
openai-agents-python
A lightweight, powerful framework for multi-agent workflows
Stars: 18853
The OpenAI Agents SDK is a lightweight framework for building multi-agent workflows. It includes concepts like Agents, Handoffs, Guardrails, and Tracing to facilitate the creation and management of agents. The SDK is compatible with any model providers supporting the OpenAI Chat Completions API format. It offers flexibility in modeling various LLM workflows and provides automatic tracing for easy tracking and debugging of agent behavior. The SDK is designed for developers to create deterministic flows, iterative loops, and more complex workflows.
README:
The OpenAI Agents SDK is a lightweight yet powerful framework for building multi-agent workflows. It is provider-agnostic, supporting the OpenAI Responses and Chat Completions APIs, as well as 100+ other LLMs.
[!NOTE] Looking for the JavaScript/TypeScript version? Check out Agents SDK JS/TS.
- Agents: LLMs configured with instructions, tools, guardrails, and handoffs
- Handoffs: A specialized tool call used by the Agents SDK for transferring control between agents
- Guardrails: Configurable safety checks for input and output validation
- Sessions: Automatic conversation history management across agent runs
- Tracing: Built-in tracking of agent runs, allowing you to view, debug and optimize your workflows
Explore the examples directory to see the SDK in action, and read our documentation for more details.
To get started, set up your Python environment (Python 3.9 or newer required), and then install OpenAI Agents SDK package.
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate # On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate
pip install openai-agentsFor voice support, install with the optional voice group: pip install 'openai-agents[voice]'.
For Redis session support, install with the optional redis group: pip install 'openai-agents[redis]'.
If you're familiar with uv, installing the package would be even easier:
uv init
uv add openai-agentsFor voice support, install with the optional voice group: uv add 'openai-agents[voice]'.
For Redis session support, install with the optional redis group: uv add 'openai-agents[redis]'.
from agents import Agent, Runner
agent = Agent(name="Assistant", instructions="You are a helpful assistant")
result = Runner.run_sync(agent, "Write a haiku about recursion in programming.")
print(result.final_output)
# Code within the code,
# Functions calling themselves,
# Infinite loop's dance.(If running this, ensure you set the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable)
(For Jupyter notebook users, see hello_world_jupyter.ipynb)
from agents import Agent, Runner
import asyncio
spanish_agent = Agent(
name="Spanish agent",
instructions="You only speak Spanish.",
)
english_agent = Agent(
name="English agent",
instructions="You only speak English",
)
triage_agent = Agent(
name="Triage agent",
instructions="Handoff to the appropriate agent based on the language of the request.",
handoffs=[spanish_agent, english_agent],
)
async def main():
result = await Runner.run(triage_agent, input="Hola, ¿cómo estás?")
print(result.final_output)
# ¡Hola! Estoy bien, gracias por preguntar. ¿Y tú, cómo estás?
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())import asyncio
from agents import Agent, Runner, function_tool
@function_tool
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
return f"The weather in {city} is sunny."
agent = Agent(
name="Hello world",
instructions="You are a helpful agent.",
tools=[get_weather],
)
async def main():
result = await Runner.run(agent, input="What's the weather in Tokyo?")
print(result.final_output)
# The weather in Tokyo is sunny.
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())When you call Runner.run(), we run a loop until we get a final output.
- We call the LLM, using the model and settings on the agent, and the message history.
- The LLM returns a response, which may include tool calls.
- If the response has a final output (see below for more on this), we return it and end the loop.
- If the response has a handoff, we set the agent to the new agent and go back to step 1.
- We process the tool calls (if any) and append the tool responses messages. Then we go to step 1.
There is a max_turns parameter that you can use to limit the number of times the loop executes.
Final output is the last thing the agent produces in the loop.
- If you set an
output_typeon the agent, the final output is when the LLM returns something of that type. We use structured outputs for this. - If there's no
output_type(i.e. plain text responses), then the first LLM response without any tool calls or handoffs is considered as the final output.
As a result, the mental model for the agent loop is:
- If the current agent has an
output_type, the loop runs until the agent produces structured output matching that type. - If the current agent does not have an
output_type, the loop runs until the current agent produces a message without any tool calls/handoffs.
The Agents SDK is designed to be highly flexible, allowing you to model a wide range of LLM workflows including deterministic flows, iterative loops, and more. See examples in examples/agent_patterns.
