DeepTutor
"DeepTutor: AI-Powered Personalized Learning Assistant"
Stars: 10154
DeepTutor is an AI-powered personalized learning assistant that offers a suite of modules for massive document knowledge Q&A, interactive learning visualization, knowledge reinforcement with practice exercise generation, deep research, and idea generation. The tool supports multi-agent collaboration, dynamic topic queues, and structured outputs for various tasks. It provides a unified system entry for activity tracking, knowledge base management, and system status monitoring. DeepTutor is designed to streamline learning and research processes by leveraging AI technologies and interactive features.
README:

Quick Start · Core Modules · FAQ
🇨🇳 中文 · 🇯🇵 日本語 · 🇪🇸 Español · 🇫🇷 Français · 🇸🇦 العربية · 🇷🇺 Русский · 🇮🇳 हिन्दी · 🇵🇹 Português
📚 Massive Document Knowledge Q&A • 🎨 Interactive Learning Visualization
🎯 Knowledge Reinforcement • 🔍 Deep Research & Idea Generation
[2026.1.1] Happy New Year! Join our Discord Community, Wechat Community, or Discussions - shape the future of DeepTutor! 💬
[2025.12.30] Visit our Official Website for more details!
[2025.12.29] DeepTutor is now live! ✨
[2026.1.23] Release v0.6.0 - Frontend session persistence, full Chinese support, Docker deployment updates, and minor bug fixes -- Thanks for all the feedback!
History releases
[2026.1.18] Release v0.5.2 - Enhance RAG pipeline with Docling support and improve CI/CD workflows with several minor bugs fixed -- Thanks to all the feedbacks!
[2026.1.15] Release v0.5.0 - Unified LLM & Embedding services, RAG pipeline selection, and major enhancements to Home, History, QuestionGen & Settings modules -- Thanks to all the contributors!
[2026.1.9] Release v0.4.1 with LLM Provider system overhaul, Question Generation robustness improvements, and codebase cleanup - Thanks to all the contributors!
[2026.1.9] Release v0.4.0 with new code structure, multiple llm & embeddings support - Thanks to all the contributors!
[2026.1.5] v0.3.0 - Unified PromptManager architecture, CI/CD automation & pre-built Docker images on GHCR
[2026.1.2] v0.2.0 - Docker deployment, Next.js 16 & React 19 upgrade, WebSocket security & critical vulnerability fixes
• Smart Knowledge Base: Upload textbooks, research papers, technical manuals, and domain-specific documents. Build a comprehensive AI-powered knowledge repository for instant access.
• Multi-Agent Problem Solving: Dual-loop reasoning architecture with RAG, web search, and code execution -- delivering step-by-step solutions with precise citations.
• Knowledge Simplification & Explanations: Transform complex concepts, knowledge, and algorithms into easy-to-understand visual aids, detailed step-by-step breakdowns, and engaging interactive demonstrations.
• Personalized Q&A: Context-aware conversations that adapt to your learning progress, with interactive pages and session-based knowledge tracking.
• Intelligent Exercise Creation: Generate targeted quizzes, practice problems, and customized assessments tailored to your current knowledge level and specific learning objectives.
• Authentic Exam Simulation: Upload reference exams to generate practice questions that perfectly match the original style, format, and difficulty—giving you realistic preparation for the actual test.
• Comprehensive Research & Literature Review: Conduct in-depth topic exploration with systematic analysis. Identify patterns, connect related concepts across disciplines, and synthesize existing research findings.
• Novel Insight Discovery: Generate structured learning materials and uncover knowledge gaps. Identify promising new research directions through intelligent cross-domain knowledge synthesis.

Multi-agent Problem Solving with Exact Citations |

Step-by-step Visual Explanations with Personal QAs. |

Custom Questions |

Mimic Questions |

Personal Knowledge Base |

Personal Notebook |
🌙 Use DeepTutor in Dark Mode!
• Intuitive Interaction: Simple bidirectional query-response flow for intuitive interaction.
• Structured Output: Structured response generation that organizes complex information into actionable outputs.
• Problem Solving & Assessment: Step-by-step problem solving and custom assessment generation.
• Research & Learning: Deep Research for topic exploration and Guided Learning with visualization.
• Idea Generation: Automated and interactive concept development with multi-source insights.
• Information Retrieval: RAG hybrid retrieval, real-time web search, and academic paper databases.
• Processing & Analysis: Python code execution, query item lookup, and PDF parsing for document analysis.
• Knowledge Graph: Entity-relation mapping for semantic connections and knowledge discovery.
• Vector Store: Embedding-based semantic search for intelligent content retrieval.
• Memory System: Session state management and citation tracking for contextual continuity.
🌟 Star to follow our future updates!
- [ x ] Multi-linguistic support
- [ x ] DeepTutor Community
- [ x ] Video & Audio file support
- [ x ] Atomic RAG pipeline customize
- [ - ] Incremental Knowledge-base Edit
- [ - ] Personalized Workspace
- [ - ] DataBase Visualization
- [ - ] Online Demo
① Clone Repository
git clone https://github.com/HKUDS/DeepTutor.git
cd DeepTutor② Set Up Environment Variables
cp .env.example .env
# Edit .env file with your API keys📋 Environment Variables Reference
| Variable | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
LLM_MODEL |
Yes | Model name (e.g., gpt-4o) |
LLM_API_VERSION |
No | API version for Azure OpenAI (e.g., 2024-02-15-preview) |
LLM_API_KEY |
Yes | Your LLM API key |
LLM_HOST |
Yes | API endpoint URL |
EMBEDDING_MODEL |
Yes | Embedding model name |
EMBEDDING_API_VERSION |
No | API version for Azure OpenAI Embeddings |
EMBEDDING_API_KEY |
Yes | Embedding API key |
EMBEDDING_HOST |
Yes | Embedding API endpoint |
BACKEND_PORT |
No | Backend port (default: 8001) |
FRONTEND_PORT |
No | Frontend port (default: 3782) |
NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE |
No |
Frontend API URL - Set this for remote/LAN access (e.g., http://192.168.1.100:8001) |
TTS_* |
No | Text-to-Speech settings |
SEARCH_PROVIDER |
No | Search provider (options: perplexity, tavily, serper, jina, exa, baidu, default: perplexity) |
SEARCH_API_KEY |
No | Unified API key for all search providers |
💡 Remote Access: If accessing from another device (e.g.,
192.168.31.66:3782), add to.env:NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE=http://192.168.31.66:8001
③ Configure Ports & LLM (Optional)
-
Ports: Set in
.envfile →BACKEND_PORT/FRONTEND_PORT(defaults: 8001/3782) -
LLM: Edit
config/agents.yaml→temperature/max_tokensper module - See Configuration Docs for details
④ Try Demo Knowledge Bases (Optional)
📚 Available Demos
- Research Papers — 5 papers from our lab (AI-Researcher, LightRAG, etc.)
