
roam-code
Instant codebase comprehension for AI coding agents
Stars: 58
Roam is a tool that builds a semantic graph of your codebase and allows AI agents to query it with one shell command. It pre-indexes your codebase into a semantic graph stored in a local SQLite DB, providing architecture-level graph queries offline, cross-language, and compact. Roam understands functions, modules, tests coverage, and overall architecture structure. It is best suited for agent-assisted coding, large codebases, architecture governance, safe refactoring, and multi-repo projects. Roam is not suitable for real-time type checking, dynamic/runtime analysis, small scripts, or pure text search. It offers speed, dependency-awareness, LLM-optimized output, fully local operation, and CI readiness.
README:
Roam builds a semantic graph of your codebase and lets AI agents query it with one shell command.
5 core commands · advanced tools when you need them
Roam pre-indexes your codebase into a semantic graph -- symbols, dependencies, call graphs, architecture, and git history -- stored in a local SQLite DB. Agents query it via CLI instead of repeatedly grepping files and guessing structure.
Unlike LSPs (editor-bound and language-specific) or Sourcegraph (hosted search), Roam provides architecture-level graph queries -- offline, cross-language, and compact.
A semantic graph means Roam understands what functions call what, how modules depend on each other, which tests cover which code, and the overall architecture structure.
Codebase ──> [Index] ──> Semantic Graph ──> CLI ──> AI Agent
│ │ │
tree-sitter symbols one call
17 languages + edges replaces
git history + metrics 5-10 tool calls
Coding agents explore codebases inefficiently: dozens of grep/read cycles, high token cost, no structural understanding. Roam replaces this with one graph query:
$ roam context Flask
Callers: 47 Callees: 3
Affected tests: 31
Files to read:
src/flask/app.py:76-963 # definition
src/flask/__init__.py:1-15 # re-export
src/flask/testing.py:22-45 # caller: FlaskClient.__init__
tests/test_basic.py:12-30 # caller: test_app_factory
...12 more files
$ roam understand # full codebase briefing
$ roam context <name> # files-to-read with exact line ranges
$ roam preflight <name> # blast radius + tests + complexity + architecture rules
$ roam health # composite score (0-100)
$ roam diff # blast radius of uncommitted changes- Agent-assisted coding -- structured answers that reduce token usage vs raw file exploration
- Large codebases (100+ files) -- graph queries beat linear search at scale
- Architecture governance -- health scores, CI quality gates, dependency cycle detection
- Safe refactoring -- blast radius, affected tests, pre-change safety checks
- Multi-repo projects -- cross-repo API edge detection between frontend and backend
- Real-time type checking -- use an LSP (pyright, gopls, tsserver). Roam is static and offline.
- Dynamic / runtime analysis -- Roam cannot trace reflection, eval, or dynamic dispatch.
- Small scripts (<10 files) -- just read the files directly.
- Pure text search -- ripgrep is faster for raw string matching.
Speed. One command replaces 5-10 tool calls (in typical workflows). Under 0.5s for any query.
Dependency-aware. Computes structure, not string matches. Knows Flask has 47 dependents and 31 affected tests. grep knows it appears 847 times.
LLM-optimized output. Plain ASCII, compact abbreviations (fn, cls, meth), --json envelopes. Designed for agent consumption, not human decoration.
Fully local. No API keys, telemetry, or network calls. Works in air-gapped environments.
CI-ready. --json output, --gate quality gates, GitHub Action, SARIF 2.1.0.
| Without Roam | With Roam | |
|---|---|---|
| Tool calls | 8 | 1 |
| Wall time | ~11s | <0.5s |
| Tokens consumed | ~15,000 | ~3,000 |
Measured on a typical agent workflow in a 200-file Python project (Flask). See benchmarks for more.
Table of Contents
Getting Started: What is Roam? · Best for · Why use Roam · Install · Quick Start
Using Roam: Commands · Walkthrough · AI Coding Tools · MCP Server
Operations: CI/CD Integration · SARIF Output · For Teams
Reference: Language Support · Performance · How It Works · How Roam Compares · FAQ
More: Limitations · Troubleshooting · Update / Uninstall · Development · Contributing
pip install roam-code
# Recommended: isolated environment
pipx install roam-code
# or
uv tool install roam-code
# From source
pip install git+https://github.com/Cranot/roam-code.gitRequires Python 3.9+. Works on Linux, macOS, and Windows.
Windows: If
roamis not found after installing withuv, runuv tool update-shelland restart your terminal.
cd your-project
roam init # indexes codebase, creates config + CI workflow
roam understand # full codebase briefingFirst index takes ~5s for 200 files, ~15s for 1,000 files. Subsequent runs are incremental and near-instant.
Next steps:
-
Set up your AI agent:
roam describe --write(auto-detects CLAUDE.md, AGENTS.md, .cursor/rules, etc. — see integration instructions) -
Explore:
roam health→roam weather→roam map -
Add to CI:
roam initalready generated a GitHub Action
Try it on Roam itself
git clone https://github.com/Cranot/roam-code.git
cd roam-code
pip install -e .
roam init
roam understand
roam healthClaude Code • Cursor • Windsurf • GitHub Copilot • Aider • Cline • Gemini CLI • OpenAI Codex CLI • MCP • GitHub Actions • GitLab CI • Azure DevOps
The 5 core commands shown above cover ~80% of agent workflows. 58 total commands are organized into 8 categories.
