speculators
A unified library for building, evaluating, and storing speculative decoding algorithms for LLM inference in vLLM
Stars: 241
Speculators is a unified library for building, training, and storing speculative decoding algorithms for large language model (LLM) inference. It speeds up LLM inference by using a smaller, faster draft model (the speculator) to propose tokens, which are then verified by the larger base model, reducing latency without compromising output quality. Trained models can seamlessly run in vLLM, enabling the deployment of speculative decoding in production-grade inference servers.
README:
Speculators is a unified library for building, training and storing speculative decoding algorithms for large language model (LLM) inference, including in frameworks like vLLM. Speculative decoding is a lossless technique that speeds up LLM inference by using a smaller, faster draft model (i.e "the speculator") to propose tokens, which are then verified by the larger base model, reducing latency without compromising output quality. The speculator intelligently drafts multiple tokens ahead of time, and the base model verifies them in a single forward pass. This approach boosts performance without sacrificing output quality, as every accepted token is guaranteed to match what the main model would have generated on its own.
Speculators standardizes this process by providing a productionized end-to-end framework to train draft models with reusable formats and tools. Trained models can seamlessly run in vLLM, enabling the deployment of speculative decoding in production-grade inference servers.
💬 Join us on the vLLM Community Slack and share your questions, thoughts, or ideas in:
#speculators#feat-spec-decode
🎥 Watch our Office Hours presentation: Video | Slides
- Offline Training Data Generation using vLLM: Enable the generation of hidden states using vLLM. Data samples are saved to disk and can be used for draft model training.
- Draft Model Training Support: E2E training support of single and multi-layer draft models. Training is supported for both non-MoE and MoE models. VL Training is coming soon.
- Standardized, Extensible Format: Provides a Hugging Face-compatible format for defining speculative models, with tools to convert from external research repositories into a standard speculators format for easy adoption.
- Seamless vLLM Integration: Built for direct deployment into vLLM, enabling low-latency, production-grade inference with minimal overhead.
[!TIP] Read more about Speculators features in this vLLM blog post.
The following table summarizes the models that have been trained end-to-end by our team as well as others in the roadmap:
| Verifier Architecture | Verifier Size | Training Support | vLLM Deployment Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Llama | 8B-Instruct | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ |
| 70B-Instruct | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ | |
| Qwen3 | 8B | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ |
| 14B | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ | |
| 32B | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ | |
| gpt-oss | 20b | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ |
| 120b | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ | |
| Qwen3 MoE | 30B-Instruct | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ |
| 235B-Instruct | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ | |
| 235B | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ | |
| Qwen3-VL | 235B-A22B | EAGLE-3 ✅ | ✅ |
| Mistral 3 Large | 675B-Instruct | EAGLE-3 ⏳ | ⏳ |
✅ = Supported, ⏳ = In Progress, ❌ = Not Yet Supported
End-To-End Training Examples:
Models trained through Speculators can run seamlessly in vLLM using a simple vllm serve <speculator_model> command. This will run the model in vLLM using default arguments, defined in the speculator_config of the model's config.json.
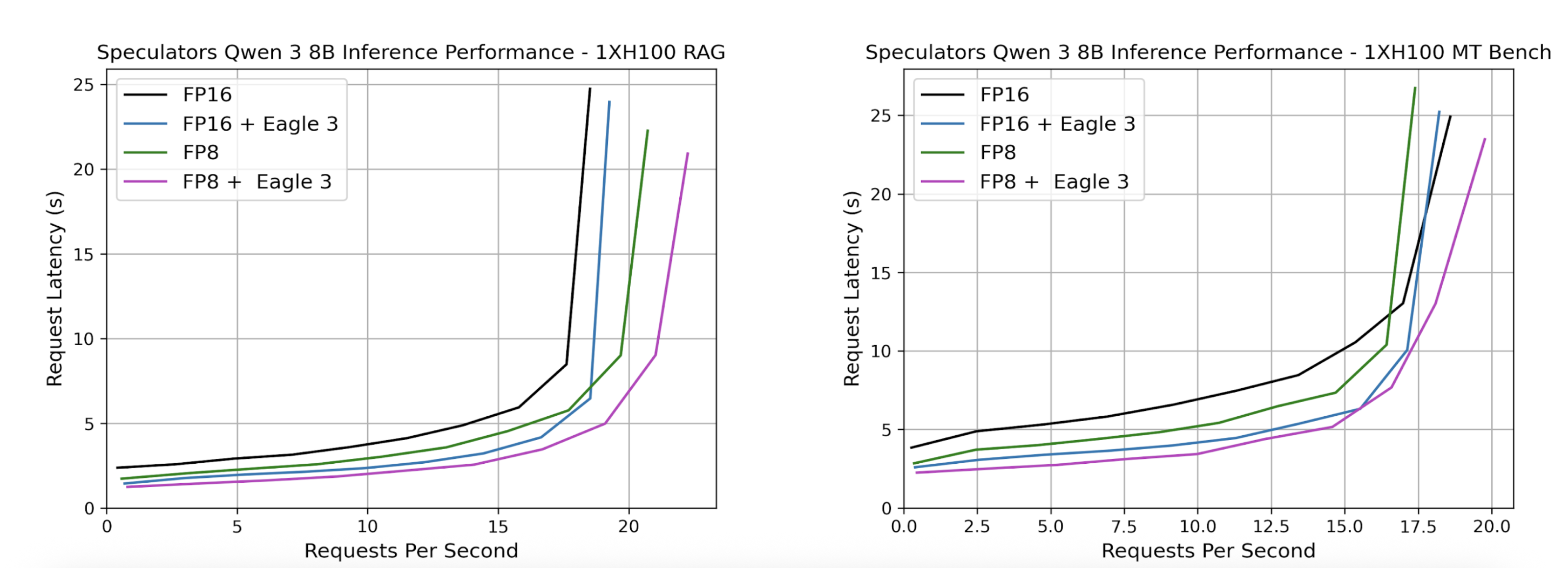
vllm serve RedHatAI/Qwen3-8B-speculator.eagle3Served models can then be benchmarked using GuideLLM. Below, we show sample benchmark results where we compare our speculator with its dense counterpart. We also additionally compare quantization to explore additional performance improvements by swapping the dense verifier, Qwen/Qwen3-8B with the quantized FP8 model, RedHatAI/Qwen3-8B-FP8-dynamic in the speculator_config.
Before installing, ensure you have the following:
- Operating System: Linux or macOS
- Python: 3.10 or higher
- Package Manager: pip (recommended) or conda
Install the latest stable release from PyPI:
pip install speculatorsFor the latest development version or to contribute to the project:
git clone https://github.com/vllm-project/speculators.git
cd speculators
pip install -e .For development with additional tools:
pip install -e ".[dev]"To enable the generation of data (i.e hidden states) from vLLM for speculator training:
pip install -e ".[datagen]"You can verify your installation by checking the version:
speculators --versionOr by importing the package in Python:
import speculators
print(speculators.__version__)Speculators is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
If you find Speculators helpful in your research or projects, please consider citing it:
@misc{speculators2025,
title={Speculators: A Unified Library for Speculative Decoding Algorithms in LLM Serving},
author={Red Hat},
year={2025},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/vllm-project/speculators}},
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for speculators
Similar Open Source Tools

