
KsanaLLM
None
Stars: 264
KsanaLLM is a high-performance engine for LLM inference and serving. It utilizes optimized CUDA kernels for high performance, efficient memory management, and detailed optimization for dynamic batching. The tool offers flexibility with seamless integration with popular Hugging Face models, support for multiple weight formats, and high-throughput serving with various decoding algorithms. It enables multi-GPU tensor parallelism, streaming outputs, and an OpenAI-compatible API server. KsanaLLM supports NVIDIA GPUs and Huawei Ascend NPU, and seamlessly integrates with verified Hugging Face models like LLaMA, Baichuan, and Qwen. Users can create a docker container, clone the source code, compile for Nvidia or Huawei Ascend NPU, run the tool, and distribute it as a wheel package. Optional features include a model weight map JSON file for models with different weight names.
README:
KsanaLLM is a high performance and easy-to-use engine for LLM inference and serving.
High Performance and Throughput:
- Utilizes optimized CUDA kernels, including high performance kernels from vLLM, TensorRT-LLM, FastTransformer
- Efficient management of attention key and value memory with PagedAttention
- Detailed optimization of task-scheduling and memory-uitlization for dynamic batching
- (Experimental) Prefix caching support
- Sufficient testing has been conducted on GPU cards such as A10, A100, L40, etc
Flexibility and easy to use:
-
Seamless integration with popular Hugging Face models, and support multiple weight formats, such as pytorch and SafeTensors
-
High-throughput serving with various decoding algorithms, including parallel sampling, beam search, and more
-
Enables multi-gpu tensor parallelism
-
Streaming outputs
-
OpenAI-compatible API server
-
Support NVIDIA GPUs and Huawei Ascend NPU
KsanaLLM seamlessly supports many Hugging Face models, including the below models that have been verified:
- LLaMA 7B/13B & LLaMA-2 7B/13B & LLaMA3 8B/70B
- Baichuan1 7B/13B & Baichuan2 7B/13B
- Qwen 7B/14B & QWen1.5 7B/14B/72B/110B
- Yi1.5-34B
Supported Hardware
- Nvidia GPUs: A10, A100, L40, L20
- Huawei Ascend NPUs: 910B2C
# need install nvidia-docker from https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-container-toolkit
sudo nvidia-docker run -itd --network host --privileged \
nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:24.03-py3 bash
pip install -r requirements.txt
# for download huggingface model
apt update && apt install git-lfs -yPlease install Huawei Ascend NPU driver and CANN: driver download link
Recommend version: CANN 8.0RC2
Only Support Ascend NPU + X86 CPU
cd docker
docker build -f Dockerfile.npu -t ksana-npu .
docker run \
-u root \
-itd --privileged \
--shm-size=50g \
--network host \
--cap-add=SYS_ADMIN \
--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE \
--security-opt seccomp:unconfined $(find /dev/ -regex ".*/davinci$" | awk '{print " --device "$0}') \
--device=/dev/devmm_svm \
--device=/dev/hisi_hdc \
-v /usr/local/sbin/npu-smi:/usr/local/sbin/npu-smi \
-v /usr/local/sbin/:/usr/local/sbin/ \
-v /var/log/npu/conf/slog/slog.conf:/var/log/npu/conf/slog/slog.conf \
-v /var/log/npu/slog/:/var/log/npu/slog \
-v /var/log/npu/profiling/:/var/log/npu/profiling \
-v /var/log/npu/dump/:/var/log/npu/dump \
-v /var/log/npu/:/usr/slog \
-v /usr/local/Ascend/driver:/usr/local/Ascend/driver \
-v /etc/ascend_install.info:/etc/ascend_install.info \
ksana-npu bash
# install Ascend-cann-toolkit, Ascend-cann-nnal from https://www.hiascend.com/document/detail/zh/canncommercial/80RC2/softwareinst/instg/instg_0000.html?Mode=PmIns&OS=Ubuntu&Software=cannToolKit
# download torch_npu-2.1.0.post6-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl from https://www.hiascend.com/document/detail/zh/canncommercial/80RC2/softwareinst/instg/instg_0000.html?Mode=PmIns&OS=Ubuntu&Software=cannToolKit
pip3 install torch==2.1.0+cpu --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
pip install torch_npu-2.1.0.post6-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl
pip install -r requirements.txtgit clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/pcg-mlp/KsanaLLM
export GIT_PROJECT_REPO_ROOT=`pwd`/KsanaLLMcd ${GIT_PROJECT_REPO_ROOT}
mkdir build && cd build# SM for A10 is 86, change it when using other gpus.