- Data Science Textbook — 8 chapters, 296 pages (Book Link)
- Download from Google Drive
- Extract into
data/directory
Demo KBs use
text-embedding-3-largewithdimensions = 3072
⑤ Create Your Own Knowledge Base (After Launch)
- Go to http://localhost:3782/knowledge
- Click "New Knowledge Base" → Enter name → Upload PDF/TXT/MD files
- Monitor progress in terminal
No Python/Node.js setup required
Prerequisites: Docker & Docker Compose
Quick Start — Build from source:
docker compose up # Build and start (~11 min first run on mac mini M4)
docker compose build --no-cache # Clear cache and rebuild after pull the newest repoOr use pre-built image (faster):
# Works on all platforms - Docker auto-detects your architecture
docker run -d --name deeptutor \
-p 8001:8001 -p 3782:3782 \
--env-file .env \
-v $(pwd)/data:/app/data \
-v $(pwd)/config:/app/config:ro \
ghcr.io/hkuds/deeptutor:latest
# Windows PowerShell: use ${PWD} instead of $(pwd)Common Commands:
docker compose up -d # Start
docker compose down # Stop
docker compose logs -f # View logs
docker compose up --build # Rebuild after changes📋 More Docker Options (Pre-built images, Cloud deployment, Custom ports)
Pre-built Image Tags:
| Tag | Architectures | Description |
|---|---|---|
:latest |
AMD64 + ARM64 | Latest stable release (auto-detects your architecture) |
:v0.5.x |
AMD64 + ARM64 | Specific version (auto-detects your architecture) |
:v0.5.x-amd64 |
AMD64 only | Explicit AMD64 image |
:v0.5.x-arm64 |
ARM64 only | Explicit ARM64 image |
💡 The
:latesttag is a multi-architecture image — Docker automatically pulls the correct version for your system (Intel/AMD or Apple Silicon/ARM)
Cloud Deployment — Must set external API URL:
docker run -d --name deeptutor \
-p 8001:8001 -p 3782:3782 \
-e NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_EXTERNAL=https://your-server.com:8001 \
--env-file .env \
-v $(pwd)/data:/app/data \
ghcr.io/hkuds/deeptutor:latestCustom Ports Example:
docker run -d --name deeptutor \
-p 9001:9001 -p 3000:3000 \
-e BACKEND_PORT=9001 \
-e FRONTEND_PORT=3000 \
-e NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_EXTERNAL=https://your-server.com:9001 \
--env-file .env \
-v $(pwd)/data:/app/data \
ghcr.io/hkuds/deeptutor:latestFor development or non-Docker environments
Prerequisites: Python 3.10+, Node.js 18+
1. Set Up Environment:
# Using conda (Recommended)
conda create -n deeptutor python=3.10 && conda activate deeptutor
# Or using venv
python -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activate # Windows: venv\Scripts\activate2. Install Dependencies:
# One-click installation (Recommended)
python scripts/install_all.py
# Or: bash scripts/install_all.sh
# Or manual installation
pip install -r requirements.txt
npm install --prefix web3. Launch:
python scripts/start_web.py # Start frontend + backend
# Or: python scripts/start.py # CLI only
# Stop: Ctrl+C🔧 Start Frontend & Backend Separately
Backend (FastAPI):
python src/api/run_server.py
# Or: uvicorn src.api.main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8001 --reloadFrontend (Next.js):
cd web && npm install && npm run dev -- -p 3782Note: Create web/.env.local:
NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE=http://localhost:8001| Service | Default Port |
|---|---|
| Backend | 8001 |
| Frontend | 3782 |
| Service | URL | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Frontend | http://localhost:3782 | Main web interface |
| API Docs | http://localhost:8001/docs | Interactive API documentation |
All user content and system data are stored in the data/ directory:
data/
├── knowledge_bases/ # Knowledge base storage
└── user/ # User activity data
├── solve/ # Problem solving results and artifacts
├── question/ # Generated questions
├── research/ # Research reports and cache
├── co-writer/ # Interactive IdeaGen documents and audio files
├── notebook/ # Notebook records and metadata
├── guide/ # Guided learning sessions
├── logs/ # System logs
└── run_code_workspace/ # Code execution workspace
Results are automatically saved during all activities. Directories are created automatically as needed.
🧠 Smart Solver
Intelligent problem-solving system based on Analysis Loop + Solve Loop dual-loop architecture, supporting multi-mode reasoning and dynamic knowledge retrieval.
Core Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Dual-Loop Architecture |
Analysis Loop: InvestigateAgent → NoteAgent Solve Loop: PlanAgent → ManagerAgent → SolveAgent → CheckAgent → Format |
| Multi-Agent Collaboration | Specialized agents: InvestigateAgent, NoteAgent, PlanAgent, ManagerAgent, SolveAgent, CheckAgent |
| Real-time Streaming | WebSocket transmission with live reasoning process display |
| Tool Integration | RAG (naive/hybrid), Web Search, Query Item, Code Execution |
| Persistent Memory | JSON-based memory files for context preservation |
| Citation Management | Structured citations with reference tracking |
Usage
- Visit http://localhost:{frontend_port}/solver
- Select a knowledge base
- Enter your question, click "Solve"
- Watch the real-time reasoning process and final answer
Python API
import asyncio
from src.agents.solve import MainSolver
async def main():
solver = MainSolver(kb_name="ai_textbook")
result = await solver.solve(
question="Calculate the linear convolution of x=[1,2,3] and h=[4,5]",
mode="auto"
)
print(result['formatted_solution'])
asyncio.run(main())Output Location
data/user/solve/solve_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS/
├── investigate_memory.json # Analysis Loop memory
├── solve_chain.json # Solve Loop steps & tool records
├── citation_memory.json # Citation management
├── final_answer.md # Final solution (Markdown)
├── performance_report.json # Performance monitoring
└── artifacts/ # Code execution outputs
📝 Question Generator
Dual-mode question generation system supporting custom knowledge-based generation and reference exam paper mimicking with automatic validation.
Core Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom Mode |
Background Knowledge → Question Planning → Generation → Single-Pass Validation Analyzes question relevance without rejection logic |
| Mimic Mode |
PDF Upload → MinerU Parsing → Question Extraction → Style Mimicking Generates questions based on reference exam structure |
| ReAct Engine | QuestionGenerationAgent with autonomous decision-making (think → act → observe) |
| Validation Analysis | Single-pass relevance analysis with kb_coverage and extension_points
|
| Question Types | Multiple choice, fill-in-the-blank, calculation, written response, etc. |
| Batch Generation | Parallel processing with progress tracking |
| Complete Persistence | All intermediate files saved (background knowledge, plan, individual results) |
| Timestamped Output | Mimic mode creates batch folders: mimic_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS_{pdf_name}/
|
Usage
Custom Mode:
- Visit http://localhost:{frontend_port}/question
- Fill in requirements (topic, difficulty, question type, count)
- Click "Generate Questions"
- View generated questions with validation reports
Mimic Mode:
- Visit http://localhost:{frontend_port}/question
- Switch to "Mimic Exam" tab
- Upload PDF or provide parsed exam directory
- Wait for parsing → extraction → generation
- View generated questions alongside original references
Python API
Custom Mode - Full Pipeline:
import asyncio
from src.agents.question import AgentCoordinator
async def main():
coordinator = AgentCoordinator(
kb_name="ai_textbook",
output_dir="data/user/question"
)
# Generate multiple questions from text requirement
result = await coordinator.generate_questions_custom(
requirement_text="Generate 3 medium-difficulty questions about deep learning basics",
difficulty="medium",
question_type="choice",
count=3
)
print(f"✅ Generated {result['completed']}/{result['requested']} questions")
for q in result['results']:
print(f"- Relevance: {q['validation']['relevance']}")
asyncio.run(main())Mimic Mode - PDF Upload:
from src.agents.question.tools.exam_mimic import mimic_exam_questions
result = await mimic_exam_questions(
pdf_path="exams/midterm.pdf",
kb_name="calculus",
output_dir="data/user/question/mimic_papers",
max_questions=5
)
print(f"✅ Generated {result['successful_generations']} questions")
print(f"Output: {result['output_file']}")Output Location
Custom Mode:
data/user/question/custom_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS/
├── background_knowledge.json # RAG retrieval results
├── question_plan.json # Question planning
├── question_1_result.json # Individual question results
├── question_2_result.json
└── ...
