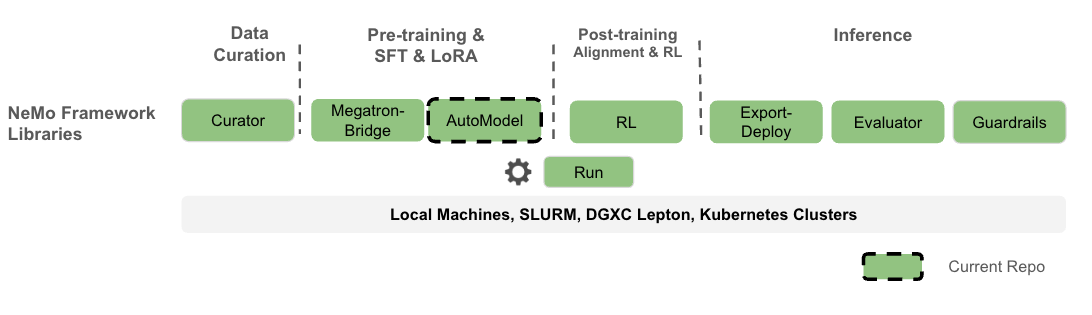
Automodel
Pytorch Distributed native training library for LLMs/VLMs with OOTB Hugging Face support
Stars: 301
Automodel is a Python library for automating the process of building and evaluating machine learning models. It provides a set of tools and utilities to streamline the model development workflow, from data preprocessing to model selection and evaluation. With Automodel, users can easily experiment with different algorithms, hyperparameters, and feature engineering techniques to find the best model for their dataset. The library is designed to be user-friendly and customizable, allowing users to define their own pipelines and workflows. Automodel is suitable for data scientists, machine learning engineers, and anyone looking to quickly build and test machine learning models without the need for manual intervention.
README:
📖 Documentation • 🔥 Ready-to-Use Recipes • 💡 Examples • Model Coverage • Performance • 🤝 Contributing
- [02/13/2026]MiniMax-M2.5 We support finetuning for
MiniMaxAI/MiniMax-M2.5. Checkout our recipe - [02/11/2026]GLM-4.7-Flash We now support finetuning GLM-4.7-Flash. Checkout our packed sequence recipe
- [02/09/2026]MiniMax-M2 We support finetuning for
MiniMaxAI/MiniMax-M2. Checkout our recipe - [02/06/2026]Qwen3 VL 235B We support finetuning for
Qwen/Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B-Instruct. Checkout our recipe - [02/06/2026]GLM4.7 We now support finetuning GLM4.7. Checkout our recipe
- [02/06/2026]Step3.5-flash is out! Finetune it with our finetune recipe
- [02/05/2026]DeepSeek-V3.2 is out! Checkout out the finetune recipe!
- [02/04/2026]Kimi K2.5 VL is out! Finetune it with NeMo AutoModel
- [12/18/2025]FunctionGemma is out! Finetune it with NeMo AutoModel!
- [12/15/2025]NVIDIA-Nemotron-3-Nano-30B-A3B is out! Finetune it with NeMo AutoModel!
- [11/6/2025]Accelerating Large-Scale Mixture-of-Experts Training in PyTorch
- [10/6/2025]Enabling PyTorch Native Pipeline Parallelism for 🤗 Hugging Face Transformer Models
- [9/22/2025]Fine-tune Hugging Face Models Instantly with Day-0 Support with NVIDIA NeMo AutoModel
- [9/18/2025]🚀 NeMo Framework Now Supports Google Gemma 3n: Efficient Multimodal Fine-tuning Made Simple
Nemo AutoModel is a Pytorch DTensor‑native SPMD open-source training library under NVIDIA NeMo Framework, designed to streamline and scale training and finetuning for LLMs and VLMs. Designed for flexibility, reproducibility, and scale, NeMo AutoModel enables both small-scale experiments and massive multi-GPU, multi-node deployments for fast experimentation in research and production environments.
What you can expect:
- Hackable with a modular design that allows easy integration, customization and quick research prototypes.
- Minimal ceremony: YAML‑driven recipes; override any field via CLI.
