
commonplace-bot
An LLM augmented commonplace book, available for public viewing
Stars: 54
Commonplace Bot is a modern representation of the commonplace book, leveraging modern technological advancements in computation, data storage, machine learning, and networking. It aims to capture, engage, and share knowledge by providing a platform for users to collect ideas, quotes, and information, organize them efficiently, engage with the data through various strategies and triggers, and transform the data into new mediums for sharing. The tool utilizes embeddings and cached transformations for efficient data storage and retrieval, flips traditional engagement rules by engaging with the user, and enables users to alchemize raw data into new forms like art prompts. Commonplace Bot offers a unique approach to knowledge management and creative expression.
README:
CHECK OUT THE SISTER LIBRARY, QUOORDINATES!
Or check out the general purpose prototype editor I'm working on using Quill JS!
Commonplace Bot is a modern representation of the commonplace book. By using a combination of the newest computation technologies and creative design techniques, Commonplace Bot is the first of its kind to show what the commonplace book of the future may look like.
For millennia, people have kept commonplace books to capture, engage, and share knowledge. The commonplace book is a notebook where people write down quotes, ideas, and other information that they want to remember. It has gone by many names historically: zibaldone, zettelkasten, florilegium, and more. But all commonplace books have served roughly the same purpose: to serve as both an external memory and compute augmentation for human ideas. They are slightly seperate from diaries and journals, which are more focused on capturing the author's thoughts and feelings. Commonplace books are more focused on capturing ideas as raw material, and then transforming them into something new.
Before we talk about Commonplace Bot, let's talk about the history of the commonplace book and its modern implementations.
The first layer of the commonplace book is the book itself, the raw collection of ideas. Whether the author prefers paper or digital capture they follow the same basic principles: the author of the commonplace book collects ideas, quotes, and other information that they want to remember. The author can then organize these ideas into a structure that makes sense to them. This structure can be as simple as a table of contents, or as complex as a full-blown taxonomy. The author can then add metadata to each idea to help them find it later. This metadata can be as simple as a date, or as complex as a full-blown ontology like complex tagging systems. Next, many authors then add their own thoughts and ideas to each idea, and link ideas together in a bid to increase the utility of any particular node of knowledge. This is the basic structure of the commonplace book.
Modern techniques like the Zettelkasten and Second Brain movements have focused on making the capture process as efficient as possible. Thanks to apps like Notion, Obsidian, Readwise, etc. eliminating friction, the endgame idea is that the commonplace book will become a natural extension of the author's mind. The author will be able to capture ideas as they come, and then organize them in a way that makes sense to them.
Engaging with the data from the capture section in the commonplace book is all about strategy and triggers. Strategies include: spaced repetition, tickler files, exhaustive table of contents, etc. Triggers include: time, location, and context. The goal of engaging is to make the commonplace book a useful tool for the author. The author should be able to find the right data at the right time, and use it to solve problems and generate new ideas.
Modern techniques for engaging with data roughly oscillate around tagging and recommendation systems. This is done by tagging data with metadata, and then using that metadata to surface relevant data to the author. Explicit tagging systems can be found in apps like Notion, and in library systems like Dewey Decimal.
When you browse through a site like YouTube, you are engaging with a recommendation system, which functions as an implicit tagging machine. The recommendation system is using metadata to recommend videos to you, it's just not front and center. The same principle applies to the commonplace book. The author can use smart metadata to recommend data to themselves.
Sharing data is where the commonplace book "pays off". Sharing in the context of a commonplace book is in reality, transformation. Data in the commonplace book becomes a meme template of sorts, for a creative author to either change the message or change the medium. People have shared their entire commonplace books down to their decesendants. Some have even shared their commonplace books with the world, for example, Leonardo Da Vinci's notebooks -- but this is rare as it requires the author to have spent the effort curating honing and organizing their commonplace book into something that is useful to others.
