
files-to-prompt
Concatenate a directory full of files into a single prompt for use with LLMs
Stars: 264
files-to-prompt is a tool that concatenates a directory full of files into a single prompt for use with Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to provide the path to one or more files or directories for processing, outputting the contents of each file with relative paths and separators. The tool offers options to include hidden files, ignore specific patterns, and exclude files specified in .gitignore. It is designed to streamline the process of preparing text data for LLMs by simplifying file concatenation and customization.
README:
Concatenate a directory full of files into a single prompt for use with LLMs
For background on this project see Building files-to-prompt entirely using Claude 3 Opus.
Install this tool using pip:
pip install files-to-promptTo use files-to-prompt, provide the path to one or more files or directories you want to process:
files-to-prompt path/to/file_or_directory [path/to/another/file_or_directory ...]This will output the contents of every file, with each file preceded by its relative path and separated by ---.
-
--include-hidden: Include files and folders starting with.(hidden files and directories).files-to-prompt path/to/directory --include-hidden
-
--ignore-gitignore: Ignore.gitignorefiles and include all files.files-to-prompt path/to/directory --ignore-gitignore
-
--ignore <pattern>: Specify one or more patterns to ignore. Can be used multiple times.files-to-prompt path/to/directory --ignore "*.log" --ignore "temp*"
Suppose you have a directory structure like this:
my_directory/
├── file1.txt
├── file2.txt
├── .hidden_file.txt
├── temp.log
└── subdirectory/
└── file3.txt
Running files-to-prompt my_directory will output:
my_directory/file1.txt
---
Contents of file1.txt
---
my_directory/file2.txt
---
Contents of file2.txt
---
my_directory/subdirectory/file3.txt
---
Contents of file3.txt
---
If you run files-to-prompt my_directory --include-hidden, the output will also include .hidden_file.txt:
my_directory/.hidden_file.txt
---
Contents of .hidden_file.txt
---
...
If you run files-to-prompt my_directory --ignore "*.log", the output will exclude temp.log:
my_directory/file1.txt
---
Contents of file1.txt
---
my_directory/file2.txt
---
Contents of file2.txt
---
my_directory/subdirectory/file3.txt
---
Contents of file3.txt
---
To contribute to this tool, first checkout the code. Then create a new virtual environment:
cd files-to-prompt
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activateNow install the dependencies and test dependencies:
pip install -e '.[test]'To run the tests:
pytestFor Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for files-to-prompt
Similar Open Source Tools

files-to-prompt
files-to-prompt is a tool that concatenates a directory full of files into a single prompt for use with Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to provide the path to one or more files or directories for processing, outputting the contents of each file with relative paths and separators. The tool offers options to include hidden files, ignore specific patterns, and exclude files specified in .gitignore. It is designed to streamline the process of preparing text data for LLMs by simplifying file concatenation and customization.
aim
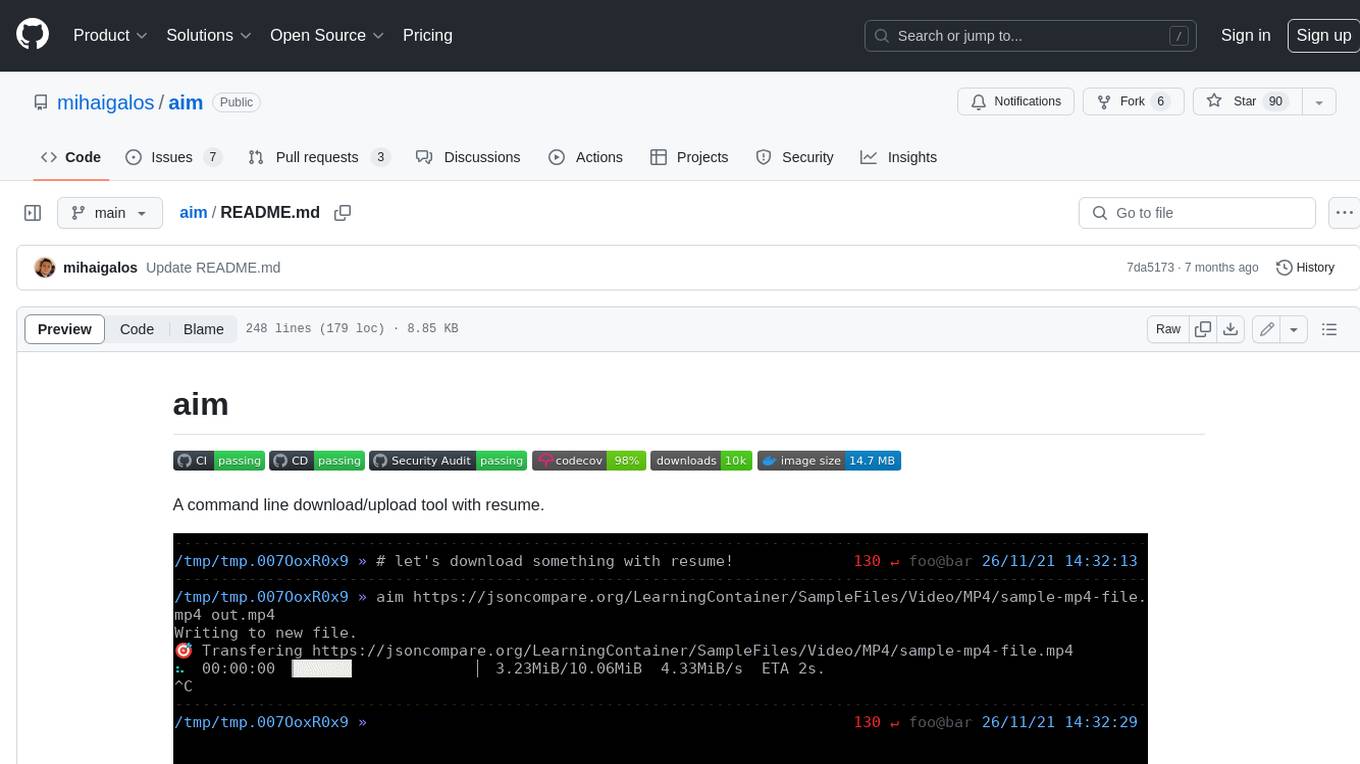
Aim is a command-line tool for downloading and uploading files with resume support. It supports various protocols including HTTP, FTP, SFTP, SSH, and S3. Aim features an interactive mode for easy navigation and selection of files, as well as the ability to share folders over HTTP for easy access from other devices. Additionally, it offers customizable progress indicators and output formats, and can be integrated with other commands through piping. Aim can be installed via pre-built binaries or by compiling from source, and is also available as a Docker image for platform-independent usage.