Full command reference
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
roam index [--force] [--verbose] |
Build or rebuild the codebase index |
roam init |
Guided onboarding: creates .roam/fitness.yaml, CI workflow, runs index, shows health |
roam understand |
Full codebase briefing: tech stack, architecture, key abstractions, health, conventions, complexity overview, entry points |
roam tour [--write PATH] |
Auto-generated onboarding guide: top symbols, reading order, entry points, language breakdown. --write saves to Markdown |
roam describe [--write] [--force] [-o PATH] [--agent-prompt] |
Auto-generate project description for AI agents. --write auto-detects your agent's config file. --agent-prompt returns a compact (<500 token) system prompt |
roam map [-n N] [--full] [--budget N] |
Project skeleton: files, languages, entry points, top symbols by PageRank. --budget caps output to N tokens |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
roam file <path> [--full] [--changed] [--deps-of PATH] |
File skeleton: all definitions with signatures, cognitive load index, health score |
roam symbol <name> [--full] |
Symbol definition + callers + callees + metrics. Supports file:symbol disambiguation |
roam context <symbol> [--task MODE] [--for-file PATH] |
AI-optimized context: definition + callers + callees + files-to-read with line ranges |
roam search <pattern> [--kind KIND] |
Find symbols by name pattern, PageRank-ranked |
roam grep <pattern> [-g glob] [-n N] |
Text search annotated with enclosing symbol context |
roam deps <path> [--full] |
What a file imports and what imports it |
roam trace <source> <target> [-k N] |
Dependency paths with coupling strength and hub detection |
roam impact <symbol> |
Blast radius: what breaks if a symbol changes (Personalized PageRank weighted) |
roam diff [--staged] [--full] [REV_RANGE] |
Blast radius of uncommitted changes or a commit range |
roam pr-risk [REV_RANGE] |
PR risk score (0-100, multiplicative model) + structural spread + suggested reviewers |
roam diagnose <symbol> [--depth N] |
Root cause analysis: ranks suspects by z-score normalized risk |
roam preflight <symbol|file> |
Compound pre-change check: blast radius + tests + complexity + coupling + fitness |
roam safe-delete <symbol> |
Safe deletion check: SAFE/REVIEW/UNSAFE verdict |
roam test-map <name> |
Map a symbol or file to its test coverage |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
roam health [--no-framework] |
Composite health score (0-100): weighted geometric mean of tangle ratio, god components, bottlenecks, layer violations. Includes propagation cost and algebraic connectivity |
roam complexity [--bumpy-road] |
Per-function cognitive complexity (SonarSource-compatible, triangular nesting penalty) + Halstead metrics (volume, difficulty, effort, bugs) + cyclomatic density |
roam weather [-n N] |
Hotspots ranked by geometric mean of churn x complexity (percentile-normalized) |
roam debt |
Hotspot-weighted tech debt prioritization with SQALE remediation cost estimates |
roam fitness [--explain] |
Architectural fitness functions from .roam/fitness.yaml
|
roam alerts |
Health degradation trend detection (Mann-Kendall + Sen's slope) |
roam snapshot [--tag TAG] |
Persist health metrics snapshot for trend tracking |
roam trend |
Health score history with sparkline visualization |
roam digest [--brief] [--since TAG] |
Compare current metrics against last snapshot |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
roam clusters [--min-size N] |
Community detection vs directory structure. Modularity Q-score (Newman 2004) + per-cluster conductance |
roam layers |
Topological dependency layers + upward violations + Gini balance |
roam dead [--all] [--summary] [--clusters] |
Unreferenced exported symbols with safety verdicts + confidence scoring (60-95%) |
roam fan [symbol|file] [-n N] [--no-framework] |
Fan-in/fan-out: most connected symbols or files |
roam risk [-n N] [--domain KW] [--explain] |
Domain-weighted risk ranking |
roam why <name> [name2 ...] |
Role classification (Hub/Bridge/Core/Leaf), reach, criticality |
roam split <file> |
Internal symbol groups with isolation % and extraction suggestions |
roam entry-points |
Entry point catalog with protocol classification |
roam patterns |
Architectural pattern recognition: Strategy, Factory, Observer, etc. |
roam visualize [--format mermaid|dot] [--focus NAME] [--limit N] |
Generate Mermaid or DOT architecture diagrams. Smart filtering via PageRank, cluster grouping, cycle highlighting |
roam safe-zones |
Graph-based containment boundaries |
roam coverage-gaps |
Unprotected entry points with no path to gate symbols |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
roam module <path> |
Directory contents: exports, signatures, dependencies, cohesion |
roam sketch <dir> [--full] |
Compact structural skeleton of a directory |
roam uses <name> |
All consumers: callers, importers, inheritors |
roam owner <path> |
Code ownership: who owns a file or directory |
roam coupling [-n N] [--set] |
Temporal coupling: file pairs that change together (NPMI + lift) |
roam fn-coupling |
Function-level temporal coupling across files |
roam bus-factor [--brain-methods] |
Knowledge loss risk per module |
roam doc-staleness |
Detect stale docstrings |
roam conventions |
Auto-detect naming styles, import preferences. Flags outliers |
roam breaking [REV_RANGE] |
Breaking change detection: removed exports, signature changes |
roam affected-tests <symbol|file> |
Trace reverse call graph to test files |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
roam report [--list] [--config FILE] [PRESET] |
Compound presets: first-contact, security, pre-pr, refactor
|
roam describe --write |
Generate agent config (auto-detects: CLAUDE.md, AGENTS.md, .cursor/rules, etc.) |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
roam ws init <repo1> <repo2> [--name NAME] |
Initialize a workspace from sibling repos. Auto-detects frontend/backend roles |
roam ws status |
Show workspace repos, index ages, cross-repo edge count |
roam ws resolve |
Scan for REST API endpoints and match frontend calls to backend routes |
roam ws understand |
Unified workspace overview: per-repo stats + cross-repo connections |
roam ws health |
Workspace-wide health report with cross-repo coupling assessment |
roam ws context <symbol> |
Cross-repo augmented context: find a symbol across repos + show API callers |
roam ws trace <source> <target> |
Trace cross-repo paths via API edges |
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
roam --json <command> |
Structured JSON output with consistent envelope |
roam --compact <command> |
Token-efficient output: TSV tables, minimal JSON envelope |
roam <command> --gate EXPR |
CI quality gate (e.g., --gate score>=70). Exit code 1 on failure |
10-step walkthrough using Flask as an example (click to expand)
Here's how you'd use Roam to understand a project you've never seen before. Using Flask as an example:
Step 1: Onboard and get the full picture
$ roam init
Created .roam/fitness.yaml (6 starter rules)
Created .github/workflows/roam.yml
Done. 226 files, 1132 symbols, 233 edges.
Health: 78/100
$ roam understand
Tech stack: Python (flask, jinja2, werkzeug)
Architecture: Monolithic — 3 layers, 5 clusters
Key abstractions: Flask, Blueprint, Request, Response
Health: 78/100 — 1 god component (Flask)
Entry points: src/flask/__init__.py, src/flask/cli.py
Conventions: snake_case functions, PascalCase classes, relative imports
Complexity: avg 4.2, 3 high (>15), 0 critical (>25)
Step 2: Drill into a key file
$ roam file src/flask/app.py
src/flask/app.py (python, 963 lines)
cls Flask(App) :76-963
meth __init__(self, import_name, ...) :152
meth route(self, rule, **options) :411
meth register_blueprint(self, blueprint, ...) :580
meth make_response(self, rv) :742
...12 more methods
Step 3: Who depends on this?
$ roam deps src/flask/app.py
Imported by:
file symbols
-------------------------- -------
src/flask/__init__.py 3
src/flask/testing.py 2
tests/test_basic.py 1
...18 files total
Step 4: Find the hotspots
$ roam weather
=== Hotspots (churn x complexity) ===
Score Churn Complexity Path Lang
----- ----- ---------- ---------------------- ------
18420 460 40.0 src/flask/app.py python
12180 348 35.0 src/flask/blueprints.py python
Step 5: Check architecture health
$ roam health
Health: 78/100
Tangle: 0.0% (0/1132 symbols in cycles)
1 god component (Flask, degree 47, actionable)
0 bottlenecks, 0 layer violations
=== God Components (degree > 20) ===
Sev Name Kind Degree Cat File
------- ----- ---- ------ --- ------------------
WARNING Flask cls 47 act src/flask/app.py
Step 6: Get AI-ready context for a symbol
$ roam context Flask
Files to read:
src/flask/app.py:76-963 # definition
src/flask/__init__.py:1-15 # re-export
src/flask/testing.py:22-45 # caller: FlaskClient.__init__
tests/test_basic.py:12-30 # caller: test_app_factory
...12 more files
Callers: 47 Callees: 3
Step 7: Pre-change safety check
$ roam preflight Flask
=== Preflight: Flask ===
Blast radius: 47 callers, 89 transitive
Affected tests: 31 (DIRECT: 12, TRANSITIVE: 19)
Complexity: cc=40 (critical), nesting=6
Coupling: 3 hidden co-change partners
Fitness: 1 violation (max-complexity exceeded)
Verdict: HIGH RISK — consider splitting before modifying
Step 8: Decompose a large file
$ roam split src/flask/app.py
=== Split analysis: src/flask/app.py ===
87 symbols, 42 internal edges, 95 external edges
Cross-group coupling: 18%
Group 1 (routing) — 12 symbols, isolation: 83% [extractable]
meth route L411 PR=0.0088
meth add_url_rule L450 PR=0.0045
...
