noScribe
Cutting edge AI technology for automated audio transcription. A nice GUI for OpenAIs Whisper and pyannote (speaker identification)
Stars: 1364
noScribe is an AI-based software designed for automated audio transcription, specifically tailored for transcribing interviews for qualitative social research or journalistic purposes. It is a free and open-source tool that runs locally on the user's computer, ensuring data privacy. The software can differentiate between speakers and supports transcription in 99 languages. It includes a user-friendly editor for reviewing and correcting transcripts. Developed by Kai Dröge, a PhD in sociology with a background in computer science, noScribe aims to streamline the transcription process and enhance the efficiency of qualitative analysis.
README:
- An AI-based software that transcribes interviews for qualitative social research or journalistic use
- noScribe is free and open source (GPL-3.0)
- It runs completely local on your computer. No data is sent to the internet. No cloud, no worries
- It can distinguish different speakers and understands around 60 languages (more or less, see below)
- It includes a nice editor to review, verify and correct the resulting transcript
- It is standing on the shoulders of giants: Whisper from OpenAI, faster-whisper by Guillaume Klein and pyannote from Hervé Bredin
 (The transcript is from this interview which I did in May 2022 with the Russian sociologist Natalia Savelyeva.)
(The transcript is from this interview which I did in May 2022 with the Russian sociologist Natalia Savelyeva.)
- noScribe needs a fairly up-to-date computer, or the transcription will take very long. (Consider letting it run over night on a slower machine.)
- Since it uses sophisticated AI models, the download is quite large – about 3.7 GB
- Poor audio quality will lead to poor transcription results.
- No automatic transcription is perfect, there will always be some manual revision necessary. Use the included Editor to check your transcripts thouroughly. (See also "Factors Influencing the Quality" and "Known Issues" below.)
- If you want to know more an can understand German, Rebecca Schmidt from the University of Paderborn wrote a nice review of noScribe, also discussing its limitations. Also the German computer magazine c't recommended noScribe in a recent review.
The urban dictionary defines scribe as "a person whose entire miserable existence has been reduced to academic grunge and pain". I hope this software will make your academic life a little less painful and grungy, hence the name noScribe :)
Kai Dröge, PhD in sociology (with a background in computer science), qualitative researcher and teacher, Lucerne University for Applied Science (Switzerland) and Institute for Social Research, Frankfurt/M. (Germany).
Current Version Number: 0.6.2 (see changelog)
All releases are hosted on SWITCHdrive, a secure data sharing platform for Swiss universities.
- The general purpose version for normal PCs without a NVIDIA graphics card: https://drive.switch.ch/index.php/s/HtKDKYRZRNaYBeI?path=%2FWindows%2Fnormal2
- A special version using CUDA acceleration on NVIDIA graphics cards with at least 6 GB of VRAM: https://drive.switch.ch/index.php/s/HtKDKYRZRNaYBeI?path=%2FWindows%2Fcuda1. You must also install the CUDA toolkit from here (a reboot is required afterwards).
-
Installation:
- Start the downloaded setup file. This may take a while, be patient.
- If you get a warning that "Windows protected your PC" and the app comes from an "Unknown publisher", you have to trust us and click "Run anyway"
- To do a silent install on a larger group of computers, start the setup with the argument
/S.
ported by gernophil
-
Newer Macs with Apple Silicon M1-M4 processors
- Download: https://drive.switch.ch/index.php/s/HtKDKYRZRNaYBeI?path=%2FmacOS%2Farm64%20(Apple%20Silicon)
- Double-click on the downloaded dmg-file, then drag noScribe and noScribeEdit into the link to your applications folder (labeled "drag both here to install").
- You will need Apple's Rosetta2 Intel emulator since one component (ffmpeg) is still made the Intel CPUs. If you don't have it installed already, do this as follows:
- Open the Terminal (located at
/Applications/Utilities/Terminal.app). - Type
softwareupdate --install-rosettaorsoftwareupdate --install-rosetta --agree-to-license. - Hit enter and follow the instructions on the screen.
- Open the Terminal (located at
- Start noScribe and/or noScribeEdit by double-clicking the app within your applications.
