
langrila
useful tool to use API-based LLM in an easy way
Stars: 62
Langrila is a library that provides an easy way to use API-based LLM (Large Language Models) with an emphasis on simple architecture for readability. It supports various AI models for chat and embedding tasks, as well as retrieval functionalities using Qdrant, Chroma, and Usearch. Langrila also includes modules for function calling, conversation memory management, and prompt templates. It enforces coding policies for simplicity, responsibility independence, and minimum module implementation. The library requires Python version 3.10 to 3.13 and additional dependencies like OpenAI, Gemini, Qdrant, Chroma, and Usearch for specific functionalities.
README:
NOTE: This package is under rebuilding including significant changes on the interface.
Langrila is an open-source third-party python package allows you to develop type-safe multi-agent in an easy way. This package is just personal project.
Widely used existing agent framework is all awesome, but I feel like:
- Often highly abstracted, making their behavior unclear at times and causes low extensibility.
- Code readability has some issues derived from many decorators and special operator when we are developing agent using that framework.
- Handling an agent's state or context is a little annoying. Typically it requires special arguments in functions and the state is updated hidden by tool. This might causes confusion on treaceability of the state. Ideally, functions implemented in regular development should be usable as-is with an agent, and state scope is explained by dependencies of agents, I think.
- The arguments, specifications, and available models of client APIs are frequently updated. To follow that is a little cumbersome.
To address these issues, I breathed new life into langrila, which has the following features:
- Minimal wrapper classes for each client API:
- Wrapper classes are minimally designed, avoiding unnecessary unification of arguments and eliminating processing dependent on model names.
- No need for special argument to inject context into tools:
- There is no requirement to set instances of special classes as arguments when injecting context into tools.
- Support for sub-agents as tools:
- In addition to passing tools to agents, sub-agents can be passed directly to the agent. Sub-agents are dynamically converted into tools internally and controlled by the parent agent, enabling easy construction of multi-agent systems. This feature brings to you intuitive coding and readability of the multi-agent.
- Unified message-response model independent of client APIs:
- Langrila defines a standardized message-response model that allows multi-agent systems to be built across different clients.
- Serializable conversation history:
- The standardized message-response model can be serialized to JSON and easily stored not only in memory but also in formats like JSON, Pickle, Azure Cosmos DB, and AWS S3.
- Type-safe structured output:
- Inspired by PydanticAI.
- Multi-modal I/O:
- Whatever the client supports like image/video/pdf/audio/uri input, image/audio generation, embed texts and so on.
- I will be rolling out support progressively.
- Whatever the client supports like image/video/pdf/audio/uri input, image/audio generation, embed texts and so on.
- Others:
- Automatic retry when error raised.
- Customizable internal prompts.
- Usage gathering for all sub-agents.
- All we have to do to support new client is to implement a single class in many cases.
If necessary, set environment variables to use OpenAI API, Azure OpenAI Service, Gemini API, and Claude API; if using VertexAI or Amazon Bedrock, check each platform's user guide and authenticate in advance VertexAI and Amazon Bedrock.
- OpenAI
- Azure OpenAI
- Gemini on Google AI Studio
- Gemini on VertexAI
- Claude on Anthropic
- Claude on Amazon Bedrock
- Claude on VertexAI (not tested)
Significant breaking changes will be introduced to become agent framework. It's more like a rebuild than just an update. Please be careful to update from the previous version.
Coming soon.
python = ">=3.10,<3.13"
matplotlib = "^3.8.0"
plotly = "^5.17.0"
numpy = "^1.26.1"
pandas = "^2.1.1"
scipy = "^1.11.3"
scikit-learn = "^1.3.2"
pydantic = "^2.10.0"
griffe = "^1.5.1"
loguru = "^0.7.3"
Langrila has various extra installation options. See the following installation section and pyproject.toml.
See extra dependencies section in pyproject.toml for more detail installation options.