ragflow
RAGFlow is an open-source Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) engine that combines deep document understanding with Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide accurate question-answering capabilities. It offers a streamlined RAG workflow for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to extract knowledge from unstructured data in various formats, including Word documents, slides, Excel files, images, and more. RAGFlow's key features include deep document understanding, template-based chunking, grounded citations with reduced hallucinations, compatibility with heterogeneous data sources, and an automated and effortless RAG workflow. It supports multiple recall paired with fused re-ranking, configurable LLMs and embedding models, and intuitive APIs for seamless integration with business applications.
Flowise
Flowise is a tool that allows users to build customized LLM flows with a drag-and-drop UI. It is open-source and self-hostable, and it supports various deployments, including AWS, Azure, Digital Ocean, GCP, Railway, Render, HuggingFace Spaces, Elestio, Sealos, and RepoCloud. Flowise has three different modules in a single mono repository: server, ui, and components. The server module is a Node backend that serves API logics, the ui module is a React frontend, and the components module contains third-party node integrations. Flowise supports different environment variables to configure your instance, and you can specify these variables in the .env file inside the packages/server folder.
UCAgent
UCAgent is an AI-powered automated UT verification agent for chip design. It automates chip verification workflow, supports functional and code coverage analysis, ensures consistency among documentation, code, and reports, and collaborates with mainstream Code Agents via MCP protocol. It offers three intelligent interaction modes and requires Python 3.11+, Linux/macOS OS, 4GB+ memory, and access to an AI model API. Users can clone the repository, install dependencies, configure qwen, and start verification. UCAgent supports various verification quality improvement options and basic operations through TUI shortcuts and stage color indicators. It also provides documentation build and preview using MkDocs, PDF manual build using Pandoc + XeLaTeX, and resources for further help and contribution.
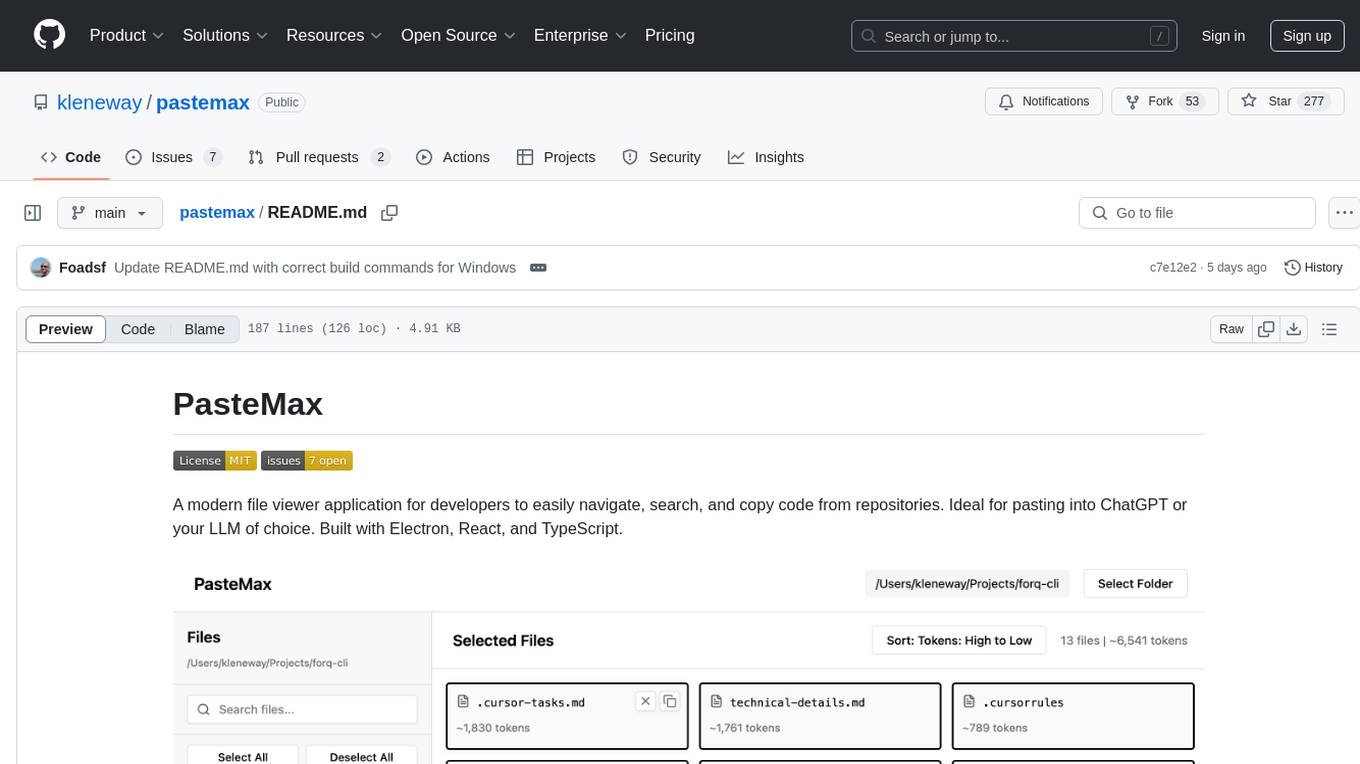
pastemax
PasteMax is a modern file viewer application designed for developers to easily navigate, search, and copy code from repositories. It provides features such as file tree navigation, token counting, search capabilities, selection management, sorting options, dark mode, binary file detection, and smart file exclusion. Built with Electron, React, and TypeScript, PasteMax is ideal for pasting code into ChatGPT or other language models. Users can download the application or build it from source, and customize file exclusions. Troubleshooting steps are provided for common issues, and contributions to the project are welcome under the MIT License.

