Liger-Kernel
Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training
Stars: 4776
Liger Kernel is a collection of Triton kernels designed for LLM training, increasing training throughput by 20% and reducing memory usage by 60%. It includes Hugging Face Compatible modules like RMSNorm, RoPE, SwiGLU, CrossEntropy, and FusedLinearCrossEntropy. The tool works with Flash Attention, PyTorch FSDP, and Microsoft DeepSpeed, aiming to enhance model efficiency and performance for researchers, ML practitioners, and curious novices.
README:
| Stable | Nightly | Discord | Build | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|
|
|
Installation | Getting Started | Examples | High-level APIs | Low-level APIs | Cite our work
Latest News 🔥
- [2025/03/06] We release a joint blog post on TorchTune × Liger - Peak Performance, Minimized Memory: Optimizing torchtune’s performance with torch.compile & Liger Kernel
- [2024/12/11] We release v0.5.0: 80% more memory efficient post training losses (DPO, ORPO, CPO, etc)!
- [2024/12/5] We release LinkedIn Engineering Blog - Liger-Kernel: Empowering an open source ecosystem of Triton Kernels for Efficient LLM Training
- [2024/11/6] We release v0.4.0: Full AMD support, Tech Report, Modal CI, Llama-3.2-Vision!
- [2024/10/21] We have released the tech report of Liger Kernel on Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2410.10989
- [2024/9/6] We release v0.2.1 (X post). 2500+ Stars, 10+ New Contributors, 50+ PRs, 50k Downloads in two weeks!