# For OpenAI
pip install langrila[openai]
# For Gemini
pip install langrila[gemini]
# For Claude
pip install langrila[claude]
# For multiple clients
pip install langrila[openai,gemini,claude]
# With dependencies to handle specific data. Here is an example using gemini
pip install langrila[gemini,audio,video,pdf]
# With dependencies for specific platform. Here is an example using gemini on VertexAI
pip install langrila[gemini,vertexai]
# With dependencies for specific vectorDB. Here is an example using Qdrant
pip install langrila[openai,qdrant]
# For OpenAI
poetry add langrila --extras openai
# For Gemini
poetry add langrila --extras gemini
# For Claude
poetry add langrila --extras claude
# For multiple clients
poetry add langrila --extras "openai gemini claude"
# With dependencies to handle specific data. Here is an example using gemini
poetry add langrila --extras "gemini audio video pdf"
# With dependencies for specific platform. Here is an example using gemini on VertexAI
poetry add langrila --extras "gemini vertexai"
# With dependencies for specific vectorDB. Here is an example using Qdrant
poetry add langrila --extras "openai qdrant"
git clone [email protected]:taikinman/langrila.git
cd langrila
pip install -e .{extra packages}
# For OpenAI
poetry add --editable /path/to/langrila/ --extras "{extra packages}"
In langrila, we can build orchestrator-typed multi-agent, not graph-based multi-agent. The orchestrator routes the execution of tools to individual agents, aggregates the results, and outputs the final answer.
Here is a fragment of the example code with dummy tools.
from langrila import Agent, InMemoryConversationMemory
from langrila.anthropic import AnthropicClient
from langrila.google import GoogleClient
from langrila.openai import OpenAIClient
from enum import Enum
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
#################################
# Client wrapper
#################################
# For OpenAI
openai_client = OpenAIClient(api_key_env_name="OPENAI_API_KEY")
# For Gemini on Google AI Studio
google_client = GoogleClient(api_key_env_name="GEMINI_API_KEY")
# For Claude of Anthropic
anthropic_client = AnthropicClient(api_key_env_name="ANTHROPIC_API_KEY")
#################################
# Tool definition
#################################
def power_disco_ball(power: bool) -> bool:
"""
Powers the spinning dissco ball.
Parameters
----------
power : bool
Whether to power the disco ball or not.
Returns
----------
bool
Whether the disco ball is spinning or not.
"""
return f"Disco ball is {'spinning!' if power else 'stopped.'}"
...
#################################
# Definition of response schema
#################################
class DiscoBallSchema(BaseModel):
power: bool = Field(..., description="Whether to power the disco ball.")
spinning: bool = Field(..., description="Whether the disco ball is spinning.")
class MusicGenre(str, Enum):
rock = "rock"
pop = "pop"
jazz = "jazz"
classical = "classical"
hip_hop = "hip-hop"
class MusicSchema(BaseModel):
genre: MusicGenre = Field(
...,
description="The genre of music to play.",
)
bpm: int = Field(
...,
description="The BPM of the music.",
ge=60,
le=180,
)
volume: float = Field(
...,
description="The volume level to set the music to.",
ge=0,
le=1,
)
class LightsSchema(BaseModel):
brightness: float = Field(
...,
description="The brightness level to set the lights to.",
ge=0,
le=1,
)
class ResponseSchema(BaseModel):
disco_ball: DiscoBallSchema = Field(None, description="The disco ball settings.")
music: MusicSchema = Field(None, description="The music settings.")
lights: LightsSchema = Field(None, description="The lights settings.")
#################################
# Orchestration
#################################
lights_agent = Agent(
client=openai_client,
model="gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18",
temperature=0.0,
tools=[dim_lights, brighten_lights, turn_light_on],
)
disco_ball_agent = Agent(
client=openai_client,
model="gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18",
temperature=0.0,
tools=[power_disco_ball, stop_disco_ball],
max_tokens=500,
)
music_power_agent = Agent(
client=openai_client,
model="gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18",
temperature=0.0,
tools=[start_music],
)
music_control_agent = Agent(
client=openai_client,
model="gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18",
temperature=0.0,
tools=[change_music, adjust_volume, change_bpm],
)
# Orchestrator as a sub-agent
music_agent_orchesrator = Agent(
client=anthropic_client,
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
temperature=0.0,
subagents=[music_power_agent, music_control_agent],
max_tokens=500,
)
# Master orchestrator
master_orchesrator = Agent(
client=google_client,
model="gemini-2.0-flash-exp",
temperature=0.0,
subagents=[lights_agent, disco_ball_agent, music_agent_orchesrator],
response_schema_as_tool=ResponseSchema,
conversation_memory=InMemoryConversationMemory(),
)
#################################
# Invoke agent
#################################
prompt = "Turn this place into a party mood."
