
nosia
Nosia is a platform that allows you to run an AI model on your own data. It is designed to be easy to install and use.
Stars: 97
Nosia is a platform that allows users to run an AI model on their own data. It is designed to be easy to install and use. Users can follow the provided guides for quickstart, API usage, upgrading, starting, stopping, and troubleshooting. The platform supports custom installations with options for remote Ollama instances, custom completion models, and custom embeddings models. Advanced installation instructions are also available for macOS with a Debian or Ubuntu VM setup. Users can access the platform at 'https://nosia.localhost' and troubleshoot any issues by checking logs and job statuses.
README:
Nosia is a platform that allows you to run an AI model on your own data. It is designed to be easy to install and use.
You can follow this README or go to the Nosia Guides.
https://github.com/nosia-ai/nosia/assets/1692273/ce60094b-abb5-4ed4-93aa-f69485e058b0
https://github.com/nosia-ai/nosia/assets/1692273/671ccb6a-054c-4dc2-bcd9-2b874a888548
It will install Docker, Ollama, and Nosia on a macOS, Debian or Ubuntu machine.
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nosia-ai/nosia-install/main/nosia-install.sh | shYou should see the following output:
[x] Setting up environment
[x] Setting up Docker
[x] Setting up Ollama
[x] Starting Ollama
[x] Starting Nosia
You can now access Nosia at https://nosia.localhost
By default, Nosia sets up ollama locally.
To use a remote Ollama instance, set the OLLAMA_BASE_URL environment variable during configuration.
Example:
Replace $OLLAMA_HOST_IP with the FQDN or IP address of your Ollama host and run:
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nosia-ai/nosia-install/main/nosia-install.sh \
| OLLAMA_BASE_URL=http://$OLLAMA_HOST_IP:11434 shBy default, Nosia uses:
- Completion model:
granite3.3:2b - Embeddings model:
granite-embedding:278m - Checking model:
granite3-guardian:2b
You can use any completion model available on Ollama by setting the LLM_MODEL environment variable during the installation.
Example:
To use the mistral model, run:
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nosia-ai/nosia-install/main/nosia-install.sh \
| LLM_MODEL=mistral shAt this time, the granite-embedding:278m embeddings model is required for Nosia to work.
If you use new dimensions by using a new embeddings model, you'll need to:
-
Change the
EMBEDDING_DIMENSIONSenvironment variable. -
Re-execute the change vector limit database migration:
bin/rails db:migrate:redo:primary VERSION=20241216213448- Re-vectorize your chunks (this could take a while):
bin/rails cDocument.find_each(&:vectorize!)On macOS, install Homebrew:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"Then install Ollama with Homebrew:
Replace $OLLAMA_HOST_IP with the IP address of the Ollama host machine and run the following command:
brew install ollama
ollama pull granite3.3:2b
ollama pull granite3-guardian:2b
ollama pull granite-embedding:278m
OLLAMA_BASE_URL=$OLLAMA_HOST_IP:11434 OLLAMA_KEEP_ALIVE=0 OLLAMA_MAX_LOADED_MODELS=3 ollama serveOn the Debian/Ubuntu VM:
Replace $OLLAMA_HOST_IP with the IP address of the host machine and run the following command:
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nosia-ai/nosia-install/main/nosia-install.sh \
| OLLAMA_BASE_URL=http://$OLLAMA_HOST_IP:11434 shYou should see the following output:
[x] Setting up environment
[x] Setting up Docker
[x] Setting up Ollama
[x] Starting Ollama
[x] Starting Nosia
From the VM, you can access Nosia at https://nosia.localhost
If you want to access Nosia from the host machine, you may need to forward the port from the VM to the host machine.
Replace $USER with the username of the VM, $VM_IP with the IP address of the VM, and $LOCAL_PORT with the port you want to use on the host machine, 8443 for example, and run the following command:
ssh $USER@$VM_IP -L $LOCAL_PORT:localhost:443After running the command, you can access Nosia at https://nosia.localhost:$LOCAL_PORT.
- Go as a logged in user to
https://nosia.localhost/api_tokens - Generate and copy your token
- Use your favorite OpenAI chat completion API client by configuring API base to
https://nosia.localhost/v1and API key with your token.
