
kvcached
kvcached: Elastic KV cache for dynamic GPU sharing and efficient multi-LLM inference.
Stars: 92
kvcached is a new KV cache management system that supports on-demand KV cache allocation. It implements the concept of GPU virtual memory, allowing applications to reserve virtual address space without immediately committing physical memory. Physical memory is then automatically allocated and mapped as needed at runtime. This capability allows multiple LLMs to run concurrently on a single GPU or a group of GPUs (TP) and flexibly share the GPU memory, significantly improving GPU utilization and reducing memory fragmentation. kvcached is compatible with popular LLM serving engines, including SGLang and vLLM.
README:
kvcached is a new KV cache management system that supports on-demand KV cache allocation. It implements the concept of GPU virtual memory, allowing applications to reserve virtual address space without immediately committing physical memory. Physical memory is then automatically allocated and mapped as needed at runtime. This capability allows multiple LLMs to run concurrently on a single GPU or a group of GPUs (TP) and flexibly share the GPU memory, significantly improving GPU utilization and reducing memory fragmentation.
kvcached is compatible with popular LLM serving engines, including SGLang and vLLM.
- Python (tested with 3.9 - 3.11)
- PyTorch (compatible with SGLang and vLLM)
kvcached can be installed as a plugin with SGLang and vLLM.
cd engine_integration/scripts
# install kvcached with SGLang v0.4.9
./setup.sh --engine sglang --engine-method source --engine-version 0.4.9
# install kvcached with vLLM v0.9.2
./setup.sh --engine vllm --engine-method source --engine-version 0.9.2This script will download the specified versions of SGLang and vLLM, create separate venv environments (using uv), compile the code, apply the necessary patches, and install kvcached.
You can test or develop kvcached with Docker.
To test kvcached with SGLang or VLLM.
docker pull ghcr.io/ovg-project/[kvcached-sglang|kvcached-vllm]:latestFor developmenet:
docker pull ghcr.io/ovg-project/kvcached-dev:latestMore instructions can be found here.
kvcached can be enabled or disabled by export ENABLE_KVCACHED=true or false. To verify the successful installation and benchmark the performance of SGLang/vLLM with kvcached, run:
cd benchmarks/simple_bench
export VENV_PATH=../../engine_integration/[sglang|vllm]-kvcached-venv
./start_server.sh [sglang|vllm] --venv-path $VENV_PATH --model meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B
# Wait until LLM server is ready
./start_client.sh [sglang|vllm] --venv-path $VENV_PATH --model meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1BThe benchmark scripts automatically set ENABLE_KVCACHED=true. Please refer to each script for instructions on how to run SGLang/vLLM with kvcached.
kvcached includes a built-in CLI tool that allows you to monitor GPU memory usage and manage memory limits across different applications. A command kvctl is installed along with kvcached package:
kvctlOnce inside the CLI, type help to view all supported commands:
kvcached> help
Available commands:
list [ipc ...] List IPC segments and usage
limit <ipc> <size> Set absolute limit (e.g. 512M, 2G)
limit-percent <ipc> <pct> Set limit as percentage of total GPU RAM
watch [-n sec] [ipc ...] Continuously display usage table
kvtop [ipc ...] [--refresh r] Launch curses kvtop UI (q to quit)
!<shell cmd> Run command in system shell
help Show this help message
delete <ipc> Delete IPC segment and its limit entry
exit | quit Exit the shell
kvcached>
Use the kvtop command for real-time visualization of memory usage:
KVCache Memory Usage IPC: SGLANG [==##################----------------------------------------] Prealloc: 792.0 MB | Used: 11.2 GB / 39.9 GB (30.1%) | Free: 27.9 GB IPC: VLLM [==#######--------------------------------------------------- ] Prealloc: 768.0 MB | Used: 3.6 GB / 37.4 GB (11.7%) | Free: 33.0 GB GPU Memory Usage [########################################--------------------] Used: 52.9 GB / 79.2 GB (66.8%) | Free: 26.3 GB Press 'q' to quit
We are grateful for and open to contributions and collaborations of any kind.
We use pre-commit to ensure a consistent coding style. You can set it up by
pip install pre-commit
pre-commit install
Before pushing your code, please run the following check and make sure your code passes all checks.
pre-commit run --all-files
Feel free to contact us for contributions and collaborations.