- High performance and flexibility with custom kernels and DTensor support.
- Seamless integration with Hugging Face for day-0 model support, ease of use, and wide range of supported models.
- Efficient resource management using k8s and Slurm, enabling scalable and flexible deployment across configurations.
- Comprehensive documentation that is both detailed and user-friendly, with practical examples.
⚠️ Note: NeMo AutoModel is under active development. New features, improvements, and documentation updates are released regularly. We are working toward a stable release, so expect the interface to solidify over time. Your feedback and contributions are welcome, and we encourage you to follow along as new updates roll out.
- One program, any scale: The same training script runs on 1 GPU or 1000+ by changing the mesh.
-
PyTorch Distributed native: Partition model/optimizer states with
DeviceMesh+ placements (Shard,Replicate). - SPMD first: Parallelism is configuration. No model rewrites when scaling up or changing strategy.
- Decoupled concerns: Model code stays pure PyTorch; parallel strategy lives in config.
- Composability: Mix tensor, sequence, and data parallel by editing placements.
- Portability: Fewer bespoke abstractions; easier to reason about failure modes and restarts.
- Feature Roadmap
- Getting Started
- LLM
- VLM
- Supported Models
- Performance
- Interoperability
- Contributing
- License
TL;DR: SPMD turns “how to parallelize” into a runtime layout choice, not a code fork.
✅ Available now | 🔜 Coming in 26.02
-
✅ Advanced Parallelism - PyTorch native FSDP2, TP, CP, and SP for distributed training.
-
✅ HSDP - Multi-node Hybrid Sharding Data Parallelism based on FSDP2.
-
✅ Pipeline Support - Torch-native support for pipelining composable with FSDP2 and DTensor (3D Parallelism).
-
✅ Environment Support - Support for SLURM and interactive training.
-
✅ Learning Algorithms - SFT (Supervised Fine-Tuning), and PEFT (Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning).
-
✅ Pre-training - Support for model pre-training, including DeepSeekV3.
-
✅ Knowledge Distillation - Support for knowledge distillation with LLMs; VLM support will be added post 25.09.
-
✅ HuggingFace Integration - Works with dense models (e.g., Qwen, Llama3, etc) and large MoEs (e.g., DSv3).
-
✅ Sequence Packing - Sequence packing for huge training perf gains.
-
✅ FP8 and mixed precision - FP8 support with torchao, requires torch.compile-supported models.
-
✅ DCP - Distributed Checkpoint support with SafeTensors output.
-
✅ VLM: Support for finetuning VLMs (e.g., Qwen2-VL, Gemma-3-VL). More families to be included in the future.
-
✅ Extended MoE support - GPT-OSS, Qwen3 (Coder-480B-A35B, etc), Qwen-next.
-
🔜 Transformers v5 🤗 - Support for transformers v5 🤗 with device-mesh driven parallelism.
-
🔜 Muon & Dion - Support for Muon and Dion optimizers.
-
🔜 SonicMoE - Optimized MoE implementation for faster expert computation.
-
🔜 FP8 MoE - FP8 precision training and inference for MoE models.
-
🔜 Cudagraph with MoE - CUDA graph support for MoE layers to reduce kernel launch overhead.
-
🔜 Extended VLM Support - DeepSeek OCR, Qwen3 VL 235B, Kimi-VL, GLM4.5V
-
🔜 Extended LLM Support - QWENCoder 480B Instruct, MiniMax2.1, and more
-
🔜 Kubernetes - Multi-node job launch with k8s.
We recommend using uv for reproducible Python environments.