# refer to: https://developer.nvidia.cn/cuda-gpus
cmake -DSM=86 -DWITH_TESTING=ON .. && make -j32cmake -DWITH_TESTING=ON -DWITH_CUDA=OFF -DWITH_ACL=ON .. && make -j32cd ${GIT_PROJECT_REPO_ROOT}/src/ksana_llm/python
ln -s ${GIT_PROJECT_REPO_ROOT}/build/lib .
# download huggingface model for example:
# Note: Make sure git-lfs is installed.
git clone https://huggingface.co/NousResearch/Llama-2-7b-hf
# change the model_dir in ${GIT_PROJECT_REPO_ROOT}/examples/ksana_llm2-7b.yaml if needed
# set environment variable `KLLM_LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG` before run to get more log info
# the serving log locate in log/ksana_llm.log
# ${GIT_PROJECT_REPO_ROOT}/examples/ksana_llm2-7b.yaml's tensor_para_size equal the GPUs/NPUs number
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=xx
# launch server
python serving_server.py \
--config_file ${GIT_PROJECT_REPO_ROOT}/examples/ksana_llm2-7b.yaml \
--port 8080Inference test with one shot conversation
# open another session
cd ${GIT_PROJECT_REPO_ROOT}/src/ksana_llm/python
python serving_generate_client.py --port 8080Inference test with forward(Single round inference without generate sampling)
python serving_forward_client.py --port 8080cd ${GIT_PROJECT_REPO_ROOT}
# for distribute wheel
python setup.py bdist_wheel
# install wheel
pip install dist/ksana_llm-0.1-*-linux_x86_64.whl
# check install success
pip show -f ksana_llm
python -c "import ksana_llm"You can include an optional weight map JSON file for models that share the same structure as the Llama model but have different weight names.
For more detailed information, please refer to the following link: Optional Weight Map Guide
Custom plugins can perform some special pre-process and post-processing. You need to place ksana_plugin.py in the model directory. Example
When enabling FP8 E4M3 KV Cache quantization, it is necessary to provide scaling factors to ensure inference accuracy.
For more detailed information, please refer to the following link: Optional KV Scale Guide
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for KsanaLLM
Similar Open Source Tools

KsanaLLM
KsanaLLM is a high-performance engine for LLM inference and serving. It utilizes optimized CUDA kernels for high performance, efficient memory management, and detailed optimization for dynamic batching. The tool offers flexibility with seamless integration with popular Hugging Face models, support for multiple weight formats, and high-throughput serving with various decoding algorithms. It enables multi-GPU tensor parallelism, streaming outputs, and an OpenAI-compatible API server. KsanaLLM supports NVIDIA GPUs and Huawei Ascend NPU, and seamlessly integrates with verified Hugging Face models like LLaMA, Baichuan, and Qwen. Users can create a docker container, clone the source code, compile for Nvidia or Huawei Ascend NPU, run the tool, and distribute it as a wheel package. Optional features include a model weight map JSON file for models with different weight names.

sim
Sim is a platform that allows users to build and deploy AI agent workflows quickly and easily. It provides cloud-hosted and self-hosted options, along with support for local AI models. Users can set up the application using Docker Compose, Dev Containers, or manual setup with PostgreSQL and pgvector extension. The platform utilizes technologies like Next.js, Bun, PostgreSQL with Drizzle ORM, Better Auth for authentication, Shadcn and Tailwind CSS for UI, Zustand for state management, ReactFlow for flow editor, Fumadocs for documentation, Turborepo for monorepo management, Socket.io for real-time communication, and Trigger.dev for background jobs.

comp
Comp AI is an open-source compliance automation platform designed to assist companies in achieving compliance with standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and GDPR. It transforms compliance into an engineering problem solved through code, automating evidence collection, policy management, and control implementation while maintaining data and infrastructure control.