speculators
Speculators is a unified library for building, training, and storing speculative decoding algorithms for large language model (LLM) inference. It speeds up LLM inference by using a smaller, faster draft model (the speculator) to propose tokens, which are then verified by the larger base model, reducing latency without compromising output quality. Trained models can seamlessly run in vLLM, enabling the deployment of speculative decoding in production-grade inference servers.
TokenFormer
TokenFormer is a fully attention-based neural network architecture that leverages tokenized model parameters to enhance architectural flexibility. It aims to maximize the flexibility of neural networks by unifying token-token and token-parameter interactions through the attention mechanism. The architecture allows for incremental model scaling and has shown promising results in language modeling and visual modeling tasks. The codebase is clean, concise, easily readable, state-of-the-art, and relies on minimal dependencies.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.
RD-Agent
RD-Agent is a tool designed to automate critical aspects of industrial R&D processes, focusing on data-driven scenarios to streamline model and data development. It aims to propose new ideas ('R') and implement them ('D') automatically, leading to solutions of significant industrial value. The tool supports scenarios like Automated Quantitative Trading, Data Mining Agent, Research Copilot, and more, with a framework to push the boundaries of research in data science. Users can create a Conda environment, install the RDAgent package from PyPI, configure GPT model, and run various applications for tasks like quantitative trading, model evolution, medical prediction, and more. The tool is intended to enhance R&D processes and boost productivity in industrial settings.
labo
LABO is a time series forecasting and analysis framework that integrates pre-trained and fine-tuned LLMs with multi-domain agent-based systems. It allows users to create and tune agents easily for various scenarios, such as stock market trend prediction and web public opinion analysis. LABO requires a specific runtime environment setup, including system requirements, Python environment, dependency installations, and configurations. Users can fine-tune their own models using LABO's Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for computational efficiency and continuous model updates. Additionally, LABO provides a Python library for building model training pipelines and customizing agents for specific tasks.
evalverse
Evalverse is an open-source project designed to support Large Language Model (LLM) evaluation needs. It provides a standardized and user-friendly solution for processing and managing LLM evaluations, catering to AI research engineers and scientists. Evalverse supports various evaluation methods, insightful reports, and no-code evaluation processes. Users can access unified evaluation with submodules, request evaluations without code via Slack bot, and obtain comprehensive reports with scores, rankings, and visuals. The tool allows for easy comparison of scores across different models and swift addition of new evaluation tools.
cognee
Cognee is an open-source framework designed for creating self-improving deterministic outputs for Large Language Models (LLMs) using graphs, LLMs, and vector retrieval. It provides a platform for AI engineers to enhance their models and generate more accurate results. Users can leverage Cognee to add new information, utilize LLMs for knowledge creation, and query the system for relevant knowledge. The tool supports various LLM providers and offers flexibility in adding different data types, such as text files or directories. Cognee aims to streamline the process of working with LLMs and improving AI models for better performance and efficiency.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.