# synchronous generation
response = master_orchesrator.generate_text(prompt=prompt)
# asynchronous generation
response = await master_orchesrator.generate_text_async(prompt=prompt)
#################################
# Result
#################################
ResponseSchema.model_validate_json(response.contents[0].text)
# >>> ResponseSchema(disco_ball=DiscoBallSchema(power=True, spinning=True), music=MusicSchema(genre=<MusicGenre.pop: 'pop'>, bpm=120, volume=0.7), lights=LightsSchema(brightness=1.0))
#################################
# Usage
#################################
list(response.usage.items())
# >>> [('music_power_agent',
# >>> Usage(model_name='gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', prompt_tokens=123, output_tokens=23, raw=None)),
# >>> ('music_agent_orchesrator',
# >>> Usage(model_name='claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620', prompt_tokens=2510, output_tokens=368, raw=None)),
# >>> ('music_control_agent',
# >>> Usage(model_name='gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', prompt_tokens=541, output_tokens=83, raw=None)),
# >>> ('lights_agent',
# >>> Usage(model_name='gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', prompt_tokens=345, output_tokens=60, raw=None)),
# >>> ('root',
# >>> Usage(model_name='gemini-2.0-flash-exp', prompt_tokens=3273, output_tokens=82, raw=None)),
# >>> ('disco_ball_agent',
# >>> Usage(model_name='gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', prompt_tokens=211, output_tokens=31, raw=None))]- [ ] Error handling more
- [ ] Preparing example notebooks
- [ ] Linting and refactor
- [ ] Supporting Huggingface
- [ ] Aim integration
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for langrila
Similar Open Source Tools

langrila
Langrila is a library that provides an easy way to use API-based LLM (Large Language Models) with an emphasis on simple architecture for readability. It supports various AI models for chat and embedding tasks, as well as retrieval functionalities using Qdrant, Chroma, and Usearch. Langrila also includes modules for function calling, conversation memory management, and prompt templates. It enforces coding policies for simplicity, responsibility independence, and minimum module implementation. The library requires Python version 3.10 to 3.13 and additional dependencies like OpenAI, Gemini, Qdrant, Chroma, and Usearch for specific functionalities.
GraphRAG-SDK
Build fast and accurate GenAI applications with GraphRAG SDK, a specialized toolkit for building Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG) systems. It integrates knowledge graphs, ontology management, and state-of-the-art LLMs to deliver accurate, efficient, and customizable RAG workflows. The SDK simplifies the development process by automating ontology creation, knowledge graph agent creation, and query handling, enabling users to interact and query their knowledge graphs effectively. It supports multi-agent systems and orchestrates agents specialized in different domains. The SDK is optimized for FalkorDB, ensuring high performance and scalability for large-scale applications. By leveraging knowledge graphs, it enables semantic relationships and ontology-driven queries that go beyond standard vector similarity, enhancing retrieval-augmented generation capabilities.
lionagi
LionAGI is a powerful intelligent workflow automation framework that introduces advanced ML models into any existing workflows and data infrastructure. It can interact with almost any model, run interactions in parallel for most models, produce structured pydantic outputs with flexible usage, automate workflow via graph based agents, use advanced prompting techniques, and more. LionAGI aims to provide a centralized agent-managed framework for "ML-powered tools coordination" and to dramatically lower the barrier of entries for creating use-case/domain specific tools. It is designed to be asynchronous only and requires Python 3.10 or higher.
lionagi
LionAGI is a robust framework for orchestrating multi-step AI operations with precise control. It allows users to bring together multiple models, advanced reasoning, tool integrations, and custom validations in a single coherent pipeline. The framework is structured, expandable, controlled, and transparent, offering features like real-time logging, message introspection, and tool usage tracking. LionAGI supports advanced multi-step reasoning with ReAct, integrates with Anthropic's Model Context Protocol, and provides observability and debugging tools. Users can seamlessly orchestrate multiple models, integrate with Claude Code CLI SDK, and leverage a fan-out fan-in pattern for orchestration. The framework also offers optional dependencies for additional functionalities like reader tools, local inference support, rich output formatting, database support, and graph visualization.
