
LLM-Fine-Tuning-Azure
A fine-tuning guide for both OpenAI and Open-Source Large Language Models on Azure.
Stars: 103
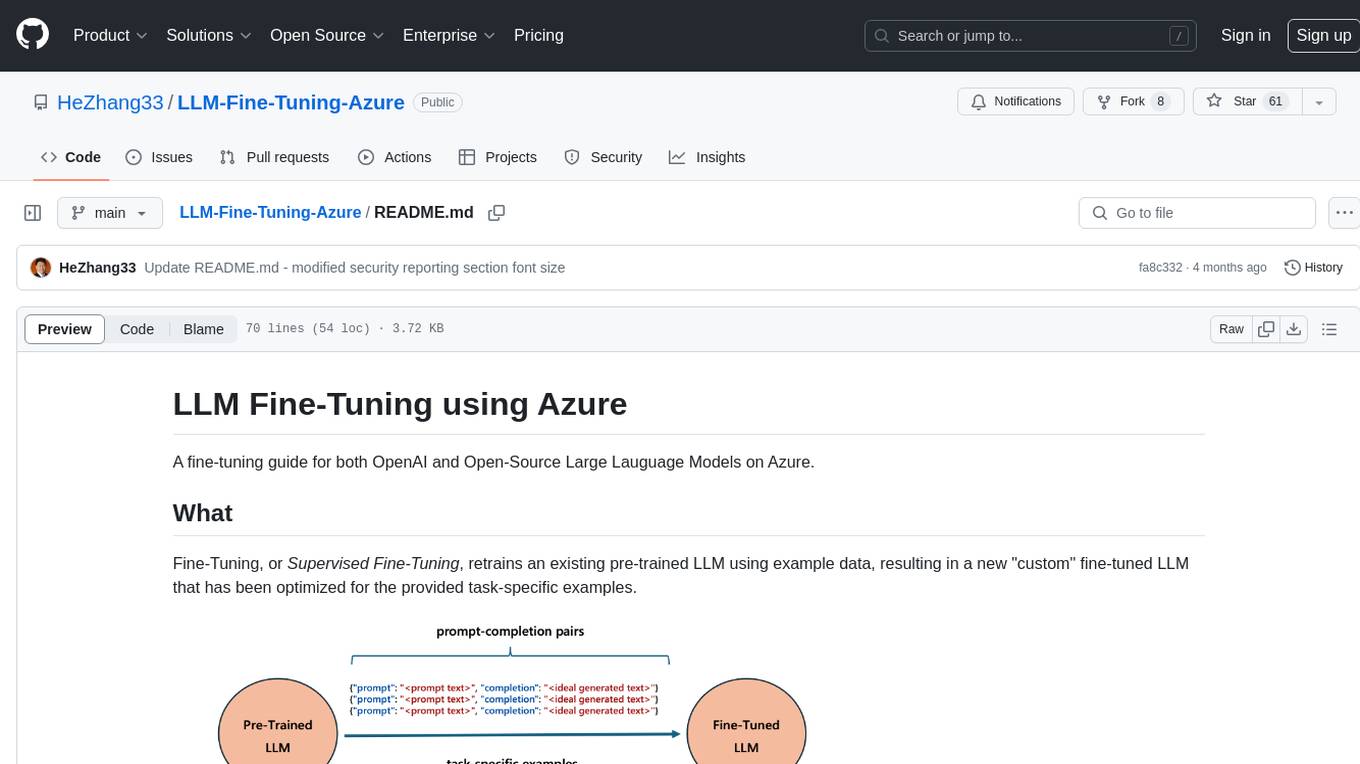
A fine-tuning guide for both OpenAI and Open-Source Large Language Models on Azure. Fine-Tuning retrains an existing pre-trained LLM using example data, resulting in a new 'custom' fine-tuned LLM optimized for task-specific examples. Use cases include improving LLM performance on specific tasks and introducing information not well represented by the base LLM model. Suitable for cases where latency is critical, high accuracy is required, and clear evaluation metrics are available. Learning path includes labs for fine-tuning GPT and Llama2 models via Dashboards and Python SDK.
