
ai-powered-search
The codebase for the book "AI-Powered Search" (Manning Publications, 2024)
Stars: 172
AI-Powered Search provides code examples for the book 'AI-Powered Search' by Trey Grainger, Doug Turnbull, and Max Irwin. The book teaches modern machine learning techniques for building search engines that continuously learn from users and content to deliver more intelligent and domain-aware search experiences. It covers semantic search, retrieval augmented generation, question answering, summarization, fine-tuning transformer-based models, personalized search, machine-learned ranking, click models, and more. The code examples are in Python, leveraging PySpark for data processing and Apache Solr as the default search engine. The repository is open source under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
README:
Code examples for the book AI-Powered Search by Trey Grainger, Doug Turnbull, and Max Irwin. Published by Manning Publications.
AI-Powered Search teaches you the latest machine learning techniques to build search engines that continuously learn from your users and your content to drive more domain-aware and intelligent search.
Search engine technology is rapidly evolving, with Artificial Intelligence (AI) driving much of that innovation. Crowdsourced relevance and the integration of large language models (LLMs) like GPT and other foundation models are massively accelerating the capabilities and expectations of search technology.
AI-Powered Search will teach you modern, data-science-driven search techniques like:
- Semantic search using dense vector embeddings from foundation models
- Retrieval Augmented Generation
- Question answering and summarization combining search and LLMs
- Fine-tuning transformer-based LLMs
- Personalized search based on user signals and vector embeddings
- Collecting user behavioral signals and building signals boosting models
- Semantic knowledge graphs for domain-specific learning
- Implementing machine-learned ranking models (learning to rank)
- Building click models to automate machine-learned ranking
- Generative search, hybrid search, and the search frontier
Today’s search engines are expected to be smart, understanding the nuances of natural language queries, as well as each user’s preferences and context. This book empowers you to build search engines that take advantage of user interactions and the hidden semantic relationships in your content to automatically deliver better, more relevant search experiences.
For simplicity of setup, all code is shipped in Jupyter Notebooks and packaged in Docker containers. This means that installing Docker and then pulling (or building) and running the book's Docker containers is the only necessary setup. Appendix A of the book provides full step-by-step instructions for running the code examples, but you can run the following to get up and running quickly:
If you haven't already pulled the source code locally, run:
git clone https://github.com/treygrainger/ai-powered-search.git
Then, to build and start the codebase with interactive Jupyter notebooks, run:
cd ai-powered-search
docker compose up
That's all it takes! Once the containers are built and running (this may take a while, especially on the first build), visit:
http://localhost:8888 to launch the Welcome notebook and see a Table of Contents for all the live code examples from throughout the book.
AI-Powered Search teaches many modern search techniques leveraging machine learning approaches. While we utilize specific technologies to demonstrate concepts, most techniques are applicable to many modern search engines and vector databases.
Throughout the book, all code examples are in Python, with PySpark (the Python interface to Apache Spark) being utilized heavily for data processing tasks. The default search engine leveraged by the book's examples is Apache Solr, but most examples are abstracted away from the particular search engine, and swappable implementation will be soon available for most popular search engines and vector databases. For more information about the search engine abstractions and custom integrations check out the engine documentation.
See Full List: Supported Search Engines and Vector Databases
[ Note: if you work for a search engine / vector database company, project, or hosting provider and want to work with us on getting your engine supported, please reach out to [email protected] ]
Your purchase of AI-Powered Search includes online access to Manning's LiveBook forum. This allows you to provide comments and ask questions about any parts of the book. Additionally, feel free to submit pull requests, Github issues, or comments on the project's official Github repo at https://github.com/treygrainger/ai-powered-search.
All code in this repository is open source under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (ASL 2.0), unless otherwise specified.