Modern versions of sharing have largely been relegated to blogs and social profiles, where creators build a backlog of information, engage with it by transforming it in their expertise, and then share it with their audience. The commonplace book is the raw material for the creative process, but afaik, isn't the arbiter of transformation and sharing itself.
Using modern technological advancements in computation, data storage, machine learning, and networking, Commonplace Bot is a working example of what the Commonplace book of the future may look like, and what it may be capable of. It shows how a commonplace book can be leveraged by the individual author as well as their community to proliferate knowledge and ideas.
Let's revisit the three layers of the commonplace book in the context of Commonplace Bot.
The important evolution to the capture workflow for Commonplace Bot is to leverage embeddings and cached transformations. Basically, captured data is embedded into vector space where it can be combined and organized differently depending on the direction that the data is referenced from. Imagine having 1000 different table of contents, each with its own unique structure. This is the power of embeddings.
Cached transformations are the idea that the commonplace book can store the results of transformations, so that the author doesn't have to recompute them every time they want to use them. For example, Commonplace Bot transforms every quote into a question with the following prompt:
Generate a single question from this quote.
The end user cannot see the quote so DO NOT use any abstract concepts like "the speaker" or "the writer" in your question. BE EXPLICIT. DO NOT ASSUME the reader has read the quote.
DO NOT use passive voice and do not use passive pronouns like he/she/they/him/her etc.
You can use any of who/what/where/when/why.
Say nothing else.\n\nQuote:\n\n${highlight}\n\nQ:
This question is stored in the row of the database that contains the quote. This transformation is important for the engagement section of the data, which we will be taking a look at next.
In Commonplace Bot, the traditional rules of engagement are flipped on their head. Instead of the author engaging with the commonplace book and coming up with different strategies to interact with the same data, the commonplace book engages with the author (or in this case, any user).
In many semantic search systems, designers stop at the level of embedding the data, tossing up a search bar and calling it a day. I think that this is a faux pas, that embeddings can do so much more. For example, instead of merely performing a search we can use our paired questions to surface three starting points from the dataset for the user to engage with. This is akin to a museum guide helping the reader "wander" successfully. This greatly decreases the friction of the potential overwhelm from a commonplace set that has potentially tens of thousands of entries.
Once we have a starting point for our search, we can "delve" into the node, and return all of its neighbors, giving the user a local exhaustive search of a concept. This is a great way to explore a concept, to find new ideas that you may not have thought of before, and make connections.
We can "tldr" our data, making it easier to consume, or translate it, or whatever!
Basically, we can use Commonplace Bot to make the task of interfacing with a large set of curated data engaging from end to end.
The final layer of the commonplace book is sharing. In Commonplace Bot, sharing is the act of alchemizing raw data alongside the context of the user into something new, creating a new medium. For example, drawing. "Draw" extracts the substance of a quote, converts it to an art prompt and then uses a diffusion model to generate a unique image. This image is then stored alongside the quote, and can be shared with the world. Imagine just in time art galleries, visual links to the same data set.
Summarize the following into a theme and create an art prompt from the feel of the text aesthetically along the lines of: 'an abstract of [some unique lesser known art style from history] version of {x}' where x is the feel of the text aesthetically.
Just return the art prompt, say nothing else.
I've really only scratched the surface of the capabities of Commonplace Bot. If you read this far, it would behoove you to join the Discord and try it out yourself! Try typing /wander, choose a starting point, and then /delve into it. You can also /draw and /tldr quotes. Finally if you like a quote, you can /share it with the world.
- Birds of a Feather integration to fetch new interesting ideas
- Storytelling YT channel
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for commonplace-bot
Similar Open Source Tools

commonplace-bot
Commonplace Bot is a modern representation of the commonplace book, leveraging modern technological advancements in computation, data storage, machine learning, and networking. It aims to capture, engage, and share knowledge by providing a platform for users to collect ideas, quotes, and information, organize them efficiently, engage with the data through various strategies and triggers, and transform the data into new mediums for sharing. The tool utilizes embeddings and cached transformations for efficient data storage and retrieval, flips traditional engagement rules by engaging with the user, and enables users to alchemize raw data into new forms like art prompts. Commonplace Bot offers a unique approach to knowledge management and creative expression.
