
aiologic
GIL-powered* locking library for Python
Stars: 59
aiologic is a locking library for tasks synchronization and their communication. It provides primitives that are both async-aware and thread-aware, and can be used for interaction between async codes (async <-> async) in one thread as regular async primitives, async codes (async <-> async) in multiple threads, async code and sync one (async <-> sync) in one thread, async code and sync one (async <-> sync) in multiple threads, sync codes (sync <-> sync) in one thread as regular sync primitives, sync codes (sync <-> sync) in multiple threads as regular sync primitives. It offers synchronization primitives like events, barriers, semaphores, capacity limiters, locks, readers-writer locks, condition variables, communication primitives like queues, non-blocking primitives like flags and resource guards, and supports various concurrency libraries like asyncio, curio, trio, anyio, eventlet, gevent, and threading. aiologic is implemented entirely on effectively atomic operations, providing incredible speedup on PyPy compared to alternatives from the threading module. It works in free-threaded mode and ensures atomic operations even with GIL.
README:
.. SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2024 Ilya Egorov [email protected] SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-4.0
.. role:: class(literal) .. role:: exc(literal) .. role:: mod(literal)
.. badges-start-marker
|pypi-dw| |pypi-impl| |pypi-pyv| |pypi-types|
.. |pypi-dw| image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/dw/aiologic :target: https://pypistats.org/packages/aiologic :alt: .. |pypi-impl| image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/implementation/aiologic :target: #features :alt: .. |pypi-pyv| image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/pyversions/aiologic :target: #features :alt: .. |pypi-types| image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/types/aiologic :target: #features :alt:
.. badges-end-marker
.. description-start-marker
aiologic is a locking library for tasks synchronization and their communication. It provides primitives that are both async-aware and thread-aware, and can be used for interaction between:
- async codes (async <-> async) in one thread as regular async primitives
- async codes (async <-> async) in multiple threads (!)
- async code and sync one (async <-> sync) in one thread (!)
- async code and sync one (async <-> sync) in multiple threads (!)
- sync codes (sync <-> sync) in one thread as regular sync primitives
- sync codes (sync <-> sync) in multiple threads as regular sync primitives
Let's take a look at the example:
.. code:: python
import asyncio
from threading import Thread
import aiologic
lock = aiologic.Lock()
async def func(i: int, j: int) -> None:
print(f"thread={i} task={j} start")
async with lock:
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print(f"thread={i} task={j} end")
async def main(i: int) -> None:
await asyncio.gather(func(i, 0), func(i, 1))
Thread(target=asyncio.run, args=[main(0)]).start()
Thread(target=asyncio.run, args=[main(1)]).start()
It prints something like this:
.. code-block::
thread=0 task=0 start
thread=1 task=0 start
thread=0 task=1 start
thread=1 task=1 start
thread=0 task=0 end
thread=1 task=0 end
thread=0 task=1 end
thread=1 task=1 end
As you can see, tasks from different event loops are all able to acquire
:class:aiologic.Lock. In the same case if you use :class:asyncio.Lock, it
will raise a :exc:RuntimeError. And :class:threading.Lock will cause a
deadlock.
.. description-end-marker
.. features-start-marker
-
Python 3.8+ support
-
CPython <https://www.python.org/>__ andPyPy <https://pypy.org/>__ support -
Pickling <https://docs.python.org/3/library/pickle.html>__ andweakrefing <https://docs.python.org/3/library/weakref.html>__ support -
Cancellation and timeouts support
-
Optional
Trio-style checkpoints <https://trio.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ reference-core.html#checkpoints>__:- enabled by default for Trio itself
- disabled by default for all others
-
Only one checkpoint per asynchronous call:
- exactly one context switch if checkpoints are enabled
- zero or one context switch if checkpoints are disabled
-
Fairness wherever possible (with some caveats)
-
Thread-safety wherever possible
-
Lock-free implementation
-
Bundled stub files
Synchronization primitives:
- Events: one-time, reusable, and countdown
- Barriers: single-use, cyclic, and reusable
- Semaphores: counting, bounded, and binary
- Capacity limiters: borrowable, and reentrant
- Locks: ownable, and reentrant
-
Readers-writer locks (external) <https://gist.github.com/x42005e1f/ a50d0744013b7bbbd7ded608d6a3845b>__ - Condition variables
Communication primitives:
- Queues: FIFO, LIFO, and priority
Non-blocking primitives:
- Flags
- Resource guards
Supported concurrency libraries:
.. libraries-start-marker
-
asyncio,curio,trio, andanyio(coroutine-based) -
eventlet, andgevent(greenlet-based) -
threading_ (thread-based)
.. _asyncio: https://docs.python.org/3/library/asyncio.html .. _curio: https://curio.readthedocs.io .. _trio: https://trio.readthedocs.io .. _anyio: https://anyio.readthedocs.io .. _eventlet: https://eventlet.readthedocs.io .. _gevent: https://www.gevent.org/ .. _threading: https://docs.python.org/3/library/threading.html
.. libraries-end-marker
All synchronization, communication, and non-blocking primitives are implemented
entirely on effectively atomic operations, which gives an incredible speedup on PyPy <https://gist.github.com/x42005e1f/149d3994d5f7bd878def71d5404e6ea4>__
compared to alternatives from the :mod:threading module. All this works
because of GIL, but per-object locks also ensure that the same operations are still atomic <https://peps.python.org/pep-0703/#container-thread-safety>, so
aiologic also works when running in a free-threaded mode <https:// docs.python.org/3.13/whatsnew/3.13.html#free-threaded-cpython>.
