the added system prompt to encourag the LLM to use step-by-step reasoning in applying the tools. If your LLM is smart enough enough it would first get the (supposed) date today and then convrt that to a format suitable for the database lookip.
Unfortunately mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit fumbles this, ignoring the spoon-fed date from the first tool call, and instead grabs an example date mentioned in the tool definition. This results in no birthday lookup results, and the LLM generates no output.
⚙️Calling tool today with args {}
⚙️Tool call result: 07-01
⚙️Calling tool birthday_lookup with args {'date': '05-03'}
⚙️Tool call result: No one has a birthday today
Final response:
It's a good example of how tool-calling can pretty easily go wrong. As LLMs get more and more capable this should become more reliable. It may well be that top-end LLMs such as OpenAI's GPT and Anthropic's Claude would be able to handle this case, but of course you can't run these privately on MLX.
Study the examples in the pylib/tools and in the demo directories to see how easy it is.
LLMs actually get trained for tool calling, and sometimes get trained to expect different patterns. Toolio supports some flags for adapting the tool flow based on the LLM you're using on the server.
For notes on more models see https://github.com/OoriData/Toolio/wiki/Notes-on-how-MLX-models-handle-tool%E2%80%90calling
Tool-calling is very neat, but it involves delegating process control to the LLM. For many use-cases this is an extremely resource-intensive way to implement processes which may be reasonably
determinate, or which may be broken down into subprocesses which the LLM can at least orchestrate
more eficiently and reliably. You can often get farther faster by using Toolio's schema-steered structured output instead (i.e. the json_schema parameter). For example, you can give the LLM
a simpler context and a simple list of next steps to take, rather than have it mastermind the entire process at once.
See the demo directory for some examples of this.
You can also query the server from Python code, using toolio.client.struct_mlx_chat_api. Here's an example, including a (dummied up) custom tool:
import asyncio
from ogbujipt.llm_wrapper import prompt_to_chat
from toolio.client import struct_mlx_chat_api
from toolio.tool import tool, param
@tool('currency_exchange', params=[param('from', str, 'Currency to be converted from, e.g. USD, GBP, JPY', True, rename='from_'), param('to', str, 'Currency to be converted to, e.g. USD, GBP, JPY', True), param('amount', float, 'Amount to convert from one currency to another. Just a number, with no other symbols', True)])
def currency_exchange(from_=None, to=None, amount=None):
'Tool to convert one currency to another'
# Just a dummy implementation
lookup = {('JPY', 'USD'): 1234.56}
rate = lookup.get((from_, to))
print(f'{from_=}, {to=}, {amount=}, {rate=}')
# Look up the conversion online here
return rate * amount
prompt = 'I need to import a car from Japan. It costs 5 million Yen.'
'How much must I withdraw from my US bank account'
llm = struct_mlx_chat_api(base_url='http://localhost:8000', tool_reg=[currency_exchange])
resp = asyncio.run(llm(prompt_to_chat(prompt), trip_timeout=60))
print(resp.first_choice_text)Notice the use of the rename parameter metadata. In Python the param name we've asked the LLM to use, from, is a keyword, so to avoid confusion the actual function definition uses from_, and the rename instructs Toolio to make that change in the background.
You can also define asynchronous tools, e.g. async def currency_exchange, which I would actually recommend if, e.g. you are truly web scraping.
You might study the command line pylib/cli/request.py for further insight.
You can also, of course, just load the model and run inference on it without bothering with HTTP client/server. The local_model_runner class is a convenient interface for this.
import asyncio
from toolio.llm_helper import local_model_runner
toolio_mm = local_model_runner('mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit')
async def say_hello(tmm):
msgs = [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello! How are you?"}]
print(await tmm.complete(msgs))
asyncio.run(say_hello(toolio_mm))You should just get a simple text response from the LLm printed to the screen.
You can also do this via synchronous API, but I highly recommend leaing hard on the async habit.
The chat_complete method also takes a list of tools or a JSON schema, as well as some model parameters.