Note that when executing the code, it may pull additional dependencies that follow alternate licenses, so please be sure to inspect those licenses before using them in your projects to ensure they are suitable. The code may also pull in datasets subject to various licenses, some of which may be derived from AI models and some of which may be derived from web crawls of data subject to fair use under the copyright laws in the country of publication (the USA). Any such datasets are published "as-is", for the sole purpose of demonstrating the concepts in the book, and these datasets and their associated licenses may be subject to change over time.
If you don't yet have a copy, please support the authors and the publisher by purchasing a copy of AI-Powered Search. It will walk you step by step through the concepts and techniques shown in the code examples in this repository, providing needed context and insights to help you better understand the techniques.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ai-powered-search
Similar Open Source Tools

ai-powered-search
AI-Powered Search provides code examples for the book 'AI-Powered Search' by Trey Grainger, Doug Turnbull, and Max Irwin. The book teaches modern machine learning techniques for building search engines that continuously learn from users and content to deliver more intelligent and domain-aware search experiences. It covers semantic search, retrieval augmented generation, question answering, summarization, fine-tuning transformer-based models, personalized search, machine-learned ranking, click models, and more. The code examples are in Python, leveraging PySpark for data processing and Apache Solr as the default search engine. The repository is open source under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
PythonDataScienceFullThrottle
PythonDataScienceFullThrottle is a comprehensive repository containing various Python scripts, libraries, and tools for data science enthusiasts. It includes a wide range of functionalities such as data preprocessing, visualization, machine learning algorithms, and statistical analysis. The repository aims to provide a one-stop solution for individuals looking to dive deep into the world of data science using Python.
chat-with-your-data-solution-accelerator
Chat with your data using OpenAI and AI Search. This solution accelerator uses an Azure OpenAI GPT model and an Azure AI Search index generated from your data, which is integrated into a web application to provide a natural language interface, including speech-to-text functionality, for search queries. Users can drag and drop files, point to storage, and take care of technical setup to transform documents. There is a web app that users can create in their own subscription with security and authentication.

NaLLM
The NaLLM project repository explores the synergies between Neo4j and Large Language Models (LLMs) through three primary use cases: Natural Language Interface to a Knowledge Graph, Creating a Knowledge Graph from Unstructured Data, and Generating a Report using static and LLM data. The repository contains backend and frontend code organized for easy navigation. It includes blog posts, a demo database, instructions for running demos, and guidelines for contributing. The project aims to showcase the potential of Neo4j and LLMs in various applications.
TagUI
TagUI is an open-source RPA tool that allows users to automate repetitive tasks on their computer, including tasks on websites, desktop apps, and the command line. It supports multiple languages and offers features like interacting with identifiers, automating data collection, moving data between TagUI and Excel, and sending Telegram notifications. Users can create RPA robots using MS Office Plug-ins or text editors, run TagUI on the cloud, and integrate with other RPA tools. TagUI prioritizes enterprise security by running on users' computers and not storing data. It offers detailed logs, enterprise installation guides, and support for centralised reporting.
magic
Magic Cloud is a software development automation platform based on AI, Low-Code, and No-Code. It allows dynamic code creation and orchestration using Hyperlambda, generative AI, and meta programming. The platform includes features like CRUD generation, No-Code AI, Hyperlambda programming language, AI agents creation, and various components for software development. Magic is suitable for backend development, AI-related tasks, and creating AI chatbots. It offers high-level programming capabilities, productivity gains, and reduced technical debt.
dstoolkit-text2sql-and-imageprocessing
This repository provides sample code for improving RAG applications with rich data sources including SQL Warehouses and documents analysed with Azure Document Intelligence. It includes components for Text2SQL generation and querying, linking Azure Document Intelligence with AI Search for processing complex documents, and deploying AI search indexes. The plugins and skills aim to enhance response quality in RAG applications by accessing and pulling data from SQL tables, drawing insights from complex charts and images, and intelligently grouping similar sentences.