.. features-end-marker
.. installation-start-marker
Install from PyPI <https://pypi.org/project/aiologic/>__ (stable):
.. code:: console
pip install aiologic
Or from GitHub <https://github.com/x42005e1f/aiologic>__ (latest):
.. code:: console
pip install git+https://github.com/x42005e1f/aiologic.git
You can also use other package managers, such as uv <https://github.com/ astral-sh/uv>__.
.. installation-end-marker
Read the Docs: https://aiologic.readthedocs.io (official)
DeepWiki: https://deepwiki.com/x42005e1f/aiologic (AI generated)
GitHub Discussions: https://github.com/x42005e1f/aiologic/discussions (ideas, questions)
GitHub Issues: https://github.com/x42005e1f/aiologic/issues (bug tracker)
You can also send an email to [email protected] with any feedback.
If you like aiologic and want to support its development, please star its repository on GitHub <https://github.com/x42005e1f/aiologic>__.
.. image:: https://starchart.cc/x42005e1f/aiologic.svg?variant=adaptive :target: https://starchart.cc/x42005e1f/aiologic
.. license-start-marker
The aiologic library is REUSE-compliant <https://api.reuse.software/info/ github.com/x42005e1f/aiologic>__ and is offered under multiple licenses:
- All original source code is licensed under
ISC_. - All original test code is licensed under
0BSD_. - All documentation is licensed under
CC-BY-4.0_. - All configuration is licensed under
CC0-1.0_.
For more accurate information, check the individual files.
.. _ISC: https://choosealicense.com/licenses/isc/ .. _0BSD: https://choosealicense.com/licenses/0bsd/ .. _CC-BY-4.0: https://choosealicense.com/licenses/cc-by-4.0/ .. _CC0-1.0: https://choosealicense.com/licenses/cc0-1.0/
.. license-end-marker
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aiologic
Similar Open Source Tools

aiologic
aiologic is a locking library for tasks synchronization and their communication. It provides primitives that are both async-aware and thread-aware, and can be used for interaction between async codes (async <-> async) in one thread as regular async primitives, async codes (async <-> async) in multiple threads, async code and sync one (async <-> sync) in one thread, async code and sync one (async <-> sync) in multiple threads, sync codes (sync <-> sync) in one thread as regular sync primitives, sync codes (sync <-> sync) in multiple threads as regular sync primitives. It offers synchronization primitives like events, barriers, semaphores, capacity limiters, locks, readers-writer locks, condition variables, communication primitives like queues, non-blocking primitives like flags and resource guards, and supports various concurrency libraries like asyncio, curio, trio, anyio, eventlet, gevent, and threading. aiologic is implemented entirely on effectively atomic operations, providing incredible speedup on PyPy compared to alternatives from the threading module. It works in free-threaded mode and ensures atomic operations even with GIL.
Tutel
Tutel MoE is an optimized Mixture-of-Experts implementation that offers a parallel solution with 'No-penalty Parallism/Sparsity/Capacity/Switching' for modern training and inference. It supports Pytorch framework (version >= 1.10) and various GPUs including CUDA and ROCm. The tool enables Full Precision Inference of MoE-based Deepseek R1 671B on AMD MI300. Tutel provides features like all-to-all benchmarking, tensorcore option, NCCL timeout settings, Megablocks solution, and dynamic switchable configurations. Users can run Tutel in distributed mode across multiple GPUs and machines. The tool allows for custom MoE implementations and offers detailed usage examples and reference documentation.