Toolio uses OpenAI API conventions a lot under the hood. If you run the following:
import asyncio
from toolio.llm_helper import local_model_runner, extract_content
toolio_mm = local_model_runner('mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit')
async def say_hello(tmm):
msgs = [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello! How are you?"}]
# FYI, there is a fnction toolio.common.response_text which can help cnsume iter_* methods
async for chunk_struct in tmm.iter_complete(msgs):
print(chunk_struct)
break
asyncio.run(say_hello(toolio_mm))from
You should see something like:
{'choices': [{'index': 0, 'delta': {'role': 'assistant', 'content': 'Hi'}, 'finish_reason': None}], 'object': 'chat.completion.chunk', 'id': 'chatcmpl-17588006160_1721823730', 'created': 1721823730, 'model': 'mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit'}The LLM response is delivered in such structures ("deltas") as they're generated. chunk_struct['choices'][0]['delta']['content'] is a bit of the actual text we teased out in the previous snippet. chunk_struct['choices'][0]['finish_reason'] is None because it's not yet finished, etc. This is based on OpenAI API.
extract_content, used in the previous snippet, is a very simple coroutine that extracts the actual text content from this series of response structures.
The final chunk would look something like this:
{'choices': [{'index': 0, 'delta': {'role': 'assistant', 'content': ''}, 'finish_reason': 'stop'}], 'usage': {'completion_tokens': 20, 'prompt_tokens': 12, 'total_tokens': 32}, 'object': 'chat.completion.chunk', 'id': 'chatcmpl-18503717840_1721824385', 'created': 1721824385, 'model': 'mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit'}Notice there is more information, now that it's finished ('finish_reason': 'stop'). Say you want the metadata such as the number of tokens generated:
import asyncio
from toolio.llm_helper import local_model_runner, extract_content
toolio_mm = local_model_runner('mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit')
async def say_hello(tmm):
msgs = [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello! How are you?"}]
async for chunk in tmm.iter_complete(msgs):
content = chunk['choices'][0]['delta']['content']
if content is not None:
print(content, end='')
# Final chunk has the stats
print('\n', '-'*80, '\n', 'Number of tokens generated:', chunk['usage']['total_tokens'])
asyncio.run(say_hello(toolio_mm))You'll get something like:
*waves* Hi there! I'm doing well, thank you for asking. How about you?
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of tokens generated: 32
Tip: don't forget all the various, useful bits to be found in itertools and the like.
As mentioned, you can specify tools and schemata.
import asyncio
from toolio.llm_helper import local_model_runner
toolio_mm = local_model_runner('mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit')
async def say_hello(tmm):
prompt = ('Which countries are mentioned in the sentence \'Adamma went home to Nigeria for the hols\'?'
'Your answer should be only JSON, according to this schema: #!JSON_SCHEMA!#')
schema = ('{"type": "array", "items":'
'{"type": "object", "properties": {"name": {"type": "string"}, "continent": {"type": "string"}}, "required": ["name", "continent"]}}')
print(await tmm.complete([{'role': 'user', 'content': prompt}], json_schema=schema))
asyncio.run(say_hello(toolio_mm))import asyncio
from math import sqrt
from toolio.llm_helper import local_model_runner
SQUARE_ROOT_METADATA = {'name': 'square_root', 'description': 'Get the square root of the given number',
'parameters': {'type': 'object', 'properties': {
'square': {'type': 'number',
'description': 'Number from which to find the square root'}},
'required': ['square']}}
toolio_mm = local_model_runner('mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit',
tool_reg=[(sqrt, SQUARE_ROOT_METADATA)])
async def query_sq_root(tmm):
msgs = [ {'role': 'user', 'content': 'What is the square root of 256?'} ]
print(await tmm.complete_with_tools(msgs, tools=['square_root']))
asyncio.run(query_sq_root(toolio_mm))Part of the process of getting an LLM to stick to a schema, or to call tools is to give it a system prompt to that effect. Toolio has built in prompt language for this purpose. We believe strongly in the design principle of separating natural language (e.g. prompts) from code, so the latyter is packaged into the resource/language.toml file, using Word Loom conventions.
