
FuseAI
FuseAI Project
Stars: 77
FuseAI is a repository that focuses on knowledge fusion of large language models. It includes FuseChat, a state-of-the-art 7B LLM on MT-Bench, and FuseLLM, which surpasses Llama-2-7B by fusing three open-source foundation LLMs. The repository provides tech reports, releases, and datasets for FuseChat and FuseLLM, showcasing their performance and advancements in the field of chat models and large language models.
README:




- Jan 21, 2025: 🔥 FuseO1-Preview is our initial endeavor to enhance the System-II reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) through innovative model fusion techniques. By employing our advanced SCE merging methodologies, we integrate multiple open-source o1-like LLMs into a unified model. Our goal is to incorporate the distinct knowledge and strengths from different reasoning LLMs into a single, unified model with strong System-II reasoning abilities, particularly in mathematics, coding, and science domains.
To achieve this, we conduct two types of model merging:
- Long-Long Reasoning Merging: This approach involves model fusion across LLMs that utilize long-CoT reasoning, with the goal of enhancing long-CoT reasoning capabilities. The resulted FuseAI/FuseO1-DeepSeekR1-QwQ-SkyT1-32B-Preview achieves a Pass@1 accuracy of 74.0 on AIME24, demonstrating significant performance improvements compared to the OpenAI o1-preview (44.6) and OpenAI o1-mini (63.4), even approaching OpenAI o1 (79.2).
- Long-Short Reasoning Merging: This approach involves model fusion between long-CoT and short-CoT LLMs, aiming to improve reasoning capabilities in both long and short reasoning processes. The resulted FuseAI/FuseO1-DeepSeekR1-Qwen2.5-Instruct-32B-Preview is capable of utilizing both long and short reasoning processes and demonstrates relatively strong performance in long reasoning tasks.
- Dec 12, 2024: 🔥 We release FuseChat-3.0 and Blog Post. FuseChat-3.0 contains a series of models crafted to enhance performance by integrating the strengths of multiple source LLMs into more compact target LLMs. To achieve this fusion, we utilized four powerful source LLMs: Gemma-2-27b-It, Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407, Qwen-2.5-72B-Instruct, and Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct. For the target LLMs, we employed three widely-used smaller models—Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct, Gemma-2-9B-It, and Qwen-2.5-7B-Instruct—along with two even more compact models—Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct and Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct. . The implicit model fusion process involves a two-stage training pipeline comprising Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) to mitigate distribution discrepancies between target and source LLMs, and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) for learning preferences from multiple source LLMs. The resulting FuseChat-3.0 models demonstrated substantial improvements in tasks related to general conversation, instruction following, mathematics, and coding. Notably, when Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct served as the target LLM, our fusion approach achieved an average improvement of 6.8 points across 14 benchmarks. Moreover, it showed significant improvements of 37.1 and 30.1 points on instruction-following test sets AlpacaEval-2 and Arena-Hard respectively.
-
Aug 16, 2024: 🔥🔥🔥🔥 We update the FuseChat tech report and release FuseChat-7B-v2.0, which is the fusion of six prominent chat LLMs with diverse architectures and scales, namely OpenChat-3.5-7B, Starling-LM-7B-alpha, NH2-Solar-10.7B, InternLM2-Chat-20B, Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct, and Qwen1.5-Chat-72B. FuseChat-7B-v2.0 achieves an average performance of 7.38 on MT-Bench (GPT-4-0125-Preview as judge LLM), which is comparable to Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct and approaches GPT-3.5-Turbo-1106.
-
Mar 13, 2024: 🔥🔥🔥 We release a HuggingFace Space for FuseChat-7B, try it now!
-
Feb 26, 2024: 🔥🔥 We release FuseChat-7B-VaRM, which is the fusion of three prominent chat LLMs with diverse architectures and scales, namely NH2-Mixtral-8x7B, NH2-Solar-10.7B, and OpenChat-3.5-7B. FuseChat-7B-VaRM achieves an average performance of 8.22 on MT-Bench, outperforming various powerful chat LLMs like Starling-7B, Yi-34B-Chat, and Tulu-2-DPO-70B, even surpassing GPT-3.5 (March), Claude-2.1, and approaching Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct.