=== Extraction Suggestions ===
Extract 'routing' group: route, add_url_rule, endpoint (+9 more)
83% isolated, only 3 edges to other groups
Step 9: Understand why a symbol matters
$ roam why Flask url_for Blueprint
Symbol Role Fan Reach Risk Verdict
--------- ------------ ---------- -------- -------- --------------------------------------------------
Flask Hub fan-in:47 reach:89 CRITICAL God symbol (47 in, 12 out). Consider splitting.
url_for Core utility fan-in:31 reach:45 HIGH Widely used utility (31 callers). Stable interface.
Blueprint Bridge fan-in:18 reach:34 moderate Coupling point between clusters.
Step 10: Generate docs and set up CI
$ roam describe --write
Wrote CLAUDE.md (98 lines) # auto-detects: CLAUDE.md, AGENTS.md, .cursor/rules, etc.
$ roam health --gate score>=70
Health: 78/100 — PASS
Ten commands. Complete picture: structure, dependencies, hotspots, health, context, safety checks, decomposition, and CI gates.
Roam is designed to be called by coding agents via shell commands. Instead of repeatedly grepping and reading files, the agent runs one roam command and gets structured output.
Decision order for agents:
| Situation | Command |
|---|---|
| First time in a repo |
roam understand then roam tour
|
| Need to modify a symbol |
roam preflight <name> (blast radius + tests + fitness) |
| Debugging a failure |
roam diagnose <name> (root cause ranking) |
| Need files to read |
roam context <name> (files + line ranges) |
| Need to find a symbol | roam search <pattern> |
| Need file structure | roam file <path> |
| Pre-PR check | roam pr-risk HEAD~3..HEAD |
| What breaks if I change X? | roam impact <symbol> |
Fastest setup:
roam describe --write # auto-detects your agent's config file
roam describe --write -o AGENTS.md # or specify an explicit path
roam describe --agent-prompt # compact ~500-token prompt (append to any config)Copy-paste agent instructions
## Codebase navigation
This project uses `roam` for codebase comprehension. Always prefer roam over Glob/Grep/Read exploration.
Before modifying any code:
1. First time in the repo: `roam understand` then `roam tour`
2. Find a symbol: `roam search <pattern>`
3. Before changing a symbol: `roam preflight <name>` (blast radius + tests + fitness)
4. Need files to read: `roam context <name>` (files + line ranges, prioritized)
5. Debugging a failure: `roam diagnose <name>` (root cause ranking)
6. After making changes: `roam diff` (blast radius of uncommitted changes)
Additional: `roam health` (0-100 score), `roam impact <name>` (what breaks),
`roam pr-risk` (PR risk), `roam file <path>` (file skeleton).
Run `roam --help` for all commands. Use `roam --json <cmd>` for structured output.Where to put this for each tool
| Tool | Config file |
|---|---|
| Claude Code |
CLAUDE.md in your project root |
| OpenAI Codex CLI |
AGENTS.md in your project root |
| Gemini CLI |
GEMINI.md in your project root |
| Cursor |
.cursor/rules/roam.mdc (add alwaysApply: true frontmatter) |
| Windsurf |
.windsurf/rules/roam.md (add trigger: always_on frontmatter) |
| GitHub Copilot | .github/copilot-instructions.md |
| Aider | CONVENTIONS.md |
| Continue.dev |
config.yaml rules |
| Cline |
.clinerules/ directory |
Roam vs native tools
| Task | Use Roam | Use native tools |
|---|---|---|
| "What calls this function?" | roam symbol <name> |
LSP / Grep |
| "What files do I need to read?" | roam context <name> |
Manual tracing (5+ calls) |
| "Is it safe to change X?" | roam preflight <name> |
Multiple manual checks |
| "Show me this file's structure" | roam file <path> |
Read the file directly |
| "Understand project architecture" | roam understand |
Manual exploration |
| "What breaks if I change X?" | roam impact <symbol> |
No direct equivalent |
| "What tests to run?" | roam affected-tests <name> |
Grep for imports (misses indirect) |
| "What's causing this bug?" | roam diagnose <name> |
Manual call-chain tracing |
| "Codebase health score for CI" | roam health --gate score>=70 |
No equivalent |
Roam includes a Model Context Protocol server for direct integration with tools that support MCP.
pip install fastmcp
fastmcp run roam.mcp_server:mcp19 read-only tools and 2 resources. All tools query the index -- they never modify your code.
MCP tool list
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
understand |
Full codebase briefing |
health |
Health score (0-100) + issues |
preflight |
Pre-change safety check |
search_symbol |
Find symbols by name |
context |
Files-to-read for modifying a symbol |
trace |
Dependency path between two symbols |
impact |
Blast radius of changing a symbol |
file_info |
File skeleton with all definitions |
pr_risk |
Risk score for pending changes |
breaking_changes |
Detect breaking changes between refs |
affected_tests |
Find tests affected by a change |
dead_code |
List unreferenced exports |
complexity_report |
Per-symbol cognitive complexity |
repo_map |
Project skeleton with key symbols |
tour |
Auto-generated onboarding guide |
diagnose |
Root cause analysis for debugging |
visualize |
Generate Mermaid or DOT architecture diagrams |
ws_understand |
Unified multi-repo workspace overview |
ws_context |
Cross-repo augmented symbol context |
Resources: roam://health (current health score), roam://summary (project overview)
Claude Code
claude mcp add roam -- fastmcp run roam.mcp_server:mcpOr add to .mcp.json in your project root:
{
"mcpServers": {
"roam": {
"command": "fastmcp",
"args": ["run", "roam.mcp_server:mcp"]
}
}
}Claude Desktop
Add to your claude_desktop_config.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"roam": {
"command": "fastmcp",
"args": ["run", "roam.mcp_server:mcp"],
"cwd": "/path/to/your/project"
}
}
}Cursor
Add to .cursor/mcp.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"roam": {
"command": "fastmcp",
"args": ["run", "roam.mcp_server:mcp"]
}
}
}VS Code + Copilot
Add to .vscode/mcp.json:
{
"servers": {
"roam": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "fastmcp",
"args": ["run", "roam.mcp_server:mcp"]
}
}
}All you need is Python 3.9+ and pip install roam-code.
# .github/workflows/roam.yml
name: Roam Analysis
on: [pull_request]
jobs:
roam:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- uses: Cranot/roam-code@main
with:
command: health --gate score>=70
comment: true
fail-on-violation: trueUse roam init to auto-generate this workflow.
| Input | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
command |
health |
Roam command to run |
python-version |
3.12 |
Python version |
comment |
false |
Post results as PR comment |
fail-on-violation |
false |
Fail the job on violations |
roam-version |
(latest) | Pin to a specific version |
GitLab CI
roam-analysis:
stage: test
image: python:3.12-slim
before_script:
- pip install roam-code
script:
- roam index
- roam health --gate score>=70
- roam --json pr-risk origin/main..HEAD > roam-report.json
artifacts:
paths:
- roam-report.json
rules:
- if: $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IIDAzure DevOps / any CI
Universal pattern:
pip install roam-code
roam index
roam health --gate score>=70 # exit 1 on failure
roam --json health > report.jsonRoam exports analysis results in SARIF 2.1.0 format for GitHub Code Scanning.
from roam.output.sarif import health_to_sarif, write_sarif
sarif = health_to_sarif(health_data)
write_sarif(sarif, "roam-health.sarif")- uses: github/codeql-action/upload-sarif@v3
with:
sarif_file: roam-health.sarifZero infrastructure, zero vendor lock-in, zero data leaving your network.
| Tool | Annual cost (20-dev team) | Infrastructure | Setup time |
|---|---|---|---|
| SonarQube Server | $15,000-$45,000 | Self-hosted server | Days |
| CodeScene | $20,000-$60,000 | SaaS or on-prem | Hours |
| Code Climate | $12,000-$36,000 | SaaS | Hours |
| Roam | $0 (MIT license) | None (local) | 5 minutes |
Team rollout guide
Week 1-2 (pilot): 1-2 developers run roam init on one repo. Use roam preflight before changes, roam pr-risk before PRs.