You can of course override the built-in prompting.
echo 'What is the square root of 256?' > /tmp/llmprompt.txt
echo '{"tools": [{"type": "function","function": {"name": "square_root","description": "Get the square root of the given number","parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"square": {"type": "number", "description": "Number from which to find the square root"}},"required": ["square"]},"pyfunc": "math|sqrt"}}], "tool_choice": "auto"}' > /tmp/toolspec.json
toolio_request --apibase="http://localhost:8000" --prompt-file=/tmp/llmprompt.txt --tools-file=/tmp/toolspec.json --sysprompt="You are a helpful assistant with access to a tool that you may invoke if needed to answer the user's request. Please use the tool as applicable, even if you think you already know the answer. Give your final answer in Shakespearean English The tool is:
Tool"In order to override the system prompt from code, just set it in the initial chat message as the system role.
import asyncio
from math import sqrt
from toolio.llm_helper import local_model_runner
SQUARE_ROOT_METADATA = {'name': 'square_root', 'description': 'Get the square root of the given number',
'parameters': {'type': 'object', 'properties': {
'square': {'type': 'number',
'description': 'Number from which to find the square root'}},
'required': ['square']}}
toolio_mm = local_model_runner('mlx-community/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B-4bit',
tool_reg=[(sqrt, SQUARE_ROOT_METADATA)])
# System prompt will be used to direct the LLM's tool-calling
SYSPROMPT = 'You are a tutor from Elizabethan England, with access to a tool that you may invoke if needed to answer'
'the user\'s request. Please use the tool as applicable, even if you think you already know the answer. '
'Remember to give your final answer in Elizabethan English. The tool is:\nTool'
async def query_sq_root(tmm):
msgs = [
{'role': 'system', 'content': SYSPROMPT},
{'role': 'user', 'content': 'What is the square root of 256?'}
]
print(await tmm.complete_with_tools(msgs))
asyncio.run(query_sq_root(toolio_mm))In which case you can express a response such as:
By the tool's decree, the square root of 256, a number most fair, Is sixteen, a digit most true, and a figure most rare.
- Documentation
- More examples in the
demodirectory
- otriscon's llm-structured-output is the foundation of this package
- OgbujiPT provides the client-side Open-AI-style LLM framework, and also the Word Loom convention for separating prompt text from code.
Apache 2
- Outlines - Structured Text Generation vis Pydantic, JSON schema or EBNF. Similarly to Toolio, it does steered sampling, i.e. builds a finite-state machine to guide sampling based on schema
- Instructor - LLM structured output via prompt engineering, validation & retries rather than steered sampling.
In our thinking, and that of many others working in the space for a while, compound AI agent systems are where GenAI are most likely to deliver practical value. Watch out, though, because McKinsey has seen fit to apply their $1,000/hr opinions along the same lines. "Why agents are the next frontier of generative AI" (July 2024). The Toolio mindset adds in an aesthetic of data privacy, and smaller, cooperating, individually capable LLMs; rather than huge, monolithic LLMs hosted on someone else's black box server.
Named after the legend himself. Best don't pretend you don't know Coolio, fool! Popular rapper (R.I.P.) from LA. You watched Cookin' with Coolio, now it's time to Tool up with Toolio! ♪*Slide slide, but that's the past; I got something brand new for that aß.*🎼
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Toolio
Similar Open Source Tools

Toolio
Toolio is an OpenAI-like HTTP server API implementation that supports structured LLM response generation, making it conform to a JSON schema. It is useful for reliable tool calling and agentic workflows based on schema-driven output. Toolio is based on the MLX framework for Apple Silicon, specifically M1/M2/M3/M4 Macs. It allows users to host MLX-format LLMs for structured output queries and provides a command line client for easier usage of tools. The tool also supports multiple tool calls and the creation of custom tools for specific tasks.
smartfunc
smartfunc is a Python library that turns docstrings into LLM-functions. It wraps around the llm library to parse docstrings and generate prompts at runtime using Jinja2 templates. The library offers syntactic sugar on top of llm, supporting backends for different LLM providers, async support for microbatching, schema support using Pydantic models, and the ability to store API keys in .env files. It simplifies rapid prototyping by focusing on specific features and providing flexibility in prompt engineering. smartfunc also supports async functions and debug mode for debugging prompts and responses.