-
Older Macs with Intel processors
Note: Version 0.6.2 on Intel based Macs is currently experimental and may not fully work. Please help us testing it. You can download it here.
Otherwise, you can use the stable version version 0.5:
- for macOS Sonoma (14) and Sequoia (15): https://drive.switch.ch/index.php/s/EIVup04qkSHb54j?path=%2FnoScribe%20vers.%200.5%2FmacOS%2Fx86_64%20(Intel)
- for macOS 11 (Big Sur), 12 (Monterey) and 13 (Ventura): https://drive.switch.ch/index.php/s/EIVup04qkSHb54j?path=%2FnoScribe%20vers.%200.5%2FmacOS%2Fx86_64_legacy%20(old%20Intel)
- Note: Unfortunately, we are currently not able to sign the x86_64 package correctly, so you will get a warning that noScribe and noScribeEdit are from unregistered developers. You have to manually allow noScribe and noScribeEdit to be executed, if your Gatekeeper is active. Follow these steps:
- Double-click the downloaded dmg-file.
- Drag noScribe and noScribeEdit into the link to your applications folder (labeled "drag both here to install").
- Start noScribe by double-clicking the app within your applications folder. You will get an error that noScribe is from an unregistered developer. Do the same with the noScribe Editor.
- Go to Settings -> Privacy and Security -> Scroll down until you see a message stating noScribe was prevented from starting and click "open anyway". Again, do the same with the noScribe Editor.
- From now on, both programs should start without issues.
ported by Eckhard Kadasch and Florian Dobener; executable generated by gernophil.
-
Executable installation:
- Download the CUDA or CPU version of noScribe 0.6.2 for Linux here: https://drive.switch.ch/index.php/s/HtKDKYRZRNaYBeI?path=%2FLinux
- Untar the file using the terminal command
tar -xzvf noScribe_0.6.2_cpu_linux_amd64.tar.gzortar -xzvf noScribe_0.6.2_cuda_linux_amd64.tar.gz. - Execute noScribe using the terminal by
cding into the noScribe folder and executing./noScribe. - Optionally: Edit the files
noScribe.desktopandnoScribeEdit.desktopwith a text editor and enter the complete path in the lines starting withExce=andIcon=.
-
Manual installation from source: Based on instructions by mael-lenoc
# release ( must be > 0.6 in order to include the latest fixes for linux!) NOS_REL=0.6.1 wget https://github.com/kaixxx/noScribe/archive/refs/tags/v${NOS_REL).tar.gz tar xvz -f v${NOS_REL).tar.gz cd noScribe-${NOS_REL)/ # from here on all happens in this directory # alternative: current main branch wget -O noScribe-main.zip https://github.com/kaixxx/noScribe/archive/refs/heads/main.zip unzip noScribe-main.zip cd noScribe-main # from here on all happens in this directory # install noScribeEdit rm -rf noScribeEdit/ git clone https://github.com/kaixxx/noScribeEditor.git noScribeEdit # venv python3 -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate # from here on all happens in the venv # requirements pip install -r environments/requirements_linux.txt pip install -r noScribeEdit/environments/requirements.txt # models/precise # this assumes you have git large file support enabled: apt install git-lfs rm -rf models/precise git clone https://huggingface.co/mobiuslabsgmbh/faster-whisper-large-v3-turbo models/precise for f in config.json model.bin preprocessor_config.json tokenizer.json vocabulary.json; do wget -O models/fast/$f "https://huggingface.co/mukowaty/faster-whisper-int8/resolve/main/faster-whisper-large-v3-turbo-int8/${f}?download=true"; done # run python3 ./noScribe.py
Dröge, K. (2024). noScribe. AI-powered Audio Transcription (Version XXX) [Computer software]. https://github.com/kaixxx/noScribe
- Select your audio file. NoScribe supports almost any audio or video format.
- Select the filename for the transcript. You can also choose the file type: *.html is the default, supported also by the noScribe editor. *.vtt is a video subtitles format and is especially useful if you want to import your transcript into EXMARaLDA for further annotation. *.txt exports the transcript as plain text.