You can upgrade the services with the following command:
./script/upgradeYou can start the services with the following command:
./script/startYou can stop the services with the following command:
./script/stopIf you encounter any issue:
- during the installation, you can check the logs at
./log/production.log - during the use waiting for an AI response, you can check the jobs at
http://<IP>:3000/jobs - with Nosia, you can check the logs with
docker compose -f ./docker-compose.yml logs -f - with the Ollama server, you can check the logs at
~/.ollama/logs/server.log
If you need further assistance, please open an issue!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for nosia
Similar Open Source Tools

nosia
Nosia is a platform that allows users to run an AI model on their own data. It is designed to be easy to install and use. Users can follow the provided guides for quickstart, API usage, upgrading, starting, stopping, and troubleshooting. The platform supports custom installations with options for remote Ollama instances, custom completion models, and custom embeddings models. Advanced installation instructions are also available for macOS with a Debian or Ubuntu VM setup. Users can access the platform at 'https://nosia.localhost' and troubleshoot any issues by checking logs and job statuses.
lexido
Lexido is an innovative assistant for the Linux command line, designed to boost your productivity and efficiency. Powered by Gemini Pro 1.0 and utilizing the free API, Lexido offers smart suggestions for commands based on your prompts and importantly your current environment. Whether you're installing software, managing files, or configuring system settings, Lexido streamlines the process, making it faster and more intuitive.
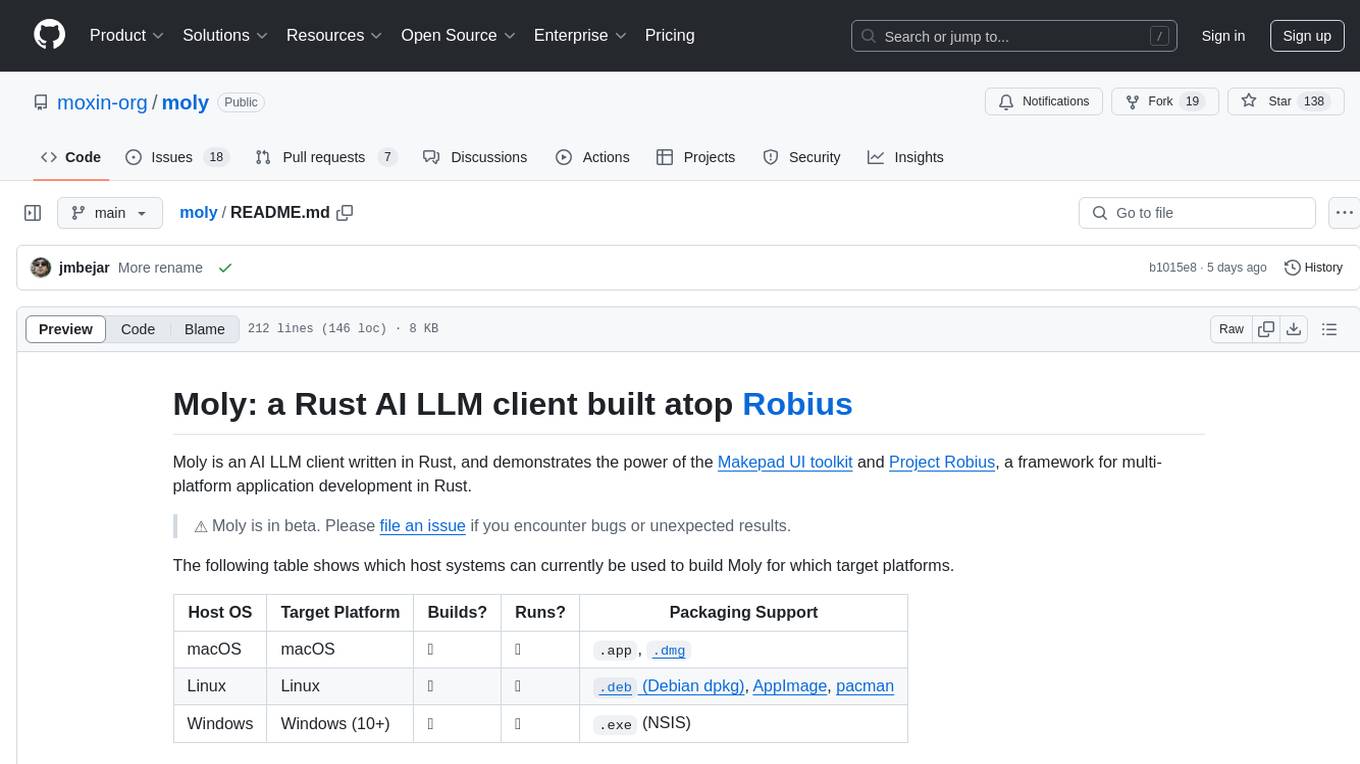
moly
Moly is an AI LLM client written in Rust, showcasing the capabilities of the Makepad UI toolkit and Project Robius, a framework for multi-platform application development in Rust. It is currently in beta, allowing users to build and run Moly on macOS, Linux, and Windows. The tool provides packaging support for different platforms, such as `.app`, `.dmg`, `.deb`, AppImage, pacman, and `.exe` (NSIS). Users can easily set up WasmEdge using `moly-runner` and leverage `cargo` commands to build and run Moly. Additionally, Moly offers pre-built releases for download and supports packaging for distribution on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
shortest
Shortest is a project for local development that helps set up environment variables and services for a web application. It provides a guide for setting up Node.js and pnpm dependencies, configuring services like Clerk, Vercel Postgres, Anthropic, Stripe, and GitHub OAuth, and running the application and tests locally.
