
SEED-Bench
(CVPR2024)A benchmark for evaluating Multimodal LLMs using multiple-choice questions.
Stars: 240
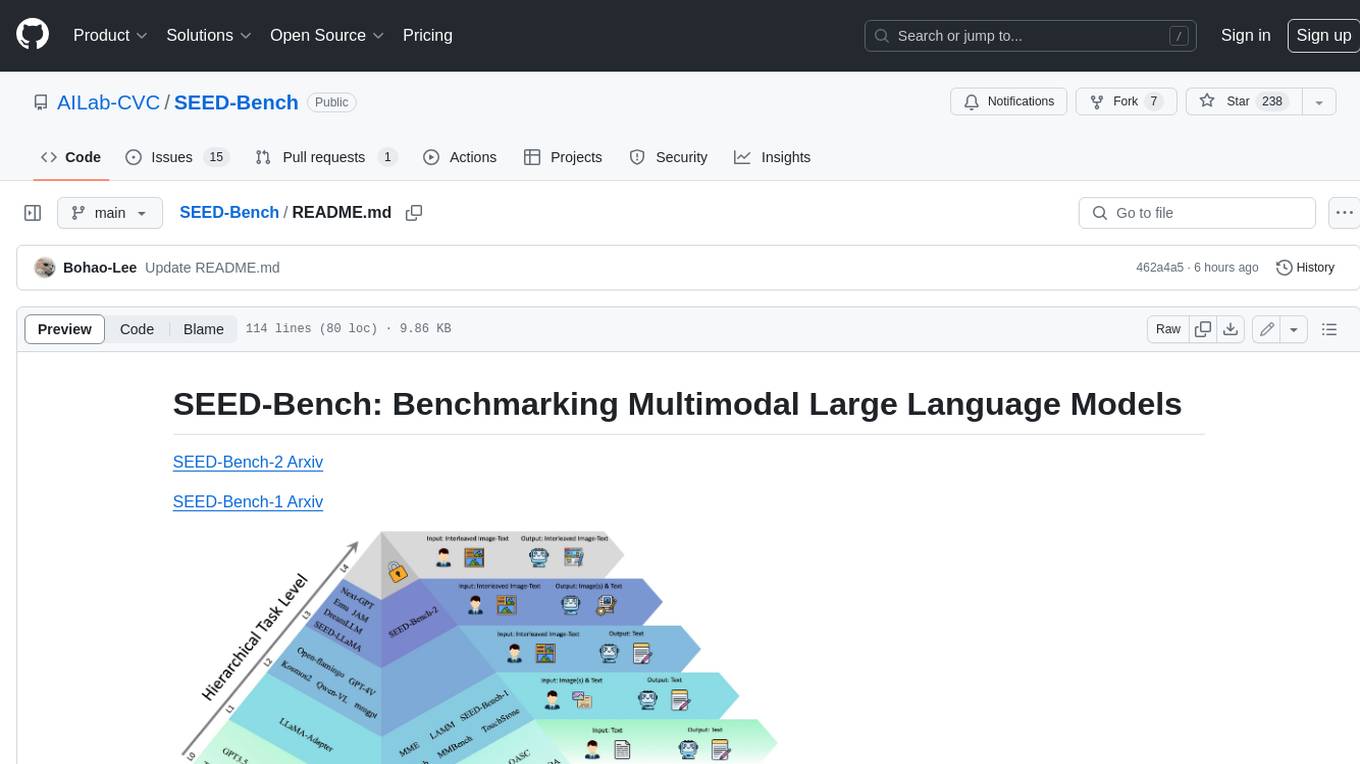
SEED-Bench is a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating the performance of multimodal large language models (LLMs) on a wide range of tasks that require both text and image understanding. It consists of two versions: SEED-Bench-1 and SEED-Bench-2. SEED-Bench-1 focuses on evaluating the spatial and temporal understanding of LLMs, while SEED-Bench-2 extends the evaluation to include text and image generation tasks. Both versions of SEED-Bench provide a diverse set of tasks that cover different aspects of multimodal understanding, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners working on LLMs.