# Setup environment before running any commands
uv venv
uv sync --frozen --all-extras
uv pip install nemo_automodel # latest release
# or: uv pip install git+https://github.com/NVIDIA-NeMo/Automodel.git
uv run python -c "import nemo_automodel; print('AutoModel ready')"To run a NeMo AutoModel recipe, you need a recipe script (e.g., LLM, VLM) and a YAML config file (e.g., LLM, VLM):
# Command invocation format:
uv run <recipe_script_path> --config <yaml_config_path>
# LLM example: multi-GPU with FSDP2
uv run torchrun --nproc-per-node=8 examples/llm_finetune/finetune.py --config examples/llm_finetune/llama3_2/llama3_2_1b_hellaswag.yaml
# VLM example: single GPU fine-tuning (Gemma-3-VL) with LoRA
uv run examples/vlm_finetune/finetune.py --config examples/vlm_finetune/gemma3/gemma3_vl_4b_cord_v2_peft.yaml
We provide an example SFT experiment using the Fineweb dataset with a nano-GPT model, ideal for quick experimentation on a single node.
uv run torchrun --nproc-per-node=8 \
examples/llm_pretrain/pretrain.py \
-c examples/llm_pretrain/nanogpt_pretrain.yamlWe provide an example SFT experiment using the SQuAD dataset.
The default SFT configuration is set to run on a single GPU. To start the experiment:
uv run python3 \
examples/llm_finetune/finetune.py \
-c examples/llm_finetune/llama3_2/llama3_2_1b_squad.yamlThis fine-tunes the Llama3.2-1B model on the SQuAD dataset using a 1 GPU.
To use multiple GPUs on a single node in an interactive environment, you can run the same command
using torchrun and adjust the --proc-per-node argument to the number of needed GPUs.
uv run torchrun --nproc-per-node=8 \
examples/llm_finetune/finetune.py \
-c examples/llm_finetune/llama3_2/llama3_2_1b_squad.yamlAlternatively, you can use the automodel CLI application to launch the same job, for example:
uv run automodel finetune llm \
--nproc-per-node=8 \
-c examples/llm_finetune/llama3_2/llama3_2_1b_squad.yamlYou can use the automodel CLI application to launch a job on a SLURM cluster, for example:
# First you need to specify the SLURM section in your YAML config, for example:
cat << EOF > examples/llm_finetune/llama3_2/llama3_2_1b_squad.yaml
slurm:
job_name: llm-finetune # set to the job name you want to use
nodes: 2 # set to the needed number of nodes
ntasks_per_node: 8
time: 00:30:00
account: your_account
partition: gpu
container_image: nvcr.io/nvidia/nemo:25.07
gpus_per_node: 8 # This adds "#SBATCH --gpus-per-node=8" to the script
# Optional: Add extra mount points if needed
extra_mounts:
- /lustre:/lustre
# Optional: Specify custom HF_HOME location (will auto-create if not specified)
hf_home: /path/to/your/HF_HOME
# Optional : Specify custom env vars
# env_vars:
# ENV_VAR: value
# Optional: Specify custom job directory (defaults to cwd/slurm_jobs)
# job_dir: /path/to/slurm/jobs
EOF
# using the updated YAML you can launch the job.
uv run automodel finetune llm \
-c examples/llm_finetune/llama3_2/llama3_2_1b_squad.yamlWe provide a PEFT example using the HellaSwag dataset.
# Memory‑efficient SFT with LoRA
uv run examples/llm_finetune/finetune.py \
--config examples/llm_finetune/llama3_2/llama3_2_1b_hellaswag_peft.yaml
# You can always overwrite parameters by appending them to the command, for example,
# if you want to increase the micro-batch size you can do
uv run examples/llm_finetune/finetune.py \
--config examples/llm_finetune/llama3_2/llama3_2_1b_hellaswag_peft.yaml \
--step_scheduler.local_batch_size 16
# The above command will modify the `local_batch_size` variable to have value 16 in the
# section `step_scheduler` of the yaml file.[!NOTE] Launching a multi-node PEFT example requires only adding a
slurmsection to your config, similarly to the SFT case.
We provide a VLM SFT example using Qwen2.5‑VL for end‑to‑end fine‑tuning on image‑text data.
# Qwen2.5‑VL on a 8 GPUs
uv run torchrun --nproc-per-node=8 \
examples/vlm_finetune/finetune.py \
--config examples/vlm_finetune/qwen2_5/qwen2_5_vl_3b_rdr.yamlWe provide a VLM PEFT (LoRA) example for memory‑efficient adaptation with Gemma3 VLM.