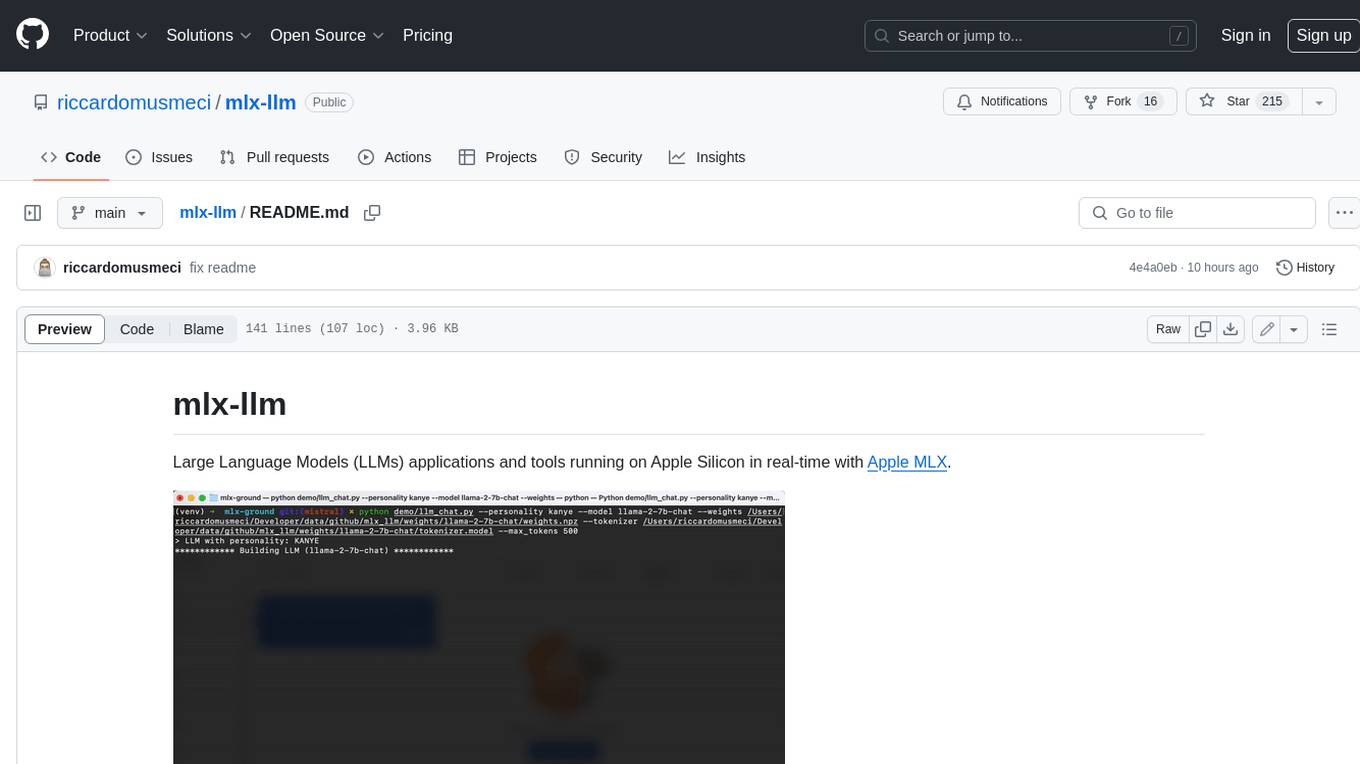
mlx-llm
mlx-llm is a library that allows you to run Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple Silicon devices in real-time using Apple's MLX framework. It provides a simple and easy-to-use API for creating, loading, and using LLM models, as well as a variety of applications such as chatbots, fine-tuning, and retrieval-augmented generation.
map-anything
MapAnything is an end-to-end trained transformer model for 3D reconstruction tasks, supporting over 12 different tasks including multi-image sfm, multi-view stereo, monocular metric depth estimation, and more. It provides a simple and efficient way to regress the factored metric 3D geometry of a scene from various inputs like images, calibration, poses, or depth. The tool offers flexibility in combining different geometric inputs for enhanced reconstruction results. It includes interactive demos, support for COLMAP & GSplat, data processing for training & benchmarking, and pre-trained models on Hugging Face Hub with different licensing options.
pandas-ai
PandaAI is a Python platform that enables users to interact with their data in natural language, catering to both non-technical and technical users. It simplifies data querying and analysis, offering conversational data analytics capabilities with minimal code. Users can ask questions, visualize charts, and compare dataframes effortlessly. The tool aims to streamline data exploration and decision-making processes by providing a user-friendly interface for data manipulation and analysis.