-
Feb 25, 2024: 🔥 We release FuseChat-Mixture, which is a comprehensive training dataset covers different styles and capabilities, featuring both human-written and model-generated, and spanning general instruction-following and specific skills.
- Jan 22, 2024: 🔥 We release FuseLLM-7B, which is the fusion of three open-source foundation LLMs with distinct architectures, including Llama-2-7B, OpenLLaMA-7B, and MPT-7B.
Please cite the following paper if you reference our model, code, data, or paper related to FuseLLM.
@inproceedings{wan2024knowledge,
title={Knowledge Fusion of Large Language Models},
author={Fanqi Wan and Xinting Huang and Deng Cai and Xiaojun Quan and Wei Bi and Shuming Shi},
booktitle={The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/pdf?id=jiDsk12qcz}
}
Please cite the following paper if you reference our model, code, data, or paper related to FuseChat.
@article{wan2024fusechat,
title={FuseChat: Knowledge Fusion of Chat Models},
author={Fanqi Wan and Longguang Zhong and Ziyi Yang and Ruijun Chen and Xiaojun Quan},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.07990},
year={2024}
}
Please cite the following paper if you reference our model, code, data, or paper related to WRPO.
@inproceedings{yang2025weightedreward,
title={Weighted-Reward Preference Optimization for Implicit Model Fusion},
author={Ziyi Yang and Fanqi Wan and Longguang Zhong and Tianyuan Shi and Xiaojun Quan},
booktitle={The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2025},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=fq24pEb8SL}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for FuseAI
Similar Open Source Tools

FuseAI
FuseAI is a repository that focuses on knowledge fusion of large language models. It includes FuseChat, a state-of-the-art 7B LLM on MT-Bench, and FuseLLM, which surpasses Llama-2-7B by fusing three open-source foundation LLMs. The repository provides tech reports, releases, and datasets for FuseChat and FuseLLM, showcasing their performance and advancements in the field of chat models and large language models.

LightLLM
LightLLM is a lightweight library for linear and logistic regression models. It provides a simple and efficient way to train and deploy machine learning models for regression tasks. The library is designed to be easy to use and integrate into existing projects, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists. With LightLLM, users can quickly build and evaluate regression models using a variety of algorithms and hyperparameters. The library also supports feature engineering and model interpretation, allowing users to gain insights from their data and make informed decisions based on the model predictions.

AutoPatent
AutoPatent is a multi-agent framework designed for automatic patent generation. It challenges large language models to generate full-length patents based on initial drafts. The framework leverages planner, writer, and examiner agents along with PGTree and RRAG to craft lengthy, intricate, and high-quality patent documents. It introduces a new metric, IRR (Inverse Repetition Rate), to measure sentence repetition within patents. The tool aims to streamline the patent generation process by automating the creation of detailed and specialized patent documents.