Jiarong Xing ([email protected])
Yifan Qiao ([email protected])
Shan Yu ([email protected])
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for kvcached
Similar Open Source Tools

kvcached
kvcached is a new KV cache management system that supports on-demand KV cache allocation. It implements the concept of GPU virtual memory, allowing applications to reserve virtual address space without immediately committing physical memory. Physical memory is then automatically allocated and mapped as needed at runtime. This capability allows multiple LLMs to run concurrently on a single GPU or a group of GPUs (TP) and flexibly share the GPU memory, significantly improving GPU utilization and reducing memory fragmentation. kvcached is compatible with popular LLM serving engines, including SGLang and vLLM.
E2B
E2B Sandbox is a secure sandboxed cloud environment made for AI agents and AI apps. Sandboxes allow AI agents and apps to have long running cloud secure environments. In these environments, large language models can use the same tools as humans do. For example: * Cloud browsers * GitHub repositories and CLIs * Coding tools like linters, autocomplete, "go-to defintion" * Running LLM generated code * Audio & video editing The E2B sandbox can be connected to any LLM and any AI agent or app.
shinkai-apps
Shinkai apps unlock the full capabilities/automation of first-class LLM (AI) support in the web browser. It enables creating multiple agents, each connected to either local or 3rd-party LLMs (ex. OpenAI GPT), which have permissioned (meaning secure) access to act in every webpage you visit. There is a companion repo called Shinkai Node, that allows you to set up the node anywhere as the central unit of the Shinkai Network, handling tasks such as agent management, job processing, and secure communications.
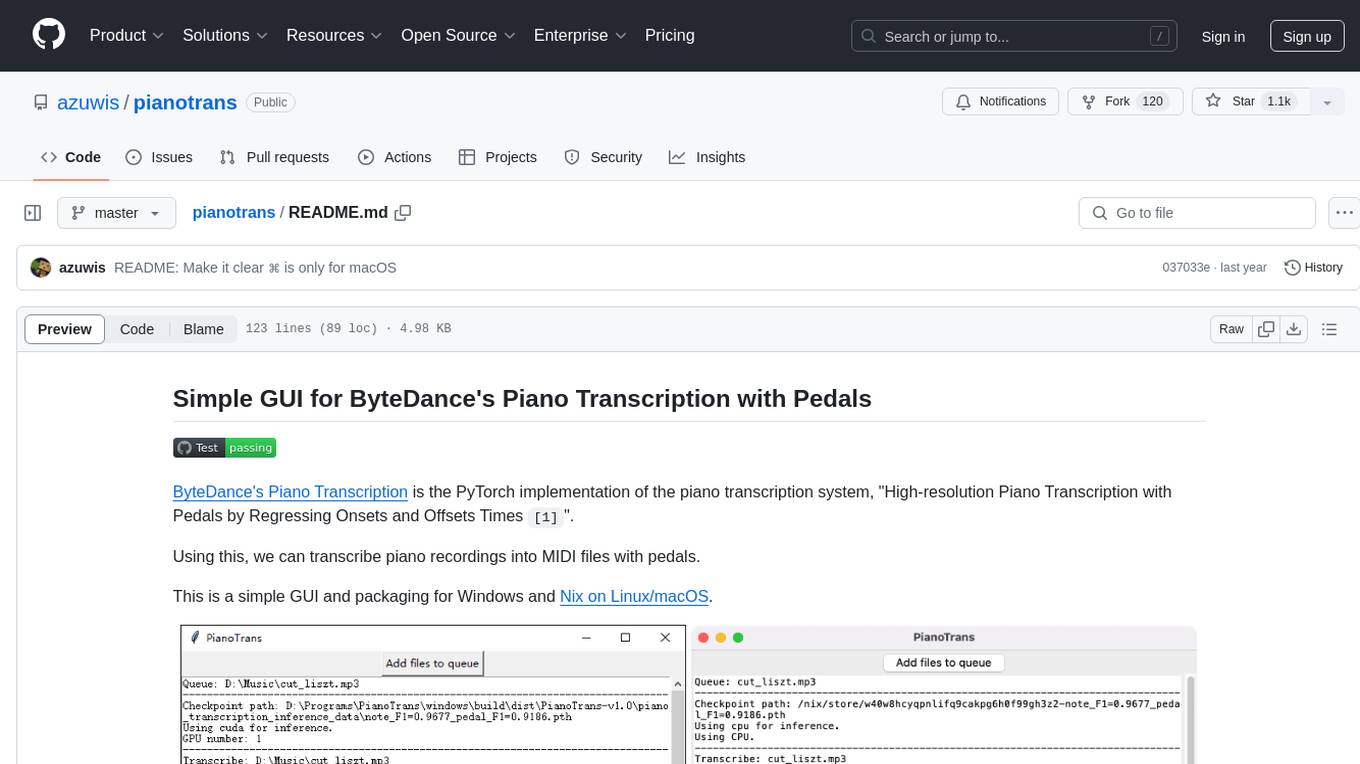
pianotrans
ByteDance's Piano Transcription is a PyTorch implementation for transcribing piano recordings into MIDI files with pedals. This repository provides a simple GUI and packaging for Windows and Nix on Linux/macOS. It supports using GPU for inference and includes CLI usage. Users can upgrade the tool and report issues to the upstream project. The tool focuses on providing MIDI files, and any other improvements to transcription results should be directed to the original project.