Flowise
Flowise is a tool that allows users to build customized LLM flows with a drag-and-drop UI. It is open-source and self-hostable, and it supports various deployments, including AWS, Azure, Digital Ocean, GCP, Railway, Render, HuggingFace Spaces, Elestio, Sealos, and RepoCloud. Flowise has three different modules in a single mono repository: server, ui, and components. The server module is a Node backend that serves API logics, the ui module is a React frontend, and the components module contains third-party node integrations. Flowise supports different environment variables to configure your instance, and you can specify these variables in the .env file inside the packages/server folder.
yams
YAMS (Yet Another Memory System) is a persistent memory system designed for Large Language Models (LLMs) and applications. It provides content-addressed storage with features such as deduplication, compression, full-text search, and vector search. The system is built with SHA-256 content-addressed store, block-level deduplication, full-text search using SQLite FTS5, semantic search with embeddings, WAL-backed durability, high-throughput I/O, and thread-safe operations. YAMS supports Linux x86_64/ARM64 and macOS x86_64/ARM64 platforms. It is recommended to build using Conan for managing dependencies and ensuring proper installation. Users can interact with YAMS through a command-line interface for tasks like initialization, adding content, searching, and retrieving data. Additionally, YAMS provides LLM-friendly patterns for caching web content, storing code diffs, and integrating with other systems through an API in C++. Troubleshooting tips include creating a default Conan profile and handling PDF support issues during the build process. The project is licensed under Apache-2.0.
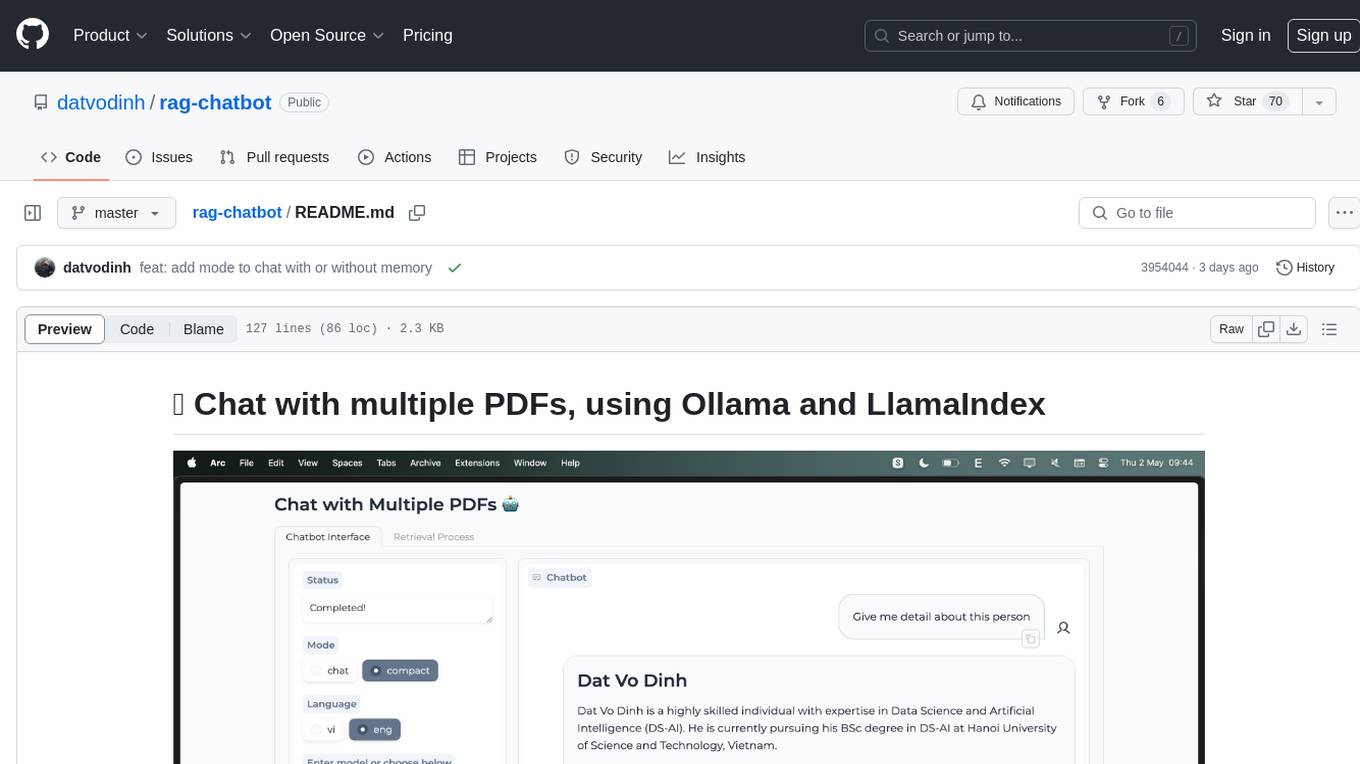
rag-chatbot
rag-chatbot is a tool that allows users to chat with multiple PDFs using Ollama and LlamaIndex. It provides an easy setup for running on local machines or Kaggle notebooks. Users can leverage models from Huggingface and Ollama, process multiple PDF inputs, and chat in multiple languages. The tool offers a simple UI with Gradio, supporting chat with history and QA modes. Setup instructions are provided for both Kaggle and local environments, including installation steps for Docker, Ollama, Ngrok, and the rag_chatbot package. Users can run the tool locally and access it via a web interface. Future enhancements include adding evaluation, better embedding models, knowledge graph support, improved document processing, MLX model integration, and Corrective RAG.