WritingAIPaper
WritingAIPaper is a comprehensive guide for beginners on crafting AI conference papers. It covers topics like paper structure, core ideas, framework construction, result analysis, and introduction writing. The guide aims to help novices navigate the complexities of academic writing and contribute to the field with clarity and confidence. It also provides tips on readability improvement, logical strength, defensibility, confusion time reduction, and information density increase. The appendix includes sections on AI paper production, a checklist for final hours, common negative review comments, and advice on dealing with paper rejection.
deep-seek
DeepSeek is a new experimental architecture for a large language model (LLM) powered internet-scale retrieval engine. Unlike current research agents designed as answer engines, DeepSeek aims to process a vast amount of sources to collect a comprehensive list of entities and enrich them with additional relevant data. The end result is a table with retrieved entities and enriched columns, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic. DeepSeek utilizes both standard keyword search and neural search to find relevant content, and employs an LLM to extract specific entities and their associated contents. It also includes a smaller answer agent to enrich the retrieved data, ensuring thoroughness. DeepSeek has the potential to revolutionize research and information gathering by providing a comprehensive and structured way to access information from the vastness of the internet.
prompt-tuning-playbook
The LLM Prompt Tuning Playbook is a comprehensive guide for improving the performance of post-trained Language Models (LLMs) through effective prompting strategies. It covers topics such as pre-training vs. post-training, considerations for prompting, a rudimentary style guide for prompts, and a procedure for iterating on new system instructions. The playbook emphasizes the importance of clear, concise, and explicit instructions to guide LLMs in generating desired outputs. It also highlights the iterative nature of prompt development and the need for systematic evaluation of model responses.
Large-Language-Model-Notebooks-Course
This practical free hands-on course focuses on Large Language models and their applications, providing a hands-on experience using models from OpenAI and the Hugging Face library. The course is divided into three major sections: Techniques and Libraries, Projects, and Enterprise Solutions. It covers topics such as Chatbots, Code Generation, Vector databases, LangChain, Fine Tuning, PEFT Fine Tuning, Soft Prompt tuning, LoRA, QLoRA, Evaluate Models, Knowledge Distillation, and more. Each section contains chapters with lessons supported by notebooks and articles. The course aims to help users build projects and explore enterprise solutions using Large Language Models.
Deep-Dive-Into-AI-With-MLX-PyTorch
Deep Dive into AI with MLX and PyTorch is an educational initiative focusing on AI, machine learning, and deep learning using Apple's MLX and Meta's PyTorch frameworks. The repository contains comprehensive guides, in-depth analyses, and resources for learning and exploring AI concepts. It aims to cater to audiences ranging from beginners to experienced individuals, providing detailed explanations, examples, and translations between PyTorch and MLX. The project emphasizes open-source contributions, knowledge sharing, and continuous learning in the field of AI.
ClipboardConqueror
Clipboard Conqueror is a multi-platform omnipresent copilot alternative. Currently requiring a kobold united or openAI compatible back end, this software brings powerful LLM based tools to any text field, the universal copilot you deserve. It simply works anywhere. No need to sign in, no required key. Provided you are using local AI, CC is a data secure alternative integration provided you trust whatever backend you use. *Special thank you to the creators of KoboldAi, KoboldCPP, llamma, openAi, and the communities that made all this possible to figure out.
raft
RAFT (Retrieval-Augmented Fine-Tuning) is a method for creating conversational agents that realistically emulate specific human targets. It involves a dual-phase process of fine-tuning and retrieval-based augmentation to generate nuanced and personalized dialogue. The tool is designed to combine interview transcripts with memories from past writings to enhance language model responses. RAFT has the potential to advance the field of personalized, context-sensitive conversational agents.