Week 3-4 (expand): Add roam health --gate score>=60 to CI as a non-blocking check.
Month 2+ (standardize): Tighten to --gate score>=70. Expand to additional repos. Track trajectory with roam trend.
Complements your existing stack
| If you use... | Roam adds... |
|---|---|
| SonarQube | Architecture-level analysis: dependency cycles, god components, blast radius, health scoring |
| CodeScene | Free, local alternative for health scoring and hotspot analysis |
| ESLint / Pylint | Cross-language architecture checks. Linters enforce style per file; Roam enforces architecture across the codebase |
| LSP | AI-agent-optimized queries. roam context answers "what calls this?" with PageRank-ranked results in one call |
| Language | Extensions | Symbols | References | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Python |
.py .pyi
|
classes, functions, methods, decorators, variables | imports, calls, inheritance | extends, __all__ exports |
| JavaScript |
.js .jsx .mjs .cjs
|
classes, functions, arrow functions, CJS exports | imports, require(), calls | extends |
| TypeScript |
.ts .tsx .mts .cts
|
interfaces, type aliases, enums + all JS | imports, calls, type refs | extends, implements |
| Java | .java |
classes, interfaces, enums, constructors, fields | imports, calls | extends, implements |
| Go | .go |
structs, interfaces, functions, methods, fields | imports, calls | embedded structs |
| Rust | .rs |
structs, traits, impls, enums, functions | use, calls | impl Trait for Struct |
| C / C++ |
.c .h .cpp .hpp .cc
|
structs, classes, functions, namespaces, templates | includes, calls | extends |
| PHP | .php |
classes, interfaces, traits, enums, methods, properties | namespace use, calls, static calls, new
|
extends, implements, use (traits) |
| Visual FoxPro | .prg |
functions, procedures, classes, methods, properties, constants | DO, SET PROCEDURE/CLASSLIB, CREATEOBJECT, =func(), obj.method()
|
DEFINE CLASS ... AS |
| Vue | .vue |
via <script> block extraction (TS/JS) |
imports, calls, type refs | extends, implements |
| Svelte | .svelte |
via <script> block extraction (TS/JS) |
imports, calls, type refs | extends, implements |
Salesforce ecosystem (Tier 1)
| Language | Extensions | Symbols | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apex |
.cls .trigger
|
classes, triggers, SOQL, annotations | imports, calls, System.Label, generic type refs |
| Aura |
.cmp .app .evt .intf .design
|
components, attributes, methods, events | controller refs, component refs |
| LWC (JavaScript) |
.js (in LWC dirs) |
anonymous class from filename |
@salesforce/apex/, @salesforce/schema/, @salesforce/label/
|
| Visualforce |
.page .component
|
pages, components | controller/extensions, merge fields, includes |
| SF Metadata XML | *-meta.xml |
objects, fields, rules, layouts | Apex class refs, formula field refs, Flow actionCalls |
Cross-language edges mean roam impact AccountService shows blast radius across Apex, LWC, Aura, Visualforce, and Flows.
Ruby (.rb), C# (.cs), Kotlin (.kt .kts), Swift (.swift), Scala (.scala .sc)
Tier 2 languages get symbol extraction and basic inheritance via a generic tree-sitter walker.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Index 200 files | ~3-5s |
| Index 3,000 files | ~2 min |
| Incremental (no changes) | <1s |
| Any query command | <0.5s |
Detailed benchmarks
| Project | Language | Files | Symbols | Edges | Index Time | Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Express | JS | 211 | 624 | 804 | 3s | 70 files/s |
| Axios | JS | 237 | 1,065 | 868 | 6s | 41 files/s |
| Vue | TS | 697 | 5,335 | 8,984 | 25s | 28 files/s |
| Laravel | PHP | 3,058 | 39,097 | 38,045 | 1m46s | 29 files/s |
| Svelte | TS | 8,445 | 16,445 | 19,618 | 2m40s | 52 files/s |
| Repo | Language | Score | Coverage | Edge Density | Commands |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laravel | PHP | 9.55 | 91.2% | 0.97 | 29/29 |
| Vue | TS | 9.27 | 85.8% | 1.68 | 29/29 |
| Svelte | TS | 9.04 | 94.7% | 1.19 | 29/29 |
| Axios | JS | 8.98 | 85.9% | 0.82 | 29/29 |
| Express | JS | 8.46 | 96.0% | 1.29 | 29/29 |
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
1,600-line file → roam file
|
~5,000 chars (~70:1 compression) |
| Full project map | ~4,000 chars |
--compact mode |
40-50% additional token reduction |
roam preflight replaces |
5-7 separate agent tool calls |
Codebase
|
[1] Discovery ──── git ls-files (respects .gitignore)
|
[2] Parse ──────── tree-sitter AST per file (17 languages)
|
[3] Extract ────── symbols + references (calls, imports, inheritance)
|
[4] Resolve ────── match references to definitions → edges
|
[5] Metrics ────── adaptive PageRank, betweenness, cognitive complexity, Halstead
|
[6] Git ────────── churn, co-change matrix, authorship, Renyi entropy
|
[7] Clusters ───── Louvain community detection
|
[8] Health ─────── per-file scores (7-factor) + composite score (0-100)
|
[9] Store ──────── .roam/index.db (SQLite, WAL mode)
After the first full index, roam index only re-processes changed files (mtime + SHA-256 hash). Incremental updates are near-instant.
Graph algorithms
-
Adaptive PageRank -- damping factor auto-tunes based on cycle density (0.82-0.92); identifies the most important symbols (used by
map,search,context) -
Personalized PageRank -- distance-weighted blast radius for
impact(Gleich, 2015) - Adaptive betweenness centrality -- exact for small graphs, sqrt-scaled sampling for large (Brandes & Pich, 2007); finds bottleneck symbols
- Edge betweenness centrality -- identifies critical cycle-breaking edges in SCCs (Brandes, 2001)
- Tarjan's SCC -- detects dependency cycles with tangle ratio
- Propagation Cost -- fraction of system affected by any change, via transitive closure (MacCormack, Rusnak & Baldwin, 2006)
- Algebraic connectivity (Fiedler value) -- second-smallest Laplacian eigenvalue; measures architectural robustness (Fiedler, 1973)
- Louvain community detection -- groups related symbols into clusters
- Modularity Q-score -- measures if cluster boundaries match natural community structure (Newman, 2004)
- Conductance -- per-cluster boundary tightness: cut(S, S_bar) / min(vol(S), vol(S_bar)) (Yang & Leskovec)
- Topological sort -- computes dependency layers, Gini coefficient for layer balance (Gini, 1912), weighted violation severity
- k-shortest simple paths -- traces dependency paths with coupling strength
- Renyi entropy (order 2) -- measures co-change distribution; more robust to outliers than Shannon (Renyi, 1961)
- Mann-Kendall trend test -- non-parametric degradation detection, robust to noise (Mann, 1945; Kendall, 1975)
- Sen's slope estimator -- robust trend magnitude, resistant to outliers (Sen, 1968)
- NPMI -- Normalized Pointwise Mutual Information for coupling strength (Bouma, 2009)
- Lift -- association rule mining metric for co-change statistical significance (Agrawal & Srikant, 1994)
- Halstead metrics -- volume, difficulty, effort, and predicted bugs from operator/operand counts (Halstead, 1977)
- SQALE remediation cost -- time-to-fix estimates per issue type for tech debt prioritization (Letouzey, 2012)
Health scoring
Composite health score (0-100) using a weighted geometric mean of sigmoid health factors. Non-compensatory: a zero in any dimension cannot be masked by high scores in others.