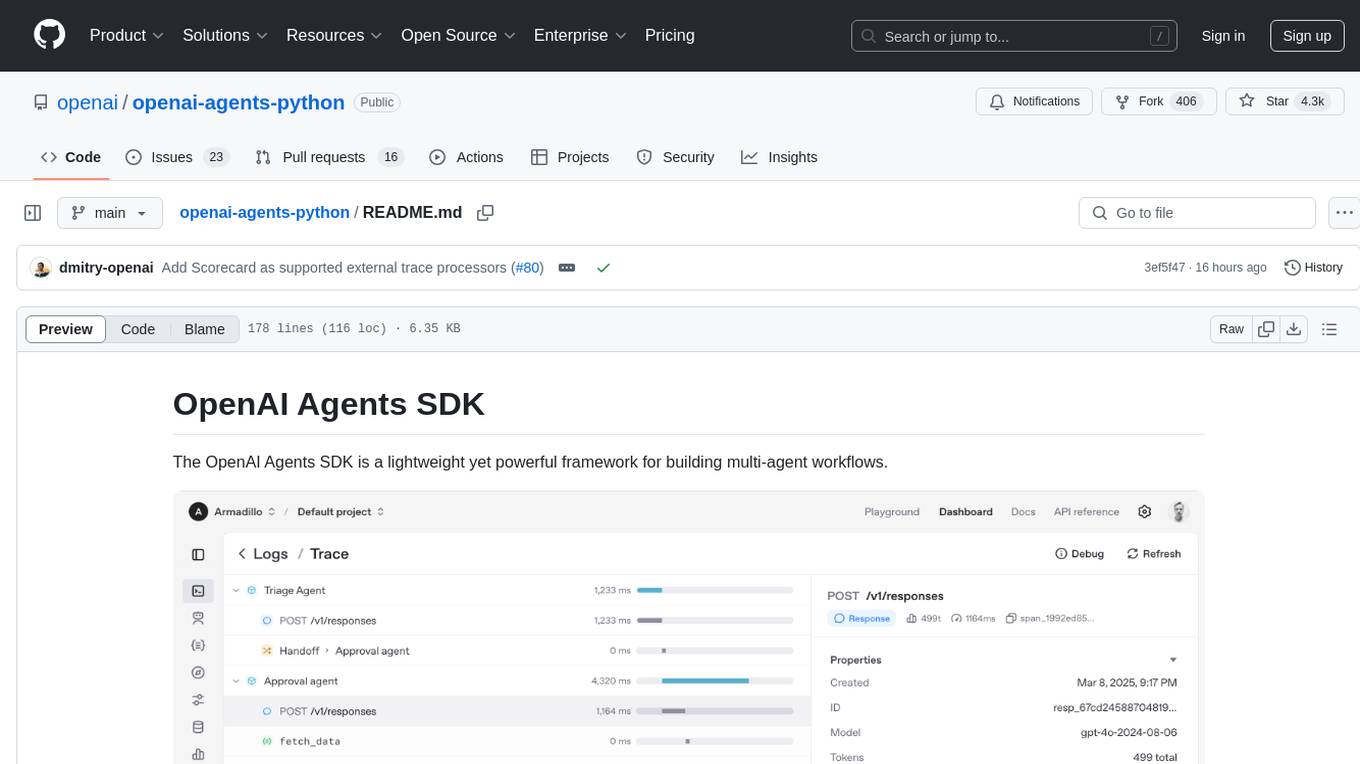
The Agents SDK automatically traces your agent runs, making it easy to track and debug the behavior of your agents. Tracing is extensible by design, supporting custom spans and a wide variety of external destinations, including Logfire, AgentOps, Braintrust, Scorecard, Keywords AI, and many more. For more details about how to customize or disable tracing, see Tracing, which also includes a larger list of external tracing processors.
There are several options for long-running agents. Refer to the documentation for details.