README:
SEED-Bench-2-Plus comprises 2.3K multiple-choice questions with precise human annotations, spanning three broad categories: Charts, Maps, and Webs, each of which covers a wide spectrum of textrich scenarios in the real world.
SEED-Bench-2 comprises 24K multiple-choice questions with accurate human annotations, which spans 27 dimensions, including the evaluation of both text and image generation.
SEED-Bench-1 consists of 19K multiple-choice questions with accurate human annotations, covering 12 evaluation dimensions including both the spatial and temporal understanding.
[2024.4.26] We are excited to announce the release of SEED-Bench-2-Plus, a benchmark specifically designed for text-rich visual comprehension. The accompanying dataset is released on SEED-Bench-2-Plus.
[2024.4.23] We are pleased to share the comprehensive evaluation results for Gemini-Vision-Pro and Claude-3-Opus on SEED-Bench-1 and SEED-Bench-2. You can access detailed performance on the SEED-Bench Leaderboard. Please note that for Gemini-Vision-Pro we only report task performance when the model responds with at least 50% valid data in the task.
[2024.2.27] SEED-Bench is accepted by CVPR 2024.
[2023.12.18] We have placed the comprehensive evaluation results for GPT-4v on SEED-Bench-1 and SEED-Bench-2. These can be accessed at GPT-4V for SEED-Bench-1 and GPT-4V for SEED-Bench-2. If you're interested, please feel free to take a look.
[2023.12.4] We have updated the SEED-Bench Leaderboard for SEED-Bench-2. Additionally, we have updated the evaluation results for GPT-4v on both SEED-Bench-1 and SEED-Bench-2. If you are interested, please visit the SEED-Bench Leaderboard for more details.
[2023.11.30] We have updated the SEED-Bench-v1 JSON (manually screening the multiple-choice questions for videos) and provided corresponding video frames for easier testing. Please refer to SEED-Bench for more information.
[2023.11.27] SEED-Bench-2 is released! Data and evaluation code is available now.
[2023.9.9] We are actively looking for self-motivated interns. Please feel free to reach out if you are interested.
[2023.8.16] SEED-Bench Leaderboard is released! You can upload your model's results now.
[2023.7.30] SEED-Bench is released! Data and evaluation code is available now.
Welcome to SEED-Bench Leaderboard!
You can submit your model results in SEED-Bench Leaderboard now. You can use our evaluation code to obtain 'results.json' in 'results' folder as below.
python eval.py --model instruct_blip --anno_path SEED-Bench.json --output-dir results --task allThen you can upload 'results.json' in SEED-Bench Leaderboard.
After submitting, please press refresh button to get the latest results.
You can download the data of SEED-Bench released on HuggingFace repo SEED-Bench, SEED-Bench-2, and SEED-Bench-2-Plus. Please refer to DATASET.md for data preparation.
Please refer to INSTALL.md.
Please refer to EVALUATION.md.
SEED-Bench is released under Apache License Version 2.0.
Data Sources: Data from the internet under CC-BY licenses.
Please contact us if you believe any data infringes upon your rights, and we will remove it.
Data Sources:
- Dimensions 1-9, 23 (In-Context Captioning): Conceptual Captions Dataset (https://ai.google.com/research/ConceptualCaptions/) under its license (https://github.com/google-research-datasets/conceptual-captions/blob/master/LICENSE). Copyright belongs to the original dataset owner.
- Dimension 9 (Text Recognition): ICDAR2003 (http://www.imglab.org/db/index.html), ICDAR2013(https://rrc.cvc.uab.es/?ch=2), IIIT5k(https://cvit.iiit.ac.in/research/projects/cvit-projects/the-iiit-5k-word-dataset), and SVT(http://vision.ucsd.edu/~kai/svt/). Copyright belongs to the original dataset owner.
- Dimension 10 (Celebrity Recognition): MME (https://github.com/BradyFU/Awesome-Multimodal-Large-Language-Models/tree/Evaluation) and MMBench (https://github.com/open-compass/MMBench) under MMBench license (https://github.com/open-compass/MMBench/blob/main/LICENSE). Copyright belongs to the original dataset owners.
- Dimension 11 (Landmark Recognition): Google Landmark Dataset v2 (https://github.com/cvdfoundation/google-landmark) under CC-BY licenses without ND restrictions.