# Qwen2.5‑VL on a 8 GPUs
uv run torchrun --nproc-per-node=8 \
examples/vlm_finetune/finetune.py \
--config examples/vlm_finetune/gemma3/gemma3_vl_4b_medpix_peft.yamlNeMo AutoModel provides native support for a wide range of models available on the Hugging Face Hub, enabling efficient fine-tuning for various domains. Below is a small sample of ready‑to‑use families (train as‑is or swap any compatible 🤗 causal LM), you can specify nearly any LLM/VLM model available on 🤗 hub:
[!NOTE] Check out more LLM and VLM examples. Any causal LM on Hugging Face Hub can be used with the base recipe template, just overwrite
--model.pretrained_model_name_or_path <model-id>in the CLI or in the YAML config.
NeMo AutoModel achieves great training performance on NVIDIA GPUs. Below are highlights from our benchmark results:
| Model | #GPUs | Seq Length | Model TFLOPs/sec/GPU | Tokens/sec/GPU | Kernel Optimizations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek V3 671B | 256 | 4096 | 250 | 1,002 | TE + DeepEP |
| GPT-OSS 20B | 8 | 4096 | 279 | 13,058 | TE + DeepEP + FlexAttn |
| Qwen3 MoE 30B | 8 | 4096 | 212 | 11,842 | TE + DeepEP |
For complete benchmark results including configuration details, see the Performance Summary.
- NeMo RL: Use AutoModel checkpoints directly as starting points for DPO/RM/GRPO pipelines.
- Hugging Face: Train any LLM/VLM from 🤗 without format conversion.
- Megatron Bridge: Optional conversions to/from Megatron formats for specific workflows.
NeMo-Automodel/
├── examples
│ ├── llm_finetune # LLM finetune recipes
│ ├── llm_kd # LLM knowledge-distillation recipes
│ ├── llm_pretrain # LLM pretrain recipes
│ ├── vlm_finetune # VLM finetune recipes
│ └── vlm_generate # VLM generate recipes
├── nemo_automodel
│ ├── _cli
│ │ └── app.py # the `automodel` CLI job launcher
│ ├── components # Core library
│ │ ├── _peft # PEFT implementations (LoRA)
│ │ ├── _transformers # HF model integrations
│ │ ├── checkpoint # Distributed checkpointing
│ │ ├── config
│ │ ├── datasets # LLM (HellaSwag, etc.) & VLM datasets
│ │ ├── distributed # FSDP2, Megatron FSDP, Pipelining, etc.
│ │ ├── launcher # The job launcher component (SLURM)
│ │ ├── loggers # loggers
│ │ ├── loss # Optimized loss functions
│ │ ├── models # User-defined model examples
│ │ ├── moe # Optimized kernels for MoE models
│ │ ├── optim # Optimizer/LR scheduler components
│ │ ├── quantization # FP8
│ │ ├── training # Train utils
│ │ └── utils # Misc utils
│ ├── recipes
│ │ ├── llm # Main LLM train loop
│ │ └── vlm # Main VLM train loop
│ └── shared
└── tests/ # Comprehensive test suite
If you use NeMo AutoModel in your research, please cite it using the following BibTeX entry:
@misc{nemo-automodel,
title = {NeMo AutoModel: DTensor‑native SPMD library for scalable and efficient training},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/NVIDIA-NeMo/Automodel}},
year = {2025},
note = {GitHub repository},
}
We welcome contributions! Please see our Contributing Guide for details.
NVIDIA NeMo AutoModel is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Automodel
Similar Open Source Tools

Automodel
Automodel is a Python library for automating the process of building and evaluating machine learning models. It provides a set of tools and utilities to streamline the model development workflow, from data preprocessing to model selection and evaluation. With Automodel, users can easily experiment with different algorithms, hyperparameters, and feature engineering techniques to find the best model for their dataset. The library is designed to be user-friendly and customizable, allowing users to define their own pipelines and workflows. Automodel is suitable for data scientists, machine learning engineers, and anyone looking to quickly build and test machine learning models without the need for manual intervention.