Mimic Mode:
data/user/question/mimic_papers/
└── mimic_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS_{pdf_name}/
├── {pdf_name}.pdf # Original PDF
├── auto/{pdf_name}.md # MinerU parsed markdown
├── {pdf_name}_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS_questions.json # Extracted questions
└── {pdf_name}_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS_generated_questions.json # Generated questions
🎓 Guided Learning
Personalized learning system based on notebook content, automatically generating progressive learning paths through interactive pages and smart Q&A.
Core Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Multi-Agent Architecture |
LocateAgent: Identifies 3-5 progressive knowledge points InteractiveAgent: Converts to visual HTML pages ChatAgent: Provides contextual Q&A SummaryAgent: Generates learning summaries |
| Smart Knowledge Location | Automatic analysis of notebook content |
| Interactive Pages | HTML page generation with bug fixing |
| Smart Q&A | Context-aware answers with explanations |
| Progress Tracking | Real-time status with session persistence |
| Cross-Notebook Support | Select records from multiple notebooks |
Usage Flow
- Select Notebook(s) — Choose one or multiple notebooks (cross-notebook selection supported)
- Generate Learning Plan — LocateAgent identifies 3-5 core knowledge points
- Start Learning — InteractiveAgent generates HTML visualization
- Learning Interaction — Ask questions, click "Next" to proceed
- Complete Learning — SummaryAgent generates learning summary
Output Location
data/user/guide/
└── session_{session_id}.json # Complete session state, knowledge points, chat history
✏️ Interactive IdeaGen (Co-Writer)
Intelligent Markdown editor supporting AI-assisted writing, auto-annotation, and TTS narration.
Core Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Rich Text Editing | Full Markdown syntax support with live preview |
| EditAgent |
Rewrite: Custom instructions with optional RAG/web context Shorten: Compress while preserving key information Expand: Add details and context |
| Auto-Annotation | Automatic key content identification and marking |
| NarratorAgent | Script generation, TTS audio, multiple voices (Cherry, Stella, Annie, Cally, Eva, Bella) |
| Context Enhancement | Optional RAG or web search for additional context |
| Multi-Format Export | Markdown, PDF, etc. |
Usage
- Visit http://localhost:{frontend_port}/co_writer
- Enter or paste text in the editor
- Use AI features: Rewrite, Shorten, Expand, Auto Mark, Narrate
- Export to Markdown or PDF
Output Location
data/user/co-writer/
├── audio/ # TTS audio files
│ └── {operation_id}.mp3
├── tool_calls/ # Tool call history
│ └── {operation_id}_{tool_type}.json
└── history.json # Edit history
🔬 Deep Research
DR-in-KG (Deep Research in Knowledge Graph) — A systematic deep research system based on Dynamic Topic Queue architecture, enabling multi-agent collaboration across three phases: Planning → Researching → Reporting.
Core Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Three-Phase Architecture |
Phase 1 (Planning): RephraseAgent (topic optimization) + DecomposeAgent (subtopic decomposition) Phase 2 (Researching): ManagerAgent (queue scheduling) + ResearchAgent (research decisions) + NoteAgent (info compression) Phase 3 (Reporting): Deduplication → Three-level outline generation → Report writing with citations |
| Dynamic Topic Queue | Core scheduling system with TopicBlock state management: PENDING → RESEARCHING → COMPLETED/FAILED. Supports dynamic topic discovery during research |
| Execution Modes |
Series Mode: Sequential topic processing Parallel Mode: Concurrent multi-topic processing with AsyncCitationManagerWrapper for thread-safe operations |
| Multi-Tool Integration | RAG (hybrid/naive), Query Item (entity lookup), Paper Search, Web Search, Code Execution — dynamically selected by ResearchAgent |
| Unified Citation System | Centralized CitationManager as single source of truth for citation ID generation, ref_number mapping, and deduplication |
| Preset Configurations |
quick: Fast research (1-2 subtopics, 1-2 iterations) medium/standard: Balanced depth (5 subtopics, 4 iterations) deep: Thorough research (8 subtopics, 7 iterations) auto: Agent autonomously decides depth |
Citation System Architecture
The citation system follows a centralized design with CitationManager as the single source of truth:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ CitationManager │
│ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ │
│ │ ID Generation │ │ ref_number Map │ │ Deduplication │ │
│ │ PLAN-XX │ │ citation_id → │ │ (papers only) │ │
│ │ CIT-X-XX │ │ ref_number │ │ │ │
│ └────────┬────────┘ └────────┬────────┘ └────────┬────────┘ │
└───────────┼────────────────────┼────────────────────┼───────────┘
│ │ │
┌──────┴──────┐ ┌──────┴──────┐ ┌──────┴──────┐
│DecomposeAgent│ │ReportingAgent│ │ References │
│ ResearchAgent│ │ (inline [N]) │ │ Section │
│ NoteAgent │ └─────────────┘ └────────────┘
└─────────────┘
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| ID Format | PLAN-XX (planning stage RAG queries) + CIT-X-XX (research stage, X=block number) |
| ref_number Mapping | Sequential 1-based numbers built from sorted citation IDs, with paper deduplication |
| Inline Citations | Simple [N] format in LLM output, post-processed to clickable [[N]](#ref-N) links |
| Citation Table | Clear reference table provided to LLM: Cite as [1] → (RAG) query preview...