The Agents SDK provides built-in session memory to automatically maintain conversation history across multiple agent runs, eliminating the need to manually handle .to_input_list() between turns.
from agents import Agent, Runner, SQLiteSession
# Create agent
agent = Agent(
name="Assistant",
instructions="Reply very concisely.",
)
# Create a session instance
session = SQLiteSession("conversation_123")
# First turn
result = await Runner.run(
agent,
"What city is the Golden Gate Bridge in?",
session=session
)
print(result.final_output) # "San Francisco"
# Second turn - agent automatically remembers previous context
result = await Runner.run(
agent,
"What state is it in?",
session=session
)
print(result.final_output) # "California"
# Also works with synchronous runner
result = Runner.run_sync(
agent,
"What's the population?",
session=session
)
print(result.final_output) # "Approximately 39 million"- No memory (default): No session memory when session parameter is omitted
-
session: Session = DatabaseSession(...): Use a Session instance to manage conversation history
from agents import Agent, Runner, SQLiteSession
# SQLite - file-based or in-memory database
session = SQLiteSession("user_123", "conversations.db")
# Redis - for scalable, distributed deployments
# from agents.extensions.memory import RedisSession
# session = RedisSession.from_url("user_123", url="redis://localhost:6379/0")
agent = Agent(name="Assistant")
# Different session IDs maintain separate conversation histories
result1 = await Runner.run(
agent,
"Hello",
session=session
)
result2 = await Runner.run(
agent,
"Hello",
session=SQLiteSession("user_456", "conversations.db")
)You can implement your own session memory by creating a class that follows the Session protocol:
from agents.memory import Session
from typing import List
class MyCustomSession:
"""Custom session implementation following the Session protocol."""
def __init__(self, session_id: str):
self.session_id = session_id
# Your initialization here
async def get_items(self, limit: int | None = None) -> List[dict]:
# Retrieve conversation history for the session
pass
async def add_items(self, items: List[dict]) -> None:
# Store new items for the session
pass
async def pop_item(self) -> dict | None:
# Remove and return the most recent item from the session
pass
async def clear_session(self) -> None:
# Clear all items for the session
pass
# Use your custom session
agent = Agent(name="Assistant")
result = await Runner.run(
agent,
"Hello",
session=MyCustomSession("my_session")
)- Ensure you have
uvinstalled.
uv --version- Install dependencies
make sync- (After making changes) lint/test
make check # run tests linter and typechecker
Or to run them individually:
make tests # run tests
make mypy # run typechecker
make lint # run linter
make format-check # run style checker
Format code if make format-check fails above by running:
make format
We'd like to acknowledge the excellent work of the open-source community, especially:
- Pydantic (data validation) and PydanticAI (advanced agent framework)
- LiteLLM (unified interface for 100+ LLMs)
- MkDocs
- Griffe
- uv and ruff
We're committed to continuing to build the Agents SDK as an open source framework so others in the community can expand on our approach.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for openai-agents-python
Similar Open Source Tools

openai-agents-python
The OpenAI Agents SDK is a lightweight framework for building multi-agent workflows. It includes concepts like Agents, Handoffs, Guardrails, and Tracing to facilitate the creation and management of agents. The SDK is compatible with any model providers supporting the OpenAI Chat Completions API format. It offers flexibility in modeling various LLM workflows and provides automatic tracing for easy tracking and debugging of agent behavior. The SDK is designed for developers to create deterministic flows, iterative loops, and more complex workflows.
phidata
Phidata is a framework for building AI Assistants with memory, knowledge, and tools. It enables LLMs to have long-term conversations by storing chat history in a database, provides them with business context by storing information in a vector database, and enables them to take actions like pulling data from an API, sending emails, or querying a database. Memory and knowledge make LLMs smarter, while tools make them autonomous.

axar
AXAR AI is a lightweight framework designed for building production-ready agentic applications using TypeScript. It aims to simplify the process of creating robust, production-grade LLM-powered apps by focusing on familiar coding practices without unnecessary abstractions or steep learning curves. The framework provides structured, typed inputs and outputs, familiar and intuitive patterns like dependency injection and decorators, explicit control over agent behavior, real-time logging and monitoring tools, minimalistic design with little overhead, model agnostic compatibility with various AI models, and streamed outputs for fast and accurate results. AXAR AI is ideal for developers working on real-world AI applications who want a tool that gets out of the way and allows them to focus on shipping reliable software.
allms
allms is a versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying Large Language Models (LLMs). Developed by Allegro engineers, it simplifies working with LLM applications by providing a user-friendly interface, asynchronous querying, automatic retrying mechanism, error handling, and output parsing. It supports various LLM families hosted on different platforms like OpenAI, Google, Azure, and GCP. The library offers features for configuring endpoint credentials, batch querying with symbolic variables, and forcing structured output format. It also provides documentation, quickstart guides, and instructions for local development, testing, updating documentation, and making new releases.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.