mindnlp
MindNLP is an open-source NLP library based on MindSpore. It provides a platform for solving natural language processing tasks, containing many common approaches in NLP. It can help researchers and developers to construct and train models more conveniently and rapidly. Key features of MindNLP include: * Comprehensive data processing: Several classical NLP datasets are packaged into a friendly module for easy use, such as Multi30k, SQuAD, CoNLL, etc. * Friendly NLP model toolset: MindNLP provides various configurable components. It is friendly to customize models using MindNLP. * Easy-to-use engine: MindNLP simplified complicated training process in MindSpore. It supports Trainer and Evaluator interfaces to train and evaluate models easily. MindNLP supports a wide range of NLP tasks, including: * Language modeling * Machine translation * Question answering * Sentiment analysis * Sequence labeling * Summarization MindNLP also supports industry-leading Large Language Models (LLMs), including Llama, GLM, RWKV, etc. For support related to large language models, including pre-training, fine-tuning, and inference demo examples, you can find them in the "llm" directory. To install MindNLP, you can either install it from Pypi, download the daily build wheel, or install it from source. The installation instructions are provided in the documentation. MindNLP is released under the Apache 2.0 license. If you find this project useful in your research, please consider citing the following paper: @misc{mindnlp2022, title={{MindNLP}: a MindSpore NLP library}, author={MindNLP Contributors}, howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/mindlab-ai/mindnlp}}, year={2022} }
llm4s
LLM4S provides a simple, robust, and scalable framework for building Large Language Models (LLM) applications in Scala. It aims to leverage Scala's type safety, functional programming, JVM ecosystem, concurrency, and performance advantages to create reliable and maintainable AI-powered applications. The framework supports multi-provider integration, execution environments, error handling, Model Context Protocol (MCP) support, agent frameworks, multimodal generation, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) workflows. It also offers observability features like detailed trace logging, monitoring, and analytics for debugging and performance insights.
Edit-Banana
Edit Banana is a universal content re-editor that allows users to transform fixed content into fully manipulatable assets. Powered by SAM 3 and multimodal large models, it enables high-fidelity reconstruction while preserving original diagram details and logical relationships. The platform offers advanced segmentation, fixed multi-round VLM scanning, high-quality OCR, user system with credits, multi-user concurrency, and a web interface. Users can upload images or PDFs to get editable DrawIO (XML) or PPTX files in seconds. The project structure includes components for segmentation, text extraction, frontend, models, and scripts, with detailed installation and setup instructions provided. The tool is open-source under the Apache License 2.0, allowing commercial use and secondary development.
AutoAgents
AutoAgents is a cutting-edge multi-agent framework built in Rust that enables the creation of intelligent, autonomous agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) and Ractor. Designed for performance, safety, and scalability. AutoAgents provides a robust foundation for building complex AI systems that can reason, act, and collaborate. With AutoAgents you can create Cloud Native Agents, Edge Native Agents and Hybrid Models as well. It is so extensible that other ML Models can be used to create complex pipelines using Actor Framework.
readme-ai
README-AI is a developer tool that auto-generates README.md files using a combination of data extraction and generative AI. It streamlines documentation creation and maintenance, enhancing developer productivity. This project aims to enable all skill levels, across all domains, to better understand, use, and contribute to open-source software. It offers flexible README generation, supports multiple large language models (LLMs), provides customizable output options, works with various programming languages and project types, and includes an offline mode for generating boilerplate README files without external API calls.
GraphGen
GraphGen is a framework for synthetic data generation guided by knowledge graphs. It enhances supervised fine-tuning for large language models (LLMs) by generating synthetic data based on a fine-grained knowledge graph. The tool identifies knowledge gaps in LLMs, prioritizes generating QA pairs targeting high-value knowledge, incorporates multi-hop neighborhood sampling, and employs style-controlled generation to diversify QA data. Users can use LLaMA-Factory and xtuner for fine-tuning LLMs after data generation.