|
| Post-processing | Automatic format conversion + validation to remove invalid citation references |
| Parallel Safety | Thread-safe async methods (get_next_citation_id_async, add_citation_async) for concurrent execution |
Parallel Execution Architecture
When execution_mode: "parallel" is enabled, multiple topic blocks are researched concurrently:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Parallel Research Execution │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ DynamicTopicQueue AsyncCitationManagerWrapper │
│ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Topic 1 (PENDING)│ ──┐ │ Thread-safe wrapper │ │
│ │ Topic 2 (PENDING)│ ──┼──→ asyncio │ for CitationManager │ │
│ │ Topic 3 (PENDING)│ ──┤ Semaphore │ │ │
│ │ Topic 4 (PENDING)│ ──┤ (max=5) │ • get_next_citation_ │ │
│ │ Topic 5 (PENDING)│ ──┘ │ id_async() │ │
│ └─────────────────┘ │ • add_citation_async() │ │
│ │ └───────────┬─────────────┘ │
│ ▼ │ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Concurrent ResearchAgent Tasks │ │
│ │ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ Task 1 │ │ Task 2 │ │ Task 3 │ │ Task 4 │ ... │ │
│ │ │(Topic 1)│ │(Topic 2)│ │(Topic 3)│ │(Topic 4)│ │ │
│ │ └────┬────┘ └────┬────┘ └────┬────┘ └────┬────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ └────────────┴────────────┴────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ ▼ │ │
│ │ AsyncManagerAgentWrapper │ │
│ │ (Thread-safe queue updates) │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
asyncio.Semaphore |
Limits concurrent tasks to max_parallel_topics (default: 5) |
AsyncCitationManagerWrapper |
Wraps CitationManager with asyncio.Lock() for thread-safe ID generation |
AsyncManagerAgentWrapper |
Ensures queue state updates are atomic across parallel tasks |
| Real-time Progress | Live display of all active research tasks with status indicators |
Agent Responsibilities
| Agent | Phase | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| RephraseAgent | Planning | Optimizes user input topic, supports multi-turn user interaction for refinement |
| DecomposeAgent | Planning | Decomposes topic into subtopics with RAG context, obtains citation IDs from CitationManager |
| ManagerAgent | Researching | Queue state management, task scheduling, dynamic topic addition |
| ResearchAgent | Researching | Knowledge sufficiency check, query planning, tool selection, requests citation IDs before each tool call |
| NoteAgent | Researching | Compresses raw tool outputs into summaries, creates ToolTraces with pre-assigned citation IDs |
| ReportingAgent | Reporting | Builds citation map, generates three-level outline, writes report sections with citation tables, post-processes citations |
Report Generation Pipeline
1. Build Citation Map → CitationManager.build_ref_number_map()
2. Generate Outline → Three-level headings (H1 → H2 → H3)
3. Write Sections → LLM uses [N] citations with provided citation table
4. Post-process → Convert [N] → [[N]](#ref-N), validate references
5. Generate References → Academic-style entries with collapsible source details
Usage
- Visit http://localhost:{frontend_port}/research
- Enter research topic
- Select research mode (quick/medium/deep/auto)
- Watch real-time progress with parallel/series execution
- View structured report with clickable inline citations
- Export as Markdown or PDF (with proper page splitting and Mermaid diagram support)
CLI
# Quick mode (fast research)
python src/agents/research/main.py --topic "Deep Learning Basics" --preset quick
# Medium mode (balanced)
python src/agents/research/main.py --topic "Transformer Architecture" --preset medium
# Deep mode (thorough research)
python src/agents/research/main.py --topic "Graph Neural Networks" --preset deep
# Auto mode (agent decides depth)
python src/agents/research/main.py --topic "Reinforcement Learning" --preset autoPython API
import asyncio
from src.agents.research import ResearchPipeline
from src.core.core import get_llm_config, load_config_with_main
async def main():
# Load configuration (main.yaml merged with any module-specific overrides)
config = load_config_with_main("research_config.yaml")
llm_config = get_llm_config()
# Create pipeline (agent parameters loaded from agents.yaml automatically)
pipeline = ResearchPipeline(
config=config,
api_key=llm_config["api_key"],
base_url=llm_config["base_url"],
kb_name="ai_textbook" # Optional: override knowledge base
)
# Run research
result = await pipeline.run(topic="Attention Mechanisms in Deep Learning")
print(f"Report saved to: {result['final_report_path']}")
asyncio.run(main())Output Location
data/user/research/
├── reports/ # Final research reports
│ ├── research_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS.md # Markdown report with clickable citations [[N]](#ref-N)
│ └── research_*_metadata.json # Research metadata and statistics
└── cache/ # Research process cache
└── research_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS/
├── queue.json # DynamicTopicQueue state (TopicBlocks + ToolTraces)
├── citations.json # Citation registry with ID counters and ref_number mapping
│ # - citations: {citation_id: citation_info}
│ # - counters: {plan_counter, block_counters}
├── step1_planning.json # Planning phase results (subtopics + PLAN-XX citations)
├── planning_progress.json # Planning progress events
├── researching_progress.json # Researching progress events
├── reporting_progress.json # Reporting progress events
├── outline.json # Three-level report outline structure
└── token_cost_summary.json # Token usage statistics
Citation File Structure (citations.json):
{
"research_id": "research_20241209_120000",
"citations": {
"PLAN-01": {"citation_id": "PLAN-01", "tool_type": "rag_hybrid", "query": "...", "summary": "..."},
"CIT-1-01": {"citation_id": "CIT-1-01", "tool_type": "paper_search", "papers": [...], ...}
},
"counters": {
"plan_counter": 2,
"block_counters": {"1": 3, "2": 2}
}
}Configuration Options
Key configuration in config/main.yaml (research section) and config/agents.yaml:
# config/agents.yaml - Agent LLM parameters
research:
temperature: 0.5
max_tokens: 12000
# config/main.yaml - Research settings
research:
# Execution Mode
researching:
execution_mode: "parallel" # "series" or "parallel"
max_parallel_topics: 5 # Max concurrent topics
max_iterations: 5 # Max iterations per topic
# Tool Switches
enable_rag_hybrid: true # Hybrid RAG retrieval
enable_rag_naive: true # Basic RAG retrieval
enable_paper_search: true # Academic paper search
enable_web_search: true # Web search (also controlled by tools.web_search.enabled)
enable_run_code: true # Code execution
# Queue Limits
queue:
max_length: 5 # Maximum topics in queue
# Reporting
reporting:
enable_inline_citations: true # Enable clickable [N] citations in report
# Presets: quick, medium, deep, auto
# Global tool switches in tools section
tools:
web_search:
enabled: true # Global web search switch (higher priority)💡 Automated IdeaGen
Research idea generation system that extracts knowledge points from notebook records and generates research ideas through multi-stage filtering.
Core Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| MaterialOrganizerAgent | Extracts knowledge points from notebook records |
| Multi-Stage Filtering | Loose Filter → Explore Ideas (5+ per point) → Strict Filter → Generate Markdown |
| Idea Exploration | Innovative thinking from multiple dimensions |
| Structured Output | Organized markdown with knowledge points and ideas |
| Progress Callbacks | Real-time updates for each stage |
Usage
- Visit http://localhost:{frontend_port}/ideagen
- Select a notebook with records
- Optionally provide user thoughts/preferences
- Click "Generate Ideas"
- View generated research ideas organized by knowledge points
Python API
import asyncio
from src.agents.ideagen import IdeaGenerationWorkflow, MaterialOrganizerAgent
from src.core.core import get_llm_config
async def main():
llm_config = get_llm_config()
# Step 1: Extract knowledge points from materials
organizer = MaterialOrganizerAgent(
api_key=llm_config["api_key"],
base_url=llm_config["base_url"]
)
knowledge_points = await organizer.extract_knowledge_points(
"Your learning materials or notebook content here"
)
# Step 2: Generate research ideas
workflow = IdeaGenerationWorkflow(
api_key=llm_config["api_key"],
base_url=llm_config["base_url"]
)
result = await workflow.process(knowledge_points)
print(result) # Markdown formatted research ideas
asyncio.run(main())📊 Dashboard + Knowledge Base Management
Unified system entry providing activity tracking, knowledge base management, and system status monitoring.
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Activity Statistics | Recent solving/generation/research records |
| Knowledge Base Overview | KB list, statistics, incremental updates |
| Notebook Statistics | Notebook counts, record distribution |
| Quick Actions | One-click access to all modules |
Usage
- Web Interface: Visit http://localhost:{frontend_port} to view system overview
- Create KB: Click "New Knowledge Base", upload PDF/Markdown documents
- View Activity: Check recent learning activities on Dashboard
📓 Notebook
Unified learning record management, connecting outputs from all modules to create a personalized learning knowledge base.
