
cactus
Kernels & AI inference engine for mobile devices.
Stars: 4253

Cactus is an energy-efficient and fast AI inference framework designed for phones, wearables, and resource-constrained arm-based devices. It provides a bottom-up approach with no dependencies, optimizing for budget and mid-range phones. The framework includes Cactus FFI for integration, Cactus Engine for high-level transformer inference, Cactus Graph for unified computation graph, and Cactus Kernels for low-level ARM-specific operations. It is suitable for implementing custom models and scientific computing on mobile devices.
README:
┌─────────────────┐ Energy-efficient inference engine for running AI on mobile devices
│ Cactus Engine │ ←── OpenAI compatible APIs for C/C++, Swift, Kotlin, Flutter & React-Native
└─────────────────┘ Supports tool call, auto RAG, NPU, INT4, and cloud handoff for complex tasks
│
┌─────────────────┐ Zero-copy computation graph, think PyTorch for mobile devices
│ Cactus Graph │ ←── You can implement custom models directly using this
└─────────────────┘ Highly optimised for RAM & lossless weight quantisation
│
┌─────────────────┐ Low-level ARM-specific SIMD kernels (Apple, Snapdragon, Google, Exynos, MediaTek & Raspberry Pi)
│ Cactus Kernels │ ←── Optimised Matrix Multiplication & n
└─────────────────┘ Custom attention kernels with KV-Cache Quantisation, chunked prefill, streaming LLM, etc.
#include cactus.h
cactus_model_t model = cactus_init(
"path/to/weight/folder",
"path to txt or dir of txts for auto-rag",
);
const char* messages = R"([
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "My name is Henry Ndubuaku"}
])";
const char* options = R"({
"max_tokens": 50,
"stop_sequences": ["<|im_end|>"]
})";
char response[4096];
int result = cactus_complete(
model, // model handle from cactus_init
messages, // JSON array of chat messages
response, // buffer to store response JSON
sizeof(response), // size of response buffer
options, // optional: generation options (nullptr for defaults)
nullptr, // optional: tools JSON for function calling
nullptr, // optional: streaming callback fn(token, id, user_data)
nullptr // optional: user data passed to callback
);Example response from Gemma3-270m
{
"success": true, // when successfully generated locally
"error": null, // returns specific errors if success = false
"cloud_handoff": false, // true when model is unconfident, simply route to cloud
"response": "Hi there!", // null when error is not null or cloud_handoff = true
"function_calls": [], // parsed to [{"name":"set_alarm","arguments":{"hour":"10","minute":"0"}}]
"confidence": 0.8193, // how confident the model is with its response
"time_to_first_token_ms": 45.23, // latency (time to first token)
"total_time_ms": 163.67, // total execution time
"prefill_tps": 1621.89, // prefill tokens per second
"decode_tps": 168.42, // decode tokens per second
"ram_usage_mb": 245.67, // current process RAM usage in MB
"prefill_tokens": 28,
"decode_tokens": 50,
"total_tokens": 78
}#include cactus.h
CactusGraph graph;
auto a = graph.input({2, 3}, Precision::FP16);
auto b = graph.input({3, 4}, Precision::INT8);
auto x1 = graph.matmul(a, b, false);
auto x2 = graph.transpose(x1);
auto result = graph.matmul(b, x2, true);
float a_data[6] = {1.1f, 2.3f, 3.4f, 4.2f, 5.7f, 6.8f};
float b_data[12] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
graph.set_input(a, a_data, Precision::FP16);