qwen-code
Qwen Code is an open-source AI agent optimized for Qwen3-Coder, designed to help users understand large codebases, automate tedious work, and expedite the shipping process. It offers an agentic workflow with rich built-in tools, a terminal-first approach with optional IDE integration, and supports both OpenAI-compatible API and Qwen OAuth authentication methods. Users can interact with Qwen Code in interactive mode, headless mode, IDE integration, and through a TypeScript SDK. The tool can be configured via settings.json, environment variables, and CLI flags, and offers benchmark results for performance evaluation. Qwen Code is part of an ecosystem that includes AionUi and Gemini CLI Desktop for graphical interfaces, and troubleshooting guides are available for issue resolution.
llamactl
llamactl is a tool for unified management and routing of llama.cpp, MLX, and vLLM models with a web dashboard. It offers easy model management with built-in model downloader, dynamic multi-model instances, smart resource management, and a modern React UI dashboard. It provides flexible integration with API compatibility for OpenAI chat completions and resources endpoints, multi-backend support, and Docker readiness. The tool supports distributed deployment with remote instances and central management. Users can quickly start by installing a backend, downloading llamactl, creating an instance, and starting inferencing.
backend.ai-webui
Backend.AI Web UI is a user-friendly web and app interface designed to make AI accessible for end-users, DevOps, and SysAdmins. It provides features for session management, inference service management, pipeline management, storage management, node management, statistics, configurations, license checking, plugins, help & manuals, kernel management, user management, keypair management, manager settings, proxy mode support, service information, and integration with the Backend.AI Web Server. The tool supports various devices, offers a built-in websocket proxy feature, and allows for versatile usage across different platforms. Users can easily manage resources, run environment-supported apps, access a web-based terminal, use Visual Studio Code editor, manage experiments, set up autoscaling, manage pipelines, handle storage, monitor nodes, view statistics, configure settings, and more.
airstore
Airstore is a filesystem for AI agents that adds any source of data into a virtual filesystem, allowing users to connect services like Gmail, GitHub, Linear, and more, and describe data needs in plain English. Results are presented as files that can be read by Claude Code. Features include smart folders for natural language queries, integrations with various services, executable MCP servers, team workspaces, and local mode operation on user infrastructure. Users can sign up, connect integrations, create smart folders, install the CLI, mount the filesystem, and use with Claude Code to perform tasks like summarizing invoices, identifying unpaid invoices, and extracting data into CSV format.