- [2024/8/31] CUDA MODE talk, Liger-Kernel: Real-world Triton kernel for LLM Training, Slides
- [2024/8/23] Official release: check out our X post
Liger Kernel is a collection of Triton kernels designed specifically for LLM training. It can effectively increase multi-GPU training throughput by 20% and reduces memory usage by 60%. We have implemented Hugging Face Compatible RMSNorm, RoPE, SwiGLU, CrossEntropy, FusedLinearCrossEntropy, and more to come. The kernel works out of the box with Flash Attention, PyTorch FSDP, and Microsoft DeepSpeed. We welcome contributions from the community to gather the best kernels for LLM training.
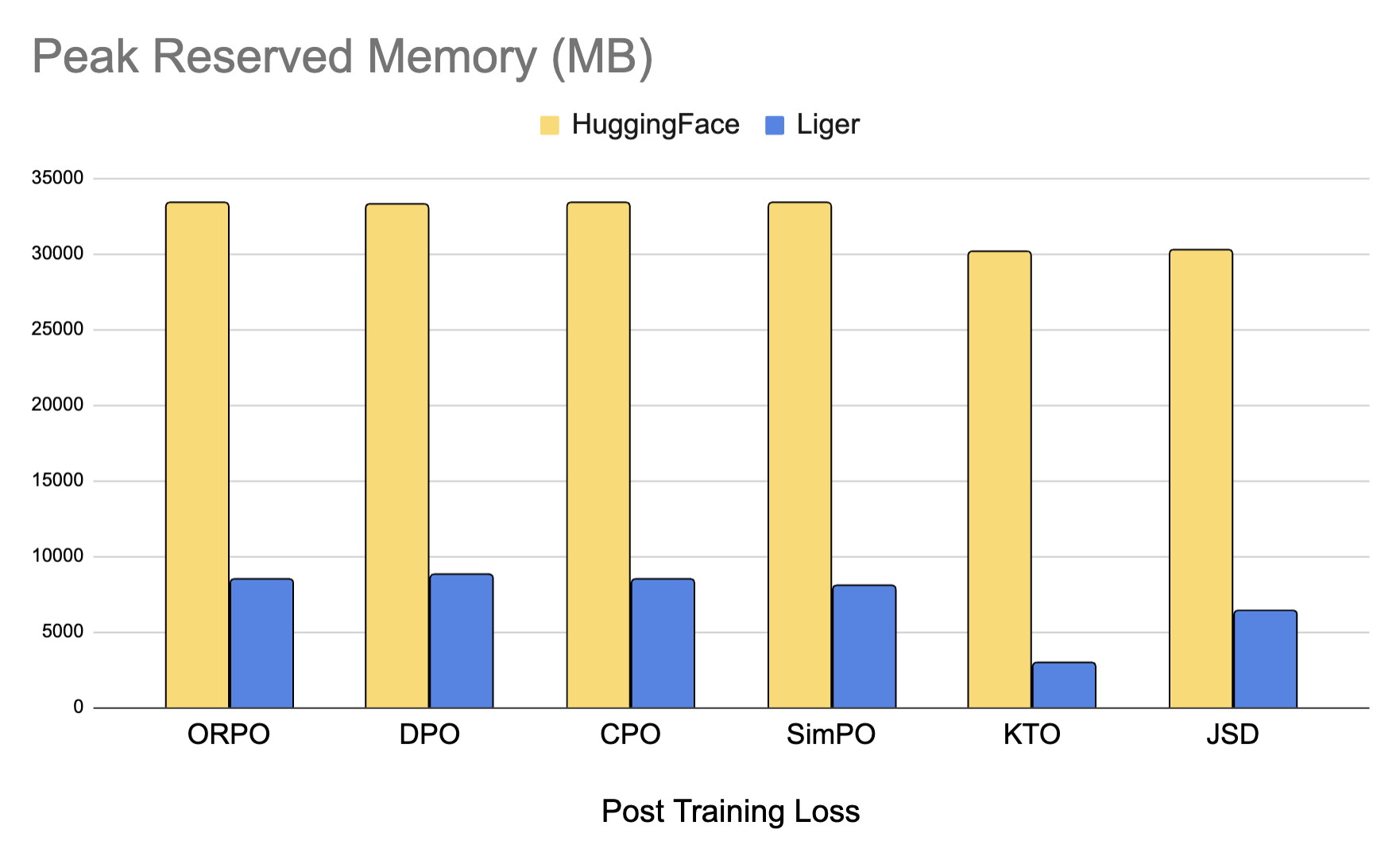
We've also added optimized Post-Training kernels that deliver up to 80% memory savings for alignment and distillation tasks. We support losses like DPO, CPO, ORPO, SimPO, KTO, JSD, and many more. Check out how we optimize the memory.
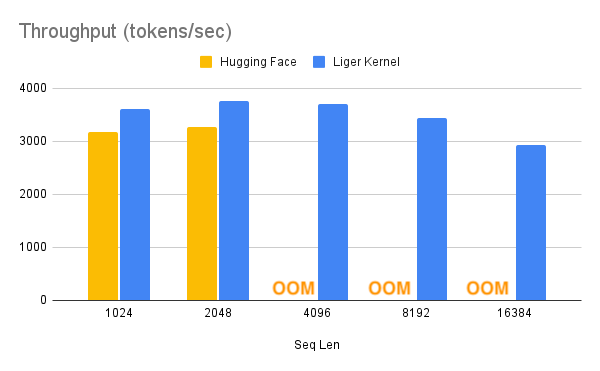
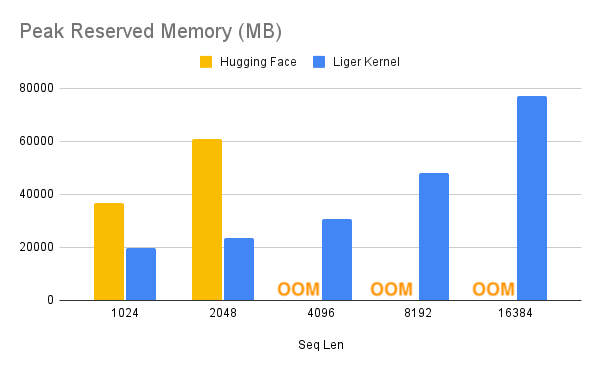
With one line of code, Liger Kernel can increase throughput by more than 20% and reduce memory usage by 60%, thereby enabling longer context lengths, larger batch sizes, and massive vocabularies.
| Speed Up | Memory Reduction |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Note:
- Benchmark conditions: LLaMA 3-8B, Batch Size = 8, Data Type =
bf16, Optimizer = AdamW, Gradient Checkpointing = True, Distributed Strategy = FSDP1 on 8 A100s.- Hugging Face models start to OOM at a 4K context length, whereas Hugging Face + Liger Kernel scales up to 16K.