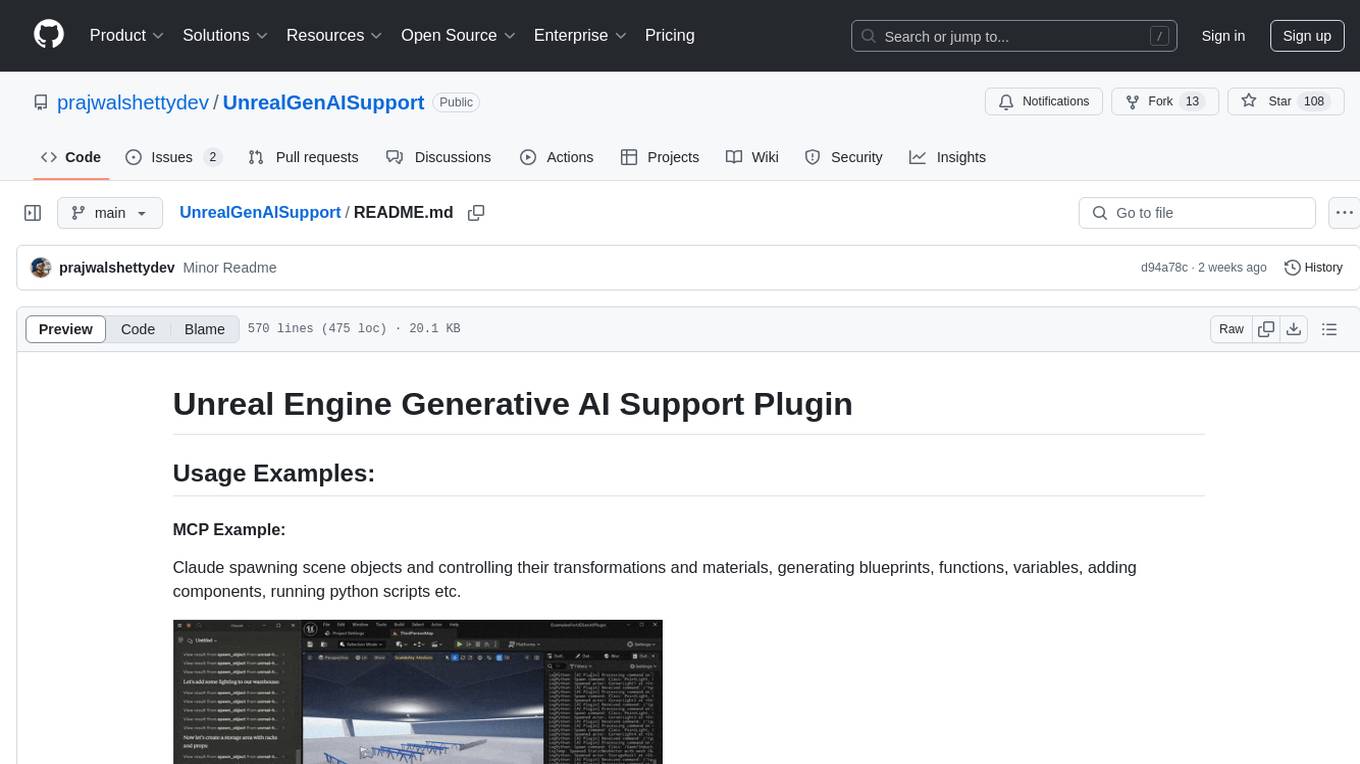
UnrealGenAISupport
The Unreal Engine Generative AI Support Plugin is a tool designed to integrate various cutting-edge LLM/GenAI models into Unreal Engine for game development. It aims to simplify the process of using AI models for game development tasks, such as controlling scene objects, generating blueprints, running Python scripts, and more. The plugin currently supports models from organizations like OpenAI, Anthropic, XAI, Google Gemini, Meta AI, Deepseek, and Baidu. It provides features like API support, model control, generative AI capabilities, UI generation, project file management, and more. The plugin is still under development but offers a promising solution for integrating AI models into game development workflows.
instructor
Instructor is a tool that provides structured outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs) in a reliable manner. It simplifies the process of extracting structured data by utilizing Pydantic for validation, type safety, and IDE support. With Instructor, users can define models and easily obtain structured data without the need for complex JSON parsing, error handling, or retries. The tool supports automatic retries, streaming support, and extraction of nested objects, making it production-ready for various AI applications. Trusted by a large community of developers and companies, Instructor is used by teams at OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, AWS, and YC startups.