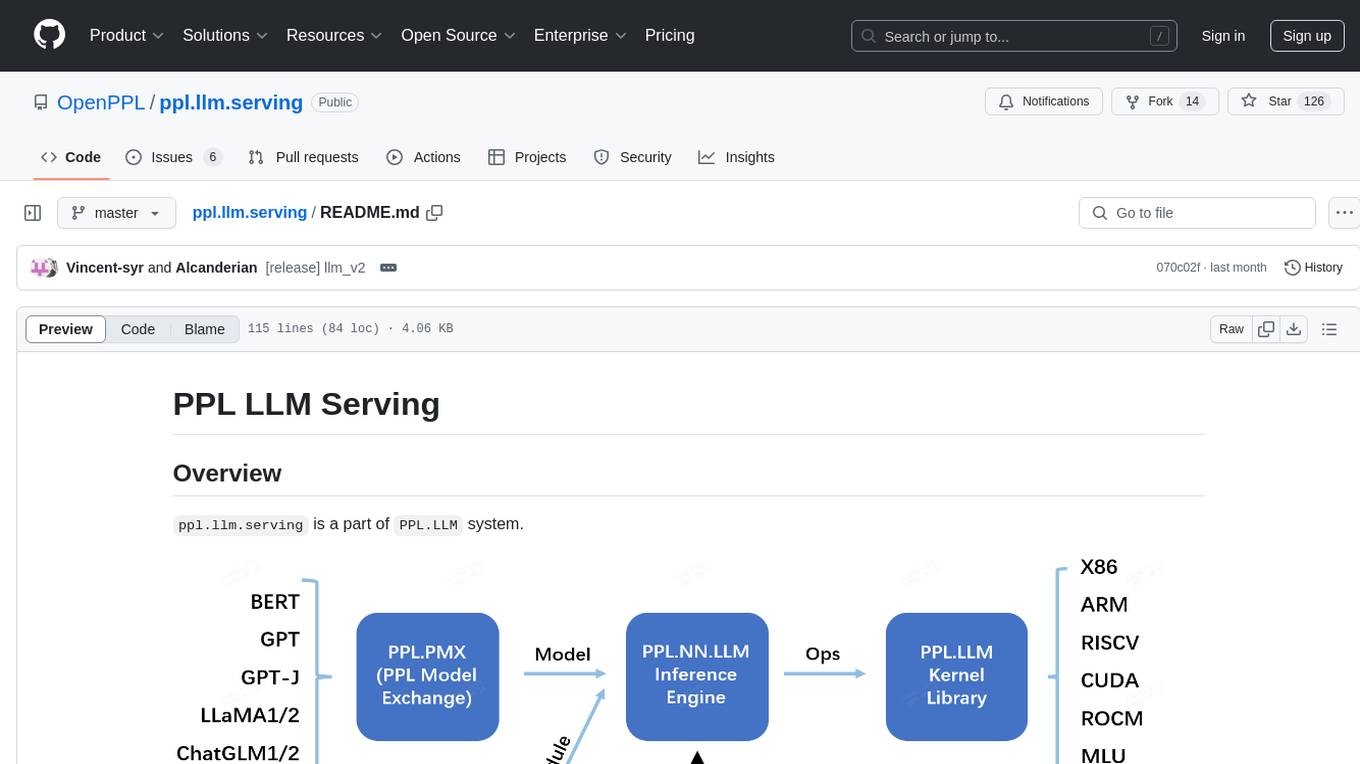
ppl.llm.serving
ppl.llm.serving is a serving component for Large Language Models (LLMs) within the PPL.LLM system. It provides a server based on gRPC and supports inference for LLaMA. The repository includes instructions for prerequisites, quick start guide, model exporting, server setup, client usage, benchmarking, and offline inference. Users can refer to the LLaMA Guide for more details on using this serving component.

mistral.rs
Mistral.rs is a fast LLM inference platform written in Rust. We support inference on a variety of devices, quantization, and easy-to-use application with an Open-AI API compatible HTTP server and Python bindings.

TalkWithGemini
Talk With Gemini is a web application that allows users to deploy their private Gemini application for free with one click. It supports Gemini Pro and Gemini Pro Vision models. The application features talk mode for direct communication with Gemini, visual recognition for understanding picture content, full Markdown support, automatic compression of chat records, privacy and security with local data storage, well-designed UI with responsive design, fast loading speed, and multi-language support. The tool is designed to be user-friendly and versatile for various deployment options and language preferences.
prime
Prime is a framework for efficient, globally distributed training of AI models over the internet. It includes features such as fault-tolerant training with ElasticDeviceMesh, asynchronous distributed checkpointing, live checkpoint recovery, custom Int8 All-Reduce Kernel, maximizing bandwidth utilization, PyTorch FSDP2/DTensor ZeRO-3 implementation, and CPU off-loading. The framework aims to optimize communication, checkpointing, and bandwidth utilization for large-scale AI model training.
codemie-code
Unified AI Coding Assistant CLI for managing multiple AI agents like Claude Code, Google Gemini, OpenCode, and custom AI agents. Supports OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, LiteLLM, Ollama, and Enterprise SSO. Features built-in LangGraph agent with file operations, command execution, and planning tools. Cross-platform support for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Ideal for developers seeking a powerful alternative to GitHub Copilot or Cursor.