hugging-chat-api
Unofficial HuggingChat Python API for creating chatbots, supporting features like image generation, web search, memorizing context, and changing LLMs. Users can log in, chat with the ChatBot, perform web searches, create new conversations, manage conversations, switch models, get conversation info, use assistants, and delete conversations. The API also includes a CLI mode with various commands for interacting with the tool. Users are advised not to use the application for high-stakes decisions or advice and to avoid high-frequency requests to preserve server resources.
rag-chat
The `@upstash/rag-chat` package simplifies the development of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) chat applications by providing Next.js compatibility with streaming support, built-in vector store, optional Redis compatibility for fast chat history management, rate limiting, and disableRag option. Users can easily set up the environment variables and initialize RAGChat to interact with AI models, manage knowledge base, chat history, and enable debugging features. Advanced configuration options allow customization of RAGChat instance with built-in rate limiting, observability via Helicone, and integration with Next.js route handlers and Vercel AI SDK. The package supports OpenAI models, Upstash-hosted models, and custom providers like TogetherAi and Replicate.
aio-pika
Aio-pika is a wrapper around aiormq for asyncio and humans. It provides a completely asynchronous API, object-oriented API, transparent auto-reconnects with complete state recovery, Python 3.7+ compatibility, transparent publisher confirms support, transactions support, and complete type-hints coverage.
ichigo
Ichigo is a local real-time voice AI tool that uses an early fusion technique to extend a text-based LLM to have native 'listening' ability. It is an open research experiment with improved multiturn capabilities and the ability to refuse processing inaudible queries. The tool is designed for open data, open weight, on-device Siri-like functionality, inspired by Meta's Chameleon paper. Ichigo offers a web UI demo and Gradio web UI for users to interact with the tool. It has achieved enhanced MMLU scores, stronger context handling, advanced noise management, and improved multi-turn capabilities for a robust user experience.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.
inferable
Inferable is an open source platform that helps users build reliable LLM-powered agentic automations at scale. It offers a managed agent runtime, durable tool calling, zero network configuration, multiple language support, and is fully open source under the MIT license. Users can define functions, register them with Inferable, and create runs that utilize these functions to automate tasks. The platform supports Node.js/TypeScript, Go, .NET, and React, and provides SDKs, core services, and bootstrap templates for various languages.
volga
Volga is a general purpose real-time data processing engine in Python for modern AI/ML systems. It aims to be a Python-native alternative to Flink/Spark Streaming with extended functionality for real-time AI/ML workloads. It provides a hybrid push+pull architecture, Entity API for defining data entities and feature pipelines, DataStream API for general data processing, and customizable data connectors. Volga can run on a laptop or a distributed cluster, making it suitable for building custom real-time AI/ML feature platforms or general data pipelines without relying on third-party platforms.

req_llm
ReqLLM is a Req-based library for LLM interactions, offering a unified interface to AI providers through a plugin-based architecture. It brings composability and middleware advantages to LLM interactions, with features like auto-synced providers/models, typed data structures, ergonomic helpers, streaming capabilities, usage & cost extraction, and a plugin-based provider system. Users can easily generate text, structured data, embeddings, and track usage costs. The tool supports various AI providers like Anthropic, OpenAI, Groq, Google, and xAI, and allows for easy addition of new providers. ReqLLM also provides API key management, detailed documentation, and a roadmap for future enhancements.