CoPilot
TigerGraph CoPilot is an AI assistant that combines graph databases and generative AI to enhance productivity across various business functions. It includes three core component services: InquiryAI for natural language assistance, SupportAI for knowledge Q&A, and QueryAI for GSQL code generation. Users can interact with CoPilot through a chat interface on TigerGraph Cloud and APIs. CoPilot requires LLM services for beta but will support TigerGraph's LLM in future releases. It aims to improve contextual relevance and accuracy of answers to natural-language questions by building knowledge graphs and using RAG. CoPilot is extensible and can be configured with different LLM providers, graph schemas, and LangChain tools.
vinagent
Vinagent is a lightweight and flexible library designed for building smart agent assistants across various industries. It provides a simple yet powerful foundation for creating AI-powered customer service bots, data analysis assistants, or domain-specific automation agents. With its modular tool system, users can easily extend their agent's capabilities by integrating a wide range of tools that are self-contained, well-documented, and can be registered dynamically. Vinagent allows users to scale and adapt their agents to new tasks or environments effortlessly.
npcsh
`npcsh` is a python-based command-line tool designed to integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) and Agents into one's daily workflow by making them available and easily configurable through the command line shell. It leverages the power of LLMs to understand natural language commands and questions, execute tasks, answer queries, and provide relevant information from local files and the web. Users can also build their own tools and call them like macros from the shell. `npcsh` allows users to take advantage of agents (i.e. NPCs) through a managed system, tailoring NPCs to specific tasks and workflows. The tool is extensible with Python, providing useful functions for interacting with LLMs, including explicit coverage for popular providers like ollama, anthropic, openai, gemini, deepseek, and openai-like providers. Users can set up a flask server to expose their NPC team for use as a backend service, run SQL models defined in their project, execute assembly lines, and verify the integrity of their NPC team's interrelations. Users can execute bash commands directly, use favorite command-line tools like VIM, Emacs, ipython, sqlite3, git, pipe the output of these commands to LLMs, or pass LLM results to bash commands.
simplemind
Simplemind is an AI library designed to simplify the experience with AI APIs in Python. It provides easy-to-use AI tools with a human-centered design and minimal configuration. Users can tap into powerful AI capabilities through simple interfaces, without needing to be experts. The library supports various APIs from different providers/models and offers features like text completion, streaming text, structured data handling, conversational AI, tool calling, and logging. Simplemind aims to make AI models accessible to all by abstracting away complexity and prioritizing readability and usability.
chatmemory
ChatMemory is a simple yet powerful long-term memory manager that facilitates communication between AI and users. It organizes conversation data into history, summary, and knowledge entities, enabling quick retrieval of context and generation of clear, concise answers. The tool leverages vector search on summaries/knowledge and detailed history to provide accurate responses. It balances speed and accuracy by using lightweight retrieval and fallback detailed search mechanisms, ensuring efficient memory management and response generation beyond mere data retrieval.

motorhead
Motorhead is a memory and information retrieval server for LLMs. It provides three simple APIs to assist with memory handling in chat applications using LLMs. The first API, GET /sessions/:id/memory, returns messages up to a maximum window size. The second API, POST /sessions/:id/memory, allows you to send an array of messages to Motorhead for storage. The third API, DELETE /sessions/:id/memory, deletes the session's message list. Motorhead also features incremental summarization, where it processes half of the maximum window size of messages and summarizes them when the maximum is reached. Additionally, it supports searching by text query using vector search. Motorhead is configurable through environment variables, including the maximum window size, whether to enable long-term memory, the model used for incremental summarization, the server port, your OpenAI API key, and the Redis URL.
