
local-assistant-examples
Build your own ChatPDF and run them locally
Stars: 281
The Local Assistant Examples repository is a collection of educational examples showcasing the use of large language models (LLMs). It was initially created for a blog post on building a RAG model locally, and has since expanded to include more examples and educational material. Each example is housed in its own folder with a dedicated README providing instructions on how to run it. The repository is designed to be simple and educational, not for production use.
README:
Welcome to the Local Assistant Examples repository — a collection of educational examples built on top of large language models (LLMs). This repository was initially created as part of my blog post, Build your own RAG and run it locally: Langchain + Ollama + Streamlit.
Previously named local-rag-example, this project has been renamed to local-assistant-example to reflect the broader scope of its content. Over time, I decided to expand this project to include more examples and educational material, consolidating everything into one place rather than maintaining multiple repositories. Each example now lives in its own folder, with a dedicated README explaining the example and providing instructions on how to run it. The first example, originally from the blog post, can now be found in the simple-rag folder.
Available Examples
- Simple RAG: Demonstrates how to build and run a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) model locally.
More examples will be added soon, so stay tuned!
Note: This repository is not intended for production use. It is designed to be as simple as possible to help newcomers understand the concepts of working with LLMs application.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for local-assistant-examples
Similar Open Source Tools

local-assistant-examples
The Local Assistant Examples repository is a collection of educational examples showcasing the use of large language models (LLMs). It was initially created for a blog post on building a RAG model locally, and has since expanded to include more examples and educational material. Each example is housed in its own folder with a dedicated README providing instructions on how to run it. The repository is designed to be simple and educational, not for production use.
Large-Language-Model-Notebooks-Course
This practical free hands-on course focuses on Large Language models and their applications, providing a hands-on experience using models from OpenAI and the Hugging Face library. The course is divided into three major sections: Techniques and Libraries, Projects, and Enterprise Solutions. It covers topics such as Chatbots, Code Generation, Vector databases, LangChain, Fine Tuning, PEFT Fine Tuning, Soft Prompt tuning, LoRA, QLoRA, Evaluate Models, Knowledge Distillation, and more. Each section contains chapters with lessons supported by notebooks and articles. The course aims to help users build projects and explore enterprise solutions using Large Language Models.
examples
This repository contains a collection of sample applications and Jupyter Notebooks for hands-on experience with Pinecone vector databases and common AI patterns, tools, and algorithms. It includes production-ready examples for review and support, as well as learning-optimized examples for exploring AI techniques and building applications. Users can contribute, provide feedback, and collaborate to improve the resource.
xef
xef.ai is a one-stop library designed to bring the power of modern AI to applications and services. It offers integration with Large Language Models (LLM), image generation, and other AI services. The library is packaged in two layers: core libraries for basic AI services integration and integrations with other libraries. xef.ai aims to simplify the transition to modern AI for developers by providing an idiomatic interface, currently supporting Kotlin. Inspired by LangChain and Hugging Face, xef.ai may transmit source code and user input data to third-party services, so users should review privacy policies and take precautions. Libraries are available in Maven Central under the `com.xebia` group, with `xef-core` as the core library. Developers can add these libraries to their projects and explore examples to understand usage.
commonplace-bot
Commonplace Bot is a modern representation of the commonplace book, leveraging modern technological advancements in computation, data storage, machine learning, and networking. It aims to capture, engage, and share knowledge by providing a platform for users to collect ideas, quotes, and information, organize them efficiently, engage with the data through various strategies and triggers, and transform the data into new mediums for sharing. The tool utilizes embeddings and cached transformations for efficient data storage and retrieval, flips traditional engagement rules by engaging with the user, and enables users to alchemize raw data into new forms like art prompts. Commonplace Bot offers a unique approach to knowledge management and creative expression.
deep-seek
DeepSeek is a new experimental architecture for a large language model (LLM) powered internet-scale retrieval engine. Unlike current research agents designed as answer engines, DeepSeek aims to process a vast amount of sources to collect a comprehensive list of entities and enrich them with additional relevant data. The end result is a table with retrieved entities and enriched columns, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic. DeepSeek utilizes both standard keyword search and neural search to find relevant content, and employs an LLM to extract specific entities and their associated contents. It also includes a smaller answer agent to enrich the retrieved data, ensuring thoroughness. DeepSeek has the potential to revolutionize research and information gathering by providing a comprehensive and structured way to access information from the vastness of the internet.