- Start and Stop accept timestamps in the format hh:mm:ss. Use this to limit the transcription to a particular part of the recording. This is especially helpful for testing your settings with a small sample before committing to transcribing the whole interview, which may take several hours. Leave Stop empty if you want to transcribe until the end of the audio file.
- Language: Select the language of your transcript, set it to 'auto' to detect the language, or choose "multilingual" if your audio contains more than one language (experimental).
- Quality: 'Precise' is the recommended setting for the most accurate transcript. On slower machines, you may opt for the 'fast' option. This will be quicker but might necessitate more manual revision later. You can also install custom models, fine-tuned for specific languages, etc.
- Mark Pause: If enabled, parts of your audio without voice activity will be marked as pauses. Pauses are transcribed as round brackets with one dot per second inside, e.g., '(..)' for a two-second pause. Pauses longer than 10 seconds are written out as '(XX seconds pause)' or '(XX minutes pause)'. You have the option to mark either pauses of one second and more ('1sec+'), two seconds and more ('2sec+'), or only the longer ones of three seconds and more ('3sec+'). Choose 'none' to disable this feature entirely.
- Speaker Detection: This feature uses the Pyannote AI model to identify distinct speakers in your audio and organizes the transcript accordingly. Choose the number of speakers if known, or select 'auto.' Opting for 'none' bypasses this step altogether, reducing the processing time by approximately half. However, the resultant transcript will be a continuous block of text without any indicators of speaker transitions.
- Overlapping Speech: If enabled, noScribe attempts to mark instances where two people speak simultaneously. The overlapping section is demarcated with //double slashes//. (Note: This is an experimental feature.)
- Disfluencies: If enabled, common speech disfluencies like filler words ("um"), unfinished words or sentences, etc. will also be transcribed.
- Timestamps: When enabled, noScribe incorporates timestamps in the format [hh:mm:ss] into the transcript either at every change of speaker or every 60 seconds. I find these timestamps somewhat distracting, hence my decision to disable them by default. However, they can be quite useful in certain contexts. Even with timestamps disabled, determining the audio timecode for a specific segment is straightforward: simply open the transcript in the noScribe Editor, navigate through the text, and the corresponding timecode will appear in the bottom right corner of the app.
- If you are ready, click the Start-button in the bottom left. Cancel will abort the process.
- Be aware that a one-hour interview can take up to three hours processing time and will put a heavy load on your machine. Doing this on battery-power is not recommended.
- A progress indicator at the bottom of the app will show how far you are into the whole process.
- The main window will log progress-messages and errors. It will also show the text of your interview during the last step of the transcription.
- The transcript will be auto saved every few seconds under the given filename.
- By default, noScribe produces an HTML-file. This can be opened in every common word editor (including MS Word, LibreOffice) or QDA-package (MAXQDA, ATLAS.ti, QualCoder...).
- Before working with the transcript though, you should check it with the included editor. There will always be some errors.
The included editor to check the final transcript.
The noScribe Editor is a separate app. It will open automatically once the transcript is finished, but can also be run independent from noScribe. It contains some handy features to check your finished transcript for errors and correct them:
- Press Ctrl + Spacebar (^Space on Mac) or the orange button in the toolbar to hear the audio which corresponds to your current position in the text.
- The selection of the text will follow the audio that you hear. If you want to make changes, click anywhere in the text with your mouse or use the arrow keys to move the cursor. The audio will stop, and you can edit the text.
- You can also stop the audio by pressing Ctrl + Spacebar again or clicking the orange button.
- If you want to speed up or slow down the audio, change the "100%"-field next to the "Play/Pause Audio"-Button to the appropriate speed.
- To change the speaker names, use the Search & Replace feature, accessible from the magnifying glass icon or the Edit menu.
- Use the plus und minus icons in the toolbar to zoom in or out
- You will find the most common features of a basic text editor in the toolbar as well as in the menu at the top (basic text formatting, cut, copy & paste, undo & redo).
- Your typical hotkeys will also work (e.g., Ctrl+S for Save, Ctrl+F for Find & Replace). You can see all the hotkeys if you open the menu. As already mentioned, 'Ctrl+Space' is the hotkey you'll use the most as it starts or pauses the audio.