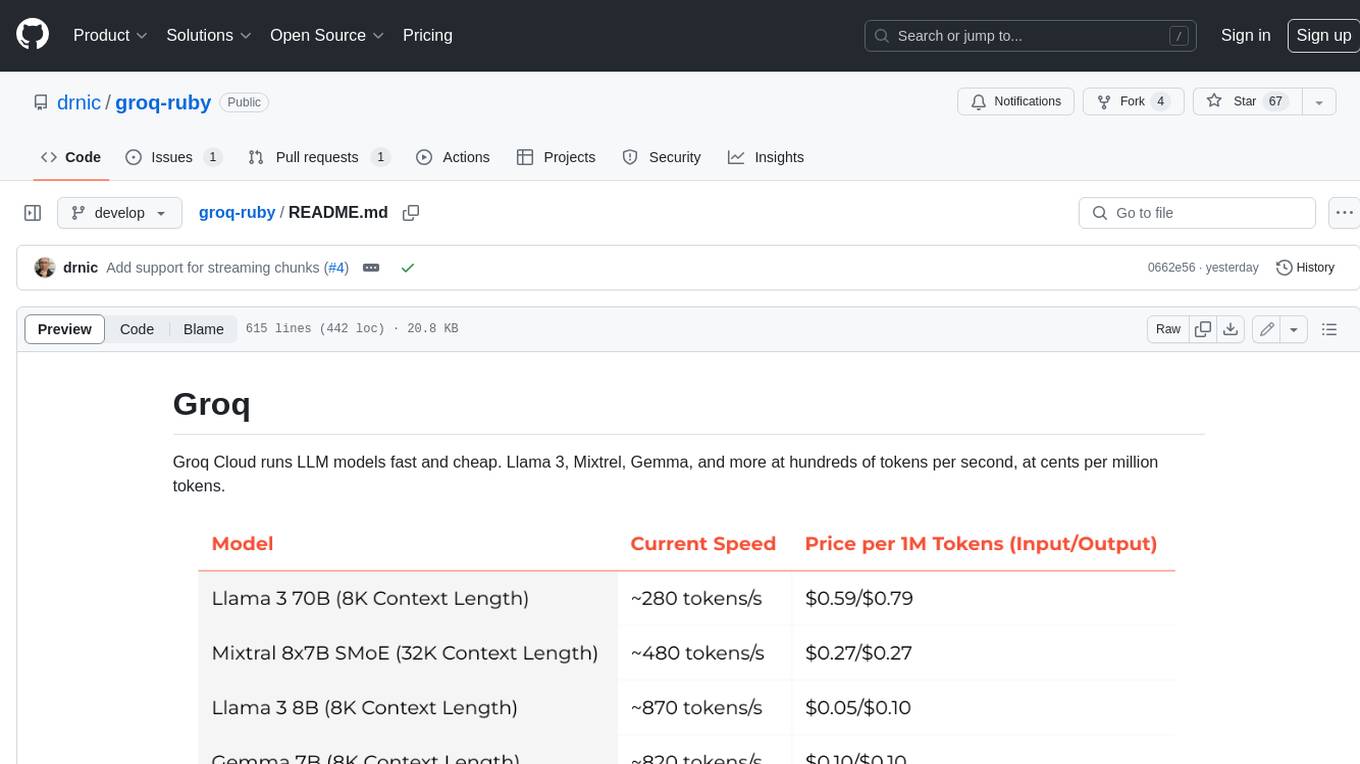
groq-ruby
Groq Cloud runs LLM models fast and cheap. Llama 3, Mixtrel, Gemma, and more at hundreds of tokens per second, at cents per million tokens.
ragtacts
Ragtacts is a Clojure library that allows users to easily interact with Large Language Models (LLMs) such as OpenAI's GPT-4. Users can ask questions to LLMs, create question templates, call Clojure functions in natural language, and utilize vector databases for more accurate answers. Ragtacts also supports RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) method for enhancing LLM output by incorporating external data. Users can use Ragtacts as a CLI tool, API server, or through a RAG Playground for interactive querying.

marqo
Marqo is more than a vector database, it's an end-to-end vector search engine for both text and images. Vector generation, storage and retrieval are handled out of the box through a single API. No need to bring your own embeddings.