- Dimension 12 (Chart Understanding): PlotQA (https://github.com/NiteshMethani/PlotQA) under its license (https://github.com/NiteshMethani/PlotQA/blob/master/LICENSE).
- Dimension 13 (Visual Referring Expression): VCR (http://visualcommonsense.com) under its license (http://visualcommonsense.com/license/).
- Dimension 14 (Science Knowledge): ScienceQA (https://github.com/lupantech/ScienceQA) under its license (https://github.com/lupantech/ScienceQA/blob/main/LICENSE-DATA).
- Dimension 15 (Emotion Recognition): FER2013 (https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/challenges-in-representation-learning-facial-expression-recognition-challenge/data) under its license (https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/challenges-in-representation-learning-facial-expression-recognition-challenge/rules#7-competition-data).
- Dimension 16 (Visual Mathematics): MME (https://github.com/BradyFU/Awesome-Multimodal-Large-Language-Models/tree/Evaluation) and data from the internet under CC-BY licenses.
- Dimension 17 (Difference Spotting): MIMICIT (https://github.com/Luodian/Otter/blob/main/mimic-it/README.md) under its license (https://github.com/Luodian/Otter/tree/main/mimic-it#eggs).
- Dimension 18 (Meme Comprehension): Data from the internet under CC-BY licenses.
- Dimension 19 (Global Video Understanding): Charades (https://prior.allenai.org/projects/charades) under its license (https://prior.allenai.org/projects/data/charades/license.txt). SEED-Bench-2 provides 8 frames per video.
- Dimensions 20-22 (Action Recognition, Action Prediction, Procedure Understanding): Something-Something v2 (https://developer.qualcomm.com/software/ai-datasets/something-something), Epic-Kitchen 100 (https://epic-kitchens.github.io/2023), and Breakfast (https://serre-lab.clps.brown.edu/resource/breakfast-actions-dataset/). SEED-Bench-2 provides 8 frames per video.
- Dimension 24 (Interleaved Image-Text Analysis): Data from the internet under CC-BY licenses.
- Dimension 25 (Text-to-Image Generation): CC-500 (https://github.com/weixi-feng/Structured-Diffusion-Guidance) and ABC-6k (https://github.com/weixi-feng/Structured-Diffusion-Guidance) under their license (https://github.com/weixi-feng/Structured-Diffusion-Guidance/blob/master/LICENSE), with images generated by Stable-Diffusion-XL (https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0) under its license (https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0/blob/main/LICENSE.md).
- Dimension 26 (Next Image Prediction): Epic-Kitchen 100 (https://epic-kitchens.github.io/2023) under its license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
- Dimension 27 (Text-Image Creation): Data from the internet under CC-BY licenses.
Please contact us if you believe any data infringes upon your rights, and we will remove it.
For the images of SEED-Bench-1, we use the data from Conceptual Captions Dataset (https://ai.google.com/research/ConceptualCaptions/) following its license (https://github.com/google-research-datasets/conceptual-captions/blob/master/LICENSE). Tencent does not hold the copyright for these images and the copyright belongs to the original owner of Conceptual Captions Dataset.
For the videos of SEED-Bench-1, we use tha data from Something-Something v2 (https://developer.qualcomm.com/software/ai-datasets/something-something), Epic-kitchen 100 (https://epic-kitchens.github.io/2023) and Breakfast (https://serre-lab.clps.brown.edu/resource/breakfast-actions-dataset/). We only provide the video name. Please download them in their official websites.
If you find this repository helpful, please consider citing it:
@article{li2023seed2,
title={SEED-Bench-2: Benchmarking Multimodal Large Language Models},
author={Li, Bohao and Ge, Yuying and Ge, Yixiao and Wang, Guangzhi and Wang, Rui and Zhang, Ruimao and Shan, Ying},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.17092},
year={2023}
}
@article{li2023seed,
title={Seed-bench: Benchmarking multimodal llms with generative comprehension},
author={Li, Bohao and Wang, Rui and Wang, Guangzhi and Ge, Yuying and Ge, Yixiao and Shan, Ying},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.16125},
year={2023}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for SEED-Bench
Similar Open Source Tools

SEED-Bench
SEED-Bench is a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating the performance of multimodal large language models (LLMs) on a wide range of tasks that require both text and image understanding. It consists of two versions: SEED-Bench-1 and SEED-Bench-2. SEED-Bench-1 focuses on evaluating the spatial and temporal understanding of LLMs, while SEED-Bench-2 extends the evaluation to include text and image generation tasks. Both versions of SEED-Bench provide a diverse set of tasks that cover different aspects of multimodal understanding, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners working on LLMs.