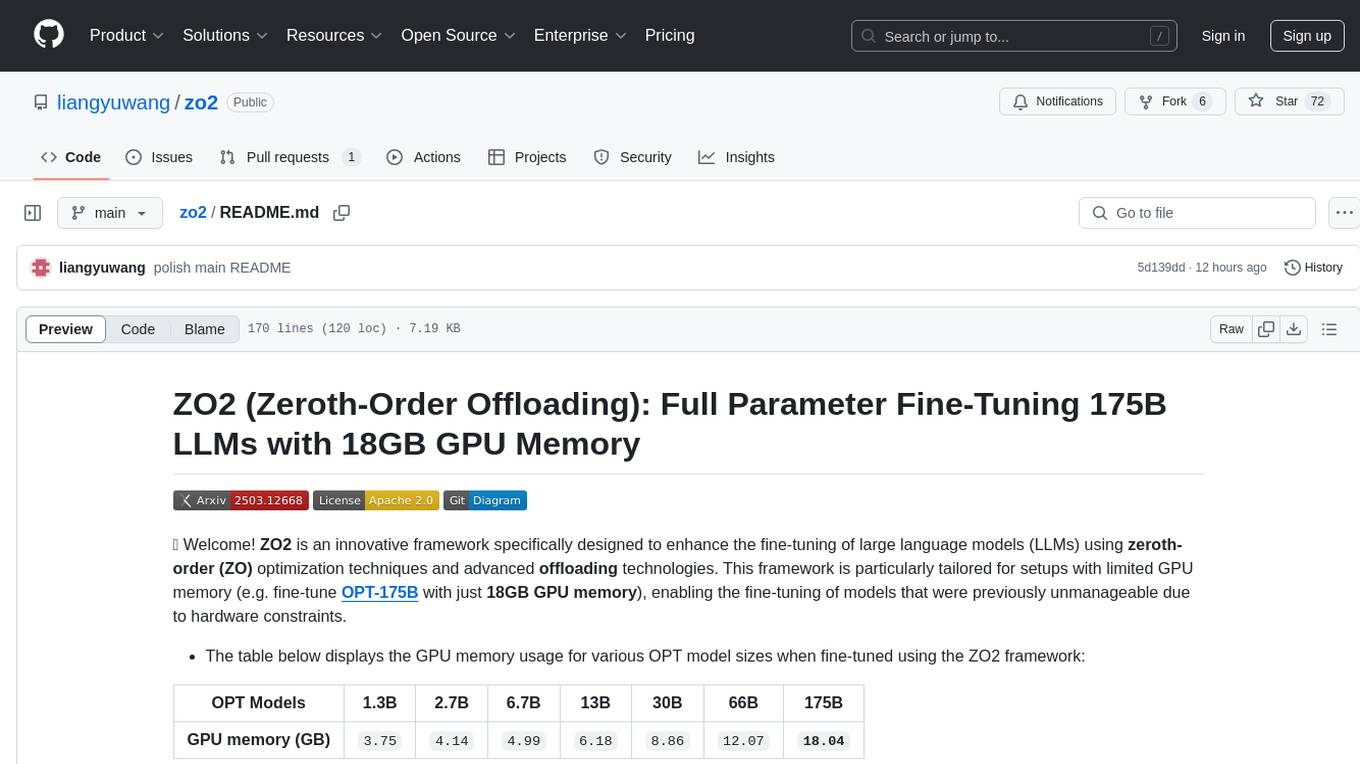
zo2
ZO2 (Zeroth-Order Offloading) is an innovative framework designed to enhance the fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) using zeroth-order (ZO) optimization techniques and advanced offloading technologies. It is tailored for setups with limited GPU memory, enabling the fine-tuning of models with over 175 billion parameters on single GPUs with as little as 18GB of memory. ZO2 optimizes CPU offloading, incorporates dynamic scheduling, and has the capability to handle very large models efficiently without extra time costs or accuracy losses.
datachain
DataChain is an open-source Python library for processing and curating unstructured data at scale. It supports AI-driven data curation using local ML models and LLM APIs, handles large datasets, and is Python-friendly with Pydantic objects. It excels at optimizing batch operations and is designed for offline data processing, curation, and ETL. Typical use cases include Computer Vision data curation, LLM analytics, and validation.
lionagi
LionAGI is a powerful intelligent workflow automation framework that introduces advanced ML models into any existing workflows and data infrastructure. It can interact with almost any model, run interactions in parallel for most models, produce structured pydantic outputs with flexible usage, automate workflow via graph based agents, use advanced prompting techniques, and more. LionAGI aims to provide a centralized agent-managed framework for "ML-powered tools coordination" and to dramatically lower the barrier of entries for creating use-case/domain specific tools. It is designed to be asynchronous only and requires Python 3.10 or higher.
claude-code.nvim
Claude Code Neovim Plugin is a seamless integration between Claude Code AI assistant and Neovim. It allows users to toggle Claude Code in a terminal window with a single key press, automatically detect and reload files modified by Claude Code, provide real-time buffer updates when files are changed externally, offer customizable window position and size, integrate with which-key, use git project root as working directory, maintain a modular code structure, provide type annotations with LuaCATS for better IDE support, offer configuration validation, and include a testing framework for reliability. The plugin creates a terminal buffer running the Claude Code CLI, sets up autocommands to detect file changes on disk, automatically reloads files modified by Claude Code, provides keymaps and commands for toggling the terminal, and detects git repositories to set the working directory to the git root.
beta9
Beta9 is an open-source platform for running scalable serverless GPU workloads across cloud providers. It allows users to scale out workloads to thousands of GPU or CPU containers, achieve ultrafast cold-start for custom ML models, automatically scale to zero to pay for only what is used, utilize flexible distributed storage, distribute workloads across multiple cloud providers, and easily deploy task queues and functions using simple Python abstractions. The platform is designed for launching remote serverless containers quickly, featuring a custom, lazy loading image format backed by S3/FUSE, a fast redis-based container scheduling engine, content-addressed storage for caching images and files, and a custom runc container runtime.
curator
Bespoke Curator is an open-source tool for data curation and structured data extraction. It provides a Python library for generating synthetic data at scale, with features like programmability, performance optimization, caching, and integration with HuggingFace Datasets. The tool includes a Curator Viewer for dataset visualization and offers a rich set of functionalities for creating and refining data generation strategies.