The source code of the editor can be found here: https://github.com/kaixxx/noScribeEditor
- A good audio recording with clear voices and no ambient noise is crucial for a high-quality transcription. Investing some effort in the quality of the recording will save you much time in the manual revision process later.
- Whisper (the AI powering noScribe) understands around 60 different languages, but the quality of the transcription varies widely between them. Spanish, Italian, English, Portuguese and German are best supported (see here for more info).
- Whisper handles dialects fairly well (e.g., Swiss-German), but the transcript might need more manual work in the revision.
- The whisper AI can sometimes get stuck in a loop of repeating text, especially on longer audio files. If this happens, try to transcribe shorter sections (using the "Start" and "Stop" fields in noScribe), and join them manually.
- Multilingual audiois now supported, but experimental.
- Nonverbal expressions like laughter are not included in the transcript and must be added later in the editor if you need them.
- Speaker identification: In some recordings, the AI used by noScribe may not be able to tell the voices of certain speakers apart, even if they sound quite different to the human ear. Check the results carefully.
- The whisper AI can sometimes hallucinate, especially in silent parts of the recording when it interprets background noise as 'text' (see this study from the Cornell University for more info about the issue).
- After the app has run for the first time, you will find a file named config.yml in the user config directory (on windows: C:\Users<username>\AppData\Local\noScribe\noScribe\config.yml; on Mac: "~/Library/Application Support/noscribe/config.yml"). Here, you can change a few extra settings, e.g., the language of the user interface.
- Also in the user config directory you will find a folder named log with detailed log-files for every transcript (also unfinished ones). This can be helpful in the case of any errors. Be aware though that these files also contain the text of your transcripts which might include sensitive information.
- If you want to use custom whisper models with noScribe, follow the instructions in the Wiki.
- I developed noScribe in python 3.12
- I cannot host the whisper-models on GitHub because they are too large. There is a readme in the models-folder with instructions on how to get them.
- I am happy to review tests, bug reports and pull requests (if my time allows it)
- The noScribe UI has already been translated into many languages (thanks mlynar-czyk).
- Since most of the translations have been created with ChatGPT, there will be problems. Please report any errors that you’ll find and make – if possible – a pull request with a better translation.
- You will find the language files in the folder "trans".
- If you change anything in the language files, make sure to follow the conventions of the YAML language.
- If you want to change the language of the user interface, you have to change the value of the "locale" setting in the advanced settings (see above).
If you are interested in open source software for the analysis of qualitative data, take a look at QualCoder and Taguette.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for noScribe
Similar Open Source Tools

noScribe
noScribe is an AI-based software designed for automated audio transcription, specifically tailored for transcribing interviews for qualitative social research or journalistic purposes. It is a free and open-source tool that runs locally on the user's computer, ensuring data privacy. The software can differentiate between speakers and supports transcription in 99 languages. It includes a user-friendly editor for reviewing and correcting transcripts. Developed by Kai Dröge, a PhD in sociology with a background in computer science, noScribe aims to streamline the transcription process and enhance the efficiency of qualitative analysis.
WDoc
WDoc is a powerful Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system designed to summarize, search, and query documents across various file types. It supports querying tens of thousands of documents simultaneously, offers tailored summaries to efficiently manage large amounts of information, and includes features like supporting multiple file types, various LLMs, local and private LLMs, advanced RAG capabilities, advanced summaries, trust verification, markdown formatted answers, sophisticated embeddings, extensive documentation, scriptability, type checking, lazy imports, caching, fast processing, shell autocompletion, notification callbacks, and more. WDoc is ideal for researchers, students, and professionals dealing with extensive information sources.
roam-extension-live-ai-assistant
Live AI is an AI Assistant tailor-made for Roam, providing access to the latest LLMs directly in Roam blocks. Users can interact with AI to extend their thinking, explore their graph, and chat with structured responses. The tool leverages Roam's features to write prompts, query graph parts, and chat with content. Users can dictate, translate, transform, and enrich content easily. Live AI supports various tasks like audio and video analysis, PDF reading, image generation, and web search. The tool offers features like Chat panel, Live AI context menu, and Ask Your Graph agent for versatile usage. Users can control privacy levels, compare AI models, create custom prompts, and apply styles for response formatting. Security concerns are addressed by allowing users to control data sent to LLMs.