comfy-cli
Comfy-cli is a command line tool designed to facilitate the installation and management of ComfyUI, an open-source machine learning framework. Users can easily set up ComfyUI, install packages, and manage custom nodes directly from the terminal. The tool offers features such as easy installation, seamless package management, custom node management, checkpoint downloads, cross-platform compatibility, and comprehensive documentation. Comfy-cli simplifies the process of working with ComfyUI, making it convenient for users to handle various tasks related to the framework.
ChatGPT
The ChatGPT API Free Reverse Proxy provides free self-hosted API access to ChatGPT (`gpt-3.5-turbo`) with OpenAI's familiar structure, eliminating the need for code changes. It offers streaming response, API endpoint compatibility, and complimentary access without an API key. Installation options include Docker, PC/Server, and Termux on Android devices. The API can be accessed through a self-hosted local server or a pre-hosted API with an API key obtained from the Discord server. Usage examples are provided for Python and Node.js, and the project is licensed under AGPL-3.0.
termax
Termax is an LLM agent in your terminal that converts natural language to commands. It is featured by: - Personalized Experience: Optimize the command generation with RAG. - Various LLMs Support: OpenAI GPT, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, Mistral AI, and more. - Shell Extensions: Plugin with popular shells like `zsh`, `bash` and `fish`. - Cross Platform: Able to run on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
comfy-cli
comfy-cli is a command line tool designed to simplify the installation and management of ComfyUI, an open-source machine learning framework. It allows users to easily set up ComfyUI, install packages, manage custom nodes, download checkpoints, and ensure cross-platform compatibility. The tool provides comprehensive documentation and examples to aid users in utilizing ComfyUI efficiently.
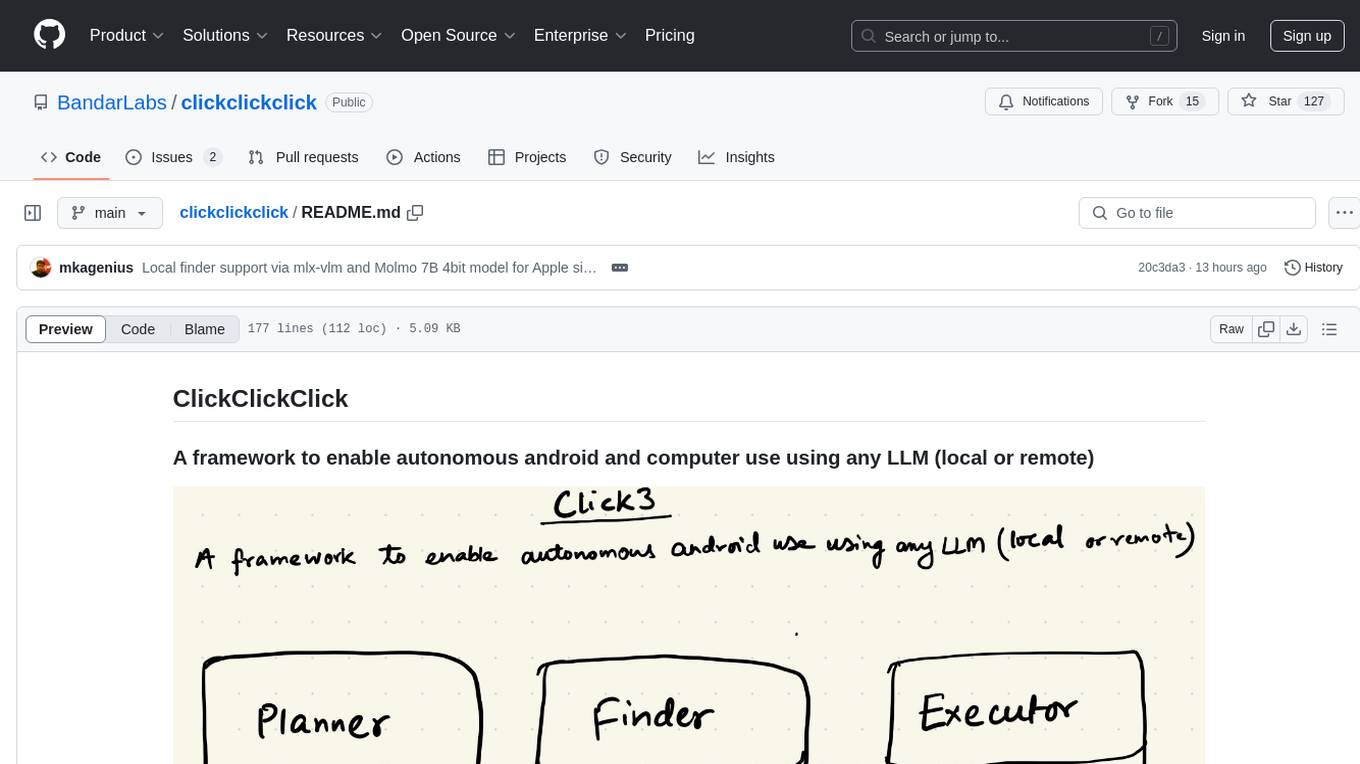
clickclickclick