| Factor | Weight | What it measures |
|---|---|---|
| Tangle ratio | 30% | % of symbols in dependency cycles |
| God components | 20% | Symbols with extreme fan-in/fan-out |
| Bottlenecks | 15% | High-betweenness chokepoints |
| Layer violations | 15% | Upward dependency violations (severity-weighted by layer distance) |
| Per-file health | 20% | Average of 7-factor file health scores |
Each factor uses sigmoid health: h = e^(-signal/scale) (1 = pristine, approaches 0 = worst). Score = 100 * product(h_i ^ w_i). Also reports propagation cost (MacCormack 2006) and algebraic connectivity (Fiedler 1973). Per-file health (1-10) combines: cognitive complexity (triangular nesting penalty per Sweller's Cognitive Load Theory), indentation complexity, cycle membership, god component membership, dead export ratio, co-change entropy, and churn amplification.
Roam is not a replacement for your linter, LSP, or SonarQube. It fills a different gap: giving AI agents structural understanding of the codebase in a format optimized for LLM consumption.
| Tool | What it does | How Roam differs |
|---|---|---|
| ctags / cscope | Symbol index for editors | Roam adds graph metrics, git signals, architecture analysis, and AI-optimized output |
| LSP (pyright, gopls) | Real-time type checking | LSP requires a running server and file:line:col queries. Roam is offline, exploratory, and cross-language |
| Sourcegraph | Code search + AI | Requires hosted deployment. Roam is local-only, MIT-licensed |
| Aider repo map | Tree-sitter + PageRank | Context selection for chat. Roam adds git signals, 50+ architecture commands, CI gates |
| CodeScene | Behavioral code analysis | Commercial SaaS. Roam is free, local, uses peer-reviewed algorithms (Mann-Kendall, NPMI, Personalized PageRank) |
| SonarQube | Code quality + security | Heavy server. Roam's cognitive complexity follows SonarSource spec |
| grep / ripgrep | Text search | No semantic understanding. Can't distinguish definitions from usage |
Does Roam send any data externally? No. Zero network calls. No telemetry, no analytics, no update checks.
Can Roam run in air-gapped environments? Yes. Once installed, no internet access is required.
Does Roam modify my source code?
No. Read-only. Creates .roam/ with an index database. Never modifies source files.
How does Roam handle monorepos? Indexes from the root. Batched SQL handles 100k+ symbols. Incremental updates stay fast.
How does Roam handle multi-repo projects (e.g., frontend + backend)?
Use roam ws init <repo1> <repo2> to create a workspace. Each repo keeps its own index; a workspace overlay DB stores cross-repo API edges. roam ws resolve scans for REST endpoints and matches frontend calls to backend routes. Then roam ws context, roam ws trace, etc. work across repos.
Is Roam compatible with SonarQube / CodeScene? Yes. Roam complements existing tools. Both can run in the same CI pipeline. SARIF output integrates with GitHub Code Scanning.
Static analysis trade-offs:
- No runtime analysis -- can't trace dynamic dispatch, reflection, or eval'd code
- Import resolution is heuristic -- complex re-exports or conditional imports may not resolve
- Limited cross-language edges -- Salesforce and multi-repo API edges are supported, but not arbitrary FFI
- Tier 2 languages (Ruby, C#, Kotlin, Swift, Scala) get basic symbol extraction only
- Large monorepos (100k+ files) may have slow initial indexing
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
roam: command not found |
Ensure install location is on PATH. For uv: uv tool update-shell
|
Another indexing process is running |
Delete .roam/index.lock and retry |
database is locked |
roam index --force to rebuild |
| Unicode errors on Windows |
chcp 65001 for UTF-8 |
| Symbol resolves to wrong file | Use file:symbol syntax: roam symbol myfile:MyFunction
|
| Health score seems wrong |
roam health --json for factor breakdown |
Index stale after git pull
|
roam index (incremental). After major refactors: roam index --force
|
# Update
pipx upgrade roam-code
uv tool upgrade roam-code
pip install --upgrade roam-code
# Uninstall
pipx uninstall roam-code
uv tool uninstall roam-code
pip uninstall roam-codeDelete .roam/ from your project root to clean up local data.
git clone https://github.com/Cranot/roam-code.git
cd roam-code
pip install -e .
pytest tests/ # 669 tests, Python 3.9-3.13Project structure
roam-code/
├── pyproject.toml
├── action.yml # Reusable GitHub Action
├── CHANGELOG.md
├── src/roam/
│ ├── __init__.py # Version (from pyproject.toml)
│ ├── cli.py # Click CLI (58 commands, 8 categories)
│ ├── mcp_server.py # MCP server (19 tools, 2 resources)
│ ├── db/
│ │ ├── connection.py # SQLite (WAL, pragmas, batched IN)
│ │ ├── schema.py # Tables, indexes, migrations
│ │ └── queries.py # Named SQL constants
│ ├── index/
│ │ ├── indexer.py # Orchestrates full pipeline
│ │ ├── discovery.py # git ls-files, .gitignore
│ │ ├── parser.py # Tree-sitter parsing
│ │ ├── symbols.py # Symbol + reference extraction
│ │ ├── relations.py # Reference resolution -> edges
│ │ ├── complexity.py # Cognitive complexity (SonarSource)
│ │ ├── git_stats.py # Churn, co-change, blame, entropy
│ │ └── incremental.py # mtime + hash change detection
│ ├── languages/
│ │ ├── base.py # Abstract LanguageExtractor
│ │ ├── registry.py # Language detection + aliasing
│ │ ├── *_lang.py # One file per language (13 Tier 1)
│ │ └── generic_lang.py # Tier 2 fallback
│ ├── workspace/
│ │ ├── config.py # .roam-workspace.json
│ │ ├── db.py # Workspace overlay DB
│ │ ├── api_scanner.py # REST API endpoint detection
│ │ └── aggregator.py # Cross-repo aggregation
│ ├── graph/
│ │ ├── builder.py, pagerank.py # DB -> NetworkX, PageRank
│ │ ├── cycles.py, clusters.py # Tarjan SCC, Louvain
│ │ ├── layers.py, pathfinding.py # Topo layers, k-shortest paths
│ │ ├── split.py, why.py # Decomposition, role classification
│ ├── commands/
│ │ ├── resolve.py # Shared symbol resolution
│ │ └── cmd_*.py # One module per command
│ └── output/
│ ├── formatter.py # Token-efficient formatting
│ └── sarif.py # SARIF 2.1.0 output
└── tests/ # 669 tests across 11 test files
| Package | Purpose |
|---|---|
| click >= 8.0 | CLI framework |
| tree-sitter >= 0.23 | AST parsing |
| tree-sitter-language-pack >= 0.6 | 165+ grammars |
| networkx >= 3.0 | Graph algorithms |
Optional: fastmcp (MCP server)
- [x] Composite health scoring (v7.0)
- [x] MCP server -- 19 tools, 2 resources (v7.0-v7.4)
- [x] SARIF 2.1.0 output (v7.0)
- [x] GitHub Action (v7.0)
- [x] Large-repo batched SQL (v7.1)
- [x] Salesforce cross-language edges (v7.1)
- [x] Cognitive load index, tour, diagnose (v7.2)
- [x] Multi-repo workspace support (v7.4)
- [x] Research-backed algorithms: adaptive PageRank, Personalized PageRank, Mann-Kendall, NPMI, Sen's slope, sigmoid-bounded health, Gini layer balance (v7.4)
- [x] Advanced math: Halstead metrics, Renyi entropy, propagation cost, algebraic connectivity, modularity Q-score, conductance, edge betweenness, SQALE remediation cost, multiplicative PR risk, weighted geometric mean health, dead code confidence scoring, cyclomatic density (v7.5)
- [ ] Terminal demo GIF
- [ ] Ruby Tier 1 support
- [ ] C# Tier 1 support
- [ ]
--sarifCLI flag for direct SARIF export - [ ] Docker image for CI
- [ ] VS Code extension
git clone https://github.com/Cranot/roam-code.git
cd roam-code
pip install -e .