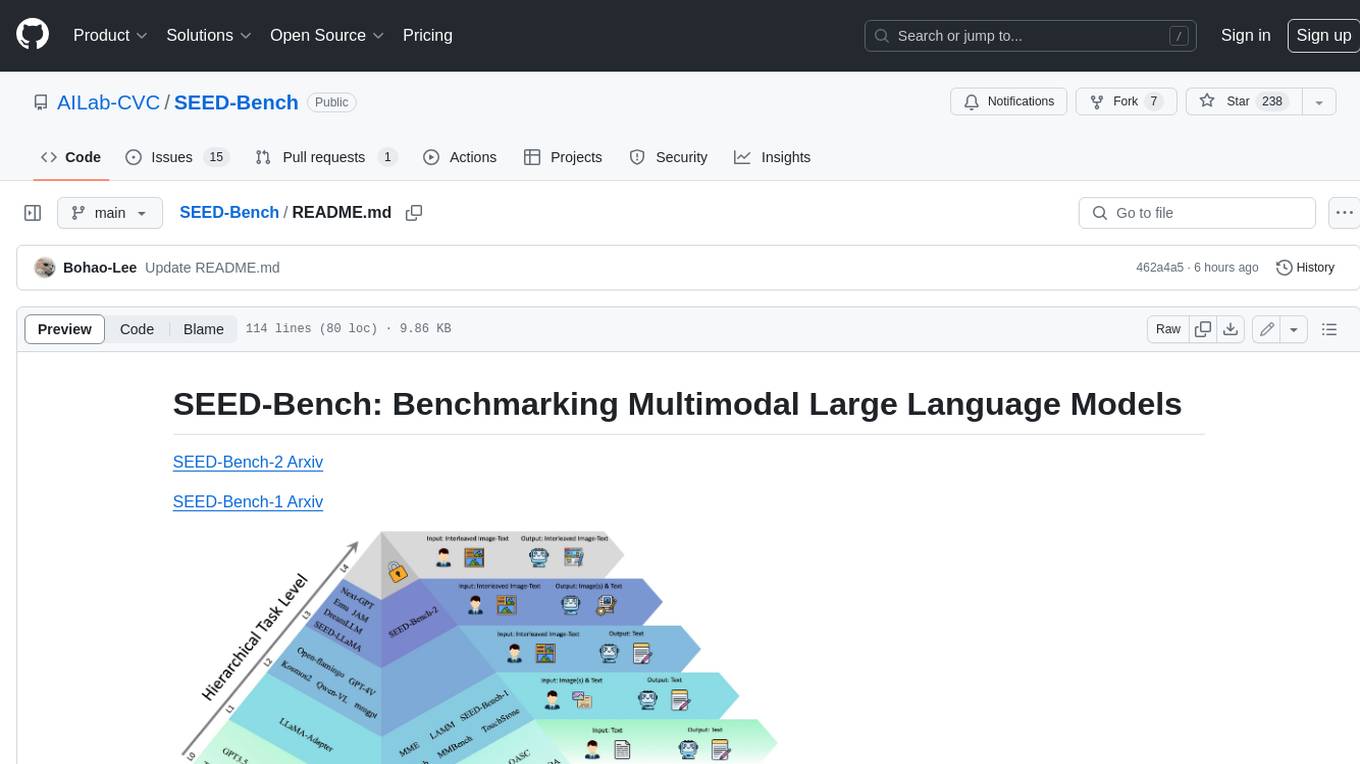
SEED-Bench
SEED-Bench is a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating the performance of multimodal large language models (LLMs) on a wide range of tasks that require both text and image understanding. It consists of two versions: SEED-Bench-1 and SEED-Bench-2. SEED-Bench-1 focuses on evaluating the spatial and temporal understanding of LLMs, while SEED-Bench-2 extends the evaluation to include text and image generation tasks. Both versions of SEED-Bench provide a diverse set of tasks that cover different aspects of multimodal understanding, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners working on LLMs.
lobe-chat
Lobe Chat is an open-source, modern-design ChatGPT/LLMs UI/Framework. Supports speech-synthesis, multi-modal, and extensible ([function call][docs-functionc-call]) plugin system. One-click **FREE** deployment of your private OpenAI ChatGPT/Claude/Gemini/Groq/Ollama chat application.
Awesome-Attention-Heads
Awesome-Attention-Heads is a platform providing the latest research on Attention Heads, focusing on enhancing understanding of Transformer structure for model interpretability. It explores attention mechanisms for behavior, inference, and analysis, alongside feed-forward networks for knowledge storage. The repository aims to support researchers studying LLM interpretability and hallucination by offering cutting-edge information on Attention Head Mining.