ClickClickClick is a framework designed to enable autonomous Android and computer use using various LLM models, both locally and remotely. It supports tasks such as drafting emails, opening browsers, and starting games, with current support for local models via Ollama, Gemini, and GPT 4o. The tool is highly experimental and evolving, with the best results achieved using specific model combinations. Users need prerequisites like `adb` installation and USB debugging enabled on Android phones. The tool can be installed via cloning the repository, setting up a virtual environment, and installing dependencies. It can be used as a CLI tool or script, allowing users to configure planner and finder models for different tasks. Additionally, it can be used as an API to execute tasks based on provided prompts, platform, and models.
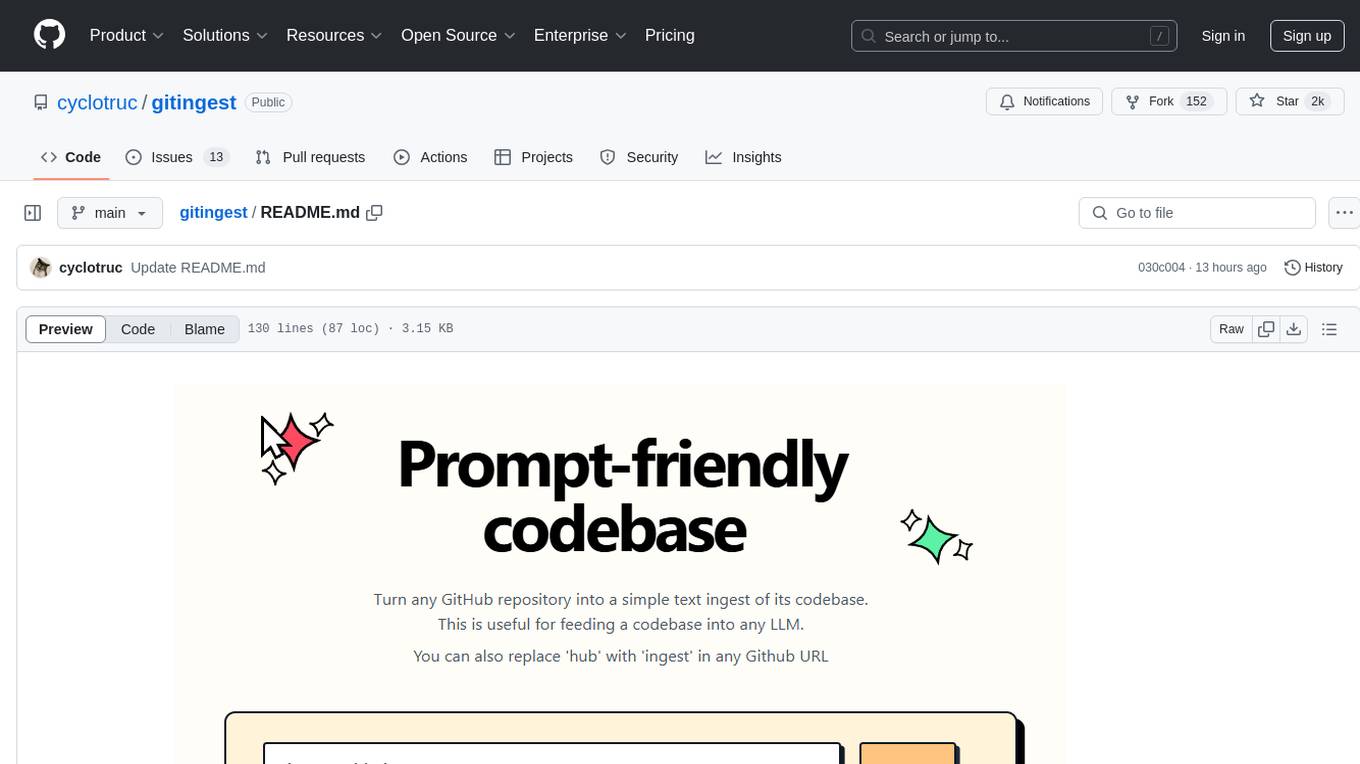
gitingest
GitIngest is a tool that allows users to turn any Git repository into a prompt-friendly text ingest for LLMs. It provides easy code context by generating a text digest from a git repository URL or directory. The tool offers smart formatting for optimized output format for LLM prompts and provides statistics about file and directory structure, size of the extract, and token count. GitIngest can be used as a CLI tool on Linux and as a Python package for code integration. The tool is built using Tailwind CSS for frontend, FastAPI for backend framework, tiktoken for token estimation, and apianalytics.dev for simple analytics. Users can self-host GitIngest by building the Docker image and running the container. Contributions to the project are welcome, and the tool aims to be beginner-friendly for first-time contributors with a simple Python and HTML codebase.
tiledesk-dashboard
Tiledesk is an open-source live chat platform with integrated chatbots written in Node.js and Express. It is designed to be a multi-channel platform for web, Android, and iOS, and it can be used to increase sales or provide post-sales customer service. Tiledesk's chatbot technology allows for automation of conversations, and it also provides APIs and webhooks for connecting external applications. Additionally, it offers a marketplace for apps and features such as CRM, ticketing, and data export.