graph.set_input(b, b_data, Precision::INT8);
graph.execute();
void* output_data = graph.get_output(result);
graph.hard_reset(); | Device | LFM2.5-1.2B (1k-Prefill/100-Decode) |
LFM2.5-VL-1.6B (256px-Latency & Decode) |
Whisper-Small-244m (30s-audio-Latency & Decode) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mac M4 Pro | 582tps/77tps (76MB RAM) | 0.2s/76tps (87MB RAM) | 0.1s/119tps (73MB RAM) |
| iPad/Mac M4 | 379tps/46tps (30MB RAM) | 0.2s/46tps (53MB RAM) | 0.2s/100tp (122MB RAM) |
| iPhone 17 Pro | 300tps/33tps (108MB RAM) | 0.3s/33tps (156MB RAM) | 0.3s/114tps (177MB RAM) |
| Galaxy S25 Ultra | 226tps/36tps (1.2GB RAM) | 2.6s/33tps (2GB RAM) | 2.3s/90tps (363MB RAM) |
| Pixel 10 Pro | - | - | - |
| Vivo X200 Pro | - | - | - |
| Device | LFM2-350m (1k-Prefill/100-Decode) |
LFM2-VL-450m (256px-Latency & Decode) |
Moonshine-Base-67m (30s-audio-Latency & Decode) |
|---|---|---|---|
| iPad/Mac M1 | - | - | - |
| iPhone 13 Mini | - | - | - |
| Galaxy A56 | - | - | - |
| Pixel 6a | 218tps/44tps (395MB RAM) | 2.5s/36tps (631MB RAM) | 1.5s/189tps (111MB RAM) |
| Nothing CMF | - | - | - |
| Raspberry Pi 5 | - | - | - |
| Model | Features |
|---|---|
| google/gemma-3-270m-it | completion |
| google/functiongemma-270m-it | completion, tools |
| LiquidAI/LFM2-350M | completion, tools, embed |
| Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B | completion, tools, embed |
| LiquidAI/LFM2-700M | completion, tools, embed |
| google/gemma-3-1b-it | completion |
| LiquidAI/LFM2.5-1.2B-Thinking | completion, tools, embed |
| LiquidAI/LFM2.5-1.2B-Instruct | completion, tools, embed |
| Qwen/Qwen3-1.7B | completion, tools, embed |
| LiquidAI/LFM2-2.6B | completion, tools, embed |
| LiquidAI/LFM2-VL-450M | vision, txt & img embed, Apple NPU |
| LiquidAI/LFM2.5-VL-1.6B | vision, txt & img embed, Apple NPU |
| UsefulSensors/moonshine-base | transcription, speech embed |
| openai/whisper-small | transcription, speech embed, Apple NPU |
| openai/whisper-medium | transcribe, speech embed, Apple NPU |
| nomic-ai/nomic-embed-text-v2-moe | embed |
| Qwen/Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B | embed |
git clone https://github.com/cactus-compute/cactus && cd cactus && source ./setupsudo apt-get install python3 python3-venv python3-pip cmake build-essential libcurl4-openssl-dev
git clone https://github.com/cactus-compute/cactus && cd cactus && source ./setup| Command | Description |
|---|---|
cactus run [model] |
Opens playground (auto downloads model) |
cactus download [model] |
Downloads model to ./weights
|
cactus convert [model] [dir] |
Converts model, supports LoRA merging (--lora <path>) |
cactus build |
Builds for ARM (--apple or --android) |
cactus test |
Runs tests (--ios / --android, --model [name/path]), --precision
|
cactus transcribe [model] |
Transcribe audio file (--file) or live microphone |
cactus clean |
Removes build artifacts |
cactus --help |
Shows all commands and flags (always run this) |
- Python for Mac
- React Native SDK
- Swift Multiplatform SDK
- Kotlin Multiplatform SDK
- Flutter SDK
- Rust SDK
- Cactus Compute, Inc
- UCLA's BruinAI
- Yale's AI Society
- National Unoversity of Singapore's AI Society
- UC Irvine's AI@UCI
- Imperial College's AI Society
- University of Pennsylvania's AI@Penn
- University of Michigan Ann-Arbor MSAIL
- University of Colorado Boulder's AI Club
- C++ Standard: Use C++20 features where appropriate.