AliceVision
AliceVision is a photogrammetric computer vision framework which provides a 3D reconstruction pipeline. It is designed to process images from different viewpoints and create detailed 3D models of objects or scenes. The framework includes various algorithms for feature detection, matching, and structure from motion. AliceVision is suitable for researchers, developers, and enthusiasts interested in computer vision, photogrammetry, and 3D modeling. It can be used for applications such as creating 3D models of buildings, archaeological sites, or objects for virtual reality and augmented reality experiences.
seemore
seemore is a vision language model developed in Pytorch, implementing components like image encoder, vision-language projector, and decoder language model. The model is built from scratch, including attention mechanisms and patch creation. It is designed for readability and hackability, with the intention to be improved upon. The implementation is based on public publications and borrows attention mechanism from makemore by Andrej Kapathy. The code was developed on Databricks using a single A100 for compute, and MLFlow is used for tracking metrics. The tool aims to provide a simplistic version of vision language models like Grok 1.5/GPT-4 Vision, suitable for experimentation and learning.
TypeChat
TypeChat is a library that simplifies the creation of natural language interfaces using types. Traditionally, building natural language interfaces has been challenging, often relying on complex decision trees to determine intent and gather necessary inputs for action. Large language models (LLMs) have simplified this process by allowing us to accept natural language input from users and match it to intent. However, this has introduced new challenges, such as the need to constrain the model's response for safety, structure responses from the model for further processing, and ensure the validity of the model's response. Prompt engineering aims to address these issues, but it comes with a steep learning curve and increased fragility as the prompt grows in size.
pearai-master
PearAI is an inventory that curates cutting-edge AI tools in one place, offering a unified interface for seamless tool integration. The repository serves as the conglomeration of all PearAI project repositories, including VSCode fork, AI chat functionalities, landing page, documentation, and server. Contributions are welcome through quests and issue tackling, with the project stack including TypeScript/Electron.js, Next.js/React, Python FastAPI, and Axiom for logging/telemetry.
husky
Husky is a research-focused programming language designed for next-generation computing. It aims to provide a powerful and ergonomic development experience for various tasks, including system level programming, web/native frontend development, parser/compiler tasks, game development, formal verification, machine learning, and more. With a strong type system and support for human-in-the-loop programming, Husky enables users to tackle complex tasks such as explainable image classification, natural language processing, and reinforcement learning. The language prioritizes debugging, visualization, and human-computer interaction, offering agile compilation and evaluation, multiparadigm support, and a commitment to a good ecosystem.
MediaAI
MediaAI is a repository containing lectures and materials for Aalto University's AI for Media, Art & Design course. The course is a hands-on, project-based crash course focusing on deep learning and AI techniques for artists and designers. It covers common AI algorithms & tools, their applications in art, media, and design, and provides hands-on practice in designing, implementing, and using these tools. The course includes lectures, exercises, and a final project based on students' interests. Students can complete the course without programming by creatively utilizing existing tools like ChatGPT and DALL-E. The course emphasizes collaboration, peer-to-peer tutoring, and project-based learning. It covers topics such as text generation, image generation, optimization, and game AI.
llm_agents
LLM Agents is a small library designed to build agents controlled by large language models. It aims to provide a better understanding of how such agents work in a concise manner. The library allows agents to be instructed by prompts, use custom-built components as tools, and run in a loop of Thought, Action, Observation. The agents leverage language models to generate Thought and Action, while tools like Python REPL, Google search, and Hacker News search provide Observations. The library requires setting up environment variables for OpenAI API and SERPAPI API keys. Users can create their own agents by importing the library and defining tools accordingly.
partykit
PartyServer is a repository containing libraries, examples, and documentation for building real-time apps with Cloudflare Workers. It includes core libraries for working with Durable Objects, WebSockets, Yjs support for real-time collaborative editing, pubsub at scale, state synchronization, and task scheduling. The repository also offers small examples in the `fixtures` directory to demonstrate usage. PartyServer aims to simplify the development of real-time applications by providing enhanced features and utilities for working with various technologies.