AutoPatent
AutoPatent is a multi-agent framework designed for automatic patent generation. It challenges large language models to generate full-length patents based on initial drafts. The framework leverages planner, writer, and examiner agents along with PGTree and RRAG to craft lengthy, intricate, and high-quality patent documents. It introduces a new metric, IRR (Inverse Repetition Rate), to measure sentence repetition within patents. The tool aims to streamline the patent generation process by automating the creation of detailed and specialized patent documents.
MME-RealWorld
MME-RealWorld is a benchmark designed to address real-world applications with practical relevance, featuring 13,366 high-resolution images and 29,429 annotations across 43 tasks. It aims to provide substantial recognition challenges and overcome common barriers in existing Multimodal Large Language Model benchmarks, such as small data scale, restricted data quality, and insufficient task difficulty. The dataset offers advantages in data scale, data quality, task difficulty, and real-world utility compared to existing benchmarks. It also includes a Chinese version with additional images and QA pairs focused on Chinese scenarios.

LightLLM
LightLLM is a lightweight library for linear and logistic regression models. It provides a simple and efficient way to train and deploy machine learning models for regression tasks. The library is designed to be easy to use and integrate into existing projects, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists. With LightLLM, users can quickly build and evaluate regression models using a variety of algorithms and hyperparameters. The library also supports feature engineering and model interpretation, allowing users to gain insights from their data and make informed decisions based on the model predictions.
vision-llms-are-blind
This repository contains the code and data for the paper 'Vision Language Models Are Blind'. It explores the limitations of large language models with vision capabilities (VLMs) in performing basic visual tasks that are easy for humans. The repository presents benchmark results showcasing the poor performance of state-of-the-art VLMs on tasks like counting line intersections, identifying circles, letters, and shapes, and following color-coded paths. The research highlights the challenges faced by VLMs in understanding visual information accurately, drawing parallels to myopia and blindness in human vision.
MicroLens
MicroLens is a content-driven micro-video recommendation dataset at scale. It provides a large dataset with multimodal data, including raw text, images, audio, video, and video comments, for tasks such as multi-modal recommendation, foundation model building, and fairness recommendation. The dataset is available in two versions: MicroLens-50K and MicroLens-100K, with extracted features for multimodal recommendation tasks. Researchers can access the dataset through provided links and reach out to the corresponding author for the complete dataset. The repository also includes codes for various algorithms like VideoRec, IDRec, and VIDRec, each implementing different video models and baselines.
NineRec
NineRec is a benchmark dataset suite for evaluating transferable recommendation models. It provides datasets for pre-training and transfer learning in recommender systems, focusing on multimodal and foundation model tasks. The dataset includes user-item interactions, item texts in multiple languages, item URLs, and raw images. Researchers can use NineRec to develop more effective and efficient methods for pre-training recommendation models beyond end-to-end training. The dataset is accompanied by code for dataset preparation, training, and testing in PyTorch environment.
SeerAttention
SeerAttention is a novel trainable sparse attention mechanism that learns intrinsic sparsity patterns directly from LLMs through self-distillation at post-training time. It achieves faster inference while maintaining accuracy for long-context prefilling. The tool offers features such as trainable sparse attention, block-level sparsity, self-distillation, efficient kernel, and easy integration with existing transformer architectures. Users can quickly start using SeerAttention for inference with AttnGate Adapter and training attention gates with self-distillation. The tool provides efficient evaluation methods and encourages contributions from the community.