shellChatGPT
ShellChatGPT is a shell wrapper for OpenAI's ChatGPT, DALL-E, Whisper, and TTS, featuring integration with LocalAI, Ollama, Gemini, Mistral, Groq, and GitHub Models. It provides text and chat completions, vision, reasoning, and audio models, voice-in and voice-out chatting mode, text editor interface, markdown rendering support, session management, instruction prompt manager, integration with various service providers, command line completion, file picker dialogs, color scheme personalization, stdin and text file input support, and compatibility with Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and Termux for a responsive experience.

LEANN
LEANN is an innovative vector database that democratizes personal AI, transforming your laptop into a powerful RAG system that can index and search through millions of documents using 97% less storage than traditional solutions without accuracy loss. It achieves this through graph-based selective recomputation and high-degree preserving pruning, computing embeddings on-demand instead of storing them all. LEANN allows semantic search of file system, emails, browser history, chat history, codebase, or external knowledge bases on your laptop with zero cloud costs and complete privacy. It is a drop-in semantic search MCP service fully compatible with Claude Code, enabling intelligent retrieval without changing your workflow.
snipkit
SnipKit is a CLI tool designed to manage snippets efficiently, allowing users to execute saved scripts or generate new ones with the help of AI directly from the terminal. It supports loading snippets from various sources, parameter substitution, different parameter types, themes, and customization options. The tool includes an interactive chat-style interface called SnipKit Assistant for generating parameterized scripts. Users can also work with different AI providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, and more. SnipKit aims to streamline script execution and script generation workflows for developers and users who frequently work with code snippets.