Core Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Multi-Notebook Management | Create, edit, delete notebooks |
| Unified Record Storage | Integrate solving/generation/research/Interactive IdeaGen records |
| Categorization Tags | Auto-categorize by type, knowledge base |
| Custom Appearance | Color, icon personalization |
Usage
- Visit http://localhost:{frontend_port}/notebook
- Create new notebook (set name, description, color, icon)
- After completing tasks in other modules, click "Add to Notebook"
- View and manage all records on the notebook page
| Configuration | Data Directory | API Backend | Core Utilities |
| Knowledge Base | Tools | Web Frontend | Solve Module |
| Question Module | Research Module | Interactive IdeaGen Module | Guide Module |
| Automated IdeaGen Module | |||
Backend fails to start?
Checklist
- Confirm Python version >= 3.10
- Confirm all dependencies installed:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Check if port 8001 is in use
- Check
.envfile configuration
Solutions
-
Change port: Set
BACKEND_PORT=9001in.envfile - Check logs: Review terminal error messages
Port occupied after Ctrl+C?
Problem
After pressing Ctrl+C during a running task (e.g., deep research), restarting shows "port already in use" error.
Cause
Ctrl+C sometimes only terminates the frontend process while the backend continues running in the background.
Solution
# macOS/Linux: Find and kill the process
lsof -i :8001
kill -9 <PID>
# Windows: Find and kill the process
netstat -ano | findstr :8001
taskkill /PID <PID> /FThen restart the service with python scripts/start_web.py.
npm: command not found error?
Problem
Running scripts/start_web.py shows npm: command not found or exit status 127.
Checklist
- Check if npm is installed:
npm --version - Check if Node.js is installed:
node --version - Confirm conda environment is activated (if using conda)
Solutions
# Option A: Using Conda (Recommended)
conda install -c conda-forge nodejs
# Option B: Using Official Installer
# Download from https://nodejs.org/
# Option C: Using nvm
nvm install 18
nvm use 18Verify Installation
node --version # Should show v18.x.x or higher
npm --version # Should show version numberLong path names on Windows installation?
Problem
On Windows, you may encounter errors related to long file paths during installation, such as "The filename or extension is too long" or similar path length issues.
Cause
Windows has a default limitation on path lengths (260 characters), which can be exceeded by DeepTutor's nested directory structures and dependencies.
Solution
Enable long path support system-wide by running the following command in an Administrator Command Prompt:
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem" /v LongPathsEnabled /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /fAfter running this command, restart your terminal for the changes to take effect.
Frontend cannot connect to backend?
Checklist
- Confirm backend is running (visit http://localhost:8001/docs)
- Check browser console for error messages
Solution
Create .env.local in web directory:
NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE=http://localhost:8001Docker: Frontend cannot connect in cloud deployment?
Problem
When deploying to a cloud server, the frontend shows connection errors like "Failed to fetch" or "NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE is not configured".
Cause
The default API URL is localhost:8001, which points to the user's local machine in the browser, not your server.
Solution
Set the NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_EXTERNAL environment variable to your server's public URL:
# Using docker run
docker run -d --name deeptutor \
-e NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_EXTERNAL=https://your-server.com:8001 \
... other options ...
ghcr.io/hkuds/deeptutor:latest
# Or in .env file
NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_EXTERNAL=https://your-server.com:8001Custom Port Example:
# If using backend port 9001
-e BACKEND_PORT=9001 \
-e NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_EXTERNAL=https://your-server.com:9001Docker: How to use custom ports?
Solution
Set both the port environment variables AND the port mappings:
docker run -d --name deeptutor \
-p 9001:9001 -p 4000:4000 \
-e BACKEND_PORT=9001 \
-e FRONTEND_PORT=4000 \
-e NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_EXTERNAL=http://localhost:9001 \
... other env vars ...
ghcr.io/hkuds/deeptutor:latestImportant: The -p port mapping must match the BACKEND_PORT/FRONTEND_PORT values.
WebSocket connection fails?
Checklist
- Confirm backend is running
- Check firewall settings
- Confirm WebSocket URL is correct
Solution
- Check backend logs
-
Confirm URL format:
ws://localhost:8001/api/v1/...
Settings page shows "Error loading data" with HTTPS reverse proxy?
Problem
When deploying behind an HTTPS reverse proxy (e.g., nginx), the Settings page shows "Error loading data" and browser DevTools reveals that HTTPS requests are being redirected to HTTP (307 redirect).
Cause
This issue has been fixed in v0.5.0+. If you're using an older version, the problem was caused by FastAPI's automatic trailing slash redirects generating HTTP URLs instead of preserving the original HTTPS protocol.
Solution (for v0.5.0+)
Update to the latest version. The fix disables automatic slash redirects to prevent protocol downgrade.
Recommended nginx Configuration
When using nginx as an HTTPS reverse proxy, use the following configuration:
# Frontend
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3782;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
# Backend API
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8001;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; # Important: preserves original protocol
}
# WebSocket support
location /api/v1/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8001;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}Environment Variable
Set in .env:
NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE=https://your-domain.com:portSee: GitHub Issue #112
Where are module outputs stored?
| Module | Output Path |
|---|---|
| Solve | data/user/solve/solve_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS/ |
| Question | data/user/question/question_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS/ |
| Research | data/user/research/reports/ |
| Interactive IdeaGen | data/user/co-writer/ |
| Notebook | data/user/notebook/ |
| Guide | data/user/guide/session_{session_id}.json |
| Logs | data/user/logs/ |
How to add a new knowledge base?
Web Interface
- Visit http://localhost:{frontend_port}/knowledge
- Click "New Knowledge Base"
- Enter knowledge base name
- Upload PDF/TXT/MD documents
- System will process documents in background
CLI
python -m src.knowledge.start_kb init <kb_name> --docs <pdf_path>How to incrementally add documents to existing KB?
CLI (Recommended)
python -m src.knowledge.add_documents <kb_name> --docs <new_document.pdf>Benefits
- Only processes new documents, saves time and API costs
- Automatically merges with existing knowledge graph
- Preserves all existing data
Numbered items extraction failed with uvloop.Loop error?
Problem
When initializing a knowledge base, you may encounter this error:
ValueError: Can't patch loop of type <class 'uvloop.Loop'>
This occurs because Uvicorn uses uvloop event loop by default, which is incompatible with nest_asyncio.