pearai-master
PearAI is an inventory that curates cutting-edge AI tools in one place, offering a unified interface for seamless tool integration. The repository serves as the conglomeration of all PearAI project repositories, including VSCode fork, AI chat functionalities, landing page, documentation, and server. Contributions are welcome through quests and issue tackling, with the project stack including TypeScript/Electron.js, Next.js/React, Python FastAPI, and Axiom for logging/telemetry.
obsidian-weaver
Obsidian Weaver is a plugin that integrates ChatGPT/GPT-3 into the note-taking workflow of Obsidian. It allows users to easily access AI-generated suggestions and insights within Obsidian, enhancing the writing and brainstorming process. The plugin respects Obsidian's philosophy of storing notes locally, ensuring data security and privacy. Weaver offers features like creating new chat sessions with the AI assistant and receiving instant responses, all within the Obsidian environment. It provides a seamless integration with Obsidian's interface, making the writing process efficient and helping users stay focused. The plugin is constantly being improved with new features and updates to enhance the note-taking experience.
Deej-AI
Deej-A.I. is an advanced machine learning project that aims to revolutionize music recommendation systems by using artificial intelligence to analyze and recommend songs based on their content and characteristics. The project involves scraping playlists from Spotify, creating embeddings of songs, training neural networks to analyze spectrograms, and generating recommendations based on similarities in music features. Deej-A.I. offers a unique approach to music curation, focusing on the 'what' rather than the 'how' of DJing, and providing users with personalized and creative music suggestions.
claudine
Claudine is an AI agent designed to reason and act autonomously, leveraging the Anthropic API, Unix command line tools, HTTP, local hard drive data, and internet data. It can administer computers, analyze files, implement features in source code, create new tools, and gather contextual information from the internet. Users can easily add specialized tools. Claudine serves as a blueprint for implementing complex autonomous systems, with potential for customization based on organization-specific needs. The tool is based on the anthropic-kotlin-sdk and aims to evolve into a versatile command line tool similar to 'git', enabling branching sessions for different tasks.
MediaAI
MediaAI is a repository containing lectures and materials for Aalto University's AI for Media, Art & Design course. The course is a hands-on, project-based crash course focusing on deep learning and AI techniques for artists and designers. It covers common AI algorithms & tools, their applications in art, media, and design, and provides hands-on practice in designing, implementing, and using these tools. The course includes lectures, exercises, and a final project based on students' interests. Students can complete the course without programming by creatively utilizing existing tools like ChatGPT and DALL-E. The course emphasizes collaboration, peer-to-peer tutoring, and project-based learning. It covers topics such as text generation, image generation, optimization, and game AI.
start-llms
This repository is a comprehensive guide for individuals looking to start and improve their skills in Large Language Models (LLMs) without an advanced background in the field. It provides free resources, online courses, books, articles, and practical tips to become an expert in machine learning. The guide covers topics such as terminology, transformers, prompting, retrieval augmented generation (RAG), and more. It also includes recommendations for podcasts, YouTube videos, and communities to stay updated with the latest news in AI and LLMs.

local-chat
LocalChat is a simple, easy-to-set-up, and open-source local AI chat tool that allows users to interact with generative language models on their own computers without transmitting data to a cloud server. It provides a chat-like interface for users to experience ChatGPT-like behavior locally, ensuring GDPR compliance and data privacy. Users can download LocalChat for macOS, Windows, or Linux to chat with open-weight generative language models.
seemore
seemore is a vision language model developed in Pytorch, implementing components like image encoder, vision-language projector, and decoder language model. The model is built from scratch, including attention mechanisms and patch creation. It is designed for readability and hackability, with the intention to be improved upon. The implementation is based on public publications and borrows attention mechanism from makemore by Andrej Kapathy. The code was developed on Databricks using a single A100 for compute, and MLFlow is used for tracking metrics. The tool aims to provide a simplistic version of vision language models like Grok 1.5/GPT-4 Vision, suitable for experimentation and learning.