- Formatting: Follow the existing code style in the project, one header per folder.
- Comments: Avoid comments, make your code read like plain english.
- AI-Generated Code: Do not bindly PR AI slop, this codebase is very complex, they miss details.
- Update docs: Please update docs when necessary, be intuitive and straightforward.
- Keep It Simple: Do not go beyond the scope of the GH issue, avoid bloated PRs, keep codes lean.
- Benchmark Your Changes: Test performance impact, Cactus is performance-critical.
- Test everything: A PR that fails to build is the biggest red flag, means it was not tested.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for cactus
Similar Open Source Tools

cactus
Cactus is an energy-efficient and fast AI inference framework designed for phones, wearables, and resource-constrained arm-based devices. It provides a bottom-up approach with no dependencies, optimizing for budget and mid-range phones. The framework includes Cactus FFI for integration, Cactus Engine for high-level transformer inference, Cactus Graph for unified computation graph, and Cactus Kernels for low-level ARM-specific operations. It is suitable for implementing custom models and scientific computing on mobile devices.
claude-flow
Claude-Flow is a workflow automation tool designed to streamline and optimize business processes. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating and managing workflows, allowing users to automate repetitive tasks and improve efficiency. With features such as drag-and-drop workflow builder, customizable templates, and integration with popular business tools, Claude-Flow empowers users to automate their workflows without the need for extensive coding knowledge. Whether you are a small business owner looking to streamline your operations or a project manager seeking to automate task assignments, Claude-Flow offers a flexible and scalable solution to meet your workflow automation needs.
runanywhere-sdks
RunAnywhere is an on-device AI tool for mobile apps that allows users to run LLMs, speech-to-text, text-to-speech, and voice assistant features locally, ensuring privacy, offline functionality, and fast performance. The tool provides a range of AI capabilities without relying on cloud services, reducing latency and ensuring that no data leaves the device. RunAnywhere offers SDKs for Swift (iOS/macOS), Kotlin (Android), React Native, and Flutter, making it easy for developers to integrate AI features into their mobile applications. The tool supports various models for LLM, speech-to-text, and text-to-speech, with detailed documentation and installation instructions available for each platform.
EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
claude-craft
Claude Craft is a comprehensive framework for AI-assisted development with Claude Code, providing standardized rules, agents, and commands across multiple technology stacks. It includes autonomous sprint capabilities, documentation accuracy improvements, CI hardening, and test coverage enhancements. With support for 10 technology stacks, 5 languages, 40 AI agents, 157 slash commands, and various project management features like BMAD v6 framework, Ralph Wiggum loop execution, skills, templates, checklists, and hooks system, Claude Craft offers a robust solution for project development and management. The tool also supports workflow methodology, development tracks, document generation, BMAD v6 project management, quality gates, batch processing, backlog migration, and Claude Code hooks integration.
llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a universal plugin for a large language model (LLM) designed to enable users to interact with LLM within neovim. Users can customize various LLMs such as gpt, glm, kimi, and local LLM. The plugin provides tools for optimizing code, comparing code, translating text, and more. It also supports integration with free models from Cloudflare, Github models, siliconflow, and others. Users can customize tools, chat with LLM, quickly translate text, and explain code snippets. The plugin offers a flexible window interface for easy interaction and customization.
sf-skills
sf-skills is a collection of reusable skills for Agentic Salesforce Development, enabling AI-powered code generation, validation, testing, debugging, and deployment. It includes skills for development, quality, foundation, integration, AI & automation, DevOps & tooling. The installation process is newbie-friendly and includes an installer script for various CLIs. The skills are compatible with platforms like Claude Code, OpenCode, Codex, Gemini, Amp, Droid, Cursor, and Agentforce Vibes. The repository is community-driven and aims to strengthen the Salesforce ecosystem.