Video-MME
Video-MME is the first-ever comprehensive evaluation benchmark of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in Video Analysis. It assesses the capabilities of MLLMs in processing video data, covering a wide range of visual domains, temporal durations, and data modalities. The dataset comprises 900 videos with 256 hours and 2,700 human-annotated question-answer pairs. It distinguishes itself through features like duration variety, diversity in video types, breadth in data modalities, and quality in annotations.
uqlm
UQLM is a Python library for Large Language Model (LLM) hallucination detection using state-of-the-art uncertainty quantification techniques. It provides response-level scorers for quantifying uncertainty of LLM outputs, categorized into four main types: Black-Box Scorers, White-Box Scorers, LLM-as-a-Judge Scorers, and Ensemble Scorers. Users can leverage different scorers to assess uncertainty in generated responses, with options for off-the-shelf usage or customization. The library offers illustrative code snippets and detailed information on available scorers for each type, along with example usage for conducting hallucination detection. Additionally, UQLM includes documentation, example notebooks, and associated research for further exploration and understanding.
swiftide
Swiftide is a fast, streaming indexing and query library tailored for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in AI applications. It is built in Rust, utilizing parallel, asynchronous streams for blazingly fast performance. With Swiftide, users can easily build AI applications from idea to production in just a few lines of code. The tool addresses frustrations around performance, stability, and ease of use encountered while working with Python-based tooling. It offers features like fast streaming indexing pipeline, experimental query pipeline, integrations with various platforms, loaders, transformers, chunkers, embedders, and more. Swiftide aims to provide a platform for data indexing and querying to advance the development of automated Large Language Model (LLM) applications.
openfoodfacts-ai
The openfoodfacts-ai repository is dedicated to tracking and storing experimental AI endeavors, models training, and wishlists related to nutrition table detection, category prediction, logos and labels detection, spellcheck, and other AI projects for Open Food Facts. It serves as a hub for integrating AI models into production and collaborating on AI-related issues. The repository also hosts trained models and datasets for public use and experimentation.
CuMo
CuMo is a project focused on scaling multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with Co-Upcycled Mixture-of-Experts. It introduces CuMo, which incorporates Co-upcycled Top-K sparsely-gated Mixture-of-experts blocks into the vision encoder and the MLP connector, enhancing the capabilities of multimodal LLMs. The project adopts a three-stage training approach with auxiliary losses to stabilize the training process and maintain a balanced loading of experts. CuMo achieves comparable performance to other state-of-the-art multimodal LLMs on various Visual Question Answering (VQA) and visual-instruction-following benchmarks.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
lobe-chat
Lobe Chat is an open-source, modern-design ChatGPT/LLMs UI/Framework. Supports speech-synthesis, multi-modal, and extensible ([function call][docs-functionc-call]) plugin system. One-click **FREE** deployment of your private OpenAI ChatGPT/Claude/Gemini/Groq/Ollama chat application.

WrenAI
WrenAI is a data assistant tool that helps users get results and insights faster by asking questions in natural language, without writing SQL. It leverages Large Language Models (LLM) with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology to enhance comprehension of internal data. Key benefits include fast onboarding, secure design, and open-source availability. WrenAI consists of three core services: Wren UI (intuitive user interface), Wren AI Service (processes queries using a vector database), and Wren Engine (platform backbone). It is currently in alpha version, with new releases planned biweekly.
For similar tasks

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

SEED-Bench
SEED-Bench is a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating the performance of multimodal large language models (LLMs) on a wide range of tasks that require both text and image understanding. It consists of two versions: SEED-Bench-1 and SEED-Bench-2. SEED-Bench-1 focuses on evaluating the spatial and temporal understanding of LLMs, while SEED-Bench-2 extends the evaluation to include text and image generation tasks. Both versions of SEED-Bench provide a diverse set of tasks that cover different aspects of multimodal understanding, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners working on LLMs.
InternGPT
InternGPT (iGPT) is a pointing-language-driven visual interactive system that enhances communication between users and chatbots by incorporating pointing instructions. It improves chatbot accuracy in vision-centric tasks, especially in complex visual scenarios. The system includes an auxiliary control mechanism to enhance the control capability of the language model. InternGPT features a large vision-language model called Husky, fine-tuned for high-quality multi-modal dialogue. Users can interact with ChatGPT by clicking, dragging, and drawing using a pointing device, leading to efficient communication and improved chatbot performance in vision-related tasks.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