For similar tasks

commonplace-bot
Commonplace Bot is a modern representation of the commonplace book, leveraging modern technological advancements in computation, data storage, machine learning, and networking. It aims to capture, engage, and share knowledge by providing a platform for users to collect ideas, quotes, and information, organize them efficiently, engage with the data through various strategies and triggers, and transform the data into new mediums for sharing. The tool utilizes embeddings and cached transformations for efficient data storage and retrieval, flips traditional engagement rules by engaging with the user, and enables users to alchemize raw data into new forms like art prompts. Commonplace Bot offers a unique approach to knowledge management and creative expression.
blinko
Blinko is an innovative open-source project designed for individuals who want to quickly capture and organize their fleeting thoughts. It allows users to seamlessly jot down ideas the moment they strike, ensuring that no spark of creativity is lost. With advanced AI-powered note retrieval, data ownership, efficient and fast capturing, lightweight architecture, and open collaboration, Blinko offers a comprehensive solution for managing and accessing notes.
blinko
Blinko is an innovative open-source project designed for individuals who want to quickly capture and organize their fleeting thoughts. It allows users to seamlessly jot down ideas, ensuring no spark of creativity is lost. With AI-enhanced note retrieval, data ownership, efficient and fast note-taking, lightweight architecture, and open collaboration, Blinko offers a robust platform for managing and accessing notes effortlessly.
Beaver-Notes
Beaver Notes is a privacy-first, local-first note-taking app designed to help users capture ideas, organize knowledge, and connect notes without sending data to the cloud by default. It offers cross-platform support, secure data storage, markdown support, community-driven development, and various features like tags, folders, note linking, locked notes, flexible sync options, and open-source collaboration. The tool prioritizes privacy, simplicity, and user control over their data, making it a reliable choice for individuals seeking a secure and efficient note-taking solution.
OpenAGI
OpenAGI is an AI agent creation package designed for researchers and developers to create intelligent agents using advanced machine learning techniques. The package provides tools and resources for building and training AI models, enabling users to develop sophisticated AI applications. With a focus on collaboration and community engagement, OpenAGI aims to facilitate the integration of AI technologies into various domains, fostering innovation and knowledge sharing among experts and enthusiasts.
allAI
allAI is a toolbox for AI-related discussions and resources. It provides a platform for sharing knowledge, tutorials, and addressing common AI-related queries. The repository aims to foster a community for AI enthusiasts to engage in meaningful conversations and collaborations. Users can access Quark Cloud for downloads and instructional videos. Additionally, the repository encourages contributions and prohibits the dissemination of spam, advertisements, or unsolicited promotions. The project is supported by Pinokio and offers users the freedom to utilize, modify, and distribute the software within the specified conditions.
mo-ai-studio
Mo AI Studio is an enterprise-level AI agent running platform that enables the operation of customized intelligent AI agents with system-level capabilities. It supports various IDEs and programming languages, allows modification of multiple files with reasoning, cross-project context modifications, customizable agents, system-level file operations, document writing, question answering, knowledge sharing, and flexible output processors. The platform also offers various setters and a custom component publishing feature. Mo AI Studio is a fusion of artificial intelligence and human creativity, designed to bring unprecedented efficiency and innovation to enterprises.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.
For similar jobs

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.
daily-poetry-image
Daily Chinese ancient poetry and AI-generated images powered by Bing DALL-E-3. GitHub Action triggers the process automatically. Poetry is provided by Today's Poem API. The website is built with Astro.
exif-photo-blog
EXIF Photo Blog is a full-stack photo blog application built with Next.js, Vercel, and Postgres. It features built-in authentication, photo upload with EXIF extraction, photo organization by tag, infinite scroll, light/dark mode, automatic OG image generation, a CMD-K menu with photo search, experimental support for AI-generated descriptions, and support for Fujifilm simulations. The application is easy to deploy to Vercel with just a few clicks and can be customized with a variety of environment variables.
SillyTavern
SillyTavern is a user interface you can install on your computer (and Android phones) that allows you to interact with text generation AIs and chat/roleplay with characters you or the community create. SillyTavern is a fork of TavernAI 1.2.8 which is under more active development and has added many major features. At this point, they can be thought of as completely independent programs.