mini-sglang
Mini-SGLang is a lightweight yet high-performance inference framework for Large Language Models. With a compact codebase of ~5,000 lines of Python, it serves as both a capable inference engine and a transparent reference for researchers and developers. It achieves state-of-the-art throughput and latency with advanced optimizations such as Radix Cache, Chunked Prefill, Overlap Scheduling, Tensor Parallelism, and Optimized Kernels integrating FlashAttention and FlashInfer for maximum efficiency. Mini-SGLang is designed to demystify the complexities of modern LLM serving systems, providing a clean, modular, and fully type-annotated codebase that is easy to understand and modify.
For similar tasks

KsanaLLM
KsanaLLM is a high-performance engine for LLM inference and serving. It utilizes optimized CUDA kernels for high performance, efficient memory management, and detailed optimization for dynamic batching. The tool offers flexibility with seamless integration with popular Hugging Face models, support for multiple weight formats, and high-throughput serving with various decoding algorithms. It enables multi-GPU tensor parallelism, streaming outputs, and an OpenAI-compatible API server. KsanaLLM supports NVIDIA GPUs and Huawei Ascend NPU, and seamlessly integrates with verified Hugging Face models like LLaMA, Baichuan, and Qwen. Users can create a docker container, clone the source code, compile for Nvidia or Huawei Ascend NPU, run the tool, and distribute it as a wheel package. Optional features include a model weight map JSON file for models with different weight names.

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking
model_server
OpenVINO™ Model Server (OVMS) is a high-performance system for serving models. Implemented in C++ for scalability and optimized for deployment on Intel architectures, the model server uses the same architecture and API as TensorFlow Serving and KServe while applying OpenVINO for inference execution. Inference service is provided via gRPC or REST API, making deploying new algorithms and AI experiments easy.
kitops
KitOps is a packaging and versioning system for AI/ML projects that uses open standards so it works with the AI/ML, development, and DevOps tools you are already using. KitOps simplifies the handoffs between data scientists, application developers, and SREs working with LLMs and other AI/ML models. KitOps' ModelKits are a standards-based package for models, their dependencies, configurations, and codebases. ModelKits are portable, reproducible, and work with the tools you already use.
CSGHub
CSGHub is an open source, trustworthy large model asset management platform that can assist users in governing the assets involved in the lifecycle of LLM and LLM applications (datasets, model files, codes, etc). With CSGHub, users can perform operations on LLM assets, including uploading, downloading, storing, verifying, and distributing, through Web interface, Git command line, or natural language Chatbot. Meanwhile, the platform provides microservice submodules and standardized OpenAPIs, which could be easily integrated with users' own systems. CSGHub is committed to bringing users an asset management platform that is natively designed for large models and can be deployed On-Premise for fully offline operation. CSGHub offers functionalities similar to a privatized Huggingface(on-premise Huggingface), managing LLM assets in a manner akin to how OpenStack Glance manages virtual machine images, Harbor manages container images, and Sonatype Nexus manages artifacts.
AI-Horde
The AI Horde is an enterprise-level ML-Ops crowdsourced distributed inference cluster for AI Models. This middleware can support both Image and Text generation. It is infinitely scalable and supports seamless drop-in/drop-out of compute resources. The Public version allows people without a powerful GPU to use Stable Diffusion or Large Language Models like Pygmalion/Llama by relying on spare/idle resources provided by the community and also allows non-python clients, such as games and apps, to use AI-provided generations.
caikit
Caikit is an AI toolkit that enables users to manage models through a set of developer friendly APIs. It provides a consistent format for creating and using AI models against a wide variety of data domains and tasks.
vertex-ai-mlops
Vertex AI is a platform for end-to-end model development. It consist of core components that make the processes of MLOps possible for design patterns of all types.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