Solution
Use one of the following methods to extract numbered items:
# Option 1: Using the shell script (recommended)
./scripts/extract_numbered_items.sh <kb_name>
# Option 2: Direct Python command
python src/knowledge/extract_numbered_items.py --kb <kb_name> --base-dir ./data/knowledge_basesThis will extract numbered items (Definitions, Theorems, Equations, etc.) from your knowledge base without reinitializing it.
| ⚡ LightRAG | 🎨 RAG-Anything | 💻 DeepCode | 🔬 AI-Researcher |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple and Fast RAG | Multimodal RAG | AI Code Assistant | Research Automation |
⭐ Star us · 🐛 Report a bug · 💬 Discussions
This project is licensed under the AGPL-3.0 License.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for DeepTutor
Similar Open Source Tools

DeepTutor
DeepTutor is an AI-powered personalized learning assistant that offers a suite of modules for massive document knowledge Q&A, interactive learning visualization, knowledge reinforcement with practice exercise generation, deep research, and idea generation. The tool supports multi-agent collaboration, dynamic topic queues, and structured outputs for various tasks. It provides a unified system entry for activity tracking, knowledge base management, and system status monitoring. DeepTutor is designed to streamline learning and research processes by leveraging AI technologies and interactive features.
cascadeflow
cascadeflow is an intelligent AI model cascading library that dynamically selects the optimal model for each query or tool call through speculative execution. It helps reduce API costs by 40-85% through intelligent model cascading and speculative execution with automatic per-query cost tracking. The tool is based on the research that shows 40-70% of queries don't require slow, expensive flagship models, and domain-specific smaller models often outperform large general-purpose models on specialized tasks. cascadeflow automatically escalates to flagship models for advanced reasoning when needed. It supports multiple providers, low latency, cost control, and transparency, and can be used for edge and local-hosted AI deployment.
mcp-prompts
mcp-prompts is a Python library that provides a collection of prompts for generating creative writing ideas. It includes a variety of prompts such as story starters, character development, plot twists, and more. The library is designed to inspire writers and help them overcome writer's block by offering unique and engaging prompts to spark creativity. With mcp-prompts, users can access a wide range of writing prompts to kickstart their imagination and enhance their storytelling skills.
sandbox
AIO Sandbox is an all-in-one agent sandbox environment that combines Browser, Shell, File, MCP operations, and VSCode Server in a single Docker container. It provides a unified, secure execution environment for AI agents and developers, with features like unified file system, multiple interfaces, secure execution, zero configuration, and agent-ready MCP-compatible APIs. The tool allows users to run shell commands, perform file operations, automate browser tasks, and integrate with various development tools and services.
VT.ai
VT.ai is a multimodal AI platform that offers dynamic conversation routing with SemanticRouter, multi-modal interactions (text/image/audio), an assistant framework with code interpretation, real-time response streaming, cross-provider model switching, and local model support with Ollama integration. It supports various AI providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, Groq, Cohere, and OpenRouter, providing a wide range of core capabilities for AI orchestration.
multi-agent-shogun
multi-agent-shogun is a system that runs multiple AI coding CLI instances simultaneously, orchestrating them like a feudal Japanese army. It supports Claude Code, OpenAI Codex, GitHub Copilot, and Kimi Code. The system allows you to command your AI army with zero coordination cost, enabling parallel execution, non-blocking workflow, cross-session memory, event-driven communication, and full transparency. It also features skills discovery, phone notifications, pane border task display, shout mode, and multi-CLI support.
lihil
Lihil is a performant, productive, and professional web framework designed to make Python the mainstream programming language for web development. It is 100% test covered and strictly typed, offering fast performance, ergonomic API, and built-in solutions for common problems. Lihil is suitable for enterprise web development, delivering robust and scalable solutions with best practices in microservice architecture and related patterns. It features dependency injection, OpenAPI docs generation, error response generation, data validation, message system, testability, and strong support for AI features. Lihil is ASGI compatible and uses starlette as its ASGI toolkit, ensuring compatibility with starlette classes and middlewares. The framework follows semantic versioning and has a roadmap for future enhancements and features.

aichildedu
AICHILDEDU is a microservice-based AI education platform for children that integrates LLMs, image generation, and speech synthesis to provide personalized storybook creation, intelligent conversational learning, and multimedia content generation. It offers features like personalized story generation, educational quiz creation, multimedia integration, age-appropriate content, multi-language support, user management, parental controls, and asynchronous processing. The platform follows a microservice architecture with components like API Gateway, User Service, Content Service, Learning Service, and AI Services. Technologies used include Python, FastAPI, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Redis, LangChain, OpenAI GPT models, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Transformers, MinIO, Elasticsearch, Docker, Docker Compose, and JWT-based authentication.

hub
Hub is an open-source, high-performance LLM gateway written in Rust. It serves as a smart proxy for LLM applications, centralizing control and tracing of all LLM calls and traces. Built for efficiency, it provides a single API to connect to any LLM provider. The tool is designed to be fast, efficient, and completely open-source under the Apache 2.0 license.
mcp-memory-service
The MCP Memory Service is a universal memory service designed for AI assistants, providing semantic memory search and persistent storage. It works with various AI applications and offers fast local search using SQLite-vec and global distribution through Cloudflare. The service supports intelligent memory management, universal compatibility with AI tools, flexible storage options, and is production-ready with cross-platform support and secure connections. Users can store and recall memories, search by tags, check system health, and configure the service for Claude Desktop integration and environment variables.

Callytics
Callytics is an advanced call analytics solution that leverages speech recognition and large language models (LLMs) technologies to analyze phone conversations from customer service and call centers. By processing both the audio and text of each call, it provides insights such as sentiment analysis, topic detection, conflict detection, profanity word detection, and summary. These cutting-edge techniques help businesses optimize customer interactions, identify areas for improvement, and enhance overall service quality. When an audio file is placed in the .data/input directory, the entire pipeline automatically starts running, and the resulting data is inserted into the database. This is only a v1.1.0 version; many new features will be added, models will be fine-tuned or trained from scratch, and various optimization efforts will be applied.
gigachad-grc
A comprehensive, modular, containerized Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platform built with modern technologies. Manage your entire security program from compliance tracking to risk management, third-party assessments, and external audits. The platform includes specialized modules for Compliance, Data Management, Risk Management, Third-Party Risk Management, Trust, Audit, Tools, AI & Automation, and Administration. It offers features like controls management, frameworks assessment, policies lifecycle management, vendor risk management, security questionnaires, knowledge base, audit management, awareness training, phishing simulations, AI-powered risk scoring, and MCP server integration. The tech stack includes Node.js, TypeScript, React, PostgreSQL, Keycloak, Traefik, Redis, and RustFS for storage.
Archon
Archon is an AI meta-agent designed to autonomously build, refine, and optimize other AI agents. It serves as a practical tool for developers and an educational framework showcasing the evolution of agentic systems. Through iterative development, Archon demonstrates the power of planning, feedback loops, and domain-specific knowledge in creating robust AI agents.
mimiclaw
MimiClaw is a pocket AI assistant that runs on a $5 chip, specifically designed for the ESP32-S3 board. It operates without Linux or Node.js, using pure C language. Users can interact with MimiClaw through Telegram, enabling it to handle various tasks and learn from local memory. The tool is energy-efficient, running on USB power 24/7. With MimiClaw, users can have a personal AI assistant on a chip the size of a thumb, making it convenient and accessible for everyday use.
nono
nono is a secure, kernel-enforced capability shell for running AI agents and any POSIX style process. It leverages OS security primitives to create an environment where unauthorized operations are structurally impossible. It provides protections against destructive commands and securely stores API keys, tokens, and secrets. The tool is agent-agnostic, works with any AI agent or process, and blocks dangerous commands by default. It follows a capability-based security model with defense-in-depth, ensuring secure execution of commands and protecting sensitive data.