MARS5-TTS
MARS5 is a novel English speech model (TTS) developed by CAMB.AI, featuring a two-stage AR-NAR pipeline with a unique NAR component. The model can generate speech for various scenarios like sports commentary and anime with just 5 seconds of audio and a text snippet. It allows steering prosody using punctuation and capitalization in the transcript. Speaker identity is specified using an audio reference file, enabling 'deep clone' for improved quality. The model can be used via torch.hub or HuggingFace, supporting both shallow and deep cloning for inference. Checkpoints are provided for AR and NAR models, with hardware requirements of 750M+450M params on GPU. Contributions to improve model stability, performance, and reference audio selection are welcome.
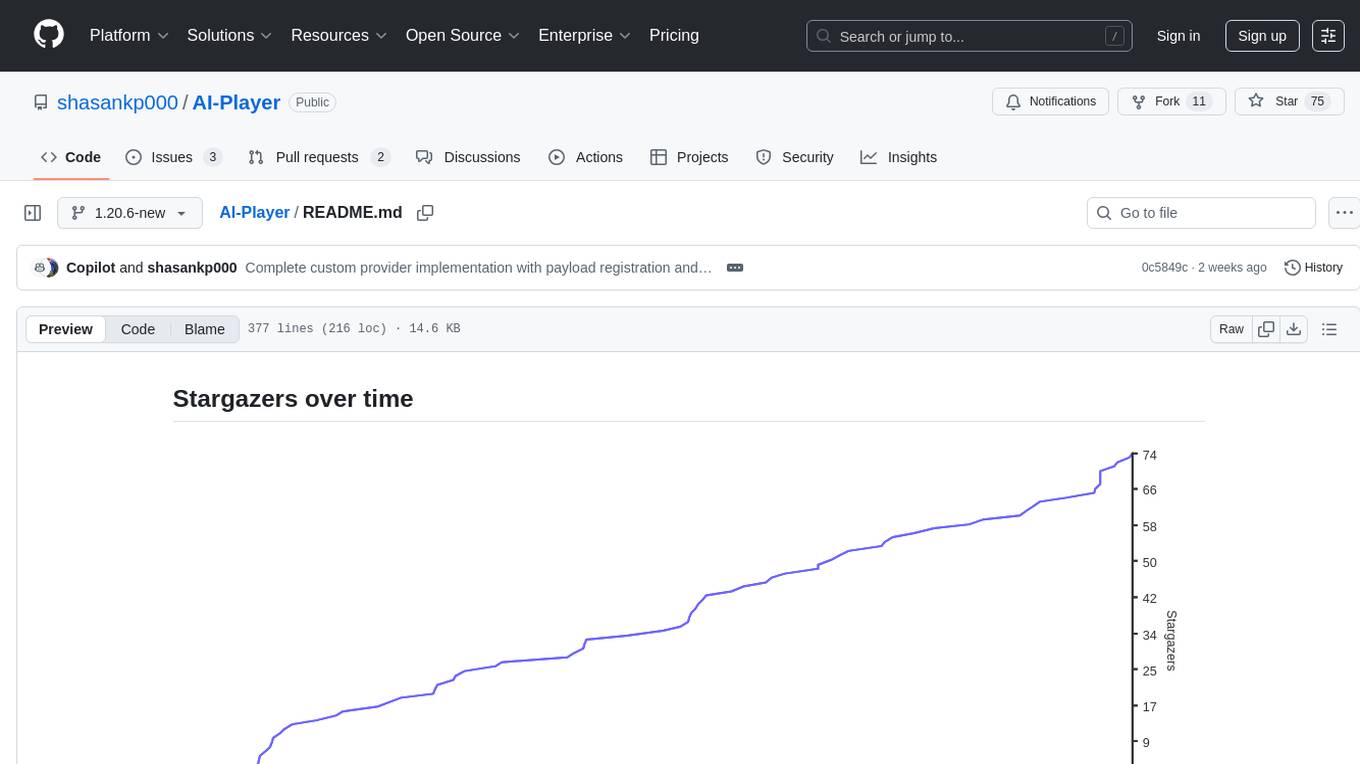
AI-Player
AI-Player is a Minecraft mod that adds an 'intelligent' second player to the game to combat loneliness while playing solo. It aims to enhance gameplay by providing companionship and interactive features. The mod leverages advanced AI algorithms and integrates with external tools to enhance the player experience. Developed with a focus on addressing the social aspect of gaming, AI-Player is a community-driven project that continues to evolve with user feedback and contributions.