glide
Glide is a cloud-native LLM gateway that provides a unified REST API for accessing various large language models (LLMs) from different providers. It handles LLMOps tasks such as model failover, caching, key management, and more, making it easy to integrate LLMs into applications. Glide supports popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock (Titan), Cohere, Google Gemini, OctoML, and Ollama. It offers high availability, performance, and observability, and provides SDKs for Python and NodeJS to simplify integration.
llmware
LLMWare is a framework for quickly developing LLM-based applications including Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Multi-Step Orchestration of Agent Workflows. This project provides a comprehensive set of tools that anyone can use - from a beginner to the most sophisticated AI developer - to rapidly build industrial-grade, knowledge-based enterprise LLM applications. Our specific focus is on making it easy to integrate open source small specialized models and connecting enterprise knowledge safely and securely.

llmaz
llmaz is an easy, advanced inference platform for large language models on Kubernetes. It aims to provide a production-ready solution that integrates with state-of-the-art inference backends. The platform supports efficient model distribution, accelerator fungibility, SOTA inference, various model providers, multi-host support, and scaling efficiency. Users can quickly deploy LLM services with minimal configurations and benefit from a wide range of advanced inference backends. llmaz is designed to optimize cost and performance while supporting cutting-edge researches like Speculative Decoding or Splitwise on Kubernetes.
OmAgent
OmAgent is an open-source agent framework designed to streamline the development of on-device multimodal agents. It enables agents to empower various hardware devices, integrates speed-optimized SOTA multimodal models, provides SOTA multimodal agent algorithms, and focuses on optimizing the end-to-end computing pipeline for real-time user interaction experience. Key features include easy connection to diverse devices, scalability, flexibility, and workflow orchestration. The architecture emphasizes graph-based workflow orchestration, native multimodality, and device-centricity, allowing developers to create bespoke intelligent agent programs.

AdalFlow
AdalFlow is a library designed to help developers build and optimize Large Language Model (LLM) task pipelines. It follows a design pattern similar to PyTorch, offering a light, modular, and robust codebase. Named in honor of Ada Lovelace, AdalFlow aims to inspire more women to enter the AI field. The library is tailored for various GenAI applications like chatbots, translation, summarization, code generation, and autonomous agents, as well as classical NLP tasks such as text classification and named entity recognition. AdalFlow emphasizes modularity, robustness, and readability to support users in customizing and iterating code for their specific use cases.
ludwig
Ludwig is a declarative deep learning framework designed for scale and efficiency. It is a low-code framework that allows users to build custom AI models like LLMs and other deep neural networks with ease. Ludwig offers features such as optimized scale and efficiency, expert level control, modularity, and extensibility. It is engineered for production with prebuilt Docker containers, support for running with Ray on Kubernetes, and the ability to export models to Torchscript and Triton. Ludwig is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.