For similar tasks
llm-random
This repository contains code for research conducted by the LLM-Random research group at IDEAS NCBR in Warsaw, Poland. The group focuses on developing and using this repository to conduct research. For more information about the group and its research, refer to their blog, llm-random.github.io.
py-gpt
Py-GPT is a Python library that provides an easy-to-use interface for OpenAI's GPT-3 API. It allows users to interact with the powerful GPT-3 model for various natural language processing tasks. With Py-GPT, developers can quickly integrate GPT-3 capabilities into their applications, enabling them to generate text, answer questions, and more with just a few lines of code.
InternLM-XComposer
InternLM-XComposer2 is a groundbreaking vision-language large model (VLLM) based on InternLM2-7B excelling in free-form text-image composition and comprehension. It boasts several amazing capabilities and applications: * **Free-form Interleaved Text-Image Composition** : InternLM-XComposer2 can effortlessly generate coherent and contextual articles with interleaved images following diverse inputs like outlines, detailed text requirements and reference images, enabling highly customizable content creation. * **Accurate Vision-language Problem-solving** : InternLM-XComposer2 accurately handles diverse and challenging vision-language Q&A tasks based on free-form instructions, excelling in recognition, perception, detailed captioning, visual reasoning, and more. * **Awesome performance** : InternLM-XComposer2 based on InternLM2-7B not only significantly outperforms existing open-source multimodal models in 13 benchmarks but also **matches or even surpasses GPT-4V and Gemini Pro in 6 benchmarks** We release InternLM-XComposer2 series in three versions: * **InternLM-XComposer2-4KHD-7B** 🤗: The high-resolution multi-task trained VLLM model with InternLM-7B as the initialization of the LLM for _High-resolution understanding_ , _VL benchmarks_ and _AI assistant_. * **InternLM-XComposer2-VL-7B** 🤗 : The multi-task trained VLLM model with InternLM-7B as the initialization of the LLM for _VL benchmarks_ and _AI assistant_. **It ranks as the most powerful vision-language model based on 7B-parameter level LLMs, leading across 13 benchmarks.** * **InternLM-XComposer2-VL-1.8B** 🤗 : A lightweight version of InternLM-XComposer2-VL based on InternLM-1.8B. * **InternLM-XComposer2-7B** 🤗: The further instruction tuned VLLM for _Interleaved Text-Image Composition_ with free-form inputs. Please refer to Technical Report and 4KHD Technical Reportfor more details.

awesome-llm
Awesome LLM is a curated list of resources related to Large Language Models (LLMs), including models, projects, datasets, benchmarks, materials, papers, posts, GitHub repositories, HuggingFace repositories, and reading materials. It provides detailed information on various LLMs, their parameter sizes, announcement dates, and contributors. The repository covers a wide range of LLM-related topics and serves as a valuable resource for researchers, developers, and enthusiasts interested in the field of natural language processing and artificial intelligence.
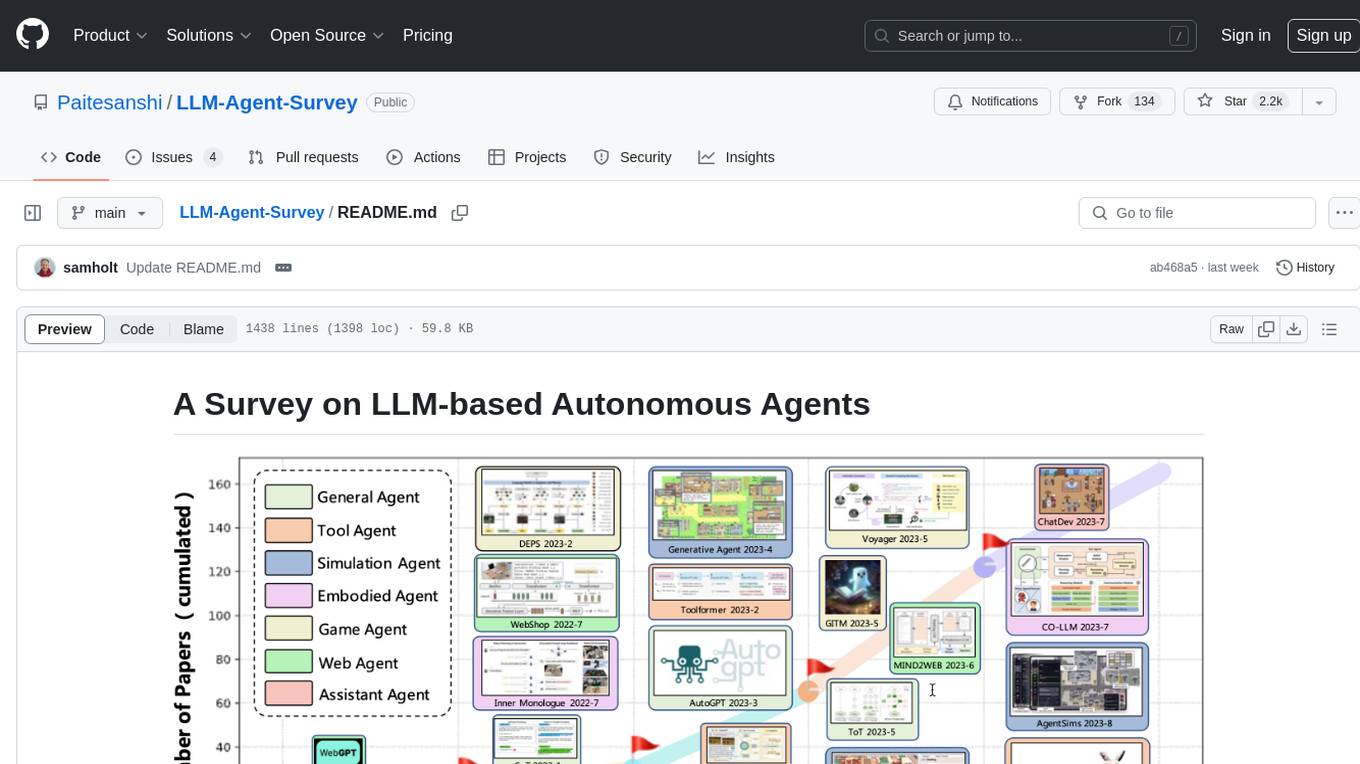
LLM-Agent-Survey
Autonomous agents are designed to achieve specific objectives through self-guided instructions. With the emergence and growth of large language models (LLMs), there is a growing trend in utilizing LLMs as fundamental controllers for these autonomous agents. This repository conducts a comprehensive survey study on the construction, application, and evaluation of LLM-based autonomous agents. It explores essential components of AI agents, application domains in natural sciences, social sciences, and engineering, and evaluation strategies. The survey aims to be a resource for researchers and practitioners in this rapidly evolving field.