local_multimodal_ai_chat
Local Multimodal AI Chat is a hands-on project that teaches you how to build a multimodal chat application. It integrates different AI models to handle audio, images, and PDFs in a single chat interface. This project is perfect for anyone interested in AI and software development who wants to gain practical experience with these technologies.
among-llms
Among LLMs is a terminal-based chatroom game where you are the only human among AI agents trying to determine and eliminate you through voting. Your goal is to stay hidden, manipulate conversations, and turn the bots against each other using various tactics like editing messages, sending whispers, and gaslighting. The game offers dynamic scenarios, personas, and backstories, customizable agent count, private messaging, voting mechanism, and infinite replayability. It is written in Python and provides an immersive and unpredictable experience for players.

HydraDragonAntivirus
Hydra Dragon Antivirus is a comprehensive tool that combines dynamic and static analysis using Sandboxie for Windows with ClamAV, YARA-X, machine learning AI, behavior analysis, NLP-based detection, website signatures, Ghidra, and Snort. The tool provides a Machine Learning Malware and Benign Database for training, along with a guide for compiling from source. It offers features like Ghidra source code analysis, Java Development Kit setup, and detailed logs for malware detections. Users can join the Discord community server for support and follow specific guidelines for preparing the analysis environment. The tool emphasizes security measures such as cleaning up directories, avoiding sharing IP addresses, and ensuring ClamAV database installation. It also includes tips for effective analysis and troubleshooting common issues.
wingman-ai
Wingman AI allows you to use your voice to talk to various AI providers and LLMs, process your conversations, and ultimately trigger actions such as pressing buttons or reading answers. Our _Wingmen_ are like characters and your interface to this world, and you can easily control their behavior and characteristics, even if you're not a developer. AI is complex and it scares people. It's also **not just ChatGPT**. We want to make it as easy as possible for you to get started. That's what _Wingman AI_ is all about. It's a **framework** that allows you to build your own Wingmen and use them in your games and programs. The idea is simple, but the possibilities are endless. For example, you could: * **Role play** with an AI while playing for more immersion. Have air traffic control (ATC) in _Star Citizen_ or _Flight Simulator_. Talk to Shadowheart in Baldur's Gate 3 and have her respond in her own (cloned) voice. * Get live data such as trade information, build guides, or wiki content and have it read to you in-game by a _character_ and voice you control. * Execute keystrokes in games/applications and create complex macros. Trigger them in natural conversations with **no need for exact phrases.** The AI understands the context of your dialog and is quite _smart_ in recognizing your intent. Say _"It's raining! I can't see a thing!"_ and have it trigger a command you simply named _WipeVisors_. * Automate tasks on your computer * improve accessibility * ... and much more
talk-to-chatgpt
Talk-To-ChatGPT is a Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge extension that enables users to interact with the ChatGPT AI using voice commands for speech recognition and text-to-speech responses. The tool enhances the conversational experience by allowing users to speak to the AI and receive spoken responses, making interactions more natural and engaging. It also supports ElevenLabs API integration for creating custom voices for text-to-speech. The extension provides settings for voice, language, and more, and can be installed from the Chrome and Edge web stores or manually. While the project has been discontinued due to upcoming desktop apps from OpenAI, it has been used to assist individuals with disabilities and the elderly in interacting with ChatGPT.
feedgen
FeedGen is an open-source tool that uses Google Cloud's state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve product titles, generate more comprehensive descriptions, and fill missing attributes in product feeds. It helps merchants and advertisers surface and fix quality issues in their feeds using Generative AI in a simple and configurable way. The tool relies on GCP's Vertex AI API to provide both zero-shot and few-shot inference capabilities on GCP's foundational LLMs. With few-shot prompting, users can customize the model's responses towards their own data, achieving higher quality and more consistent output. FeedGen is an Apps Script based application that runs as an HTML sidebar in Google Sheets, allowing users to optimize their feeds with ease.