flute
FLUTE (Flexible Lookup Table Engine for LUT-quantized LLMs) is a tool designed for uniform quantization and lookup table quantization of weights in lower-precision intervals. It offers flexibility in mapping intervals to arbitrary values through a lookup table. FLUTE supports various quantization formats such as int4, int3, int2, fp4, fp3, fp2, nf4, nf3, nf2, and even custom tables. The tool also introduces new quantization algorithms like Learned Normal Float (NFL) for improved performance and calibration data learning. FLUTE provides benchmarks, model zoo, and integration with frameworks like vLLM and HuggingFace for easy deployment and usage.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
paiml-mcp-agent-toolkit
PAIML MCP Agent Toolkit (PMAT) is a zero-configuration AI context generation system with extreme quality enforcement and Toyota Way standards. It allows users to analyze any codebase instantly through CLI, MCP, or HTTP interfaces. The toolkit provides features such as technical debt analysis, advanced monitoring, metrics aggregation, performance profiling, bottleneck detection, alert system, multi-format export, storage flexibility, and more. It also offers AI-powered intelligence for smart recommendations, polyglot analysis, repository showcase, and integration points. PMAT enforces quality standards like complexity ≤20, zero SATD comments, test coverage >80%, no lint warnings, and synchronized documentation with commits. The toolkit follows Toyota Way development principles for iterative improvement, direct AST traversal, automated quality gates, and zero SATD policy.
Liger-Kernel
Liger Kernel is a collection of Triton kernels designed for LLM training, increasing training throughput by 20% and reducing memory usage by 60%. It includes Hugging Face Compatible modules like RMSNorm, RoPE, SwiGLU, CrossEntropy, and FusedLinearCrossEntropy. The tool works with Flash Attention, PyTorch FSDP, and Microsoft DeepSpeed, aiming to enhance model efficiency and performance for researchers, ML practitioners, and curious novices.
rho
Rho is an AI agent that runs on macOS, Linux, and Android, staying active, remembering past interactions, and checking in autonomously. It operates without cloud storage, allowing users to retain ownership of their data. Users can bring their own LLM provider and have full control over the agent's functionalities. Rho is built on the pi coding agent framework, offering features like persistent memory, scheduled tasks, and real email capabilities. The agent can be customized through checklists, scheduled triggers, and personalized voice and identity settings. Skills and extensions enhance the agent's capabilities, providing tools for notifications, clipboard management, text-to-speech, and more. Users can interact with Rho through commands and scripts, enabling tasks like checking status, triggering actions, and managing preferences.
Open-dLLM
Open-dLLM is the most open release of a diffusion-based large language model, providing pretraining, evaluation, inference, and checkpoints. It introduces Open-dCoder, the code-generation variant of Open-dLLM. The repo offers a complete stack for diffusion LLMs, enabling users to go from raw data to training, checkpoints, evaluation, and inference in one place. It includes pretraining pipeline with open datasets, inference scripts for easy sampling and generation, evaluation suite with various metrics, weights and checkpoints on Hugging Face, and transparent configs for full reproducibility.
StableToolBench
StableToolBench is a new benchmark developed to address the instability of Tool Learning benchmarks. It aims to balance stability and reality by introducing features such as a Virtual API System with caching and API simulators, a new set of solvable queries determined by LLMs, and a Stable Evaluation System using GPT-4. The Virtual API Server can be set up either by building from source or using a prebuilt Docker image. Users can test the server using provided scripts and evaluate models with Solvable Pass Rate and Solvable Win Rate metrics. The tool also includes model experiments results comparing different models' performance.