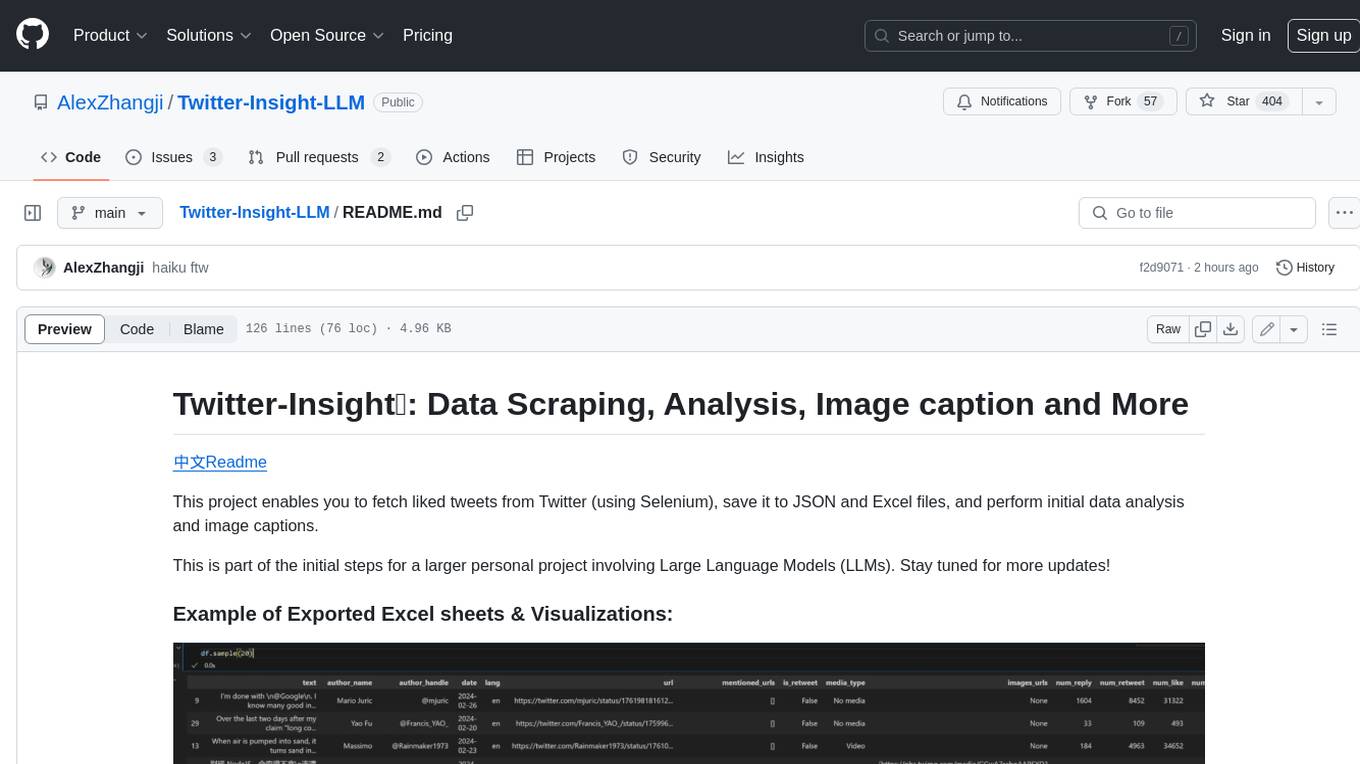
Twitter-Insight-LLM
This project enables you to fetch liked tweets from Twitter (using Selenium), save it to JSON and Excel files, and perform initial data analysis and image captions. This is part of the initial steps for a larger personal project involving Large Language Models (LLMs).