invariant
Invariant Analyzer is an open-source scanner designed for LLM-based AI agents to find bugs, vulnerabilities, and security threats. It scans agent execution traces to identify issues like looping behavior, data leaks, prompt injections, and unsafe code execution. The tool offers a library of built-in checkers, an expressive policy language, data flow analysis, real-time monitoring, and extensible architecture for custom checkers. It helps developers debug AI agents, scan for security violations, and prevent security issues and data breaches during runtime. The analyzer leverages deep contextual understanding and a purpose-built rule matching engine for security policy enforcement.
dive
Dive is an AI toolkit for Go that enables the creation of specialized teams of AI agents and seamless integration with leading LLMs. It offers a CLI and APIs for easy integration, with features like creating specialized agents, hierarchical agent systems, declarative configuration, multiple LLM support, extended reasoning, model context protocol, advanced model settings, tools for agent capabilities, tool annotations, streaming, CLI functionalities, thread management, confirmation system, deep research, and semantic diff. Dive also provides semantic diff analysis, unified interface for LLM providers, tool system with annotations, custom tool creation, and support for various verified models. The toolkit is designed for developers to build AI-powered applications with rich agent capabilities and tool integrations.
oasis
OASIS is a scalable, open-source social media simulator that integrates large language models with rule-based agents to realistically mimic the behavior of up to one million users on platforms like Twitter and Reddit. It facilitates the study of complex social phenomena such as information spread, group polarization, and herd behavior, offering a versatile tool for exploring diverse social dynamics and user interactions in digital environments. With features like scalability, dynamic environments, diverse action spaces, and integrated recommendation systems, OASIS provides a comprehensive platform for simulating social media interactions at a large scale.
vinagent
Vinagent is a lightweight and flexible library designed for building smart agent assistants across various industries. It provides a simple yet powerful foundation for creating AI-powered customer service bots, data analysis assistants, or domain-specific automation agents. With its modular tool system, users can easily extend their agent's capabilities by integrating a wide range of tools that are self-contained, well-documented, and can be registered dynamically. Vinagent allows users to scale and adapt their agents to new tasks or environments effortlessly.
GraphRAG-SDK
Build fast and accurate GenAI applications with GraphRAG SDK, a specialized toolkit for building Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG) systems. It integrates knowledge graphs, ontology management, and state-of-the-art LLMs to deliver accurate, efficient, and customizable RAG workflows. The SDK simplifies the development process by automating ontology creation, knowledge graph agent creation, and query handling, enabling users to interact and query their knowledge graphs effectively. It supports multi-agent systems and orchestrates agents specialized in different domains. The SDK is optimized for FalkorDB, ensuring high performance and scalability for large-scale applications. By leveraging knowledge graphs, it enables semantic relationships and ontology-driven queries that go beyond standard vector similarity, enhancing retrieval-augmented generation capabilities.
web-llm
WebLLM is a modular and customizable javascript package that directly brings language model chats directly onto web browsers with hardware acceleration. Everything runs inside the browser with no server support and is accelerated with WebGPU. WebLLM is fully compatible with OpenAI API. That is, you can use the same OpenAI API on any open source models locally, with functionalities including json-mode, function-calling, streaming, etc. We can bring a lot of fun opportunities to build AI assistants for everyone and enable privacy while enjoying GPU acceleration.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using a local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration for tasks, command line interface for running tasks, push to Hugging Face Hub for dataset upload, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration or Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM to interface with LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub.
mountain-goap
Mountain GOAP is a generic C# GOAP (Goal Oriented Action Planning) library for creating AI agents in games. It favors composition over inheritance, supports multiple weighted goals, and uses A* pathfinding to plan paths through sequential actions. The library includes concepts like agents, goals, actions, sensors, permutation selectors, cost callbacks, state mutators, state checkers, and a logger. It also features event handling for agent planning and execution. The project structure includes examples, API documentation, and internal classes for planning and execution.
npcsh
`npcsh` is a python-based command-line tool designed to integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) and Agents into one's daily workflow by making them available and easily configurable through the command line shell. It leverages the power of LLMs to understand natural language commands and questions, execute tasks, answer queries, and provide relevant information from local files and the web. Users can also build their own tools and call them like macros from the shell. `npcsh` allows users to take advantage of agents (i.e. NPCs) through a managed system, tailoring NPCs to specific tasks and workflows. The tool is extensible with Python, providing useful functions for interacting with LLMs, including explicit coverage for popular providers like ollama, anthropic, openai, gemini, deepseek, and openai-like providers. Users can set up a flask server to expose their NPC team for use as a backend service, run SQL models defined in their project, execute assembly lines, and verify the integrity of their NPC team's interrelations. Users can execute bash commands directly, use favorite command-line tools like VIM, Emacs, ipython, sqlite3, git, pipe the output of these commands to LLMs, or pass LLM results to bash commands.
langgraph4j
Langgraph4j is a Java library for language processing tasks such as text classification, sentiment analysis, and named entity recognition. It provides a set of tools and algorithms for analyzing text data and extracting useful information. The library is designed to be efficient and easy to use, making it suitable for both research and production applications.