OmniSteward
OmniSteward is an AI-powered steward system based on large language models that can interact with users through voice or text to help control smart home devices and computer programs. It supports multi-turn dialogue, tool calling for complex tasks, multiple LLM models, voice recognition, smart home control, computer program management, online information retrieval, command line operations, and file management. The system is highly extensible, allowing users to customize and share their own tools.
saga
SAGA is a novel-writing system that leverages a knowledge graph and specialized agents to autonomously create and refine stories. It handles complex narrative structures while maintaining coherence and consistency. Features include a Knowledge Graph using Neo4j, Modular Agent Architecture, LLM Integration, Configurable Generation Parameters, Robust Testing Framework, Code Quality enforcement, Vector Search, and Agentic Planning. The system structure includes components for specialized agents, core components, data access, documentation, initialization scripts, Pydantic models, output directory, orchestrator logic, text processing tools, UI components, utility functions, and more.
exo
Run your own AI cluster at home with everyday devices. Exo is experimental software that unifies existing devices into a powerful GPU, supporting wide model compatibility, dynamic model partitioning, automatic device discovery, ChatGPT-compatible API, and device equality. It does not use a master-worker architecture, allowing devices to connect peer-to-peer. Exo supports different partitioning strategies like ring memory weighted partitioning. Installation is recommended from source. Documentation includes example usage on multiple MacOS devices and information on inference engines and networking modules. Known issues include the iOS implementation lagging behind Python.
ControlLLM
ControlLLM is a framework that empowers large language models to leverage multi-modal tools for solving complex real-world tasks. It addresses challenges like ambiguous user prompts, inaccurate tool selection, and inefficient tool scheduling by utilizing a task decomposer, a Thoughts-on-Graph paradigm, and an execution engine with a rich toolbox. The framework excels in tasks involving image, audio, and video processing, showcasing superior accuracy, efficiency, and versatility compared to existing methods.
TokenFormer
TokenFormer is a fully attention-based neural network architecture that leverages tokenized model parameters to enhance architectural flexibility. It aims to maximize the flexibility of neural networks by unifying token-token and token-parameter interactions through the attention mechanism. The architecture allows for incremental model scaling and has shown promising results in language modeling and visual modeling tasks. The codebase is clean, concise, easily readable, state-of-the-art, and relies on minimal dependencies.
chat-ui
This repository provides a minimalist approach to create a chatbot by constructing the entire front-end UI using a single HTML file. It supports various backend endpoints through custom configurations, multiple response formats, chat history download, and MCP. Users can deploy the chatbot locally, via Docker, Cloudflare pages, Huggingface, or within K8s. The tool also supports image inputs, toggling between different display formats, internationalization, and localization.
private-ml-sdk
Private ML SDK is a secure solution for running Large Language Models (LLMs) in Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) using NVIDIA GPU TEE and Intel TDX technologies. It provides a tamper-proof data processing environment with secure execution, open-source builds, and nearly native speed performance. The system includes components like Secure Compute Environment, Remote Attestation, Secure Communication, and Key Management Service (KMS). Users can build TDX guest images, run Local KMS, and TDX guest images on TDX host machines with Nvidia GPUs. The SDK offers verifiable execution results and high performance for LLM workloads.