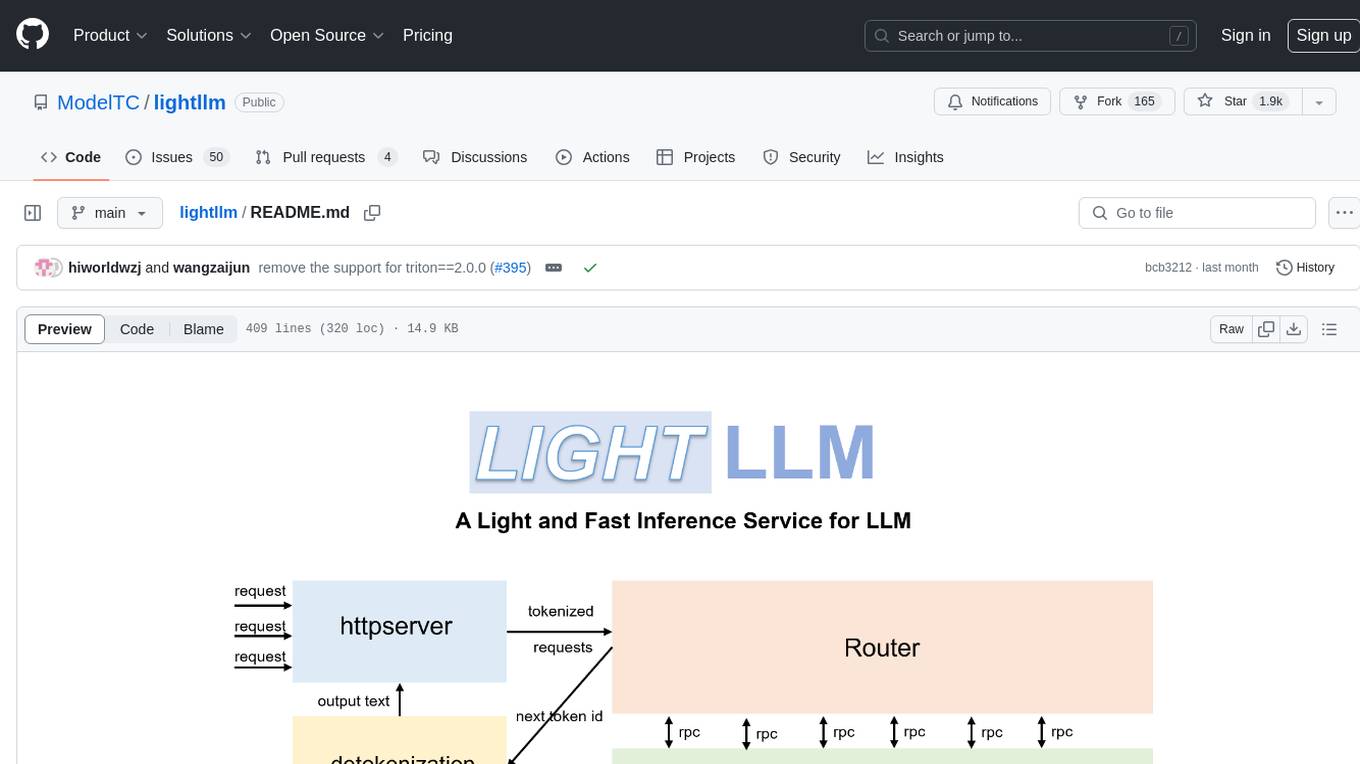
lightllm
LightLLM is a Python-based LLM (Large Language Model) inference and serving framework known for its lightweight design, scalability, and high-speed performance. It offers features like tri-process asynchronous collaboration, Nopad for efficient attention operations, dynamic batch scheduling, FlashAttention integration, tensor parallelism, Token Attention for zero memory waste, and Int8KV Cache. The tool supports various models like BLOOM, LLaMA, StarCoder, Qwen-7b, ChatGLM2-6b, Baichuan-7b, Baichuan2-7b, Baichuan2-13b, InternLM-7b, Yi-34b, Qwen-VL, Llava-7b, Mixtral, Stablelm, and MiniCPM. Users can deploy and query models using the provided server launch commands and interact with multimodal models like QWen-VL and Llava using specific queries and images.