We provide optimized post training kernels like DPO, ORPO, SimPO, and more which can reduce memory usage by up to 80%. You can easily use them as python modules.
from liger_kernel.chunked_loss import LigerFusedLinearORPOLoss
orpo_loss = LigerFusedLinearORPOLoss()
y = orpo_loss(lm_head.weight, x, target)| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Hugging Face Trainer | Train LLaMA 3-8B ~20% faster with over 40% memory reduction on Alpaca dataset using 4 A100s with FSDP |
| Lightning Trainer | Increase 15% throughput and reduce memory usage by 40% with LLaMA3-8B on MMLU dataset using 8 A100s with DeepSpeed ZeRO3 |
| Medusa Multi-head LLM (Retraining Phase) | Reduce memory usage by 80% with 5 LM heads and improve throughput by 40% using 8 A100s with FSDP |
| Vision-Language Model SFT | Finetune Qwen2-VL on image-text data using 4 A100s with FSDP |
| Liger ORPO Trainer | Align Llama 3.2 using Liger ORPO Trainer with FSDP with 50% memory reduction |
- Ease of use: Simply patch your Hugging Face model with one line of code, or compose your own model using our Liger Kernel modules.
- Time and memory efficient: In the same spirit as Flash-Attn, but for layers like RMSNorm, RoPE, SwiGLU, and CrossEntropy! Increases multi-GPU training throughput by 20% and reduces memory usage by 60% with kernel fusion, in-place replacement, and chunking techniques.
- Exact: Computation is exact—no approximations! Both forward and backward passes are implemented with rigorous unit tests and undergo convergence testing against training runs without Liger Kernel to ensure accuracy.
- Lightweight: Liger Kernel has minimal dependencies, requiring only Torch and Triton—no extra libraries needed! Say goodbye to dependency headaches!
- Multi-GPU supported: Compatible with multi-GPU setups (PyTorch FSDP, DeepSpeed, DDP, etc.).
- Trainer Framework Integration: Axolotl, LLaMa-Factory, SFTTrainer, Hugging Face Trainer, SWIFT, oumi
torch >= 2.1.2triton >= 2.3.0
-
torch >= 2.5.0Install according to the instruction in Pytorch official webpage. -
triton >= 3.0.0Install from pypi. (e.g.pip install triton==3.0.0)