OSHW-SenseCAP-Watcher
SenseCAP Watcher is a monitoring device built on ESP32S3 with Himax WiseEye2 HX6538 AI chip, excelling in image and vector data processing. It features a camera, microphone, and speaker for visual, auditory, and interactive capabilities. With LLM-enabled SenseCraft suite, it understands commands, perceives surroundings, and triggers actions. The repository provides firmware, hardware documentation, and applications for the Watcher, along with detailed guides for setup, task assignment, and firmware flashing.
EdgeChains
EdgeChains is an open-source chain-of-thought engineering framework tailored for Large Language Models (LLMs)- like OpenAI GPT, LLama2, Falcon, etc. - With a focus on enterprise-grade deployability and scalability. EdgeChains is specifically designed to **orchestrate** such applications. At EdgeChains, we take a unique approach to Generative AI - we think Generative AI is a deployment and configuration management challenge rather than a UI and library design pattern challenge. We build on top of a tech that has solved this problem in a different domain - Kubernetes Config Management - and bring that to Generative AI. Edgechains is built on top of jsonnet, originally built by Google based on their experience managing a vast amount of configuration code in the Borg infrastructure.
M.I.L.E.S
M.I.L.E.S. (Machine Intelligent Language Enabled System) is a voice assistant powered by GPT-4 Turbo, offering a range of capabilities beyond existing assistants. With its advanced language understanding, M.I.L.E.S. provides accurate and efficient responses to user queries. It seamlessly integrates with smart home devices, Spotify, and offers real-time weather information. Additionally, M.I.L.E.S. possesses persistent memory, a built-in calculator, and multi-tasking abilities. Its realistic voice, accurate wake word detection, and internet browsing capabilities enhance the user experience. M.I.L.E.S. prioritizes user privacy by processing data locally, encrypting sensitive information, and adhering to strict data retention policies.

sdk
Vikit.ai SDK is a software development kit that enables easy development of video generators using generative AI and other AI models. It serves as a langchain to orchestrate AI models and video editing tools. The SDK allows users to create videos from text prompts with background music and voice-over narration. It also supports generating composite videos from multiple text prompts. The tool requires Python 3.8+, specific dependencies, and tools like FFMPEG and ImageMagick for certain functionalities. Users can contribute to the project by following the contribution guidelines and standards provided.
For similar tasks

noScribe
noScribe is an AI-based software designed for automated audio transcription, specifically tailored for transcribing interviews for qualitative social research or journalistic purposes. It is a free and open-source tool that runs locally on the user's computer, ensuring data privacy. The software can differentiate between speakers and supports transcription in 99 languages. It includes a user-friendly editor for reviewing and correcting transcripts. Developed by Kai Dröge, a PhD in sociology with a background in computer science, noScribe aims to streamline the transcription process and enhance the efficiency of qualitative analysis.
AivisSpeech-Engine
AivisSpeech-Engine is a powerful open-source tool for speech recognition and synthesis. It provides state-of-the-art algorithms for converting speech to text and text to speech. The tool is designed to be user-friendly and customizable, allowing developers to easily integrate speech capabilities into their applications. With AivisSpeech-Engine, users can transcribe audio recordings, create voice-controlled interfaces, and generate natural-sounding speech output. Whether you are building a virtual assistant, developing a speech-to-text application, or experimenting with voice technology, AivisSpeech-Engine offers a comprehensive solution for all your speech processing needs.