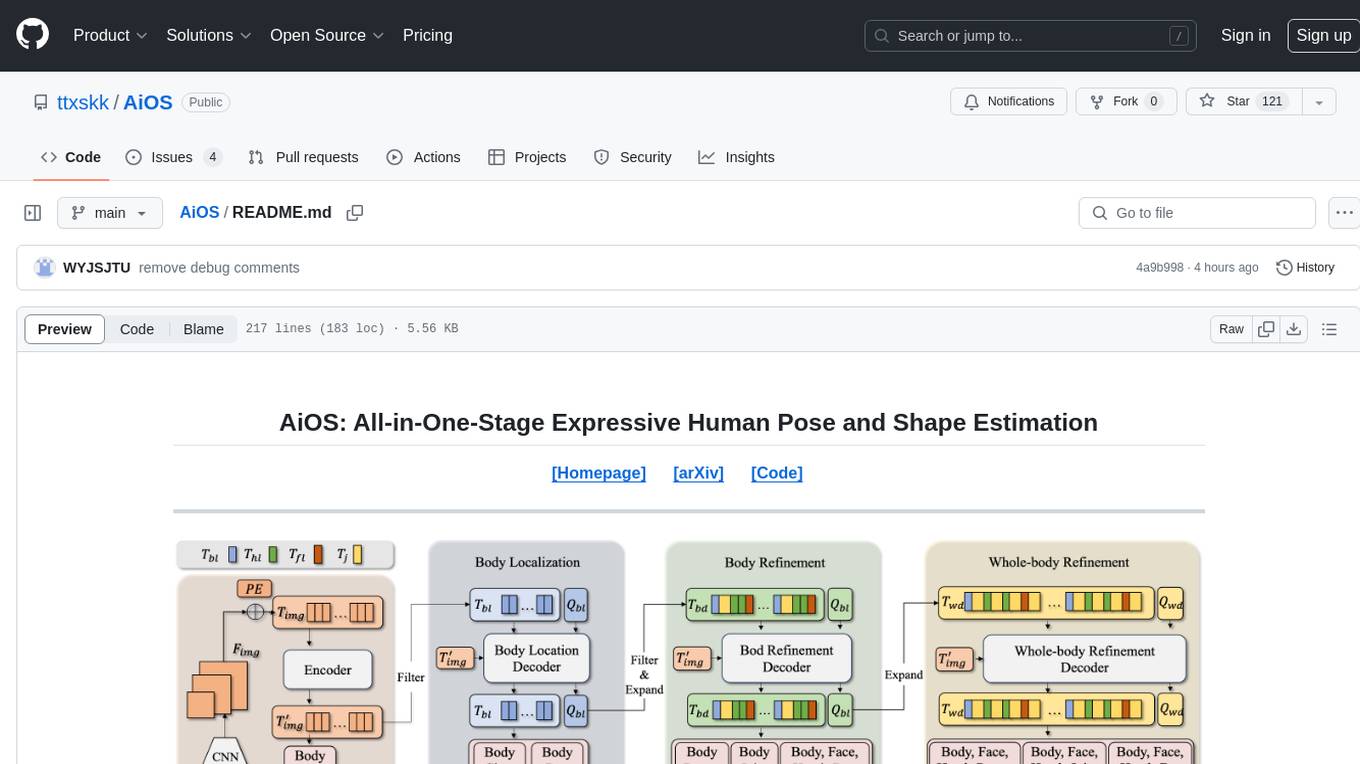
AiOS
AiOS is a tool for human pose and shape estimation, performing human localization and SMPL-X estimation in a progressive manner. It consists of body localization, body refinement, and whole-body refinement stages. Users can download datasets for evaluation, SMPL-X body models, and AiOS checkpoint. Installation involves creating a conda virtual environment, installing PyTorch, torchvision, Pytorch3D, MMCV, and other dependencies. Inference requires placing the video for inference and pretrained models in specific directories. Test results are provided for NMVE, NMJE, MVE, and MPJPE on datasets like BEDLAM and AGORA. Users can run scripts for AGORA validation, AGORA test leaderboard, and BEDLAM leaderboard. The tool acknowledges codes from MMHuman3D, ED-Pose, and SMPLer-X.