# Need to pass the url when installing
pip install -e .[dev] --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/rocm6.2-
transformers >= 4.x: Required if you plan to use the transformers models patching APIs. The specific model you are working will dictate the minimum version of transformers.
Note: Our kernels inherit the full spectrum of hardware compatibility offered by Triton.
To install the stable version:
$ pip install liger-kernelTo install the nightly version:
$ pip install liger-kernel-nightlyTo install from source:
git clone https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel.git
cd Liger-Kernel
# Install Default Dependencies
# Setup.py will detect whether you are using AMD or NVIDIA
pip install -e .
# Setup Development Dependencies
pip install -e ".[dev]"There are a couple of ways to apply Liger kernels, depending on the level of customization required.
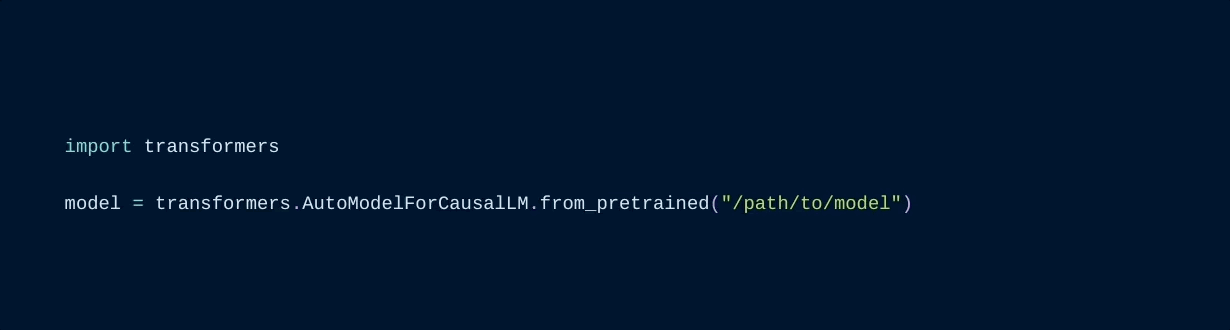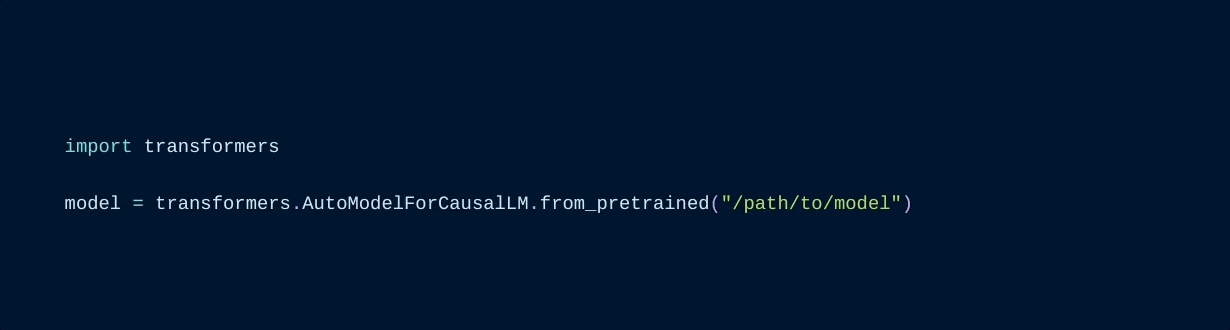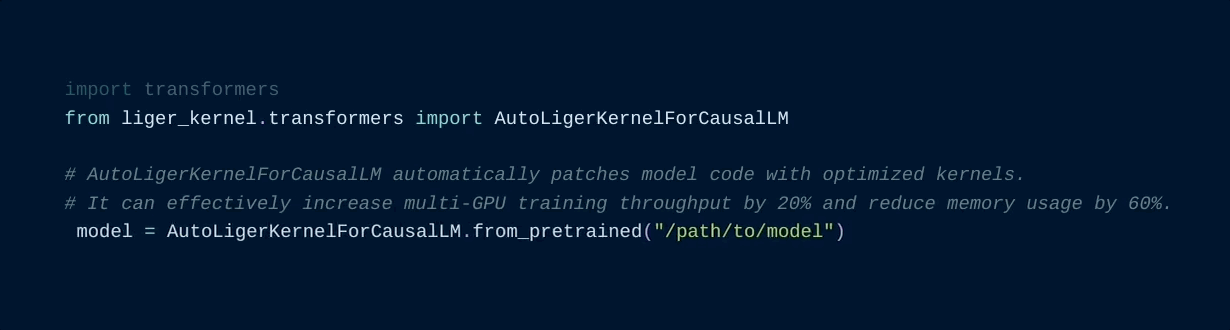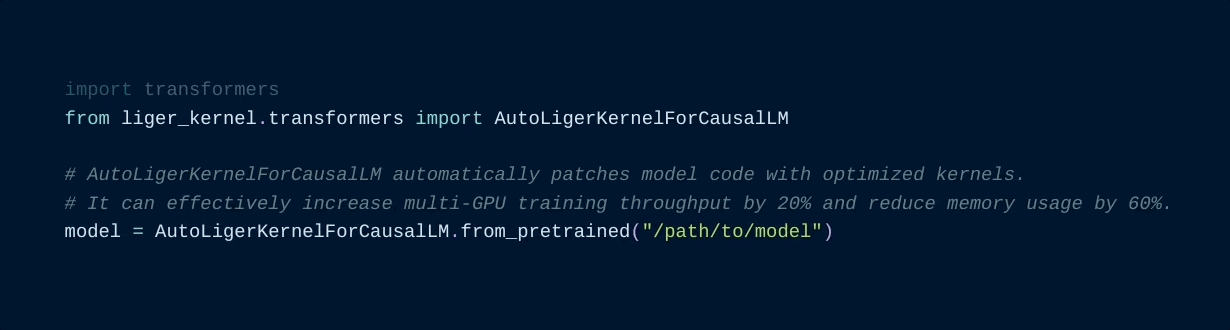
Using the AutoLigerKernelForCausalLM is the simplest approach, as you don't have to import a model-specific patching API. If the model type is supported, the modeling code will be automatically patched using the default settings.
from liger_kernel.transformers import AutoLigerKernelForCausalLM
# This AutoModel wrapper class automatically monkey-patches the
# model with the optimized Liger kernels if the model is supported.
model = AutoLigerKernelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("path/to/some/model")Using the patching APIs, you can swap Hugging Face models with optimized Liger Kernels.
import transformers
from liger_kernel.transformers import apply_liger_kernel_to_llama
# 1a. Adding this line automatically monkey-patches the model with the optimized Liger kernels
apply_liger_kernel_to_llama()
# 1b. You could alternatively specify exactly which kernels are applied
apply_liger_kernel_to_llama(
rope=True,
swiglu=True,
cross_entropy=True,
fused_linear_cross_entropy=False,
rms_norm=False
)
# 2. Instantiate patched model
model = transformers.AutoModelForCausalLM("path/to/llama/model")You can take individual kernels to compose your models.