LightLLM
LightLLM is a lightweight library for linear and logistic regression models. It provides a simple and efficient way to train and deploy machine learning models for regression tasks. The library is designed to be easy to use and integrate into existing projects, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists. With LightLLM, users can quickly build and evaluate regression models using a variety of algorithms and hyperparameters. The library also supports feature engineering and model interpretation, allowing users to gain insights from their data and make informed decisions based on the model predictions.
For similar tasks
pyllms
PyLLMs is a minimal Python library designed to connect to various Language Model Models (LLMs) such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, AI21, Cohere, Aleph Alpha, and HuggingfaceHub. It provides a built-in model performance benchmark for fast prototyping and evaluating different models. Users can easily connect to top LLMs, get completions from multiple models simultaneously, and evaluate models on quality, speed, and cost. The library supports asynchronous completion, streaming from compatible models, and multi-model initialization for testing and comparison. Additionally, it offers features like passing chat history, system messages, counting tokens, and benchmarking models based on quality, speed, and cost.
LLM-Fine-Tuning-Azure
A fine-tuning guide for both OpenAI and Open-Source Large Language Models on Azure. Fine-Tuning retrains an existing pre-trained LLM using example data, resulting in a new 'custom' fine-tuned LLM optimized for task-specific examples. Use cases include improving LLM performance on specific tasks and introducing information not well represented by the base LLM model. Suitable for cases where latency is critical, high accuracy is required, and clear evaluation metrics are available. Learning path includes labs for fine-tuning GPT and Llama2 models via Dashboards and Python SDK.
cellseg_models.pytorch
cellseg-models.pytorch is a Python library built upon PyTorch for 2D cell/nuclei instance segmentation models. It provides multi-task encoder-decoder architectures and post-processing methods for segmenting cell/nuclei instances. The library offers high-level API to define segmentation models, open-source datasets for training, flexibility to modify model components, sliding window inference, multi-GPU inference, benchmarking utilities, regularization techniques, and example notebooks for training and finetuning models with different backbones.
awesome-mobile-llm
Awesome Mobile LLMs is a curated list of Large Language Models (LLMs) and related studies focused on mobile and embedded hardware. The repository includes information on various LLM models, deployment frameworks, benchmarking efforts, applications, multimodal LLMs, surveys on efficient LLMs, training LLMs on device, mobile-related use-cases, industry announcements, and related repositories. It aims to be a valuable resource for researchers, engineers, and practitioners interested in mobile LLMs.
Medical_Image_Analysis
The Medical_Image_Analysis repository focuses on X-ray image-based medical report generation using large language models. It provides pre-trained models and benchmarks for CheXpert Plus dataset, context sample retrieval for X-ray report generation, and pre-training on high-definition X-ray images. The goal is to enhance diagnostic accuracy and reduce patient wait times by improving X-ray report generation through advanced AI techniques.

AngelSlim
AngelSlim is a comprehensive and efficient large model compression toolkit designed to be user-friendly. It integrates mainstream compression algorithms for easy one-click access, continuously innovates compression algorithms, and optimizes end-to-end performance in model compression and deployment. It supports various models for quantization and speculative sampling, with a focus on performance optimization and ease of use.

speculators
Speculators is a unified library for building, training, and storing speculative decoding algorithms for large language model (LLM) inference. It speeds up LLM inference by using a smaller, faster draft model (the speculator) to propose tokens, which are then verified by the larger base model, reducing latency without compromising output quality. Trained models can seamlessly run in vLLM, enabling the deployment of speculative decoding in production-grade inference servers.
gpt-load
GPT-Load is a high-performance, enterprise-grade AI API transparent proxy service designed for enterprises and developers needing to integrate multiple AI services. Built with Go, it features intelligent key management, load balancing, and comprehensive monitoring capabilities for high-concurrency production environments. The tool serves as a transparent proxy service, preserving native API formats of various AI service providers like OpenAI, Google Gemini, and Anthropic Claude. It supports dynamic configuration, distributed leader-follower deployment, and a Vue 3-based web management interface. GPT-Load is production-ready with features like dual authentication, graceful shutdown, and error recovery.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.