For similar tasks

aiologic
aiologic is a locking library for tasks synchronization and their communication. It provides primitives that are both async-aware and thread-aware, and can be used for interaction between async codes (async <-> async) in one thread as regular async primitives, async codes (async <-> async) in multiple threads, async code and sync one (async <-> sync) in one thread, async code and sync one (async <-> sync) in multiple threads, sync codes (sync <-> sync) in one thread as regular sync primitives, sync codes (sync <-> sync) in multiple threads as regular sync primitives. It offers synchronization primitives like events, barriers, semaphores, capacity limiters, locks, readers-writer locks, condition variables, communication primitives like queues, non-blocking primitives like flags and resource guards, and supports various concurrency libraries like asyncio, curio, trio, anyio, eventlet, gevent, and threading. aiologic is implemented entirely on effectively atomic operations, providing incredible speedup on PyPy compared to alternatives from the threading module. It works in free-threaded mode and ensures atomic operations even with GIL.
MiniAI-Face-Recognition-LivenessDetection-AndroidSDK
MiniAiLive provides system integrators with fast, flexible and extremely precise facial recognition with 3D passive face liveness detection (face anti-spoofing) that can be deployed across a number of scenarios, including security, access control, public safety, fintech, smart retail and home protection.
aiolimiter
An efficient implementation of a rate limiter for asyncio using the Leaky bucket algorithm, providing precise control over the rate a code section can be entered. It allows for limiting the number of concurrent entries within a specified time window, ensuring that a section of code is executed a maximum number of times in that period.
foundationallm
FoundationaLLM is a platform designed for deploying, scaling, securing, and governing generative AI in enterprises. It allows users to create AI agents grounded in enterprise data, integrate REST APIs, experiment with various large language models, centrally manage AI agents and their assets, deploy scalable vectorization data pipelines, enable non-developer users to create their own AI agents, control access with role-based access controls, and harness capabilities from Azure AI and Azure OpenAI. The platform simplifies integration with enterprise data sources, provides fine-grain security controls, scalability, extensibility, and addresses the challenges of delivering enterprise copilots or AI agents.
ragna
Ragna is a RAG orchestration framework designed for managing workflows and orchestrating tasks. It provides a comprehensive set of features for users to streamline their processes and automate repetitive tasks. With Ragna, users can easily create, schedule, and monitor workflows, making it an ideal tool for teams and individuals looking to improve their productivity and efficiency. The framework offers extensive documentation, community support, and a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to users of all skill levels. Whether you are a developer, data scientist, or project manager, Ragna can help you simplify your workflow management and boost your overall performance.
tegon
Tegon is an open-source AI-First issue tracking tool designed for engineering teams. It aims to simplify task management by leveraging AI and integrations to automate task creation, prioritize tasks, and enhance bug resolution. Tegon offers features like issues tracking, automatic title generation, AI-generated labels and assignees, custom views, and upcoming features like sprints and task prioritization. It integrates with GitHub, Slack, and Sentry to streamline issue tracking processes. Tegon also plans to introduce AI Agents like PR Agent and Bug Agent to enhance product management and bug resolution. Contributions are welcome, and the product is licensed under the MIT License.
Advanced-GPTs
Nerority's Advanced GPT Suite is a collection of 33 GPTs that can be controlled with natural language prompts. The suite includes tools for various tasks such as strategic consulting, business analysis, career profile building, content creation, educational purposes, image-based tasks, knowledge engineering, marketing, persona creation, programming, prompt engineering, role-playing, simulations, and task management. Users can access links, usage instructions, and guides for each GPT on their respective pages. The suite is designed for public demonstration and usage, offering features like meta-sequence optimization, AI priming, prompt classification, and optimization. It also provides tools for generating articles, analyzing contracts, visualizing data, distilling knowledge, creating educational content, exploring topics, generating marketing copy, simulating scenarios, managing tasks, and more.
aioclock
An asyncio-based scheduling framework designed for execution of periodic tasks with integrated support for dependency injection, enabling efficient and flexible task management. Aioclock is 100% async, light, fast, and resource-friendly. It offers features like task scheduling, grouping, trigger definition, easy syntax, Pydantic v2 validation, and upcoming support for running the task dispatcher on a different process and backend support for horizontal scaling.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.