CEO-Agentic-AI-Framework
CEO-Agentic-AI-Framework is an ultra-lightweight Agentic AI framework based on the ReAct paradigm. It supports mainstream LLMs and is stronger than Swarm. The framework allows users to build their own agents, assign tasks, and interact with them through a set of predefined abilities. Users can customize agent personalities, grant and deprive abilities, and assign queries for specific tasks. CEO also supports multi-agent collaboration scenarios, where different agents with distinct capabilities can work together to achieve complex tasks. The framework provides a quick start guide, examples, and detailed documentation for seamless integration into research projects.

ActionWeaver
ActionWeaver is an AI application framework designed for simplicity, relying on OpenAI and Pydantic. It supports both OpenAI API and Azure OpenAI service. The framework allows for function calling as a core feature, extensibility to integrate any Python code, function orchestration for building complex call hierarchies, and telemetry and observability integration. Users can easily install ActionWeaver using pip and leverage its capabilities to create, invoke, and orchestrate actions with the language model. The framework also provides structured extraction using Pydantic models and allows for exception handling customization. Contributions to the project are welcome, and users are encouraged to cite ActionWeaver if found useful.
Agently
Agently is a development framework that helps developers build AI agent native application really fast. You can use and build AI agent in your code in an extremely simple way. You can create an AI agent instance then interact with it like calling a function in very few codes like this below. Click the run button below and witness the magic. It's just that simple: python # Import and Init Settings import Agently agent = Agently.create_agent() agent\ .set_settings("current_model", "OpenAI")\ .set_settings("model.OpenAI.auth", {"api_key": ""}) # Interact with the agent instance like calling a function result = agent\ .input("Give me 3 words")\ .output([("String", "one word")])\ .start() print(result) ['apple', 'banana', 'carrot'] And you may notice that when we print the value of `result`, the value is a `list` just like the format of parameter we put into the `.output()`. In Agently framework we've done a lot of work like this to make it easier for application developers to integrate Agent instances into their business code. This will allow application developers to focus on how to build their business logic instead of figure out how to cater to language models or how to keep models satisfied.
simpleAI
SimpleAI is a self-hosted alternative to the not-so-open AI API, focused on replicating main endpoints for LLM such as text completion, chat, edits, and embeddings. It allows quick experimentation with different models, creating benchmarks, and handling specific use cases without relying on external services. Users can integrate and declare models through gRPC, query endpoints using Swagger UI or API, and resolve common issues like CORS with FastAPI middleware. The project is open for contributions and welcomes PRs, issues, documentation, and more.
langevals
LangEvals is an all-in-one Python library for testing and evaluating LLM models. It can be used in notebooks for exploration, in pytest for writing unit tests, or as a server API for live evaluations and guardrails. The library is modular, with 20+ evaluators including Ragas for RAG quality, OpenAI Moderation, and Azure Jailbreak detection. LangEvals powers LangWatch evaluations and provides tools for batch evaluations on notebooks and unit test evaluations with PyTest. It also offers LangEvals evaluators for LLM-as-a-Judge scenarios and out-of-the-box evaluators for language detection and answer relevancy checks.
For similar tasks

Toolio
Toolio is an OpenAI-like HTTP server API implementation that supports structured LLM response generation, making it conform to a JSON schema. It is useful for reliable tool calling and agentic workflows based on schema-driven output. Toolio is based on the MLX framework for Apple Silicon, specifically M1/M2/M3/M4 Macs. It allows users to host MLX-format LLMs for structured output queries and provides a command line client for easier usage of tools. The tool also supports multiple tool calls and the creation of custom tools for specific tasks.
crewAI-tools
The crewAI Tools repository provides a guide for setting up tools for crewAI agents, enabling the creation of custom tools to enhance AI solutions. Tools play a crucial role in improving agent functionality. The guide explains how to equip agents with a range of tools and how to create new tools. Tools are designed to return strings for generating responses. There are two main methods for creating tools: subclassing BaseTool and using the tool decorator. Contributions to the toolset are encouraged, and the development setup includes steps for installing dependencies, activating the virtual environment, setting up pre-commit hooks, running tests, static type checking, packaging, and local installation. Enhance AI agent capabilities with advanced tooling.