from liger_kernel.transformers import LigerFusedLinearCrossEntropyLoss
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
model = nn.Linear(128, 256).cuda()
# fuses linear + cross entropy layers together and performs chunk-by-chunk computation to reduce memory
loss_fn = LigerFusedLinearCrossEntropyLoss()
input = torch.randn(4, 128, requires_grad=True, device="cuda")
target = torch.randint(256, (4, ), device="cuda")
loss = loss_fn(model.weight, input, target)
loss.backward()| AutoModel Variant | API |
|---|---|
| AutoModelForCausalLM | liger_kernel.transformers.AutoLigerKernelForCausalLM |
| Model | API | Supported Operations |
|---|---|---|
| LLaMA 2 & 3 | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_llama |
RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| LLaMA 3.2-Vision | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_mllama |
RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Mistral | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_mistral |
RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Mixtral | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_mixtral |
RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Gemma1 | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_gemma |
RoPE, RMSNorm, GeGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Gemma2 | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_gemma2 |
RoPE, RMSNorm, GeGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Gemma3 (Text) | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_gemma3_text |
RoPE, RMSNorm, GeGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Gemma3 (Multimodal) | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_gemma3 |
LayerNorm, RoPE, RMSNorm, GeGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Paligemma, Paligemma2, & Paligemma2 Mix | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_paligemma |
LayerNorm, RoPE, RMSNorm, GeGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Qwen2, Qwen2.5, & QwQ | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_qwen2 |
RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Qwen2-VL, & QVQ | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_qwen2_vl |
RMSNorm, LayerNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Qwen2.5-VL | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_qwen2_5_vl |
RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Phi3 & Phi3.5 | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_phi3 |
RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
| Granite 3.0 & 3.1 | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_granite |
RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss |
| OLMo2 | liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_olmo2 |
RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
-
Fused Linearkernels combine linear layers with losses, reducing memory usage by up to 80% - ideal for HBM-constrained workloads. - Other kernels use fusion and in-place techniques for memory and performance optimization.
| Kernel | API |
|---|---|
| RMSNorm | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerRMSNorm |
| LayerNorm | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerLayerNorm |
| RoPE | liger_kernel.transformers.liger_rotary_pos_emb |
| SwiGLU | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerSwiGLUMLP |
| GeGLU | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerGEGLUMLP |
| CrossEntropy | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerCrossEntropyLoss |
| Fused Linear CrossEntropy | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerFusedLinearCrossEntropyLoss |
| Kernel | API |
|---|---|
| Fused Linear CPO Loss | liger_kernel.chunked_loss.LigerFusedLinearCPOLoss |
| Fused Linear DPO Loss | liger_kernel.chunked_loss.LigerFusedLinearDPOLoss |
| Fused Linear ORPO Loss | liger_kernel.chunked_loss.LigerFusedLinearORPOLoss |
| Fused Linear SimPO Loss | liger_kernel.chunked_loss.LigerFusedLinearSimPOLoss |
| Fused Linear KTO Loss | liger_kernel.chunked_loss.LigerFusedLinearKTOLoss |
| Kernel | API |
|---|---|
| KLDivergence | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerKLDIVLoss |
| JSD | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerJSD |
| Fused Linear JSD | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerFusedLinearJSD |
| TVD | liger_kernel.transformers.LigerTVDLoss |
| Kernel | API |
|---|---|
| Embedding | liger_kernel.transformers.experimental.LigerEmbedding |
| Matmul int2xint8 | liger_kernel.transformers.experimental.matmul |
- Glows.ai: Sponsoring NVIDIA GPUs for our open source developers.
- AMD: Providing AMD GPUs for our AMD CI.
- Intel: Providing Intel GPUs for our Intel CI.
- Modal: Free 3000 credits from GPU MODE IRL for our NVIDIA CI.
- EmbeddedLLM: Making Liger Kernel run fast and stable on AMD.
- HuggingFace: Integrating Liger Kernel into Hugging Face Transformers and TRL.
- Lightning AI: Integrating Liger Kernel into Lightning Thunder.
- Axolotl: Integrating Liger Kernel into Axolotl.
- Llama-Factory: Integrating Liger Kernel into Llama-Factory.