For similar tasks
OpenAGI
OpenAGI is an AI agent creation package designed for researchers and developers to create intelligent agents using advanced machine learning techniques. The package provides tools and resources for building and training AI models, enabling users to develop sophisticated AI applications. With a focus on collaboration and community engagement, OpenAGI aims to facilitate the integration of AI technologies into various domains, fostering innovation and knowledge sharing among experts and enthusiasts.
GPTSwarm
GPTSwarm is a graph-based framework for LLM-based agents that enables the creation of LLM-based agents from graphs and facilitates the customized and automatic self-organization of agent swarms with self-improvement capabilities. The library includes components for domain-specific operations, graph-related functions, LLM backend selection, memory management, and optimization algorithms to enhance agent performance and swarm efficiency. Users can quickly run predefined swarms or utilize tools like the file analyzer. GPTSwarm supports local LM inference via LM Studio, allowing users to run with a local LLM model. The framework has been accepted by ICML2024 and offers advanced features for experimentation and customization.
AgentForge
AgentForge is a low-code framework tailored for the rapid development, testing, and iteration of AI-powered autonomous agents and Cognitive Architectures. It is compatible with a range of LLM models and offers flexibility to run different models for different agents based on specific needs. The framework is designed for seamless extensibility and database-flexibility, making it an ideal playground for various AI projects. AgentForge is a beta-testing ground and future-proof hub for crafting intelligent, model-agnostic autonomous agents.
atomic_agents
Atomic Agents is a modular and extensible framework designed for creating powerful applications. It follows the principles of Atomic Design, emphasizing small and single-purpose components. Leveraging Pydantic for data validation and serialization, the framework offers a set of tools and agents that can be combined to build AI applications. It depends on the Instructor package and supports various APIs like OpenAI, Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. Atomic Agents is suitable for developers looking to create AI agents with a focus on modularity and flexibility.
LongRoPE
LongRoPE is a method to extend the context window of large language models (LLMs) beyond 2 million tokens. It identifies and exploits non-uniformities in positional embeddings to enable 8x context extension without fine-tuning. The method utilizes a progressive extension strategy with 256k fine-tuning to reach a 2048k context. It adjusts embeddings for shorter contexts to maintain performance within the original window size. LongRoPE has been shown to be effective in maintaining performance across various tasks from 4k to 2048k context lengths.
ax
Ax is a Typescript library that allows users to build intelligent agents inspired by agentic workflows and the Stanford DSP paper. It seamlessly integrates with multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) and VectorDBs to create RAG pipelines or collaborative agents capable of solving complex problems. The library offers advanced features such as streaming validation, multi-modal DSP, and automatic prompt tuning using optimizers. Users can easily convert documents of any format to text, perform smart chunking, embedding, and querying, and ensure output validation while streaming. Ax is production-ready, written in Typescript, and has zero dependencies.
Awesome-AI-Agents
Awesome-AI-Agents is a curated list of projects, frameworks, benchmarks, platforms, and related resources focused on autonomous AI agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository showcases a wide range of applications, multi-agent task solver projects, agent society simulations, and advanced components for building and customizing AI agents. It also includes frameworks for orchestrating role-playing, evaluating LLM-as-Agent performance, and connecting LLMs with real-world applications through platforms and APIs. Additionally, the repository features surveys, paper lists, and blogs related to LLM-based autonomous agents, making it a valuable resource for researchers, developers, and enthusiasts in the field of AI.
CodeFuse-muAgent
CodeFuse-muAgent is a Multi-Agent framework designed to streamline Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) orchestration for agents. It integrates toolkits, code libraries, knowledge bases, and sandbox environments for rapid construction of complex Multi-Agent interactive applications. The framework enables efficient execution and handling of multi-layered and multi-dimensional tasks.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