Large-Language-Models
Large Language Models (LLM) are used to browse the Wolfram directory and associated URLs to create the category structure and good word embeddings. The goal is to generate enriched prompts for GPT, Wikipedia, Arxiv, Google Scholar, Stack Exchange, or Google search. The focus is on one subdirectory: Probability & Statistics. Documentation is in the project textbook `Projects4.pdf`, which is available in the folder. It is recommended to download the document and browse your local copy with Chrome, Edge, or other viewers. Unlike on GitHub, you will be able to click on all the links and follow the internal navigation features. Look for projects related to NLP and LLM / xLLM. The best starting point is project 7.2.2, which is the core project on this topic, with references to all satellite projects. The project textbook (with solutions to all projects) is the core document needed to participate in the free course (deep tech dive) called **GenAI Fellowship**. For details about the fellowship, follow the link provided. An uncompressed version of `crawl_final_stats.txt.gz` is available on Google drive, which contains all the crawled data needed as input to the Python scripts in the XLLM5 and XLLM6 folders.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
For similar tasks

local-assistant-examples
The Local Assistant Examples repository is a collection of educational examples showcasing the use of large language models (LLMs). It was initially created for a blog post on building a RAG model locally, and has since expanded to include more examples and educational material. Each example is housed in its own folder with a dedicated README providing instructions on how to run it. The repository is designed to be simple and educational, not for production use.
llms-from-scratch-rs
This project provides Rust code that follows the text 'Build An LLM From Scratch' by Sebastian Raschka. It translates PyTorch code into Rust using the Candle crate, aiming to build a GPT-style LLM. Users can clone the repo, run examples/exercises, and access the same datasets as in the book. The project includes chapters on understanding large language models, working with text data, coding attention mechanisms, implementing a GPT model, pretraining unlabeled data, fine-tuning for classification, and fine-tuning to follow instructions.
ai-models
The `ai-models` command is a tool used to run AI-based weather forecasting models. It provides functionalities to install, run, and manage different AI models for weather forecasting. Users can easily install and run various models, customize model settings, download assets, and manage input data from different sources such as ECMWF, CDS, and GRIB files. The tool is designed to optimize performance by running on GPUs and provides options for better organization of assets and output files. It offers a range of command line options for users to interact with the models and customize their forecasting tasks.
ramalama
The Ramalama project simplifies working with AI by utilizing OCI containers. It automatically detects GPU support, pulls necessary software in a container, and runs AI models. Users can list, pull, run, and serve models easily. The tool aims to support various GPUs and platforms in the future, making AI setup hassle-free.
nosia
Nosia is a platform that allows users to run an AI model on their own data. It is designed to be easy to install and use. Users can follow the provided guides for quickstart, API usage, upgrading, starting, stopping, and troubleshooting. The platform supports custom installations with options for remote Ollama instances, custom completion models, and custom embeddings models. Advanced installation instructions are also available for macOS with a Debian or Ubuntu VM setup. Users can access the platform at 'https://nosia.localhost' and troubleshoot any issues by checking logs and job statuses.
