
ollama-operator
🚢 Yet another operator for running large language models on Kubernetes with ease. Powered by Ollama! 🐫
Stars: 183
Ollama Operator is a Kubernetes operator designed to facilitate running large language models on Kubernetes clusters. It simplifies the process of deploying and managing multiple models on the same cluster, providing an easy-to-use interface for users. With support for various Kubernetes environments and seamless integration with Ollama models, APIs, and CLI, Ollama Operator streamlines the deployment and management of language models. By leveraging the capabilities of lama.cpp, Ollama Operator eliminates the need to worry about Python environments and CUDA drivers, making it a reliable tool for running large language models on Kubernetes.
README:
Yet another operator for running large language models on Kubernetes with ease. 🙀
Powered by Ollama! 🐫
While Ollama is a powerful tool for running large language models locally, and the user experience of CLI is just the same as using Docker CLI, it's not possible yet to replicate the same user experience on Kubernetes, especially when it comes to running multiple models on the same cluster with loads of resources and configurations.
That's where the Ollama Operator kicks in:
- Install the operator on your Kubernetes cluster
- Apply the needed CRDs
- Create your models
- Wait for the models to be fetched and loaded, that's it!
Thanks to the great works of llama.cpp, no more worries about Python environment, CUDA drivers.
The journey to large language models, AIGC, localized agents, 🦜🔗 Langchain and more is just a few steps away!
- ✅ Abilities to run multiple models on the same cluster.
- ✅ Compatible with all Ollama models, APIs, and CLI.
- ✅ Able to run on general Kubernetes clusters, K3s clusters (Respberry Pi, TrueNAS SCALE, etc.), kind, minikube, etc. You name it!
- ✅ Easy to install, uninstall, and upgrade.
- ✅ Pull image once, share across the entire node (just like normal images).
- ✅ Easy to expose with existing Kubernetes services, ingress, etc.
- ✅ Doesn't require any additional dependencies, just Kubernetes
kubectl apply \
--server-side=true \
-f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nekomeowww/ollama-operator/v0.10.1/dist/install.yamlkubectl wait \
-n ollama-operator-system \
--for=jsonpath='{.status.readyReplicas}'=1 \
deployment/ollama-operator-controller-manager[!NOTE] You can also use the
kollamaCLI natively shipped by Ollama Operator, and will be easier to interact with the operator.Install
kollamaCLI:go install github.com/nekomeowww/ollama-operator/cmd/kollama@latestDeploy a model can be done with the following command:
kollama deploy phi --expose --node-port 30001More information can be found at CLI
[!IMPORTANT] Working with
kind?The default provisioned
StorageClassinkindisstandard, and will only work withReadWriteOnceaccess mode, therefore if you would need to run the operator withkind, you should specifypersistentVolumewithaccessMode: ReadWriteOncein theModelCRD:apiVersion: ollama.ayaka.io/v1 kind: Model metadata: name: phi spec: image: phi persistentVolume: accessMode: ReadWriteOnce
Let's create a Model CR for the model phi:
apiVersion: ollama.ayaka.io/v1
kind: Model
metadata:
name: phi
spec:
image: phiApply the Model CR to your Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f ollama-model-phi.yamlWait for the model to be ready:
kubectl wait --for=jsonpath='{.status.readyReplicas}'=1 deployment/ollama-model-phi- Ready! Now let's forward the ports to access the model:
kubectl port-forward svc/ollama-model-phi ollama- Interact with the model:
ollama run phiapiVersion: ollama.ayaka.io/v1
kind: Model
metadata:
name: phi
spec:
# Scale the model to 2 replicas
replicas: 2
# Use the model image `phi`
image: phi
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
storageClassName: local-path
# If you have your own PersistentVolumeClaim created
persistentVolumeClaim: your-pvc
# If you need to specify the access mode for the PersistentVolume
persistentVolume:
accessMode: ReadWriteOnceUnlock the abilities to run the following models with the Ollama Operator over Kubernetes:
[!TIP] By the power of
Modelfilebacked by Ollama, you can create and bundle any of your own model. As long as it's a GGUF formatted model.Full list of available images can be found at Ollama Library.
[!WARNING] You should have at least 8 GB of RAM available on your node to run the 7B models, 16 GB to run the 13B models, and 32 GB to run the 33B models.
[!WARNING] The actual size of downloaded large language models are huge by comparing to the size of general container images.
- Fast and stable network connection is recommended to download the models.
- Efficient storage is required to store the models if you want to run models larger than 13B.
There are two major components that the Ollama Operator will create for:
-
Model Inferencing Server: The model inferencing server is a gRPC server that runs the model and serves the model's API. It is created as a
Deploymentin the Kubernetes cluster. -
Model Image Storage: The model image storage is a
PersistentVolumethat stores the model image. It is created as aStatefulSetalong with aPersistentVolumeClaimin the Kubernetes cluster.
[!NOTE] The image that created by
Modelfileof Ollama is a valid OCI format image, however, due to the incompatiblecontentTypevalue, and the overall structure of theModelfileimage to the general container image, it's not possible to run the model directly with the general container runtime. Therefore a standalone service/deployment of Model Image Storage is required to be persisted on the Kubernetes cluster in order to hold and cache the previously downloaded model image.
The detailed resources it creates, and the relationships between them are shown in the following diagram:

- Refer to the CONTRIBUTING.md for more information.