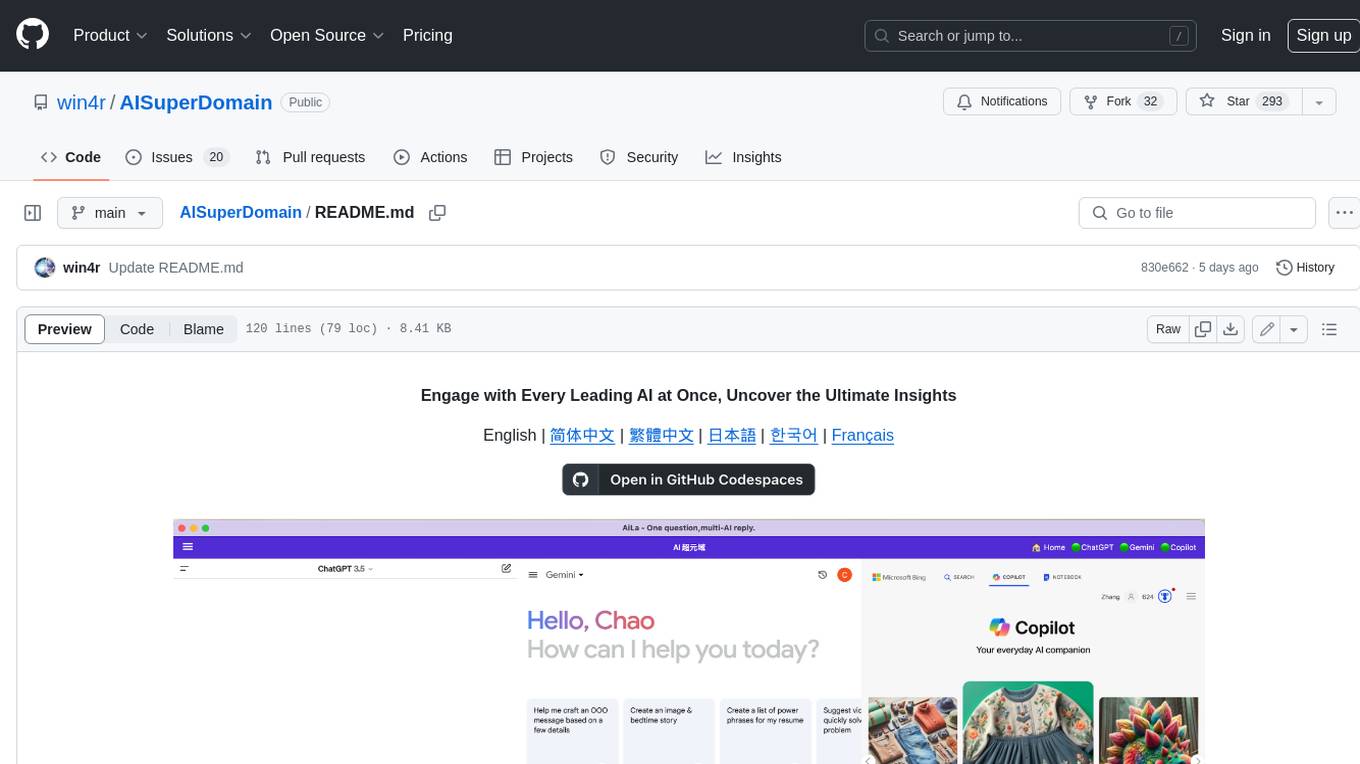
AISuperDomain
Aila Desktop Application is a powerful tool that integrates multiple leading AI models into a single desktop application. It allows users to interact with various AI models simultaneously, providing diverse responses and insights to their inquiries. With its user-friendly interface and customizable features, Aila empowers users to engage with AI seamlessly and efficiently. Whether you're a researcher, student, or professional, Aila can enhance your AI interactions and streamline your workflow.