HybridAGI
HybridAGI is the first Programmable LLM-based Autonomous Agent that lets you program its behavior using a **graph-based prompt programming** approach. This state-of-the-art feature allows the AGI to efficiently use any tool while controlling the long-term behavior of the agent. Become the _first Prompt Programmers in history_ ; be a part of the AI revolution one node at a time! **Disclaimer: We are currently in the process of upgrading the codebase to integrate DSPy**
motleycrew
Motleycrew is an ultimate framework for building multi-agent AI systems, allowing users to mix and match AI agents and tools from popular frameworks, design advanced workflows, and leverage dynamic knowledge graphs with simplicity and elegance. It acts as a conductor orchestrating a symphony of AI agents and tools, providing building blocks for creating AI systems and enabling users to focus on high-level design while taking care of the rest. The framework offers integration with various tools, flexibility in providing agents with tools or other agents, advanced flow design capabilities, and built-in observability and caching features.
xef
xef.ai is a one-stop library designed to bring the power of modern AI to applications and services. It offers integration with Large Language Models (LLM), image generation, and other AI services. The library is packaged in two layers: core libraries for basic AI services integration and integrations with other libraries. xef.ai aims to simplify the transition to modern AI for developers by providing an idiomatic interface, currently supporting Kotlin. Inspired by LangChain and Hugging Face, xef.ai may transmit source code and user input data to third-party services, so users should review privacy policies and take precautions. Libraries are available in Maven Central under the `com.xebia` group, with `xef-core` as the core library. Developers can add these libraries to their projects and explore examples to understand usage.
Web-LLM-Assistant-Llama-cpp
Web-LLM Assistant is a simple web search assistant that leverages a large language model (LLM) running via Llama.cpp to provide informative and context-aware responses to user queries. It combines the power of LLMs with real-time web searching capabilities, allowing it to access up-to-date information and synthesize comprehensive answers. The tool performs web searches, collects and scrapes information from search results, refines search queries, and provides answers based on the acquired information. Users can interact with the tool by asking questions or requesting web searches, making it a valuable resource for obtaining information beyond the LLM's training data.
autoMate
autoMate is an AI-powered local automation tool designed to help users automate repetitive tasks and reclaim their time. It leverages AI and RPA technology to operate computer interfaces, understand screen content, make autonomous decisions, and support local deployment for data security. With natural language task descriptions, users can easily automate complex workflows without the need for programming knowledge. The tool aims to transform work by freeing users from mundane activities and allowing them to focus on tasks that truly create value, enhancing efficiency and liberating creativity.
Large-Language-Models
Large Language Models (LLM) are used to browse the Wolfram directory and associated URLs to create the category structure and good word embeddings. The goal is to generate enriched prompts for GPT, Wikipedia, Arxiv, Google Scholar, Stack Exchange, or Google search. The focus is on one subdirectory: Probability & Statistics. Documentation is in the project textbook `Projects4.pdf`, which is available in the folder. It is recommended to download the document and browse your local copy with Chrome, Edge, or other viewers. Unlike on GitHub, you will be able to click on all the links and follow the internal navigation features. Look for projects related to NLP and LLM / xLLM. The best starting point is project 7.2.2, which is the core project on this topic, with references to all satellite projects. The project textbook (with solutions to all projects) is the core document needed to participate in the free course (deep tech dive) called **GenAI Fellowship**. For details about the fellowship, follow the link provided. An uncompressed version of `crawl_final_stats.txt.gz` is available on Google drive, which contains all the crawled data needed as input to the Python scripts in the XLLM5 and XLLM6 folders.