lerobot
LeRobot is a state-of-the-art AI library for real-world robotics in PyTorch. It aims to provide models, datasets, and tools to lower the barrier to entry to robotics, focusing on imitation learning and reinforcement learning. LeRobot offers pretrained models, datasets with human-collected demonstrations, and simulation environments. It plans to support real-world robotics on affordable and capable robots. The library hosts pretrained models and datasets on the Hugging Face community page.
intro_pharma_ai
This repository serves as an educational resource for pharmaceutical and chemistry students to learn the basics of Deep Learning through a collection of Jupyter Notebooks. The content covers various topics such as Introduction to Jupyter, Python, Cheminformatics & RDKit, Linear Regression, Data Science, Linear Algebra, Neural Networks, PyTorch, Convolutional Neural Networks, Transfer Learning, Recurrent Neural Networks, Autoencoders, Graph Neural Networks, and Summary. The notebooks aim to provide theoretical concepts to understand neural networks through code completion, but instructors are encouraged to supplement with their own lectures. The work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
DataDreamer
DataDreamer is a powerful open-source Python library designed for prompting, synthetic data generation, and training workflows. It is simple, efficient, and research-grade, allowing users to create prompting workflows, generate synthetic datasets, and train models with ease. The library is built for researchers, by researchers, focusing on correctness, best practices, and reproducibility. It offers features like aggressive caching, resumability, support for bleeding-edge techniques, and easy sharing of datasets and models. DataDreamer enables users to run multi-step prompting workflows, generate synthetic datasets for various tasks, and train models by aligning, fine-tuning, instruction-tuning, and distilling them using existing or synthetic data.
qgate-model
QGate-Model is a machine learning meta-model with synthetic data, designed for MLOps and feature store. It is independent of machine learning solutions, with definitions in JSON and data in CSV/parquet formats. This meta-model is useful for comparing capabilities and functions of machine learning solutions, independently testing new versions of machine learning solutions, and conducting various types of tests (unit, sanity, smoke, system, regression, function, acceptance, performance, shadow, etc.). It can also be used for external test coverage when internal test coverage is not available or weak.
Genesis
Genesis is a physics platform designed for general purpose Robotics/Embodied AI/Physical AI applications. It includes a universal physics engine, a lightweight, ultra-fast, pythonic, and user-friendly robotics simulation platform, a powerful and fast photo-realistic rendering system, and a generative data engine that transforms user-prompted natural language description into various modalities of data. It aims to lower the barrier to using physics simulations, unify state-of-the-art physics solvers, and minimize human effort in collecting and generating data for robotics and other domains.
kornia
Kornia is a differentiable computer vision library for PyTorch. It consists of a set of routines and differentiable modules to solve generic computer vision problems. At its core, the package uses PyTorch as its main backend both for efficiency and to take advantage of the reverse-mode auto-differentiation to define and compute the gradient of complex functions.

ERNIE
ERNIE 4.5 is a family of large-scale multimodal models with 10 distinct variants, including Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models with 47B and 3B active parameters. The models feature a novel heterogeneous modality structure supporting parameter sharing across modalities while allowing dedicated parameters for each individual modality. Trained with optimal efficiency using PaddlePaddle deep learning framework, ERNIE 4.5 models achieve state-of-the-art performance across text and multimodal benchmarks, enhancing multimodal understanding without compromising performance on text-related tasks. The open-source development toolkits for ERNIE 4.5 offer industrial-grade capabilities, resource-efficient training and inference workflows, and multi-hardware compatibility.
uqlm
UQLM is a Python library for Large Language Model (LLM) hallucination detection using state-of-the-art uncertainty quantification techniques. It provides response-level scorers for quantifying uncertainty of LLM outputs, categorized into four main types: Black-Box Scorers, White-Box Scorers, LLM-as-a-Judge Scorers, and Ensemble Scorers. Users can leverage different scorers to assess uncertainty in generated responses, with options for off-the-shelf usage or customization. The library offers illustrative code snippets and detailed information on available scorers for each type, along with example usage for conducting hallucination detection. Additionally, UQLM includes documentation, example notebooks, and associated research for further exploration and understanding.