Auto-Claude
Auto Claude is an autonomous multi-agent coding framework that plans, builds, and validates software for users. It provides features such as autonomous tasks handling planning, implementation, and validation, parallel execution with multiple agent terminals, isolated workspaces for safe changes, self-validating quality assurance, AI-powered merge for conflict resolution, memory layer for smarter builds, GitHub/GitLab integration, cross-platform native desktop apps, auto-updates, and more. The tool offers a visual Kanban board for task management, AI-powered terminals for parallel work, AI-assisted feature planning, insights chat interface, ideation for code improvements, performance issues, and vulnerabilities discovery, and changelog generation from completed tasks. It follows a three-layer security model with OS sandbox, filesystem restrictions, and dynamic command allowlist, ensuring security through VirusTotal scans, SHA256 checksums, and code-signing for macOS releases.
ai-dev-kit
The AI Dev Kit is a comprehensive toolkit designed to enhance AI-driven development on Databricks. It provides trusted sources for AI coding assistants like Claude Code and Cursor to build faster and smarter on Databricks. The kit includes features such as Spark Declarative Pipelines, Databricks Jobs, AI/BI Dashboards, Unity Catalog, Genie Spaces, Knowledge Assistants, MLflow Experiments, Model Serving, Databricks Apps, and more. Users can choose from different adventures like installing the kit, using the visual builder app, teaching AI assistants Databricks patterns, executing Databricks actions, or building custom integrations with the core library. The kit also includes components like databricks-tools-core, databricks-mcp-server, databricks-skills, databricks-builder-app, and ai-dev-project.
Lynkr
Lynkr is a self-hosted proxy server that unlocks various AI coding tools like Claude Code CLI, Cursor IDE, and Codex Cli. It supports multiple LLM providers such as Databricks, AWS Bedrock, OpenRouter, Ollama, llama.cpp, Azure OpenAI, Azure Anthropic, OpenAI, and LM Studio. Lynkr offers cost reduction, local/private execution, remote or local connectivity, zero code changes, and enterprise-ready features. It is perfect for developers needing provider flexibility, cost control, self-hosted AI with observability, local model execution, and cost reduction strategies.
Liger-Kernel
Liger Kernel is a collection of Triton kernels designed for LLM training, increasing training throughput by 20% and reducing memory usage by 60%. It includes Hugging Face Compatible modules like RMSNorm, RoPE, SwiGLU, CrossEntropy, and FusedLinearCrossEntropy. The tool works with Flash Attention, PyTorch FSDP, and Microsoft DeepSpeed, aiming to enhance model efficiency and performance for researchers, ML practitioners, and curious novices.

ClaraVerse
ClaraVerse is a privacy-first AI assistant and agent builder that allows users to chat with AI, create intelligent agents, and turn them into fully functional apps. It operates entirely on open-source models running on the user's device, ensuring data privacy and security. With features like AI assistant, image generation, intelligent agent builder, and image gallery, ClaraVerse offers a versatile platform for AI interaction and app development. Users can install ClaraVerse through Docker, native desktop apps, or the web version, with detailed instructions provided for each option. The tool is designed to empower users with control over their AI stack and leverage community-driven innovations for AI development.
axonhub
AxonHub is an all-in-one AI development platform that serves as an AI gateway allowing users to switch between model providers without changing any code. It provides features like vendor lock-in prevention, integration simplification, observability enhancement, and cost control. Users can access any model using any SDK with zero code changes. The platform offers full request tracing, enterprise RBAC, smart load balancing, and real-time cost tracking. AxonHub supports multiple databases, provides a unified API gateway, and offers flexible model management and API key creation for authentication. It also integrates with various AI coding tools and SDKs for seamless usage.
botserver
General Bots is a self-hosted AI automation platform and LLM conversational platform focused on convention over configuration and code-less approaches. It serves as the core API server handling LLM orchestration, business logic, database operations, and multi-channel communication. The platform offers features like multi-vendor LLM API, MCP + LLM Tools Generation, Semantic Caching, Web Automation Engine, Enterprise Data Connectors, and Git-like Version Control. It enforces a ZERO TOLERANCE POLICY for code quality and security, with strict guidelines for error handling, performance optimization, and code patterns. The project structure includes modules for core functionalities like Rhai BASIC interpreter, security, shared types, tasks, auto task system, file operations, learning system, and LLM assistance.
claude-code-ultimate-guide
The Claude Code Ultimate Guide is an exhaustive documentation resource that takes users from beginner to power user in using Claude Code. It includes production-ready templates, workflow guides, a quiz, and a cheatsheet for daily use. The guide covers educational depth, methodologies, and practical examples to help users understand concepts and workflows. It also provides interactive onboarding, a repository structure overview, and learning paths for different user levels. The guide is regularly updated and offers a unique 257-question quiz for comprehensive assessment. Users can also find information on agent teams coverage, methodologies, annotated templates, resource evaluations, and learning paths for different roles like junior developer, senior developer, power user, and product manager/devops/designer.