README:
A fine-tuning guide for both OpenAI and Open-Source Large Lauguage Models on Azure.
🔥 New (2025-03-16): Deploying and Serving DeepSeek-R1-1.5B via vLLM and AML Online Endpoint [Jump to the notebook]
🔥 New (2025-01-02): GPT-4o Vision Fine-Tuning using Azure Machine Learning (Low-Code) Python SDK [Jump to the notebook]
🔥 New (2024-11-20): Phi-3.5 Vision Fine-Tuning using LoRA [Jump to the notebook]
🔥 New (2024-10-25): Phi-3 Fine-Tuning using Q-LoRA [Jump to the notebook]
🔥 New (2024-10-05): Phi-3 Fine-Tuning using LoRA [Jump to the notebook]
🔥 New (2024-07-28): GPT-4 Fine-Tuning using Azure Machine Learning (Low-Code) Python SDK [Jump to the notebook]
🔥 New (2024-07-11): GPT-4 Fine-Tuning using Azure OpenAI UI Dashboard [Jump to the Guide]
🔥 New (2024-07-04): Phi-3 Fine-Tuning using Azure Machine Learning (Low-Code) Python SDK [Jump to the notebook]
Fine-Tuning, or Supervised Fine-Tuning, retrains an existing pre-trained LLM using example data, resulting in a new "custom" fine-tuned LLM that has been optimized for the provided task-specific examples.
Typically, we use Fine-Tuning to:
- improve LLM performance on specific tasks.
- introduce information that wasn't well represented by the base LLM model.
Good use cases include:
- steering the LLM outputs in a specific style or tone.
- too long or complex prompts to fit into the LLM prompt window.
You may consider Fine-Tuning when:
- you have tried Prompt Engineering and RAG approaches.
- latency is critically important to the use case.
- high accuracy is required to meet the customer requirement.
- you have thousands of high-quality samples with ground-truth data.
- you have clear evaluation metrics to benchmark fine-tuned models.
Lab 1: LLM Fine-Tuning via Azure Dashboards
- Lab 1.1: Fine-Tuning GPT-3.5 Model (1h duration)
- Lab 1.2: Fine-Tuning GPT-4 Model (1h duration)
- Lab 1.3: Fine-Tuning Llama2 Model (1h duration)
Lab 2: LLM Fine-Tuning via Azure Python SDK
- Lab 2.1: Fine-Tuning GPT-3.5 Model (2h duration)
- Lab 2.2: Fine-Tuning GPT-4 Model (2h duration)
- Lab 2.3: Vision Fine-Tuning GPT-4o Model (2h duration)
- Lab 2.4: Fine-Tuning Llama2 Model (2h duration)
- Lab 2.5: Fine-Tuning Phi-3 Model (2h duration)
Lab 3: LLM Fine-Tuning via Open Source Tools
- Lab 3.1: Fine-Tuning Phi-3 Model using LoRA (3h duration)
- Lab 3.2: Fine-Tuning Phi-3 Model using Q-LoRA (3h duration)
- Lab 3.3: Fine-Tuning Phi-3.5 Vision Model using LoRA (3h duration)
Lab 4: LLM Model-Serving via Open Source Tools and Azure Python SDK
- Lab 4.1: Deploying and Serving DeepSeek-R1-1.5B using vLLM and AML Online Endpoint (1h duration)
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact [email protected] with any additional questions or comments.
This project may contain trademarks or logos for projects, products, or services. Authorized use of Microsoft trademarks or logos is subject to and must follow Microsoft's Trademark & Brand Guidelines. Use of Microsoft trademarks or logos in modified versions of this project must not cause confusion or imply Microsoft sponsorship. Any use of third-party trademarks or logos are subject to those third-party's policies.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact [email protected] with any additional questions or comments.
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the MIT license.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-Fine-Tuning-Azure
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-Fine-Tuning-Azure
A fine-tuning guide for both OpenAI and Open-Source Large Language Models on Azure. Fine-Tuning retrains an existing pre-trained LLM using example data, resulting in a new 'custom' fine-tuned LLM optimized for task-specific examples. Use cases include improving LLM performance on specific tasks and introducing information not well represented by the base LLM model. Suitable for cases where latency is critical, high accuracy is required, and clear evaluation metrics are available. Learning path includes labs for fine-tuning GPT and Llama2 models via Dashboards and Python SDK.