- For issues, create a Github ticket in this repository
- For open discussion, join our discord channel on GPUMode
- For formal collaboration, send an email to [email protected] and [email protected]
Biblatex entry:
@article{hsu2024ligerkernelefficienttriton,
title={Liger Kernel: Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training},
author={Pin-Lun Hsu and Yun Dai and Vignesh Kothapalli and Qingquan Song and Shao Tang and Siyu Zhu and Steven Shimizu and Shivam Sahni and Haowen Ning and Yanning Chen},
year={2024},
eprint={2410.10989},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.10989},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.10989},
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Liger-Kernel
Similar Open Source Tools

Liger-Kernel
Liger Kernel is a collection of Triton kernels designed for LLM training, increasing training throughput by 20% and reducing memory usage by 60%. It includes Hugging Face Compatible modules like RMSNorm, RoPE, SwiGLU, CrossEntropy, and FusedLinearCrossEntropy. The tool works with Flash Attention, PyTorch FSDP, and Microsoft DeepSpeed, aiming to enhance model efficiency and performance for researchers, ML practitioners, and curious novices.
mindnlp
MindNLP is an open-source NLP library based on MindSpore. It provides a platform for solving natural language processing tasks, containing many common approaches in NLP. It can help researchers and developers to construct and train models more conveniently and rapidly. Key features of MindNLP include: * Comprehensive data processing: Several classical NLP datasets are packaged into a friendly module for easy use, such as Multi30k, SQuAD, CoNLL, etc. * Friendly NLP model toolset: MindNLP provides various configurable components. It is friendly to customize models using MindNLP. * Easy-to-use engine: MindNLP simplified complicated training process in MindSpore. It supports Trainer and Evaluator interfaces to train and evaluate models easily. MindNLP supports a wide range of NLP tasks, including: * Language modeling * Machine translation * Question answering * Sentiment analysis * Sequence labeling * Summarization MindNLP also supports industry-leading Large Language Models (LLMs), including Llama, GLM, RWKV, etc. For support related to large language models, including pre-training, fine-tuning, and inference demo examples, you can find them in the "llm" directory. To install MindNLP, you can either install it from Pypi, download the daily build wheel, or install it from source. The installation instructions are provided in the documentation. MindNLP is released under the Apache 2.0 license. If you find this project useful in your research, please consider citing the following paper: @misc{mindnlp2022, title={{MindNLP}: a MindSpore NLP library}, author={MindNLP Contributors}, howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/mindlab-ai/mindnlp}}, year={2022} }
unsloth
Unsloth is a tool that allows users to fine-tune large language models (LLMs) 2-5x faster with 80% less memory. It is a free and open-source tool that can be used to fine-tune LLMs such as Gemma, Mistral, Llama 2-5, TinyLlama, and CodeLlama 34b. Unsloth supports 4-bit and 16-bit QLoRA / LoRA fine-tuning via bitsandbytes. It also supports DPO (Direct Preference Optimization), PPO, and Reward Modelling. Unsloth is compatible with Hugging Face's TRL, Trainer, Seq2SeqTrainer, and Pytorch code. It is also compatible with NVIDIA GPUs since 2018+ (minimum CUDA Capability 7.0).
agentscope
AgentScope is a multi-agent platform designed to empower developers to build multi-agent applications with large-scale models. It features three high-level capabilities: Easy-to-Use, High Robustness, and Actor-Based Distribution. AgentScope provides a list of `ModelWrapper` to support both local model services and third-party model APIs, including OpenAI API, DashScope API, Gemini API, and ollama. It also enables developers to rapidly deploy local model services using libraries such as ollama (CPU inference), Flask + Transformers, Flask + ModelScope, FastChat, and vllm. AgentScope supports various services, including Web Search, Data Query, Retrieval, Code Execution, File Operation, and Text Processing. Example applications include Conversation, Game, and Distribution. AgentScope is released under Apache License 2.0 and welcomes contributions.
bitsandbytes
bitsandbytes enables accessible large language models via k-bit quantization for PyTorch. It provides features for reducing memory consumption for inference and training by using 8-bit optimizers, LLM.int8() for large language model inference, and QLoRA for large language model training. The library includes quantization primitives for 8-bit & 4-bit operations and 8-bit optimizers.

ruby_llm-agents
RubyLLM::Agents is a production-ready Rails engine for building, managing, and monitoring LLM-powered AI agents. It seamlessly integrates with Rails apps, providing features like automatic execution tracking, cost analytics, budget controls, and a real-time dashboard. Users can build intelligent AI agents in Ruby using a clean DSL and support various LLM providers like OpenAI GPT-4, Anthropic Claude, and Google Gemini. The engine offers features such as agent DSL configuration, execution tracking, cost analytics, reliability with retries and fallbacks, budget controls, multi-tenancy support, async execution with Ruby fibers, real-time dashboard, streaming, conversation history, image operations, alerts, and more.