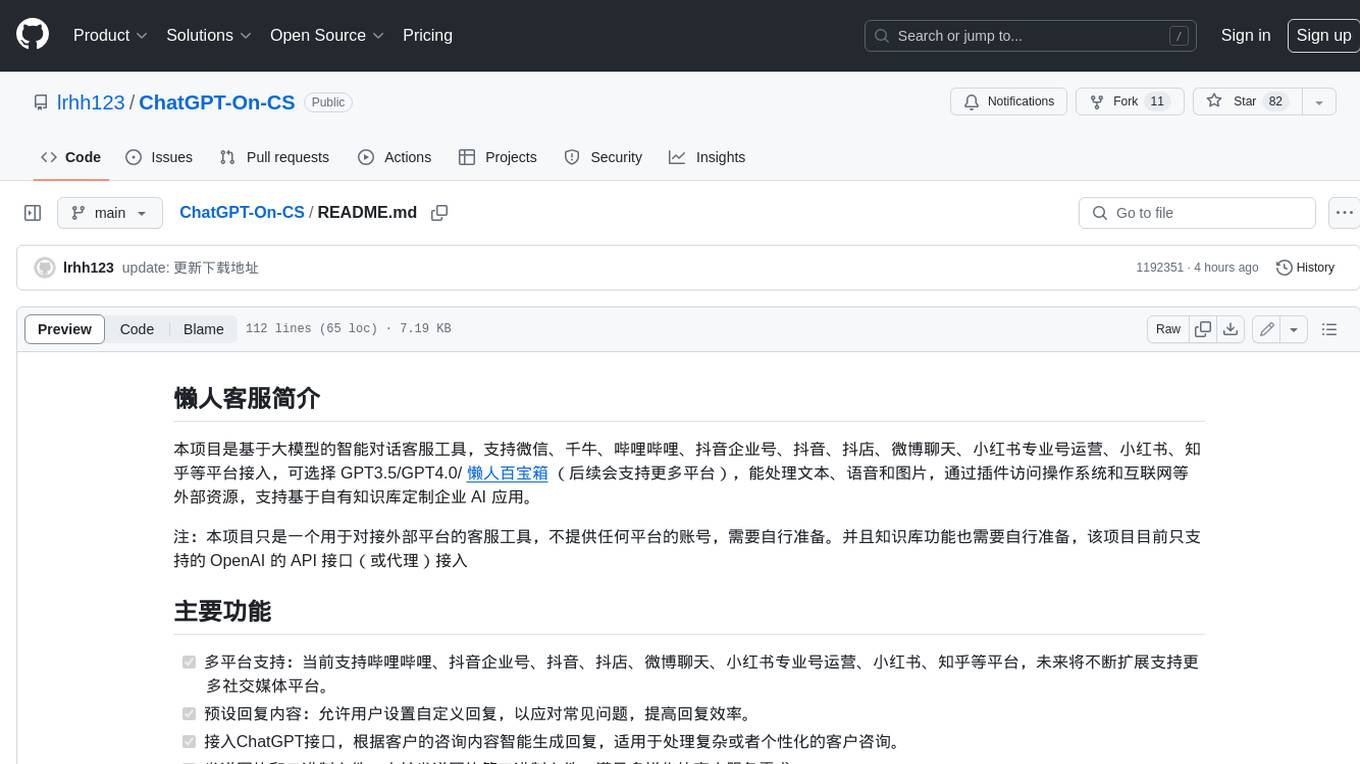
ChatGPT-On-CS
This project is an intelligent dialogue customer service tool based on a large model, which supports access to platforms such as WeChat, Qianniu, Bilibili, Douyin Enterprise, Douyin, Doudian, Weibo chat, Xiaohongshu professional account operation, Xiaohongshu, Zhihu, etc. You can choose GPT3.5/GPT4.0/ Lazy Treasure Box (more platforms will be supported in the future), which can process text, voice and pictures, and access external resources such as operating systems and the Internet through plug-ins, and support enterprise AI applications customized based on their own knowledge base.
obs-localvocal
LocalVocal is a live-streaming AI assistant plugin for OBS that allows you to transcribe audio speech into text and perform various language processing functions on the text using AI / LLMs (Large Language Models). It's privacy-first, with all data staying on your machine, and requires no GPU, cloud costs, network, or downtime.