HPT
Hyper-Pretrained Transformers (HPT) is a novel multimodal LLM framework from HyperGAI, trained for vision-language models capable of understanding both textual and visual inputs. The repository contains the open-source implementation of inference code to reproduce the evaluation results of HPT Air on different benchmarks. HPT has achieved competitive results with state-of-the-art models on various multimodal LLM benchmarks. It offers models like HPT 1.5 Air and HPT 1.0 Air, providing efficient solutions for vision-and-language tasks.
CuMo
CuMo is a project focused on scaling multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with Co-Upcycled Mixture-of-Experts. It introduces CuMo, which incorporates Co-upcycled Top-K sparsely-gated Mixture-of-experts blocks into the vision encoder and the MLP connector, enhancing the capabilities of multimodal LLMs. The project adopts a three-stage training approach with auxiliary losses to stabilize the training process and maintain a balanced loading of experts. CuMo achieves comparable performance to other state-of-the-art multimodal LLMs on various Visual Question Answering (VQA) and visual-instruction-following benchmarks.

aimo-progress-prize
This repository contains the training and inference code needed to replicate the winning solution to the AI Mathematical Olympiad - Progress Prize 1. It consists of fine-tuning DeepSeekMath-Base 7B, high-quality training datasets, a self-consistency decoding algorithm, and carefully chosen validation sets. The training methodology involves Chain of Thought (CoT) and Tool Integrated Reasoning (TIR) training stages. Two datasets, NuminaMath-CoT and NuminaMath-TIR, were used to fine-tune the models. The models were trained using open-source libraries like TRL, PyTorch, vLLM, and DeepSpeed. Post-training quantization to 8-bit precision was done to improve performance on Kaggle's T4 GPUs. The project structure includes scripts for training, quantization, and inference, along with necessary installation instructions and hardware/software specifications.

magpie
This is the official repository for 'Alignment Data Synthesis from Scratch by Prompting Aligned LLMs with Nothing'. Magpie is a tool designed to synthesize high-quality instruction data at scale by extracting it directly from an aligned Large Language Models (LLMs). It aims to democratize AI by generating large-scale alignment data and enhancing the transparency of model alignment processes. Magpie has been tested on various model families and can be used to fine-tune models for improved performance on alignment benchmarks such as AlpacaEval, ArenaHard, and WildBench.
PowerInfer
PowerInfer is a high-speed Large Language Model (LLM) inference engine designed for local deployment on consumer-grade hardware, leveraging activation locality to optimize efficiency. It features a locality-centric design, hybrid CPU/GPU utilization, easy integration with popular ReLU-sparse models, and support for various platforms. PowerInfer achieves high speed with lower resource demands and is flexible for easy deployment and compatibility with existing models like Falcon-40B, Llama2 family, ProSparse Llama2 family, and Bamboo-7B.