trieve
Trieve is an advanced relevance API for hybrid search, recommendations, and RAG. It offers a range of features including self-hosting, semantic dense vector search, typo tolerant full-text/neural search, sub-sentence highlighting, recommendations, convenient RAG API routes, the ability to bring your own models, hybrid search with cross-encoder re-ranking, recency biasing, tunable popularity-based ranking, filtering, duplicate detection, and grouping. Trieve is designed to be flexible and customizable, allowing users to tailor it to their specific needs. It is also easy to use, with a simple API and well-documented features.
air
Air is a live-reloading command line utility for developing Go applications. It provides colorful log output, customizable build or any command, support for excluding subdirectories, and allows watching new directories after Air started. Users can overwrite specific configuration from arguments and pass runtime arguments for running the built binary. Air can be installed via `go install`, `install.sh`, or `goblin.run`, and can also be used with Docker/Podman. It supports debugging, Docker Compose, and provides a Q&A section for common issues. The tool requires Go 1.16+ for development and welcomes pull requests. Air is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0.
screeps-starter-rust
screeps-starter-rust is a Rust AI starter kit for Screeps: World, a JavaScript-based MMO game. It utilizes the screeps-game-api bindings from the rustyscreeps organization and wasm-pack for building Rust code to WebAssembly. The example includes Rollup for bundling javascript, Babel for transpiling code, and screeps-api Node.js package for deployment. Users can refer to the Rust version of game APIs documentation at https://docs.rs/screeps-game-api/. The tool supports most crates on crates.io, except those interacting with OS APIs.