comp
Comp AI is an open-source compliance automation platform designed to assist companies in achieving compliance with standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and GDPR. It transforms compliance into an engineering problem solved through code, automating evidence collection, policy management, and control implementation while maintaining data and infrastructure control.
airstore
Airstore is a filesystem for AI agents that adds any source of data into a virtual filesystem, allowing users to connect services like Gmail, GitHub, Linear, and more, and describe data needs in plain English. Results are presented as files that can be read by Claude Code. Features include smart folders for natural language queries, integrations with various services, executable MCP servers, team workspaces, and local mode operation on user infrastructure. Users can sign up, connect integrations, create smart folders, install the CLI, mount the filesystem, and use with Claude Code to perform tasks like summarizing invoices, identifying unpaid invoices, and extracting data into CSV format.
yoyak
Yoyak is a small CLI tool powered by LLM for summarizing and translating web pages. It provides shell completion scripts for bash, fish, and zsh. Users can set the model they want to use and summarize web pages with the 'yoyak summary' command. Additionally, translation to other languages is supported using the '-l' option with ISO 639-1 language codes. Yoyak supports various models for summarization and translation tasks.
mLoRA
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.
llama.vim
llama.vim is a plugin that provides local LLM-assisted text completion for Vim users. It offers features such as auto-suggest on cursor movement, manual suggestion toggling, suggestion acceptance with Tab and Shift+Tab, control over text generation time, context configuration, ring context with chunks from open and edited files, and performance stats display. The plugin requires a llama.cpp server instance to be running and supports FIM-compatible models. It aims to be simple, lightweight, and provide high-quality and performant local FIM completions even on consumer-grade hardware.
gpt-translate
Markdown Translation BOT is a GitHub action that translates markdown files into multiple languages using various AI models. It supports markdown, markdown-jsx, and json files only. The action can be executed by individuals with write permissions to the repository, preventing API abuse by non-trusted parties. Users can set up the action by providing their API key and configuring the workflow settings. The tool allows users to create comments with specific commands to trigger translations and automatically generate pull requests or add translated files to existing pull requests. It supports multiple file translations and can interpret any language supported by GPT-4 or GPT-3.5.
gitingest
GitIngest is a tool that allows users to turn any Git repository into a prompt-friendly text ingest for LLMs. It provides easy code context by generating a text digest from a git repository URL or directory. The tool offers smart formatting for optimized output format for LLM prompts and provides statistics about file and directory structure, size of the extract, and token count. GitIngest can be used as a CLI tool on Linux and as a Python package for code integration. The tool is built using Tailwind CSS for frontend, FastAPI for backend framework, tiktoken for token estimation, and apianalytics.dev for simple analytics. Users can self-host GitIngest by building the Docker image and running the container. Contributions to the project are welcome, and the tool aims to be beginner-friendly for first-time contributors with a simple Python and HTML codebase.
For similar tasks
FileKitty
FileKitty is a simple file selection and concatenation tool that allows users to select files from a directory, concatenate them into a single file, save the concatenated file, and copy files to the clipboard. It is useful for concatenating files for use in a single file format and pasting file contents into an LLM to provide context to a prompt. The tool is built using Poetry to manage dependencies and build the app.

files-to-prompt
files-to-prompt is a tool that concatenates a directory full of files into a single prompt for use with Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to provide the path to one or more files or directories for processing, outputting the contents of each file with relative paths and separators. The tool offers options to include hidden files, ignore specific patterns, and exclude files specified in .gitignore. It is designed to streamline the process of preparing text data for LLMs by simplifying file concatenation and customization.
unitxt
Unitxt is a customizable library for textual data preparation and evaluation tailored to generative language models. It natively integrates with common libraries like HuggingFace and LM-eval-harness and deconstructs processing flows into modular components, enabling easy customization and sharing between practitioners. These components encompass model-specific formats, task prompts, and many other comprehensive dataset processing definitions. The Unitxt-Catalog centralizes these components, fostering collaboration and exploration in modern textual data workflows. Beyond being a tool, Unitxt is a community-driven platform, empowering users to build, share, and advance their pipelines collaboratively.
For similar jobs

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

airbyte
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that makes it easy to move data from any source to any destination. With Airbyte, you can build and manage data pipelines without writing any code. Airbyte provides a library of pre-built connectors that make it easy to connect to popular data sources and destinations. You can also create your own connectors using Airbyte's no-code Connector Builder or low-code CDK. Airbyte is used by data engineers and analysts at companies of all sizes to build and manage their data pipelines.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.