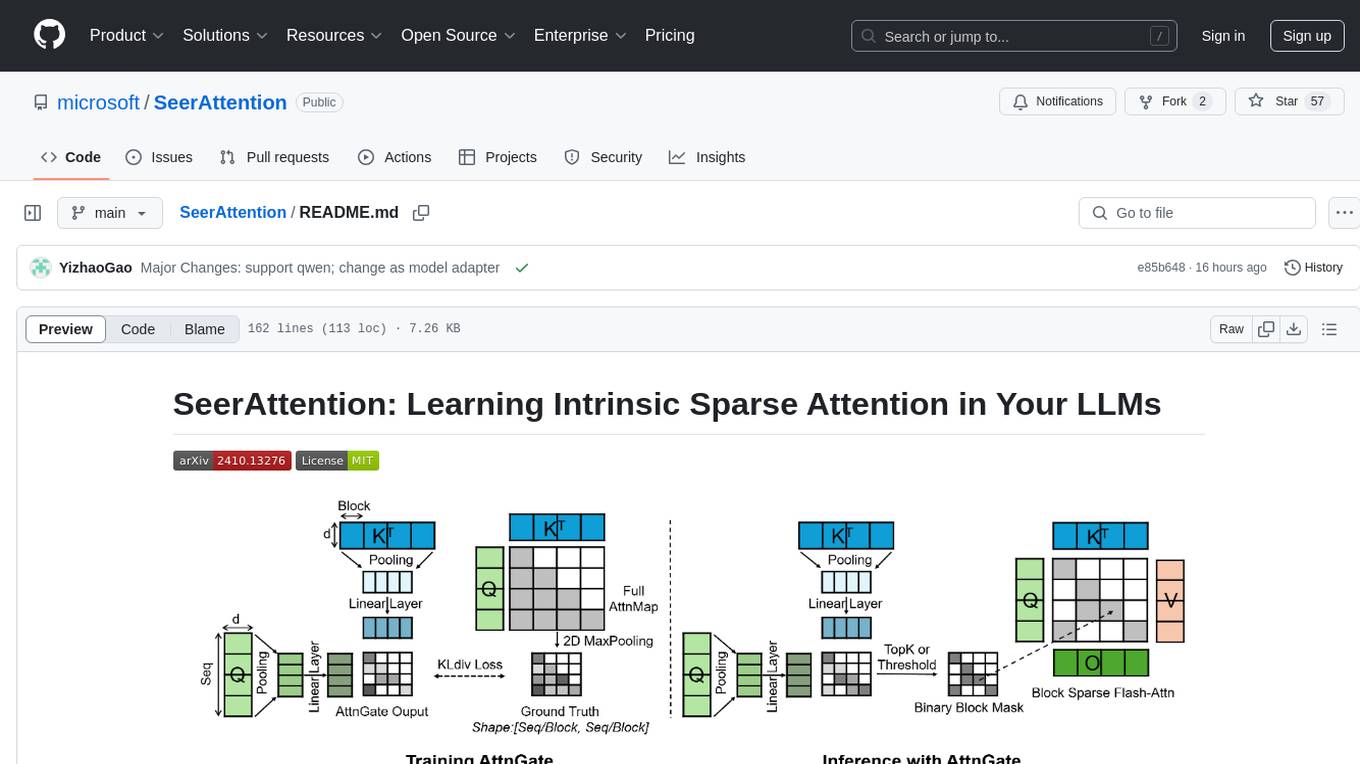
SeerAttention
SeerAttention is a novel trainable sparse attention mechanism that learns intrinsic sparsity patterns directly from LLMs through self-distillation at post-training time. It achieves faster inference while maintaining accuracy for long-context prefilling. The tool offers features such as trainable sparse attention, block-level sparsity, self-distillation, efficient kernel, and easy integration with existing transformer architectures. Users can quickly start using SeerAttention for inference with AttnGate Adapter and training attention gates with self-distillation. The tool provides efficient evaluation methods and encourages contributions from the community.

CogVideo
CogVideo is an open-source repository that provides pretrained text-to-video models for generating videos based on input text. It includes models like CogVideoX-2B and CogVideo, offering powerful video generation capabilities. The repository offers tools for inference, fine-tuning, and model conversion, along with demos showcasing the model's capabilities through CLI, web UI, and online experiences. CogVideo aims to facilitate the creation of high-quality videos from textual descriptions, catering to a wide range of applications.
model2vec
Model2Vec is a technique to turn any sentence transformer into a really small static model, reducing model size by 15x and making the models up to 500x faster, with a small drop in performance. It outperforms other static embedding models like GLoVe and BPEmb, is lightweight with only `numpy` as a major dependency, offers fast inference, dataset-free distillation, and is integrated into Sentence Transformers, txtai, and Chonkie. Model2Vec creates powerful models by passing a vocabulary through a sentence transformer model, reducing dimensionality using PCA, and weighting embeddings using zipf weighting. Users can distill their own models or use pre-trained models from the HuggingFace hub. Evaluation can be done using the provided evaluation package. Model2Vec is licensed under MIT.