pytest tests/ # All 669 tests must passGood first contributions: add a Tier 1 language (see go_lang.py or php_lang.py as templates), improve reference resolution, add benchmark repos, extend SARIF converters, add MCP tools.
Please open an issue first to discuss larger changes.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for roam-code
Similar Open Source Tools

roam-code
Roam is a tool that builds a semantic graph of your codebase and allows AI agents to query it with one shell command. It pre-indexes your codebase into a semantic graph stored in a local SQLite DB, providing architecture-level graph queries offline, cross-language, and compact. Roam understands functions, modules, tests coverage, and overall architecture structure. It is best suited for agent-assisted coding, large codebases, architecture governance, safe refactoring, and multi-repo projects. Roam is not suitable for real-time type checking, dynamic/runtime analysis, small scripts, or pure text search. It offers speed, dependency-awareness, LLM-optimized output, fully local operation, and CI readiness.
shodh-memory
Shodh-Memory is a cognitive memory system designed for AI agents to persist memory across sessions, learn from experience, and run entirely offline. It features Hebbian learning, activation decay, and semantic consolidation, packed into a single ~17MB binary. Users can deploy it on cloud, edge devices, or air-gapped systems to enhance the memory capabilities of AI agents.
sf-skills
sf-skills is a collection of reusable skills for Agentic Salesforce Development, enabling AI-powered code generation, validation, testing, debugging, and deployment. It includes skills for development, quality, foundation, integration, AI & automation, DevOps & tooling. The installation process is newbie-friendly and includes an installer script for various CLIs. The skills are compatible with platforms like Claude Code, OpenCode, Codex, Gemini, Amp, Droid, Cursor, and Agentforce Vibes. The repository is community-driven and aims to strengthen the Salesforce ecosystem.
llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a universal plugin for a large language model (LLM) designed to enable users to interact with LLM within neovim. Users can customize various LLMs such as gpt, glm, kimi, and local LLM. The plugin provides tools for optimizing code, comparing code, translating text, and more. It also supports integration with free models from Cloudflare, Github models, siliconflow, and others. Users can customize tools, chat with LLM, quickly translate text, and explain code snippets. The plugin offers a flexible window interface for easy interaction and customization.
pipelock
Pipelock is an all-in-one security harness designed for AI agents, offering control over network egress, detection of credential exfiltration, scanning for prompt injection, and monitoring workspace integrity. It utilizes capability separation to restrict the agent process with secrets and employs a separate fetch proxy for web browsing. The tool runs a 7-layer scanner pipeline on every request to ensure security. Pipelock is suitable for users running AI agents like Claude Code, OpenHands, or any AI agent with shell access and API keys.
paiml-mcp-agent-toolkit
PAIML MCP Agent Toolkit (PMAT) is a zero-configuration AI context generation system with extreme quality enforcement and Toyota Way standards. It allows users to analyze any codebase instantly through CLI, MCP, or HTTP interfaces. The toolkit provides features such as technical debt analysis, advanced monitoring, metrics aggregation, performance profiling, bottleneck detection, alert system, multi-format export, storage flexibility, and more. It also offers AI-powered intelligence for smart recommendations, polyglot analysis, repository showcase, and integration points. PMAT enforces quality standards like complexity ≤20, zero SATD comments, test coverage >80%, no lint warnings, and synchronized documentation with commits. The toolkit follows Toyota Way development principles for iterative improvement, direct AST traversal, automated quality gates, and zero SATD policy.
EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
Backlog.md
Backlog.md is a Markdown-native Task Manager & Kanban visualizer for any Git repository. It turns any folder with a Git repo into a self-contained project board powered by plain Markdown files and a zero-config CLI. Features include managing tasks as plain .md files, private & offline usage, instant terminal Kanban visualization, board export, modern web interface, AI-ready CLI, rich query commands, cross-platform support, and MIT-licensed open-source. Users can create tasks, view board, assign tasks to AI, manage documentation, make decisions, and configure settings easily.
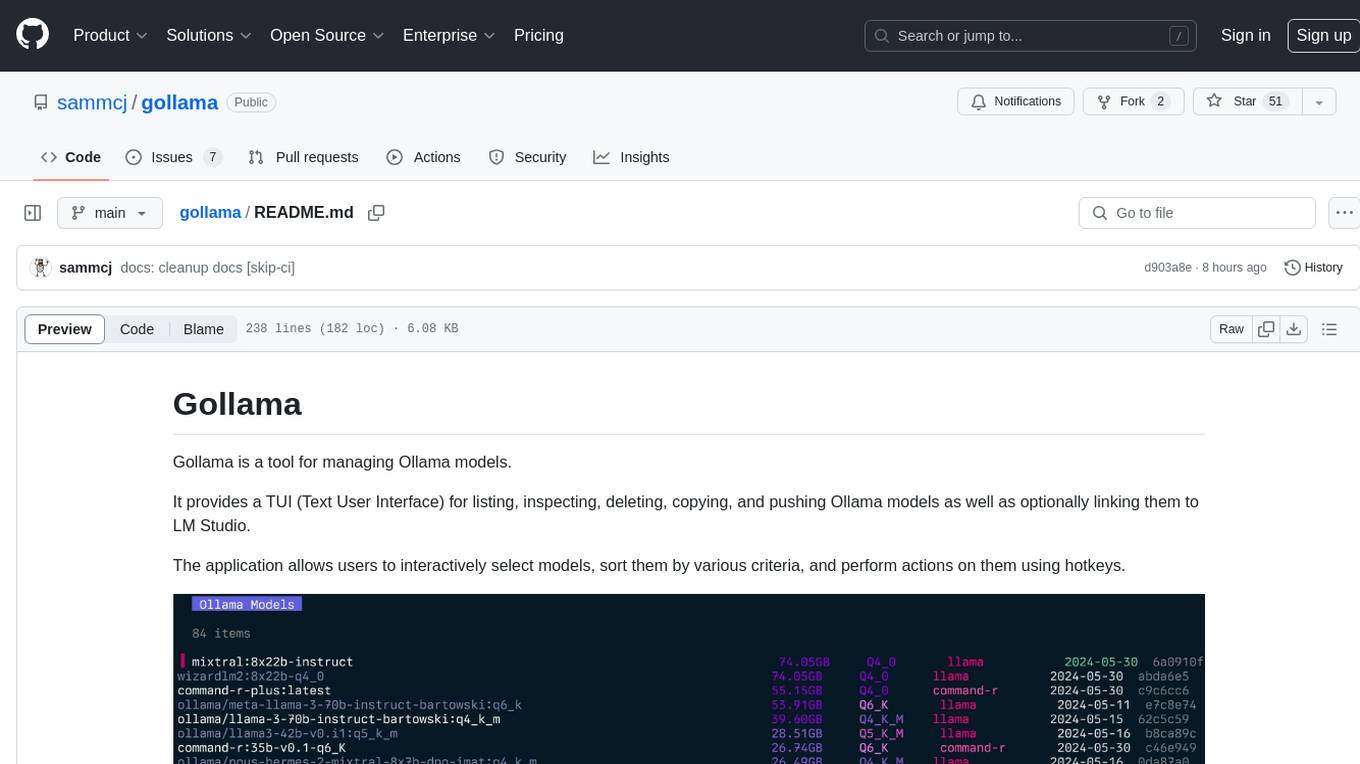
gollama
Gollama is a tool designed for managing Ollama models through a Text User Interface (TUI). Users can list, inspect, delete, copy, and push Ollama models, as well as link them to LM Studio. The application offers interactive model selection, sorting by various criteria, and actions using hotkeys. It provides features like sorting and filtering capabilities, displaying model metadata, model linking, copying, pushing, and more. Gollama aims to be user-friendly and useful for managing models, especially for cleaning up old models.