RoboMatrix
RoboMatrix is a skill-centric hierarchical framework for scalable robot task planning and execution in an open-world environment. It provides a structured approach to robot task execution using a combination of hardware components, environment configuration, installation procedures, and data collection methods. The framework is developed using the ROS2 framework on Ubuntu and supports robots from DJI's RoboMaster series. Users can follow the provided installation guidance to set up RoboMatrix and utilize it for various tasks such as data collection, task execution, and dataset construction. The framework also includes a supervised fine-tuning dataset and aims to optimize communication and release additional components in the future.

rclip
rclip is a command-line photo search tool powered by the OpenAI's CLIP neural network. It allows users to search for images using text queries, similar image search, and combining multiple queries. The tool extracts features from photos to enable searching and indexing, with options for previewing results in supported terminals or custom viewers. Users can install rclip on Linux, macOS, and Windows using different installation methods. The repository follows the Conventional Commits standard and welcomes contributions from the community.
For similar tasks
ai-models
The `ai-models` command is a tool used to run AI-based weather forecasting models. It provides functionalities to install, run, and manage different AI models for weather forecasting. Users can easily install and run various models, customize model settings, download assets, and manage input data from different sources such as ECMWF, CDS, and GRIB files. The tool is designed to optimize performance by running on GPUs and provides options for better organization of assets and output files. It offers a range of command line options for users to interact with the models and customize their forecasting tasks.
ramalama
The Ramalama project simplifies working with AI by utilizing OCI containers. It automatically detects GPU support, pulls necessary software in a container, and runs AI models. Users can list, pull, run, and serve models easily. The tool aims to support various GPUs and platforms in the future, making AI setup hassle-free.
local-assistant-examples
The Local Assistant Examples repository is a collection of educational examples showcasing the use of large language models (LLMs). It was initially created for a blog post on building a RAG model locally, and has since expanded to include more examples and educational material. Each example is housed in its own folder with a dedicated README providing instructions on how to run it. The repository is designed to be simple and educational, not for production use.

nosia
Nosia is a platform that allows users to run an AI model on their own data. It is designed to be easy to install and use. Users can follow the provided guides for quickstart, API usage, upgrading, starting, stopping, and troubleshooting. The platform supports custom installations with options for remote Ollama instances, custom completion models, and custom embeddings models. Advanced installation instructions are also available for macOS with a Debian or Ubuntu VM setup. Users can access the platform at 'https://nosia.localhost' and troubleshoot any issues by checking logs and job statuses.
inference-speed-tests
This repository contains inference speed tests on Local Large Language Models on various devices. It provides results for different models tested on Macbook Pro and Mac Studio. Users can contribute their own results by running models with the provided prompt and adding the tokens-per-second output. Note that the results are not verified.
uzu
uzu is a high-performance inference engine for AI models on Apple Silicon. It features a simple, high-level API, hybrid architecture for GPU kernel computation, unified model configurations, traceable computations, and utilizes unified memory on Apple devices. The tool provides a CLI mode for running models, supports its own model format, and offers prebuilt Swift and TypeScript frameworks for bindings. Users can quickly start by adding the uzu dependency to their Cargo.toml and creating an inference Session with a specific model and configuration. Performance benchmarks show metrics for various models on Apple M2, highlighting the tokens/s speed for each model compared to llama.cpp with bf16/f16 precision.
chatgpt-adapter
ChatGPT-Adapter is an interface service that integrates various free services together. It provides a unified interface specification and integrates services like Bing, Claude-2, Gemini. Users can start the service by running the linux-server script and set proxies if needed. The tool offers model lists for different adapters, completion dialogues, authorization methods for different services like Claude, Bing, Gemini, Coze, and Lmsys. Additionally, it provides a free drawing interface with options like coze.dall-e-3, sd.dall-e-3, xl.dall-e-3, pg.dall-e-3 based on user-provided Authorization keys. The tool also supports special flags for enhanced functionality.
ai-wechat-bot
Gewechat is a project based on the Gewechat project to implement a personal WeChat channel, using the iPad protocol for login. It can obtain wxid and send voice messages, which is more stable than the itchat protocol. The project provides documentation for the API. Users can deploy the Gewechat service and use the ai-wechat-bot project to interface with it. Configuration parameters for Gewechat and ai-wechat-bot need to be set in the config.json file. Gewechat supports sending voice messages, with limitations on the duration of received voice messages. The project has restrictions such as requiring the server to be in the same province as the device logging into WeChat, limited file download support, and support only for text and image messages.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.