lecca-io
Lecca.io is an AI platform that enables users to configure and deploy Large Language Models (LLMs) with customizable tools and workflows. Users can easily build, customize, and automate AI agents for various tasks. The platform offers features like custom LLM configuration, tool integration, workflow builder, built-in RAG functionalities, and the ability to create custom apps and triggers. Users can also automate LLMs by setting up triggers for autonomous operation. Lecca.io provides documentation for concepts, local development, creating custom apps, adding AI providers, and running Ollama locally. Contributions are welcome, and the platform is distributed under the Apache-2.0 License with Commons Clause, with enterprise features available under a Commercial License.
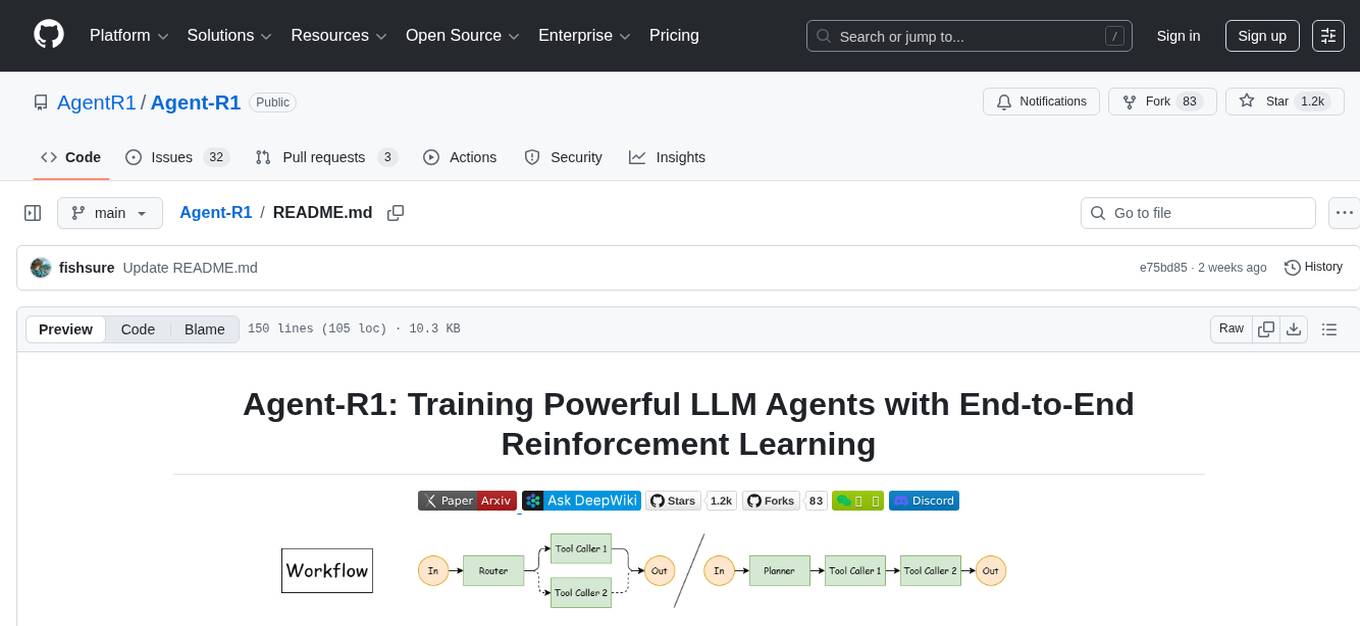
Agent-R1
Agent-R1 is an open-source framework designed to accelerate research and development at the critical intersection of RL and Agent. It employs End-to-End reinforcement learning to train agents in specific environments. Developers define domain-specific tools and reward functions to extend Agent-R1 to unique use cases, eliminating the need for complex workflow engineering. Key features include multi-turn tool calling, multi-tool coordination, process rewards, custom tools and environments, support for multiple RL algorithms, and multi-modal support. It aims to make it easier for researchers and developers to create and explore agents in their own domains, collectively advancing the development of autonomous agents.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.