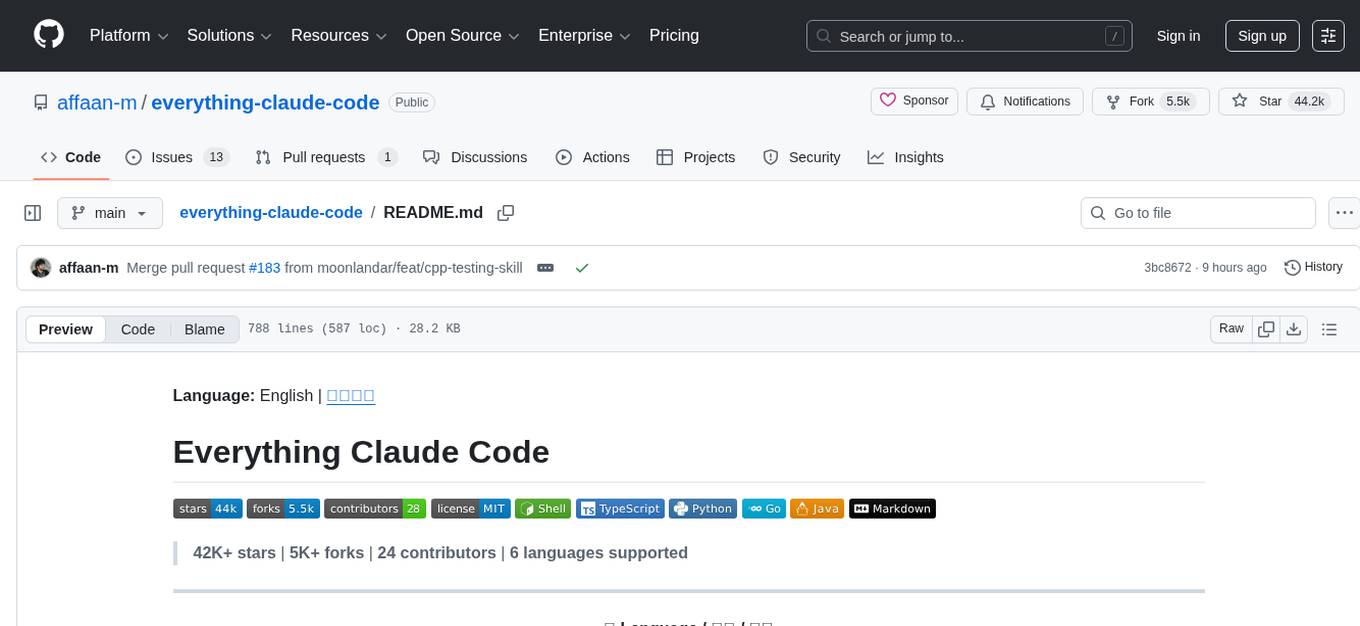
everything-claude-code
The 'Everything Claude Code' repository is a comprehensive collection of production-ready agents, skills, hooks, commands, rules, and MCP configurations developed over 10+ months. It includes guides for setup, foundations, and philosophy, as well as detailed explanations of various topics such as token optimization, memory persistence, continuous learning, verification loops, parallelization, and subagent orchestration. The repository also provides updates on bug fixes, multi-language rules, installation wizard, PM2 support, OpenCode plugin integration, unified commands and skills, and cross-platform support. It offers a quick start guide for installation, ecosystem tools like Skill Creator and Continuous Learning v2, requirements for CLI version compatibility, key concepts like agents, skills, hooks, and rules, running tests, contributing guidelines, OpenCode support, background information, important notes on context window management and customization, star history chart, and relevant links.
ai-dev-kit
The AI Dev Kit is a comprehensive toolkit designed to enhance AI-driven development on Databricks. It provides trusted sources for AI coding assistants like Claude Code and Cursor to build faster and smarter on Databricks. The kit includes features such as Spark Declarative Pipelines, Databricks Jobs, AI/BI Dashboards, Unity Catalog, Genie Spaces, Knowledge Assistants, MLflow Experiments, Model Serving, Databricks Apps, and more. Users can choose from different adventures like installing the kit, using the visual builder app, teaching AI assistants Databricks patterns, executing Databricks actions, or building custom integrations with the core library. The kit also includes components like databricks-tools-core, databricks-mcp-server, databricks-skills, databricks-builder-app, and ai-dev-project.