For similar tasks
autogen
AutoGen is a framework that enables the development of LLM applications using multiple agents that can converse with each other to solve tasks. AutoGen agents are customizable, conversable, and seamlessly allow human participation. They can operate in various modes that employ combinations of LLMs, human inputs, and tools.

tracecat
Tracecat is an open-source automation platform for security teams. It's designed to be simple but powerful, with a focus on AI features and a practitioner-obsessed UI/UX. Tracecat can be used to automate a variety of tasks, including phishing email investigation, evidence collection, and remediation plan generation.
ciso-assistant-community
CISO Assistant is a tool that helps organizations manage their cybersecurity posture and compliance. It provides a centralized platform for managing security controls, threats, and risks. CISO Assistant also includes a library of pre-built frameworks and tools to help organizations quickly and easily implement best practices.
ck
Collective Mind (CM) is a collection of portable, extensible, technology-agnostic and ready-to-use automation recipes with a human-friendly interface (aka CM scripts) to unify and automate all the manual steps required to compose, run, benchmark and optimize complex ML/AI applications on any platform with any software and hardware: see online catalog and source code. CM scripts require Python 3.7+ with minimal dependencies and are continuously extended by the community and MLCommons members to run natively on Ubuntu, MacOS, Windows, RHEL, Debian, Amazon Linux and any other operating system, in a cloud or inside automatically generated containers while keeping backward compatibility - please don't hesitate to report encountered issues here and contact us via public Discord Server to help this collaborative engineering effort! CM scripts were originally developed based on the following requirements from the MLCommons members to help them automatically compose and optimize complex MLPerf benchmarks, applications and systems across diverse and continuously changing models, data sets, software and hardware from Nvidia, Intel, AMD, Google, Qualcomm, Amazon and other vendors: * must work out of the box with the default options and without the need to edit some paths, environment variables and configuration files; * must be non-intrusive, easy to debug and must reuse existing user scripts and automation tools (such as cmake, make, ML workflows, python poetry and containers) rather than substituting them; * must have a very simple and human-friendly command line with a Python API and minimal dependencies; * must require minimal or zero learning curve by using plain Python, native scripts, environment variables and simple JSON/YAML descriptions instead of inventing new workflow languages; * must have the same interface to run all automations natively, in a cloud or inside containers. CM scripts were successfully validated by MLCommons to modularize MLPerf inference benchmarks and help the community automate more than 95% of all performance and power submissions in the v3.1 round across more than 120 system configurations (models, frameworks, hardware) while reducing development and maintenance costs.

zenml
ZenML is an extensible, open-source MLOps framework for creating portable, production-ready machine learning pipelines. By decoupling infrastructure from code, ZenML enables developers across your organization to collaborate more effectively as they develop to production.

clearml
ClearML is a suite of tools designed to streamline the machine learning workflow. It includes an experiment manager, MLOps/LLMOps, data management, and model serving capabilities. ClearML is open-source and offers a free tier hosting option. It supports various ML/DL frameworks and integrates with Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm. ClearML provides extensive logging capabilities, including source control info, execution environment, hyper-parameters, and experiment outputs. It also offers automation features, such as remote job execution and pipeline creation. ClearML is designed to be easy to integrate, requiring only two lines of code to add to existing scripts. It aims to improve collaboration, visibility, and data transparency within ML teams.
devchat
DevChat is an open-source workflow engine that enables developers to create intelligent, automated workflows for engaging with users through a chat panel within their IDEs. It combines script writing flexibility, latest AI models, and an intuitive chat GUI to enhance user experience and productivity. DevChat simplifies the integration of AI in software development, unlocking new possibilities for developers.