NotelyVoice
Notely Voice is a free, modern, cross-platform AI voice transcription and note-taking application. It offers powerful Whisper AI Voice to Text capabilities, making it ideal for students, professionals, doctors, researchers, and anyone in need of hands-free note-taking. The app features rich text editing, simple search, smart filtering, organization with folders and tags, advanced speech-to-text, offline capability, seamless integration, audio recording, theming, cross-platform support, and sharing functionality. It includes memory-efficient audio processing, chunking configuration, and utilizes OpenAI Whisper for speech recognition technology. Built with Kotlin, Compose Multiplatform, Coroutines, Android Architecture, ViewModel, Koin, Material 3, Whisper AI, and Native Compose Navigation, Notely follows Android Architecture principles with distinct layers for UI, presentation, domain, and data.
vocotype-cli
VocoType is a free desktop voice input method designed for professionals who value privacy and efficiency. All recognition is done locally, ensuring offline operation and no data upload. The CLI open-source version of the VocoType core engine on GitHub is mainly targeted at developers.
For similar jobs
SLR-FC
This repository provides a comprehensive collection of AI tools and resources to enhance literature reviews. It includes a curated list of AI tools for various tasks, such as identifying research gaps, discovering relevant papers, visualizing paper content, and summarizing text. Additionally, the repository offers materials on generative AI, effective prompts, copywriting, image creation, and showcases of AI capabilities. By leveraging these tools and resources, researchers can streamline their literature review process, gain deeper insights from scholarly literature, and improve the quality of their research outputs.
paper-ai
Paper-ai is a tool that helps you write papers using artificial intelligence. It provides features such as AI writing assistance, reference searching, and editing and formatting tools. With Paper-ai, you can quickly and easily create high-quality papers.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and follows a process of embedding docs and queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, scoring and selecting relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. Users can customize prompts and use various models for embeddings and LLMs. The tool can be used asynchronously and supports adding documents from paths, files, or URLs.
ChatData
ChatData is a robust chat-with-documents application designed to extract information and provide answers by querying the MyScale free knowledge base or uploaded documents. It leverages the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) framework, millions of Wikipedia pages, and arXiv papers. Features include self-querying retriever, VectorSQL, session management, and building a personalized knowledge base. Users can effortlessly navigate vast data, explore academic papers, and research documents. ChatData empowers researchers, students, and knowledge enthusiasts to unlock the true potential of information retrieval.

noScribe
noScribe is an AI-based software designed for automated audio transcription, specifically tailored for transcribing interviews for qualitative social research or journalistic purposes. It is a free and open-source tool that runs locally on the user's computer, ensuring data privacy. The software can differentiate between speakers and supports transcription in 99 languages. It includes a user-friendly editor for reviewing and correcting transcripts. Developed by Kai Dröge, a PhD in sociology with a background in computer science, noScribe aims to streamline the transcription process and enhance the efficiency of qualitative analysis.
AIStudyAssistant
AI Study Assistant is an app designed to enhance learning experience and boost academic performance. It serves as a personal tutor, lecture summarizer, writer, and question generator powered by Google PaLM 2. Features include interacting with an AI chatbot, summarizing lectures, generating essays, and creating practice questions. The app is built using 100% Kotlin, Jetpack Compose, Clean Architecture, and MVVM design pattern, with technologies like Ktor, Room DB, Hilt, and Kotlin coroutines. AI Study Assistant aims to provide comprehensive AI-powered assistance for students in various academic tasks.
data-to-paper
Data-to-paper is an AI-driven framework designed to guide users through the process of conducting end-to-end scientific research, starting from raw data to the creation of comprehensive and human-verifiable research papers. The framework leverages a combination of LLM and rule-based agents to assist in tasks such as hypothesis generation, literature search, data analysis, result interpretation, and paper writing. It aims to accelerate research while maintaining key scientific values like transparency, traceability, and verifiability. The framework is field-agnostic, supports both open-goal and fixed-goal research, creates data-chained manuscripts, involves human-in-the-loop interaction, and allows for transparent replay of the research process.
k2
K2 (GeoLLaMA) is a large language model for geoscience, trained on geoscience literature and fine-tuned with knowledge-intensive instruction data. It outperforms baseline models on objective and subjective tasks. The repository provides K2 weights, core data of GeoSignal, GeoBench benchmark, and code for further pretraining and instruction tuning. The model is available on Hugging Face for use. The project aims to create larger and more powerful geoscience language models in the future.