EvoMaster
EvoMaster is an open-source AI-driven tool that automatically generates system-level test cases for web/enterprise applications. It uses an Evolutionary Algorithm and Dynamic Program Analysis to evolve test cases, maximizing code coverage and fault detection. The tool supports REST, GraphQL, and RPC APIs, with whitebox testing for JVM-compiled languages. It generates JUnit tests, detects faults, handles SQL databases, and supports authentication. EvoMaster has been funded by the European Research Council and the Research Council of Norway.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
reasoning-from-scratch
This repository contains the code for developing a large language model (LLM) reasoning model. The book 'Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)' provides a hands-on approach to understanding and implementing reasoning capabilities in LLMs. It guides users through creating a small but functional reasoning model, mirroring approaches used in large-scale models like DeepSeek R1 and GPT-5 Thinking. The code includes methods for loading weights of pretrained models.
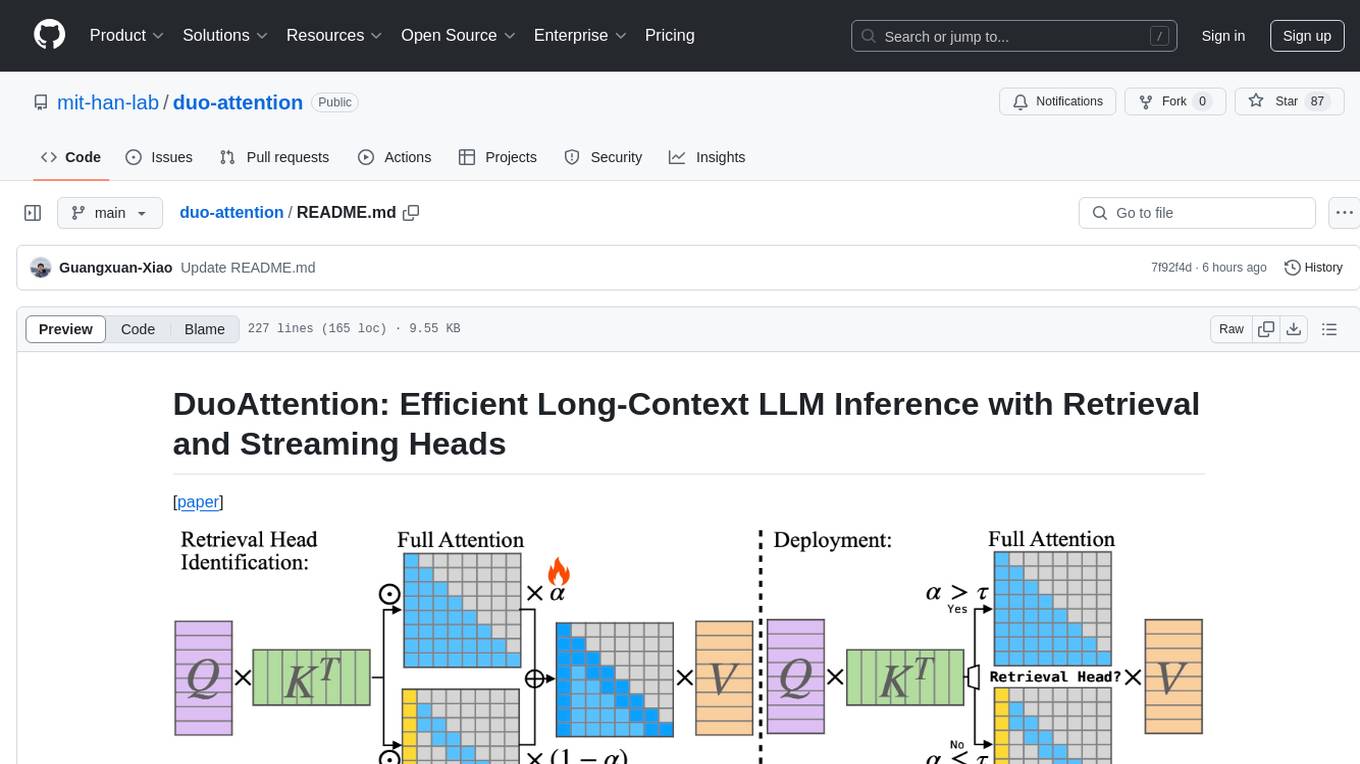
duo-attention
DuoAttention is a framework designed to optimize long-context large language models (LLMs) by reducing memory and latency during inference without compromising their long-context abilities. It introduces a concept of Retrieval Heads and Streaming Heads to efficiently manage attention across tokens. By applying a full Key and Value (KV) cache to retrieval heads and a lightweight, constant-length KV cache to streaming heads, DuoAttention achieves significant reductions in memory usage and decoding time for LLMs. The framework uses an optimization-based algorithm with synthetic data to accurately identify retrieval heads, enabling efficient inference with minimal accuracy loss compared to full attention. DuoAttention also supports quantization techniques for further memory optimization, allowing for decoding of up to 3.3 million tokens on a single GPU.