kdbai-samples
KDB.AI is a time-based vector database that allows developers to build scalable, reliable, and real-time applications by providing advanced search, recommendation, and personalization for Generative AI applications. It supports multiple index types, distance metrics, top-N and metadata filtered retrieval, as well as Python and REST interfaces. The repository contains samples demonstrating various use-cases such as temporal similarity search, document search, image search, recommendation systems, sentiment analysis, and more. KDB.AI integrates with platforms like ChatGPT, Langchain, and LlamaIndex. The setup steps require Unix terminal, Python 3.8+, and pip installed. Users can install necessary Python packages and run Jupyter notebooks to interact with the samples.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
Large-Language-Model-Notebooks-Course
This practical free hands-on course focuses on Large Language models and their applications, providing a hands-on experience using models from OpenAI and the Hugging Face library. The course is divided into three major sections: Techniques and Libraries, Projects, and Enterprise Solutions. It covers topics such as Chatbots, Code Generation, Vector databases, LangChain, Fine Tuning, PEFT Fine Tuning, Soft Prompt tuning, LoRA, QLoRA, Evaluate Models, Knowledge Distillation, and more. Each section contains chapters with lessons supported by notebooks and articles. The course aims to help users build projects and explore enterprise solutions using Large Language Models.
For similar tasks

langwatch
LangWatch is a monitoring and analytics platform designed to track, visualize, and analyze interactions with Large Language Models (LLMs). It offers real-time telemetry to optimize LLM cost and latency, a user-friendly interface for deep insights into LLM behavior, user analytics for engagement metrics, detailed debugging capabilities, and guardrails to monitor LLM outputs for issues like PII leaks and toxic language. The platform supports OpenAI and LangChain integrations, simplifying the process of tracing LLM calls and generating API keys for usage. LangWatch also provides documentation for easy integration and self-hosting options for interested users.

ai-powered-search
AI-Powered Search provides code examples for the book 'AI-Powered Search' by Trey Grainger, Doug Turnbull, and Max Irwin. The book teaches modern machine learning techniques for building search engines that continuously learn from users and content to deliver more intelligent and domain-aware search experiences. It covers semantic search, retrieval augmented generation, question answering, summarization, fine-tuning transformer-based models, personalized search, machine-learned ranking, click models, and more. The code examples are in Python, leveraging PySpark for data processing and Apache Solr as the default search engine. The repository is open source under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
posthog
PostHog is an all-in-one, open source platform for building successful products. It provides tools for product analytics, web analytics, session replays, feature flags, experiments, error tracking, surveys, data warehouse, data pipelines, LLM analytics, and workflows. Users can get started with a generous free tier, self-host the platform, or use PostHog Cloud. The platform supports various SDKs and libraries for popular languages and frameworks, making it versatile and easy to integrate. PostHog is suitable for teams looking to understand user behavior, improve product performance, and automate actions or messages to users.

countly-server
Countly is a privacy-first, AI-ready analytics and customer engagement platform built for organizations that require full data ownership and deployment flexibility. It can be deployed on-premises or in a private cloud, giving complete control over data, infrastructure, compliance, and security. Teams use Countly to understand user behavior across mobile, web, desktop, and connected devices, optimize product and customer experiences in real time, and automate and personalize customer engagement across channels. With flexible data tracking, customizable dashboards, and a modular plugin-based architecture, Countly scales with the product while ensuring long-term autonomy and zero vendor lock-in. Built for privacy, designed for flexibility, and ready for AI-driven innovation.
lance
Lance is a modern columnar data format optimized for ML workflows and datasets. It offers high-performance random access, vector search, zero-copy automatic versioning, and ecosystem integrations with Apache Arrow, Pandas, Polars, and DuckDB. Lance is designed to address the challenges of the ML development cycle, providing a unified data format for collection, exploration, analytics, feature engineering, training, evaluation, deployment, and monitoring. It aims to reduce data silos and streamline the ML development process.
RAGHub
RAGHub is a community-driven project focused on cataloging new and emerging frameworks, projects, and resources in the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) ecosystem. It aims to help users stay ahead of changes in the field by providing a platform for the latest innovations in RAG. The repository includes information on RAG frameworks, evaluation frameworks, optimization frameworks, citation frameworks, engines, search reranker frameworks, projects, resources, and real-world use cases across industries and professions.