RoboMatrix
RoboMatrix is a skill-centric hierarchical framework for scalable robot task planning and execution in an open-world environment. It provides a structured approach to robot task execution using a combination of hardware components, environment configuration, installation procedures, and data collection methods. The framework is developed using the ROS2 framework on Ubuntu and supports robots from DJI's RoboMaster series. Users can follow the provided installation guidance to set up RoboMatrix and utilize it for various tasks such as data collection, task execution, and dataset construction. The framework also includes a supervised fine-tuning dataset and aims to optimize communication and release additional components in the future.
nakafa.com
Nakafa is an open-source educational platform offering structured learning content for various educational levels along with political analysis articles. It allows users to contribute by adding content and follows a copyleft license. The platform is built with Node.js and Bun, providing a development environment and production servers for easy setup and deployment. Detailed technical documentation is available on DeepWiki, covering architecture, design decisions, and development patterns. Users can contribute by forking the repository, creating feature branches, making changes following established patterns, and submitting pull requests. Commercial licensing inquiries can be directed to [email protected]. The platform is designed with a focus on learners worldwide.
docetl
DocETL is a tool for creating and executing data processing pipelines, especially suited for complex document processing tasks. It offers a low-code, declarative YAML interface to define LLM-powered operations on complex data. Ideal for maximizing correctness and output quality for semantic processing on a collection of data, representing complex tasks via map-reduce, maximizing LLM accuracy, handling long documents, and automating task retries based on validation criteria.
ComfyUI-IF_AI_tools
ComfyUI-IF_AI_tools is a set of custom nodes for ComfyUI that allows you to generate prompts using a local Large Language Model (LLM) via Ollama. This tool enables you to enhance your image generation workflow by leveraging the power of language models.
askrepo
askrepo is a tool that reads the content of Git-managed text files in a specified directory, sends it to the Google Gemini API, and provides answers to questions based on a specified prompt. It acts as a question-answering tool for source code by using a Google AI model to analyze and provide answers based on the provided source code files. The tool leverages modules for file processing, interaction with the Google AI API, and orchestrating the entire process of extracting information from source code files.
For similar tasks
arena-hard-auto
Arena-Hard-Auto-v0.1 is an automatic evaluation tool for instruction-tuned LLMs. It contains 500 challenging user queries. The tool prompts GPT-4-Turbo as a judge to compare models' responses against a baseline model (default: GPT-4-0314). Arena-Hard-Auto employs an automatic judge as a cheaper and faster approximator to human preference. It has the highest correlation and separability to Chatbot Arena among popular open-ended LLM benchmarks. Users can evaluate their models' performance on Chatbot Arena by using Arena-Hard-Auto.

max
The Modular Accelerated Xecution (MAX) platform is an integrated suite of AI libraries, tools, and technologies that unifies commonly fragmented AI deployment workflows. MAX accelerates time to market for the latest innovations by giving AI developers a single toolchain that unlocks full programmability, unparalleled performance, and seamless hardware portability.
ai-hub
AI Hub Project aims to continuously test and evaluate mainstream large language models, while accumulating and managing various effective model invocation prompts. It has integrated all mainstream large language models in China, including OpenAI GPT-4 Turbo, Baidu ERNIE-Bot-4, Tencent ChatPro, MiniMax abab5.5-chat, and more. The project plans to continuously track, integrate, and evaluate new models. Users can access the models through REST services or Java code integration. The project also provides a testing suite for translation, coding, and benchmark testing.
long-context-attention
Long-Context-Attention (YunChang) is a unified sequence parallel approach that combines the strengths of DeepSpeed-Ulysses-Attention and Ring-Attention to provide a versatile and high-performance solution for long context LLM model training and inference. It addresses the limitations of both methods by offering no limitation on the number of heads, compatibility with advanced parallel strategies, and enhanced performance benchmarks. The tool is verified in Megatron-LM and offers best practices for 4D parallelism, making it suitable for various attention mechanisms and parallel computing advancements.

marlin
Marlin is a highly optimized FP16xINT4 matmul kernel designed for large language model (LLM) inference, offering close to ideal speedups up to batchsizes of 16-32 tokens. It is suitable for larger-scale serving, speculative decoding, and advanced multi-inference schemes like CoT-Majority. Marlin achieves optimal performance by utilizing various techniques and optimizations to fully leverage GPU resources, ensuring efficient computation and memory management.