For similar tasks

FuseAI
FuseAI is a repository that focuses on knowledge fusion of large language models. It includes FuseChat, a state-of-the-art 7B LLM on MT-Bench, and FuseLLM, which surpasses Llama-2-7B by fusing three open-source foundation LLMs. The repository provides tech reports, releases, and datasets for FuseChat and FuseLLM, showcasing their performance and advancements in the field of chat models and large language models.
For similar jobs
Awesome-AI
Awesome AI is a repository that collects and shares resources in the fields of large language models (LLM), AI-assisted programming, AI drawing, and more. It explores the application and development of generative artificial intelligence. The repository provides information on various AI tools, models, and platforms, along with tutorials and web products related to AI technologies.
sdkit
sdkit (stable diffusion kit) is an easy-to-use library for utilizing Stable Diffusion in AI Art projects. It includes features like ControlNets, LoRAs, Textual Inversion Embeddings, GFPGAN, CodeFormer for face restoration, RealESRGAN for upscaling, k-samplers, support for custom VAEs, NSFW filter, model-downloader, parallel GPU support, and more. It offers a model database, auto-scanning for malicious models, and various optimizations. The API consists of modules for loading models, generating images, filters, model merging, and utilities, all managed through the sdkit.Context object.
LearnPrompt
LearnPrompt is a permanent, free, open-source AIGC course platform that currently supports various tools like ChatGPT, Agent, Midjourney, Runway, Stable Diffusion, AI digital humans, AI voice & music, and large model fine-tuning. The platform offers features such as multilingual support, comment sections, daily selections, and submissions. Users can explore different modules, including sound cloning, RAG, GPT-SoVits, and OpenAI Sora world model. The platform aims to continuously update and provide tutorials, examples, and knowledge systems related to AI technologies.
FluxAIGridComparisons
FluxAIGridComparisons is a repository containing a collection of different image grids generated using Flux. These grids showcase various attributes such as hairstyles, clothing, nationalities, and ages. The repository serves as a visual comparison tool for exploring different characteristics within images.

FuseAI
FuseAI is a repository that focuses on knowledge fusion of large language models. It includes FuseChat, a state-of-the-art 7B LLM on MT-Bench, and FuseLLM, which surpasses Llama-2-7B by fusing three open-source foundation LLMs. The repository provides tech reports, releases, and datasets for FuseChat and FuseLLM, showcasing their performance and advancements in the field of chat models and large language models.
prajna
Prajna is an open-source programming language specifically developed for building more modular, automated, and intelligent artificial intelligence infrastructure. It aims to cater to various stages of AI research, training, and deployment by providing easy access to CPU, GPU, and various TPUs for AI computing. Prajna features just-in-time compilation, GPU/heterogeneous programming support, tensor computing, syntax improvements, and user-friendly interactions through main functions, Repl, and Jupyter, making it suitable for algorithm development and deployment in various scenarios.
LangChain-Udemy-Course
LangChain-Udemy-Course is a comprehensive course directory focusing on LangChain, a framework for generative AI applications. The course covers various aspects such as OpenAI API usage, prompt templates, Chains exploration, callback functions, memory techniques, RAG implementation, autonomous agents, hybrid search, LangSmith utilization, microservice architecture, and LangChain Expression Language. Learners gain theoretical knowledge and practical insights to understand and apply LangChain effectively in generative AI scenarios.
awesome-open-ended
A curated list of open-ended learning AI resources focusing on algorithms that invent new and complex tasks endlessly, inspired by human advancements. The repository includes papers, safety considerations, surveys, perspectives, and blog posts related to open-ended AI research.