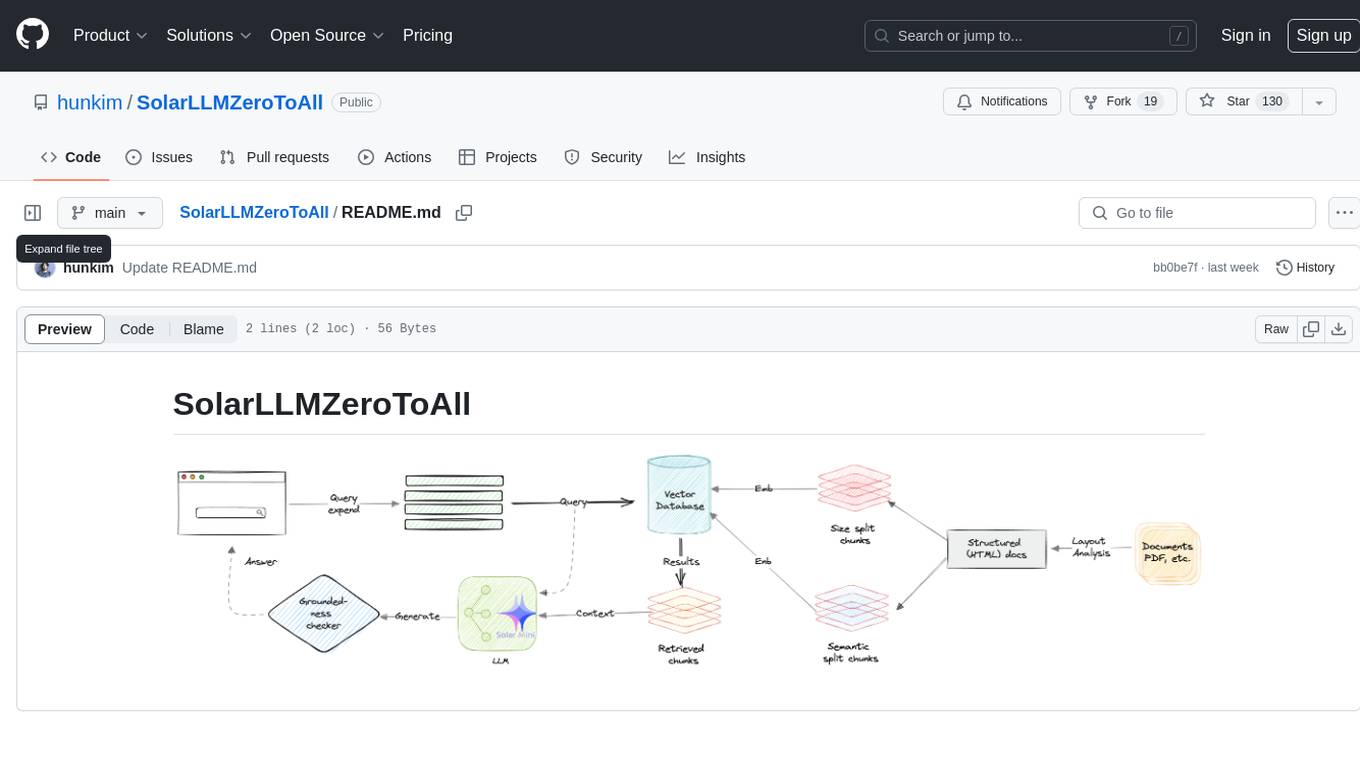
SolarLLMZeroToAll
SolarLLMZeroToAll is a comprehensive repository that provides a step-by-step guide and resources for learning and implementing Solar Longitudinal Learning Machines (SolarLLM) from scratch. The repository covers various aspects of SolarLLM, including theory, implementation, and applications, making it suitable for beginners and advanced users interested in solar energy forecasting and machine learning. The materials include detailed explanations, code examples, datasets, and visualization tools to facilitate understanding and practical implementation of SolarLLM models.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