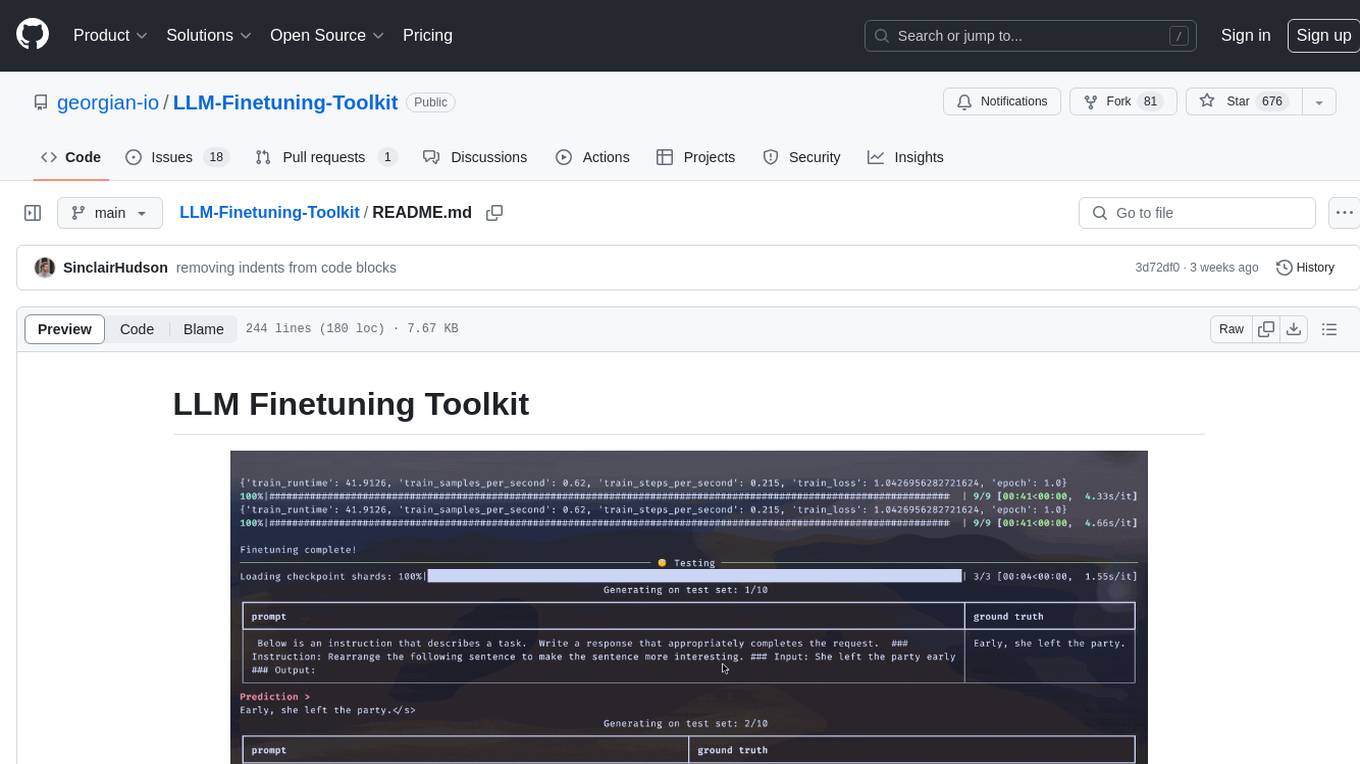
LLM-Finetuning-Toolkit
LLM Finetuning toolkit is a config-based CLI tool for launching a series of LLM fine-tuning experiments on your data and gathering their results. It allows users to control all elements of a typical experimentation pipeline - prompts, open-source LLMs, optimization strategy, and LLM testing - through a single YAML configuration file. The toolkit supports basic, intermediate, and advanced usage scenarios, enabling users to run custom experiments, conduct ablation studies, and automate fine-tuning workflows. It provides features for data ingestion, model definition, training, inference, quality assurance, and artifact outputs, making it a comprehensive tool for fine-tuning large language models.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.