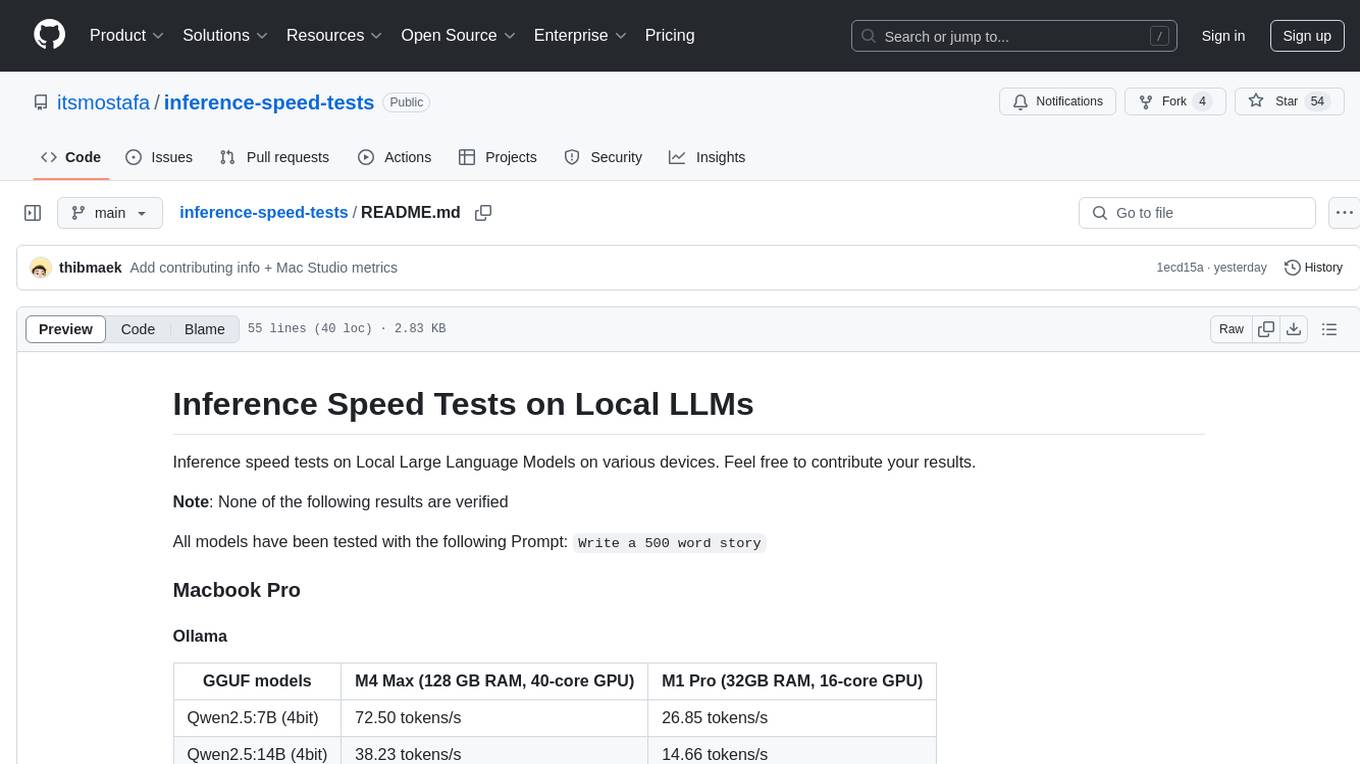
inference-speed-tests
This repository contains inference speed tests on Local Large Language Models on various devices. It provides results for different models tested on Macbook Pro and Mac Studio. Users can contribute their own results by running models with the provided prompt and adding the tokens-per-second output. Note that the results are not verified.
uzu
uzu is a high-performance inference engine for AI models on Apple Silicon. It features a simple, high-level API, hybrid architecture for GPU kernel computation, unified model configurations, traceable computations, and utilizes unified memory on Apple devices. The tool provides a CLI mode for running models, supports its own model format, and offers prebuilt Swift and TypeScript frameworks for bindings. Users can quickly start by adding the uzu dependency to their Cargo.toml and creating an inference Session with a specific model and configuration. Performance benchmarks show metrics for various models on Apple M2, highlighting the tokens/s speed for each model compared to llama.cpp with bf16/f16 precision.
intro_pharma_ai
This repository serves as an educational resource for pharmaceutical and chemistry students to learn the basics of Deep Learning through a collection of Jupyter Notebooks. The content covers various topics such as Introduction to Jupyter, Python, Cheminformatics & RDKit, Linear Regression, Data Science, Linear Algebra, Neural Networks, PyTorch, Convolutional Neural Networks, Transfer Learning, Recurrent Neural Networks, Autoencoders, Graph Neural Networks, and Summary. The notebooks aim to provide theoretical concepts to understand neural networks through code completion, but instructors are encouraged to supplement with their own lectures. The work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.