MMC
This repository, MMC, focuses on advancing multimodal chart understanding through large-scale instruction tuning. It introduces a dataset supporting various tasks and chart types, a benchmark for evaluating reasoning capabilities over charts, and an assistant achieving state-of-the-art performance on chart QA benchmarks. The repository provides data for chart-text alignment, benchmarking, and instruction tuning, along with existing datasets used in experiments. Additionally, it offers a Gradio demo for the MMCA model.
Tiktoken
Tiktoken is a high-performance implementation focused on token count operations. It provides various encodings like o200k_base, cl100k_base, r50k_base, p50k_base, and p50k_edit. Users can easily encode and decode text using the provided API. The repository also includes a benchmark console app for performance tracking. Contributions in the form of PRs are welcome.
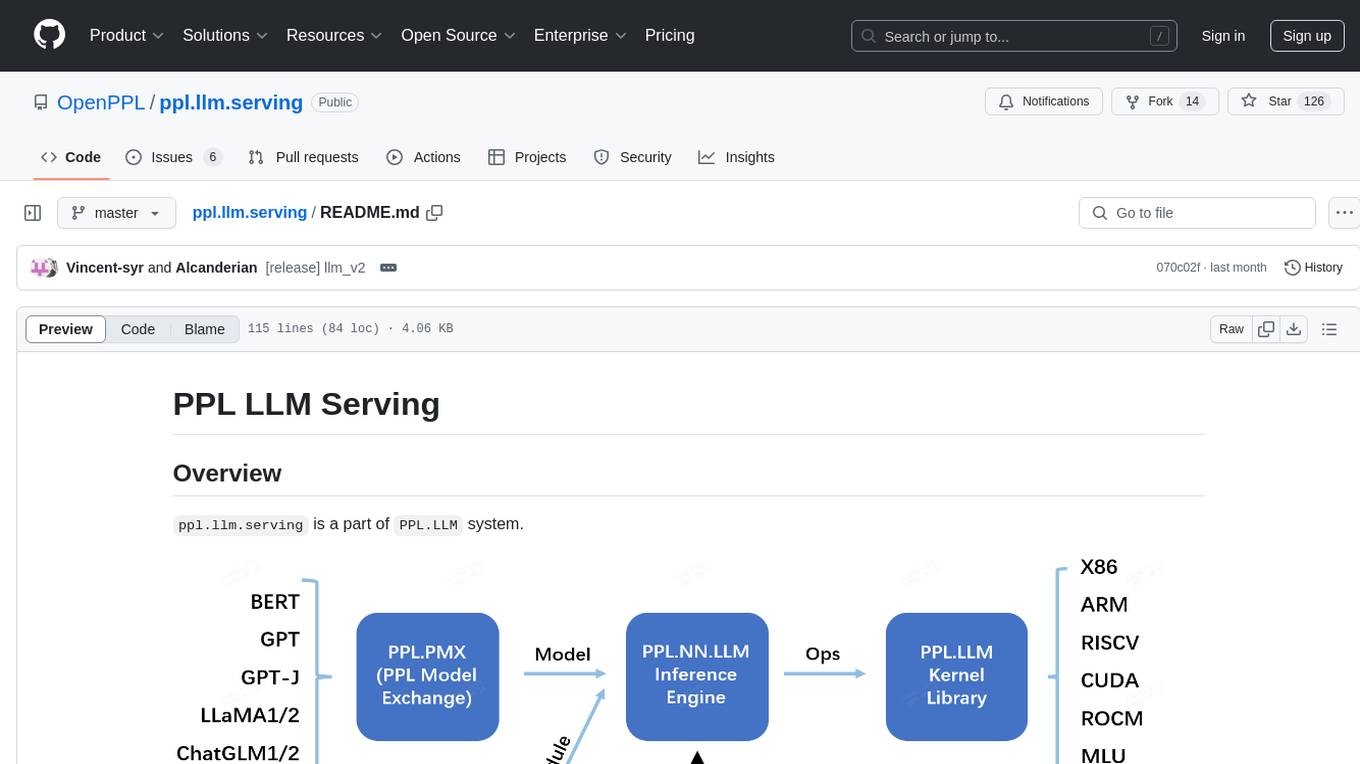
ppl.llm.serving
ppl.llm.serving is a serving component for Large Language Models (LLMs) within the PPL.LLM system. It provides a server based on gRPC and supports inference for LLaMA. The repository includes instructions for prerequisites, quick start guide, model exporting, server setup, client usage, benchmarking, and offline inference. Users can refer to the LLaMA Guide for more details on using this serving component.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.