MaixPy
MaixPy is a Python SDK that enables users to easily create AI vision projects on edge devices. It provides a user-friendly API for accessing NPU, making it suitable for AI Algorithm Engineers, STEM teachers, Makers, Engineers, Students, Enterprises, and Contestants. The tool supports Python programming, MaixVision Workstation, AI vision, video streaming, voice recognition, and peripheral usage. It also offers an online AI training platform called MaixHub. MaixPy is designed for new hardware platforms like MaixCAM, offering improved performance and features compared to older versions. The ecosystem includes hardware, software, tools, documentation, and a cloud platform.
GraphGen
GraphGen is a framework for synthetic data generation guided by knowledge graphs. It enhances supervised fine-tuning for large language models (LLMs) by generating synthetic data based on a fine-grained knowledge graph. The tool identifies knowledge gaps in LLMs, prioritizes generating QA pairs targeting high-value knowledge, incorporates multi-hop neighborhood sampling, and employs style-controlled generation to diversify QA data. Users can use LLaMA-Factory and xtuner for fine-tuning LLMs after data generation.
DeepRetrieval
DeepRetrieval is a tool designed to enhance search engines and retrievers using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). It allows LLMs to learn how to search effectively by integrating with search engine APIs and customizing reward functions. The tool provides functionalities for data preparation, training, evaluation, and monitoring search performance. DeepRetrieval aims to improve information retrieval tasks by leveraging advanced AI techniques.
Automodel
Automodel is a Python library for automating the process of building and evaluating machine learning models. It provides a set of tools and utilities to streamline the model development workflow, from data preprocessing to model selection and evaluation. With Automodel, users can easily experiment with different algorithms, hyperparameters, and feature engineering techniques to find the best model for their dataset. The library is designed to be user-friendly and customizable, allowing users to define their own pipelines and workflows. Automodel is suitable for data scientists, machine learning engineers, and anyone looking to quickly build and test machine learning models without the need for manual intervention.
qserve
QServe is a serving system designed for efficient and accurate Large Language Models (LLM) on GPUs with W4A8KV4 quantization. It achieves higher throughput compared to leading industry solutions, allowing users to achieve A100-level throughput on cheaper L40S GPUs. The system introduces the QoQ quantization algorithm with 4-bit weight, 8-bit activation, and 4-bit KV cache, addressing runtime overhead challenges. QServe improves serving throughput for various LLM models by implementing compute-aware weight reordering, register-level parallelism, and fused attention memory-bound techniques.
ai-dev-kit
The AI Dev Kit is a comprehensive toolkit designed to enhance AI-driven development on Databricks. It provides trusted sources for AI coding assistants like Claude Code and Cursor to build faster and smarter on Databricks. The kit includes features such as Spark Declarative Pipelines, Databricks Jobs, AI/BI Dashboards, Unity Catalog, Genie Spaces, Knowledge Assistants, MLflow Experiments, Model Serving, Databricks Apps, and more. Users can choose from different adventures like installing the kit, using the visual builder app, teaching AI assistants Databricks patterns, executing Databricks actions, or building custom integrations with the core library. The kit also includes components like databricks-tools-core, databricks-mcp-server, databricks-skills, databricks-builder-app, and ai-dev-project.

NornicDB
NornicDB is a high-performance graph database designed for AI agents and knowledge systems. It is Neo4j-compatible, GPU-accelerated, and features memory that evolves. The database automatically discovers and manages relationships in the data, allowing meaning to emerge from the knowledge graph. NornicDB is suitable for AI agent memory, knowledge graphs, RAG systems, session context, and research tools. It offers features like intelligent memory, auto-relationships, performance benchmarks, vector search, Heimdall AI assistant, APOC functions, and various Docker images for different platforms. The tool is built with Neo4j Bolt protocol, Cypher query engine, memory decay system, GPU acceleration, vector search, auto-relationship engine, and more.

Athena-Public
Project Athena is a Linux OS designed for AI Agents, providing memory, persistence, scheduling, and governance for AI models. It offers a comprehensive memory layer that survives across sessions, models, and IDEs, allowing users to own their data and port it anywhere. The system is built bottom-up through 1,079+ sessions, focusing on depth and compounding knowledge. Athena features a trilateral feedback loop for cross-model validation, a Model Context Protocol server with 9 tools, and a robust security model with data residency options. The repository structure includes an SDK package, examples for quickstart, scripts, protocols, workflows, and deep documentation. Key concepts cover architecture, knowledge graph, semantic memory, and adaptive latency. Workflows include booting, reasoning modes, planning, research, and iteration. The project has seen significant content expansion, viral validation, and metrics improvements.