DemoGPT
DemoGPT is an all-in-one agent library that provides tools, prompts, frameworks, and LLM models for streamlined agent development. It leverages GPT-3.5-turbo to generate LangChain code, creating interactive Streamlit applications. The tool is designed for creating intelligent, interactive, and inclusive solutions in LLM-based application development. It offers model flexibility, iterative development, and a commitment to user engagement. Future enhancements include integrating Gorilla for autonomous API usage and adding a publicly available database for refining the generation process.

LightLLM
LightLLM is a lightweight library for linear and logistic regression models. It provides a simple and efficient way to train and deploy machine learning models for regression tasks. The library is designed to be easy to use and integrate into existing projects, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists. With LightLLM, users can quickly build and evaluate regression models using a variety of algorithms and hyperparameters. The library also supports feature engineering and model interpretation, allowing users to gain insights from their data and make informed decisions based on the model predictions.
Vision-LLM-Alignment
Vision-LLM-Alignment is a repository focused on implementing alignment training for visual large language models (LLMs), including SFT training, reward model training, and PPO/DPO training. It supports various model architectures and provides datasets for training. The repository also offers benchmark results and installation instructions for users.
For similar tasks
pyllms
PyLLMs is a minimal Python library designed to connect to various Language Model Models (LLMs) such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, AI21, Cohere, Aleph Alpha, and HuggingfaceHub. It provides a built-in model performance benchmark for fast prototyping and evaluating different models. Users can easily connect to top LLMs, get completions from multiple models simultaneously, and evaluate models on quality, speed, and cost. The library supports asynchronous completion, streaming from compatible models, and multi-model initialization for testing and comparison. Additionally, it offers features like passing chat history, system messages, counting tokens, and benchmarking models based on quality, speed, and cost.

LLM-Fine-Tuning-Azure
A fine-tuning guide for both OpenAI and Open-Source Large Language Models on Azure. Fine-Tuning retrains an existing pre-trained LLM using example data, resulting in a new 'custom' fine-tuned LLM optimized for task-specific examples. Use cases include improving LLM performance on specific tasks and introducing information not well represented by the base LLM model. Suitable for cases where latency is critical, high accuracy is required, and clear evaluation metrics are available. Learning path includes labs for fine-tuning GPT and Llama2 models via Dashboards and Python SDK.
cellseg_models.pytorch
cellseg-models.pytorch is a Python library built upon PyTorch for 2D cell/nuclei instance segmentation models. It provides multi-task encoder-decoder architectures and post-processing methods for segmenting cell/nuclei instances. The library offers high-level API to define segmentation models, open-source datasets for training, flexibility to modify model components, sliding window inference, multi-GPU inference, benchmarking utilities, regularization techniques, and example notebooks for training and finetuning models with different backbones.
awesome-mobile-llm
Awesome Mobile LLMs is a curated list of Large Language Models (LLMs) and related studies focused on mobile and embedded hardware. The repository includes information on various LLM models, deployment frameworks, benchmarking efforts, applications, multimodal LLMs, surveys on efficient LLMs, training LLMs on device, mobile-related use-cases, industry announcements, and related repositories. It aims to be a valuable resource for researchers, engineers, and practitioners interested in mobile LLMs.