DownEdit
DownEdit is a fast and powerful program for downloading and editing videos from platforms like TikTok, Douyin, and Kuaishou. It allows users to effortlessly grab videos, make bulk edits, and utilize advanced AI features for generating videos, images, and sounds in bulk. The tool offers features like video, photo, and sound editing, downloading videos without watermarks, bulk AI generation, and AI editing for content enhancement.
For similar tasks

cactus
Cactus is an energy-efficient and fast AI inference framework designed for phones, wearables, and resource-constrained arm-based devices. It provides a bottom-up approach with no dependencies, optimizing for budget and mid-range phones. The framework includes Cactus FFI for integration, Cactus Engine for high-level transformer inference, Cactus Graph for unified computation graph, and Cactus Kernels for low-level ARM-specific operations. It is suitable for implementing custom models and scientific computing on mobile devices.

CopilotKit
CopilotKit is an open-source framework for building, deploying, and operating fully custom AI Copilots, including in-app AI chatbots, AI agents, and AI Textareas. It provides a set of components and entry points that allow developers to easily integrate AI capabilities into their applications. CopilotKit is designed to be flexible and extensible, so developers can tailor it to their specific needs. It supports a variety of use cases, including providing app-aware AI chatbots that can interact with the application state and take action, drop-in replacements for textareas with AI-assisted text generation, and in-app agents that can access real-time application context and take action within the application.
kitchenai
KitchenAI is an open-source toolkit designed to simplify AI development by serving as an AI backend and LLMOps solution. It aims to empower developers to focus on delivering results without being bogged down by AI infrastructure complexities. With features like simplifying AI integration, providing an AI backend, and empowering developers, KitchenAI streamlines the process of turning AI experiments into production-ready APIs. It offers built-in LLMOps features, is framework-agnostic and extensible, and enables faster time-to-production. KitchenAI is suitable for application developers, AI developers & data scientists, and platform & infra engineers, allowing them to seamlessly integrate AI into apps, deploy custom AI techniques, and optimize AI services with a modular framework. The toolkit eliminates the need to build APIs and infrastructure from scratch, making it easier to deploy AI code as production-ready APIs in minutes. KitchenAI also provides observability, tracing, and evaluation tools, and offers a Docker-first deployment approach for scalability and confidence.
react-native-executorch
React Native ExecuTorch is a framework that allows developers to run AI models on mobile devices using React Native. It bridges the gap between React Native and native platform capabilities, providing high-performance AI model execution without requiring deep knowledge of native code or machine learning internals. The tool supports ready-made models in `.pte` format and offers a Python API for custom models. It is designed to simplify the integration of AI features into React Native apps.

Mortal
Mortal (凡夫) is a free and open source AI for Japanese mahjong, powered by deep reinforcement learning. It provides a comprehensive solution for playing Japanese mahjong with AI assistance. The project focuses on utilizing deep reinforcement learning techniques to enhance gameplay and decision-making in Japanese mahjong. Mortal offers a user-friendly interface and detailed documentation to assist users in understanding and utilizing the AI effectively. The project is actively maintained and welcomes contributions from the community to further improve the AI's capabilities and performance.
AIInfra
AIInfra is an open-source project focused on AI infrastructure, specifically targeting large models in distributed clusters, distributed architecture, distributed training, and algorithms related to large models. The project aims to explore and study system design in artificial intelligence and deep learning, with a focus on the hardware and software stack for building AI large model systems. It provides a comprehensive curriculum covering key topics such as system overview, AI computing clusters, communication and storage, cluster containers and cloud-native technologies, distributed training, distributed inference, large model algorithms and data, and applications of large models.
crabml
Crabml is a llama.cpp compatible AI inference engine written in Rust, designed for efficient inference on various platforms with WebGPU support. It focuses on running inference tasks with SIMD acceleration and minimal memory requirements, supporting multiple models and quantization methods. The project is hackable, embeddable, and aims to provide high-performance AI inference capabilities.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