MooER
MooER (摩耳) is an LLM-based speech recognition and translation model developed by Moore Threads. It allows users to transcribe speech into text (ASR) and translate speech into other languages (AST) in an end-to-end manner. The model was trained using 5K hours of data and is now also available with an 80K hours version. MooER is the first LLM-based speech model trained and inferred using domestic GPUs. The repository includes pretrained models, inference code, and a Gradio demo for a better user experience.
axonhub
AxonHub is an all-in-one AI development platform that serves as an AI gateway allowing users to switch between model providers without changing any code. It provides features like vendor lock-in prevention, integration simplification, observability enhancement, and cost control. Users can access any model using any SDK with zero code changes. The platform offers full request tracing, enterprise RBAC, smart load balancing, and real-time cost tracking. AxonHub supports multiple databases, provides a unified API gateway, and offers flexible model management and API key creation for authentication. It also integrates with various AI coding tools and SDKs for seamless usage.
For similar tasks

Liger-Kernel
Liger Kernel is a collection of Triton kernels designed for LLM training, increasing training throughput by 20% and reducing memory usage by 60%. It includes Hugging Face Compatible modules like RMSNorm, RoPE, SwiGLU, CrossEntropy, and FusedLinearCrossEntropy. The tool works with Flash Attention, PyTorch FSDP, and Microsoft DeepSpeed, aiming to enhance model efficiency and performance for researchers, ML practitioners, and curious novices.
verl
veRL is a flexible and efficient reinforcement learning training framework designed for large language models (LLMs). It allows easy extension of diverse RL algorithms, seamless integration with existing LLM infrastructures, and flexible device mapping. The framework achieves state-of-the-art throughput and efficient actor model resharding with 3D-HybridEngine. It supports popular HuggingFace models and is suitable for users working with PyTorch FSDP, Megatron-LM, and vLLM backends.

litdata
LitData is a tool designed for blazingly fast, distributed streaming of training data from any cloud storage. It allows users to transform and optimize data in cloud storage environments efficiently and intuitively, supporting various data types like images, text, video, audio, geo-spatial, and multimodal data. LitData integrates smoothly with frameworks such as LitGPT and PyTorch, enabling seamless streaming of data to multiple machines. Key features include multi-GPU/multi-node support, easy data mixing, pause & resume functionality, support for profiling, memory footprint reduction, cache size configuration, and on-prem optimizations. The tool also provides benchmarks for measuring streaming speed and conversion efficiency, along with runnable templates for different data types. LitData enables infinite cloud data processing by utilizing the Lightning.ai platform to scale data processing with optimized machines.
llm-awq
AWQ (Activation-aware Weight Quantization) is a tool designed for efficient and accurate low-bit weight quantization (INT3/4) for Large Language Models (LLMs). It supports instruction-tuned models and multi-modal LMs, providing features such as AWQ search for accurate quantization, pre-computed AWQ model zoo for various LLMs, memory-efficient 4-bit linear in PyTorch, and efficient CUDA kernel implementation for fast inference. The tool enables users to run large models on resource-constrained edge platforms, delivering more efficient responses with LLM/VLM chatbots through 4-bit inference.
duo-attention
DuoAttention is a framework designed to optimize long-context large language models (LLMs) by reducing memory and latency during inference without compromising their long-context abilities. It introduces a concept of Retrieval Heads and Streaming Heads to efficiently manage attention across tokens. By applying a full Key and Value (KV) cache to retrieval heads and a lightweight, constant-length KV cache to streaming heads, DuoAttention achieves significant reductions in memory usage and decoding time for LLMs. The framework uses an optimization-based algorithm with synthetic data to accurately identify retrieval heads, enabling efficient inference with minimal accuracy loss compared to full attention. DuoAttention also supports quantization techniques for further memory optimization, allowing for decoding of up to 3.3 million tokens on a single GPU.
Awesome-Resource-Efficient-LLM-Papers
A curated list of high-quality papers on resource-efficient Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on various aspects such as architecture design, pre-training, fine-tuning, inference, system design, and evaluation metrics. The repository covers topics like efficient transformer architectures, non-transformer architectures, memory efficiency, data efficiency, model compression, dynamic acceleration, deployment optimization, support infrastructure, and other related systems. It also provides detailed information on computation metrics, memory metrics, energy metrics, financial cost metrics, network communication metrics, and other metrics relevant to resource-efficient LLMs. The repository includes benchmarks for evaluating the efficiency of NLP models and references for further reading.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.