Medical_Image_Analysis
The Medical_Image_Analysis repository focuses on X-ray image-based medical report generation using large language models. It provides pre-trained models and benchmarks for CheXpert Plus dataset, context sample retrieval for X-ray report generation, and pre-training on high-definition X-ray images. The goal is to enhance diagnostic accuracy and reduce patient wait times by improving X-ray report generation through advanced AI techniques.

AngelSlim
AngelSlim is a comprehensive and efficient large model compression toolkit designed to be user-friendly. It integrates mainstream compression algorithms for easy one-click access, continuously innovates compression algorithms, and optimizes end-to-end performance in model compression and deployment. It supports various models for quantization and speculative sampling, with a focus on performance optimization and ease of use.
For similar jobs
NanoLLM
NanoLLM is a tool designed for optimized local inference for Large Language Models (LLMs) using HuggingFace-like APIs. It supports quantization, vision/language models, multimodal agents, speech, vector DB, and RAG. The tool aims to provide efficient and effective processing for LLMs on local devices, enhancing performance and usability for various AI applications.
mslearn-ai-fundamentals
This repository contains materials for the Microsoft Learn AI Fundamentals module. It covers the basics of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data science. The content includes hands-on labs, interactive learning modules, and assessments to help learners understand key concepts and techniques in AI. Whether you are new to AI or looking to expand your knowledge, this module provides a comprehensive introduction to the fundamentals of AI.

awesome-ai-tools
Awesome AI Tools is a curated list of popular tools and resources for artificial intelligence enthusiasts. It includes a wide range of tools such as machine learning libraries, deep learning frameworks, data visualization tools, and natural language processing resources. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced AI practitioner, this repository aims to provide you with a comprehensive collection of tools to enhance your AI projects and research. Explore the list to discover new tools, stay updated with the latest advancements in AI technology, and find the right resources to support your AI endeavors.
go2coding.github.io
The go2coding.github.io repository is a collection of resources for AI enthusiasts, providing information on AI products, open-source projects, AI learning websites, and AI learning frameworks. It aims to help users stay updated on industry trends, learn from community projects, access learning resources, and understand and choose AI frameworks. The repository also includes instructions for local and external deployment of the project as a static website, with details on domain registration, hosting services, uploading static web pages, configuring domain resolution, and a visual guide to the AI tool navigation website. Additionally, it offers a platform for AI knowledge exchange through a QQ group and promotes AI tools through a WeChat public account.
AI-Notes
AI-Notes is a repository dedicated to practical applications of artificial intelligence and deep learning. It covers concepts such as data mining, machine learning, natural language processing, and AI. The repository contains Jupyter Notebook examples for hands-on learning and experimentation. It explores the development stages of AI, from narrow artificial intelligence to general artificial intelligence and superintelligence. The content delves into machine learning algorithms, deep learning techniques, and the impact of AI on various industries like autonomous driving and healthcare. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of AI technologies and their real-world applications.
promptpanel
Prompt Panel is a tool designed to accelerate the adoption of AI agents by providing a platform where users can run large language models across any inference provider, create custom agent plugins, and use their own data safely. The tool allows users to break free from walled-gardens and have full control over their models, conversations, and logic. With Prompt Panel, users can pair their data with any language model, online or offline, and customize the system to meet their unique business needs without any restrictions.
ai-demos
The 'ai-demos' repository is a collection of example code from presentations focusing on building with AI and LLMs. It serves as a resource for developers looking to explore practical applications of artificial intelligence in their projects. The code snippets showcase various techniques and approaches to leverage AI technologies effectively. The repository aims to inspire and educate developers on integrating AI solutions into their applications.
ai_summer
AI Summer is a repository focused on providing workshops and resources for developing foundational skills in generative AI models and transformer models. The repository offers practical applications for inferencing and training, with a specific emphasis on understanding and utilizing advanced AI chat models like BingGPT. Participants are encouraged to engage in interactive programming environments, decide on projects to work on, and actively participate in discussions and breakout rooms. The workshops cover topics such as generative AI models, retrieval-augmented generation, building AI solutions, and fine-tuning models. The goal is to equip individuals with the necessary skills to work with AI technologies effectively and securely, both locally and in the cloud.