fastrtc
FastRTC is a real-time communication library for Python that allows users to turn any Python function into a real-time audio and video stream over WebRTC or WebSockets. It provides features like automatic voice detection, UI launching, WebRTC support, WebSocket support, telephone support, and customizable backend for production applications. The library offers various examples and usage scenarios for audio and video streaming, object detection, voice APIs, chat applications, and more.
mcp-agent
mcp-agent is a simple, composable framework designed to build agents using the Model Context Protocol. It handles the lifecycle of MCP server connections and implements patterns for building production-ready AI agents in a composable way. The framework also includes OpenAI's Swarm pattern for multi-agent orchestration in a model-agnostic manner, making it the simplest way to build robust agent applications. It is purpose-built for the shared protocol MCP, lightweight, and closer to an agent pattern library than a framework. mcp-agent allows developers to focus on the core business logic of their AI applications by handling mechanics such as server connections, working with LLMs, and supporting external signals like human input.
llm
llm.rb is a zero-dependency Ruby toolkit for Large Language Models that includes OpenAI, Gemini, Anthropic, xAI (Grok), DeepSeek, Ollama, and LlamaCpp. The toolkit provides full support for chat, streaming, tool calling, audio, images, files, and structured outputs (JSON Schema). It offers a single unified interface for multiple providers, zero dependencies outside Ruby's standard library, smart API design, and optional per-provider process-wide connection pool. Features include chat, agents, media support (text-to-speech, transcription, translation, image generation, editing), embeddings, model management, and more.

dynamiq
Dynamiq is an orchestration framework designed to streamline the development of AI-powered applications, specializing in orchestrating retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and large language model (LLM) agents. It provides an all-in-one Gen AI framework for agentic AI and LLM applications, offering tools for multi-agent orchestration, document indexing, and retrieval flows. With Dynamiq, users can easily build and deploy AI solutions for various tasks.
cappr
CAPPr is a tool for text classification that does not require training or post-processing. It allows users to have their language models pick from a list of choices or compute the probability of a completion given a prompt. The tool aims to help users get more out of open source language models by simplifying the text classification process. CAPPr can be used with GGUF models, Hugging Face models, models from the OpenAI API, and for tasks like caching instructions, extracting final answers from step-by-step completions, and running predictions in batches with different sets of completions.
LLMRec
LLMRec is a PyTorch implementation for the WSDM 2024 paper 'Large Language Models with Graph Augmentation for Recommendation'. It is a novel framework that enhances recommenders by applying LLM-based graph augmentation strategies to recommendation systems. The tool aims to make the most of content within online platforms to augment interaction graphs by reinforcing u-i interactive edges, enhancing item node attributes, and conducting user node profiling from a natural language perspective.
gem
GEM is an open-source General Experience Maker designed for training Large Language Models (LLMs) in dynamic environments. Similar to OpenAI Gym for traditional Reinforcement Learning, GEM provides a variety of environments with standardized interfaces for seamless integration with existing LLM training frameworks. It offers tool integration, flexible wrappers, async vectorized environment execution, multi-environment training, and more to simplify LLM agent training.
For similar tasks

langrila
Langrila is a library that provides an easy way to use API-based LLM (Large Language Models) with an emphasis on simple architecture for readability. It supports various AI models for chat and embedding tasks, as well as retrieval functionalities using Qdrant, Chroma, and Usearch. Langrila also includes modules for function calling, conversation memory management, and prompt templates. It enforces coding policies for simplicity, responsibility independence, and minimum module implementation. The library requires Python version 3.10 to 3.13 and additional dependencies like OpenAI, Gemini, Qdrant, Chroma, and Usearch for specific functionalities.
lunary
Lunary is an open-source observability and prompt platform for Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a suite of features to help AI developers take their applications into production, including analytics, monitoring, prompt templates, fine-tuning dataset creation, chat and feedback tracking, and evaluations. Lunary is designed to be usable with any model, not just OpenAI, and is easy to integrate and self-host.
minimal-llm-ui
This minimalistic UI serves as a simple interface for Ollama models, enabling real-time interaction with Local Language Models (LLMs). Users can chat with models, switch between different LLMs, save conversations, and create parameter-driven prompt templates. The tool is built using React, Next.js, and Tailwind CSS, with seamless integration with LangchainJs and Ollama for efficient model switching and context storage.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.