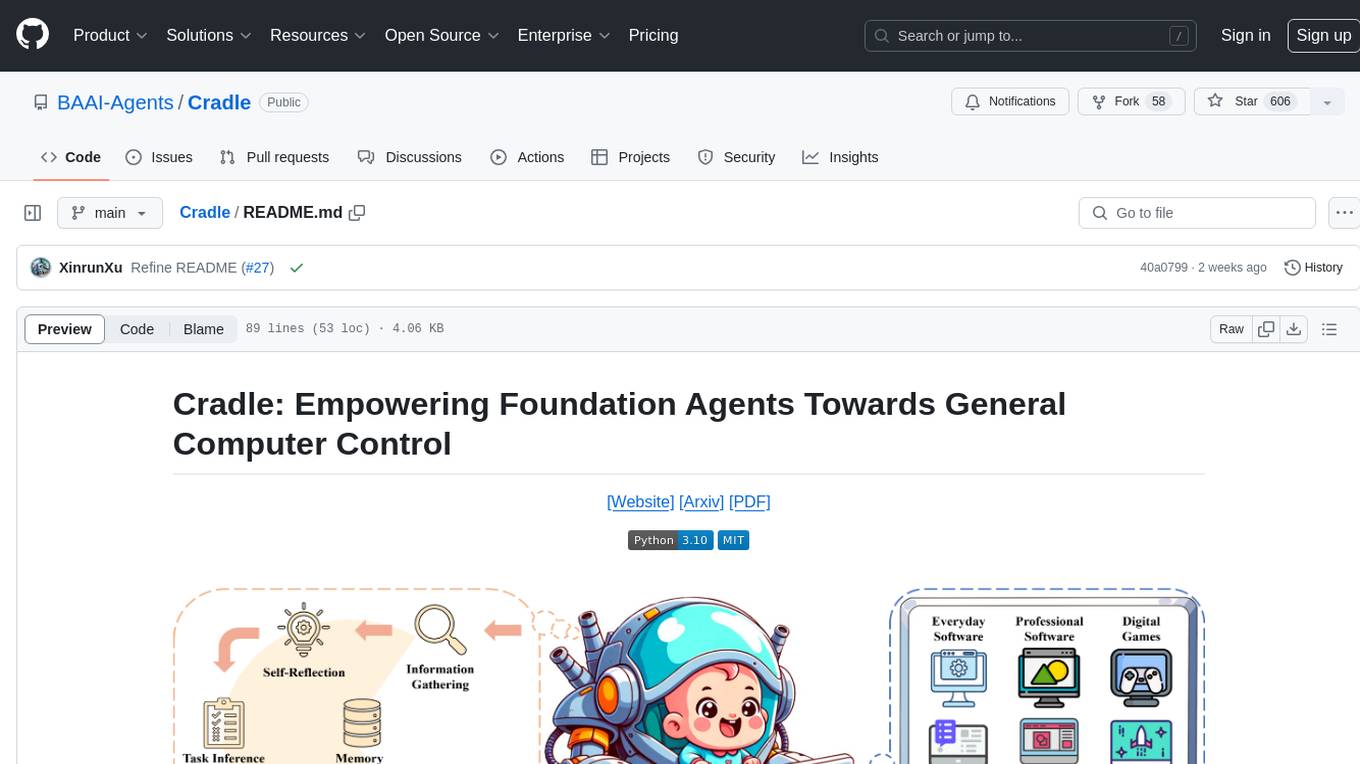
Cradle
The Cradle project is a framework designed for General Computer Control (GCC), empowering foundation agents to excel in various computer tasks through strong reasoning abilities, self-improvement, and skill curation. It provides a standardized environment with minimal requirements, constantly evolving to support more games and software. The repository includes released versions, publications, and relevant assets.
awesome-agents
Awesome Agents is a curated list of open source AI agents designed for various tasks such as private interactions with documents, chat implementations, autonomous research, human-behavior simulation, code generation, HR queries, domain-specific research, and more. The agents leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) and other generative AI technologies to provide solutions for complex tasks and projects. The repository includes a diverse range of agents for different use cases, from conversational chatbots to AI coding engines, and from autonomous HR assistants to vision task solvers.
neo
The neo is an open source robotics research platform powered by a OnePlus 3 smartphone and an STM32F205-based CAN interface board, housed in a 3d-printed casing with active cooling. It includes NEOS, a stripped down Android ROM, and offers a modern Linux environment for development. The platform leverages the high performance embedded processor and sensor capabilities of modern smartphones at a low cost. A detailed guide is available for easy construction, requiring online shopping and soldering skills. The total cost for building a neo is approximately $700.
For similar jobs
SLR-FC
This repository provides a comprehensive collection of AI tools and resources to enhance literature reviews. It includes a curated list of AI tools for various tasks, such as identifying research gaps, discovering relevant papers, visualizing paper content, and summarizing text. Additionally, the repository offers materials on generative AI, effective prompts, copywriting, image creation, and showcases of AI capabilities. By leveraging these tools and resources, researchers can streamline their literature review process, gain deeper insights from scholarly literature, and improve the quality of their research outputs.
paper-ai
Paper-ai is a tool that helps you write papers using artificial intelligence. It provides features such as AI writing assistance, reference searching, and editing and formatting tools. With Paper-ai, you can quickly and easily create high-quality papers.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and follows a process of embedding docs and queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, scoring and selecting relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. Users can customize prompts and use various models for embeddings and LLMs. The tool can be used asynchronously and supports adding documents from paths, files, or URLs.
ChatData
ChatData is a robust chat-with-documents application designed to extract information and provide answers by querying the MyScale free knowledge base or uploaded documents. It leverages the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) framework, millions of Wikipedia pages, and arXiv papers. Features include self-querying retriever, VectorSQL, session management, and building a personalized knowledge base. Users can effortlessly navigate vast data, explore academic papers, and research documents. ChatData empowers researchers, students, and knowledge enthusiasts to unlock the true potential of information retrieval.
noScribe
noScribe is an AI-based software designed for automated audio transcription, specifically tailored for transcribing interviews for qualitative social research or journalistic purposes. It is a free and open-source tool that runs locally on the user's computer, ensuring data privacy. The software can differentiate between speakers and supports transcription in 99 languages. It includes a user-friendly editor for reviewing and correcting transcripts. Developed by Kai Dröge, a PhD in sociology with a background in computer science, noScribe aims to streamline the transcription process and enhance the efficiency of qualitative analysis.
AIStudyAssistant
AI Study Assistant is an app designed to enhance learning experience and boost academic performance. It serves as a personal tutor, lecture summarizer, writer, and question generator powered by Google PaLM 2. Features include interacting with an AI chatbot, summarizing lectures, generating essays, and creating practice questions. The app is built using 100% Kotlin, Jetpack Compose, Clean Architecture, and MVVM design pattern, with technologies like Ktor, Room DB, Hilt, and Kotlin coroutines. AI Study Assistant aims to provide comprehensive AI-powered assistance for students in various academic tasks.
data-to-paper
Data-to-paper is an AI-driven framework designed to guide users through the process of conducting end-to-end scientific research, starting from raw data to the creation of comprehensive and human-verifiable research papers. The framework leverages a combination of LLM and rule-based agents to assist in tasks such as hypothesis generation, literature search, data analysis, result interpretation, and paper writing. It aims to accelerate research while maintaining key scientific values like transparency, traceability, and verifiability. The framework is field-agnostic, supports both open-goal and fixed-goal research, creates data-chained manuscripts, involves human-in-the-loop interaction, and allows for transparent replay of the research process.
k2
K2 (GeoLLaMA) is a large language model for geoscience, trained on geoscience literature and fine-tuned with knowledge-intensive instruction data. It outperforms baseline models on objective and subjective tasks. The repository provides K2 weights, core data of GeoSignal, GeoBench benchmark, and code for further pretraining and instruction tuning. The model is available on Hugging Face for use. The project aims to create larger and more powerful geoscience language models in the future.