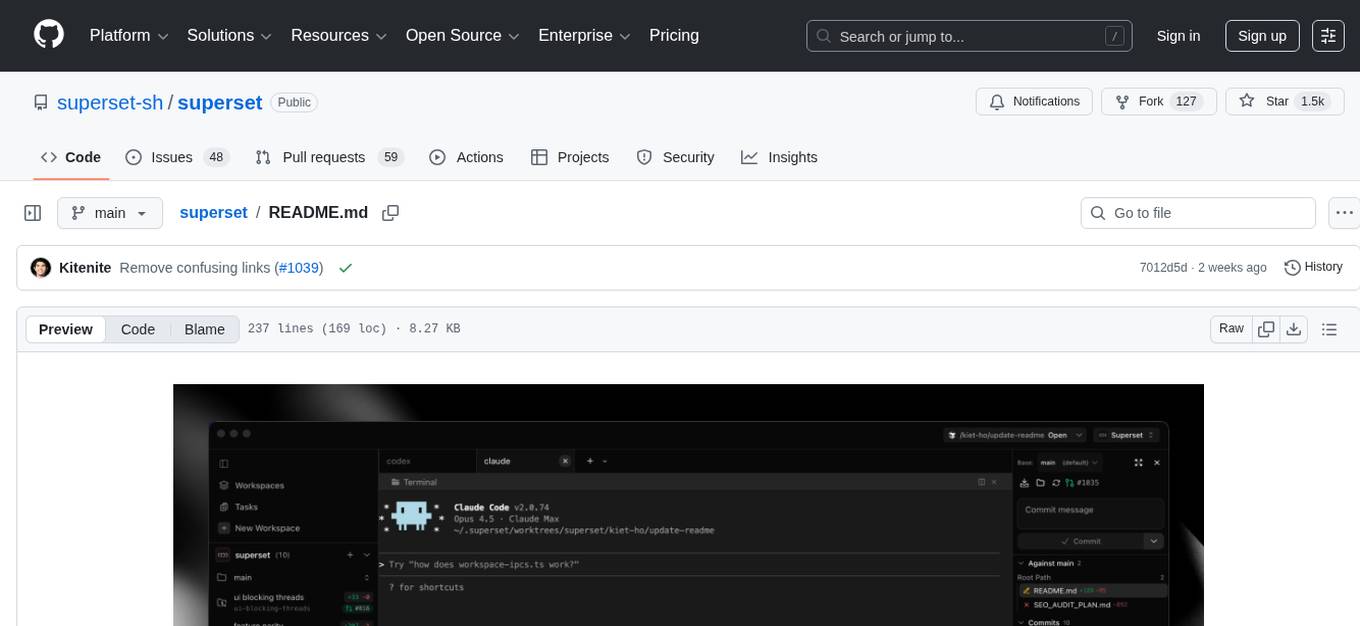
superset
Superset is a turbocharged terminal that allows users to run multiple CLI coding agents simultaneously, isolate tasks in separate worktrees, monitor agent status, review changes quickly, and enhance development workflow. It supports any CLI-based coding agent and offers features like parallel execution, worktree isolation, agent monitoring, built-in diff viewer, workspace presets, universal compatibility, quick context switching, and IDE integration. Users can customize keyboard shortcuts, configure workspace setup, and teardown, and contribute to the project. The tech stack includes Electron, React, TailwindCSS, Bun, Turborepo, Vite, Biome, Drizzle ORM, Neon, and tRPC. The community provides support through Discord, Twitter, GitHub Issues, and GitHub Discussions.
gpt-load
GPT-Load is a high-performance, enterprise-grade AI API transparent proxy service designed for enterprises and developers needing to integrate multiple AI services. Built with Go, it features intelligent key management, load balancing, and comprehensive monitoring capabilities for high-concurrency production environments. The tool serves as a transparent proxy service, preserving native API formats of various AI service providers like OpenAI, Google Gemini, and Anthropic Claude. It supports dynamic configuration, distributed leader-follower deployment, and a Vue 3-based web management interface. GPT-Load is production-ready with features like dual authentication, graceful shutdown, and error recovery.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.

cactus
Cactus is an energy-efficient and fast AI inference framework designed for phones, wearables, and resource-constrained arm-based devices. It provides a bottom-up approach with no dependencies, optimizing for budget and mid-range phones. The framework includes Cactus FFI for integration, Cactus Engine for high-level transformer inference, Cactus Graph for unified computation graph, and Cactus Kernels for low-level ARM-specific operations. It is suitable for implementing custom models and scientific computing on mobile devices.
new-api
New API is a next-generation large model gateway and AI asset management system that provides a wide range of features, including a new UI interface, multi-language support, online recharge function, key query for usage quota, compatibility with the original One API database, model charging by usage count, channel weighted randomization, data dashboard, token grouping and model restrictions, support for various authorization login methods, support for Rerank models, OpenAI Realtime API, Claude Messages format, reasoning effort setting, content reasoning, user-specific model rate limiting, request format conversion, cache billing support, and various model support such as gpts, Midjourney-Proxy, Suno API, custom channels, Rerank models, Claude Messages format, Dify, and more.
For similar tasks
glimpse
Glimpse is a blazingly fast tool for peeking at codebases, offering features like fast parallel file processing, tree-view of codebase structure, source code content viewing, token counting with multiple backends, configurable defaults, clipboard support, customizable file type detection, .gitignore respect, web content processing with Markdown conversion, Git repository support, and URL traversal with configurable depth. It supports token counting using Tiktoken or HuggingFace tokenizer backends, helping estimate context window usage for large language models. Glimpse can process local directories, multiple files, Git repositories, web pages, and convert content to Markdown. It offers various options for customization and configuration, including file type inclusions/exclusions, token counting settings, URL processing settings, and default exclude patterns. Glimpse is suitable for developers and data scientists looking to analyze codebases, estimate token counts, and process web content efficiently.

paiml-mcp-agent-toolkit
PAIML MCP Agent Toolkit (PMAT) is a zero-configuration AI context generation system with extreme quality enforcement and Toyota Way standards. It allows users to analyze any codebase instantly through CLI, MCP, or HTTP interfaces. The toolkit provides features such as technical debt analysis, advanced monitoring, metrics aggregation, performance profiling, bottleneck detection, alert system, multi-format export, storage flexibility, and more. It also offers AI-powered intelligence for smart recommendations, polyglot analysis, repository showcase, and integration points. PMAT enforces quality standards like complexity ≤20, zero SATD comments, test coverage >80%, no lint warnings, and synchronized documentation with commits. The toolkit follows Toyota Way development principles for iterative improvement, direct AST traversal, automated quality gates, and zero SATD policy.
smithers
Smithers is a tool for declarative AI workflow orchestration using React components. It allows users to define complex multi-agent workflows as component trees, ensuring composability, durability, and error handling. The tool leverages React's re-rendering mechanism to persist outputs to SQLite, enabling crashed workflows to resume seamlessly. Users can define schemas for task outputs, create workflow instances, define agents, build workflow trees, and run workflows programmatically or via CLI. Smithers supports components for pipeline stages, structured output validation with Zod, MDX prompts, validation loops with Ralph, dynamic branching, and various built-in tools like read, edit, bash, grep, and write. The tool follows a clear workflow execution process involving defining, rendering, executing, re-rendering, and repeating tasks until completion, all while storing task results in SQLite for fault tolerance.
GitVizz
GitVizz is an AI-powered repository analysis tool that helps developers understand and navigate codebases quickly. It transforms complex code structures into interactive documentation, dependency graphs, and intelligent conversations. With features like interactive dependency graphs, AI-powered code conversations, advanced code visualization, and automatic documentation generation, GitVizz offers instant understanding and insights for any repository. The tool is built with modern technologies like Next.js, FastAPI, and OpenAI, making it scalable and efficient for analyzing large codebases. GitVizz also provides a standalone Python library for core code analysis and dependency graph generation, offering multi-language parsing, AST analysis, dependency graphs, visualizations, and extensibility for custom applications.

roam-code
Roam is a tool that builds a semantic graph of your codebase and allows AI agents to query it with one shell command. It pre-indexes your codebase into a semantic graph stored in a local SQLite DB, providing architecture-level graph queries offline, cross-language, and compact. Roam understands functions, modules, tests coverage, and overall architecture structure. It is best suited for agent-assisted coding, large codebases, architecture governance, safe refactoring, and multi-repo projects. Roam is not suitable for real-time type checking, dynamic/runtime analysis, small scripts, or pure text search. It offers speed, dependency-awareness, LLM-optimized output, fully local operation, and CI readiness.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.