- More information can be found via the Kubebuilder Documentation
Gratefully thanks to the following projects and their authors, contributors:
It is because of their hard work and contributions that this program exists.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ollama-operator
Similar Open Source Tools

ollama-operator
Ollama Operator is a Kubernetes operator designed to facilitate running large language models on Kubernetes clusters. It simplifies the process of deploying and managing multiple models on the same cluster, providing an easy-to-use interface for users. With support for various Kubernetes environments and seamless integration with Ollama models, APIs, and CLI, Ollama Operator streamlines the deployment and management of language models. By leveraging the capabilities of lama.cpp, Ollama Operator eliminates the need to worry about Python environments and CUDA drivers, making it a reliable tool for running large language models on Kubernetes.
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
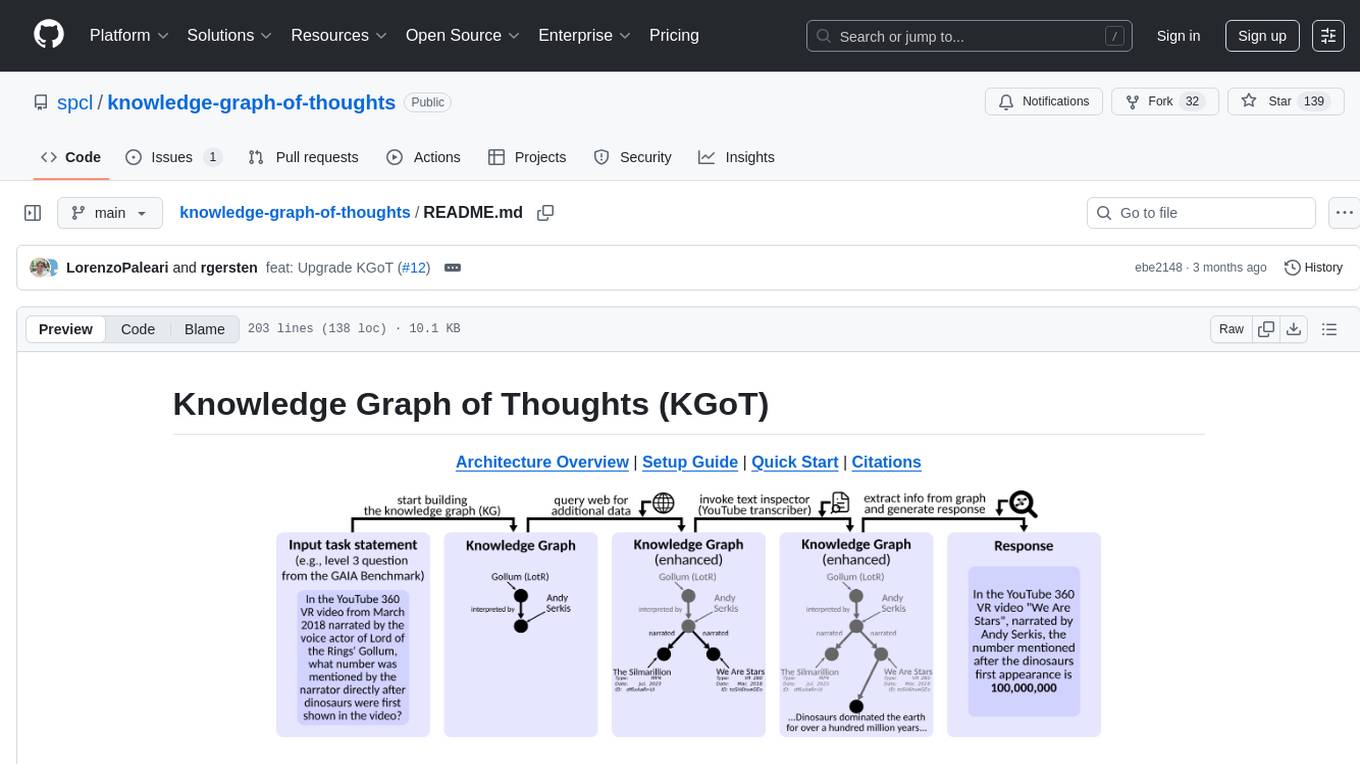
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
lmql
LMQL is a programming language designed for large language models (LLMs) that offers a unique way of integrating traditional programming with LLM interaction. It allows users to write programs that combine algorithmic logic with LLM calls, enabling model reasoning capabilities within the context of the program. LMQL provides features such as Python syntax integration, rich control-flow options, advanced decoding techniques, powerful constraints via logit masking, runtime optimization, sync and async API support, multi-model compatibility, and extensive applications like JSON decoding and interactive chat interfaces. The tool also offers library integration, flexible tooling, and output streaming options for easy model output handling.
metaflow-service
Metaflow Service is a metadata service implementation for Metaflow, providing a thin wrapper around a database to keep track of metadata associated with Flows, Runs, Steps, Tasks, and Artifacts. It includes features for managing DB migrations, launching compatible versions of the metadata service, and executing flows locally. The service can be run using Docker or as a standalone service, with options for testing and running unit/integration tests. Users can interact with the service via API endpoints or utility CLI tools.
gpt-cli
gpt-cli is a command-line interface tool for interacting with various chat language models like ChatGPT, Claude, and others. It supports model customization, usage tracking, keyboard shortcuts, multi-line input, markdown support, predefined messages, and multiple assistants. Users can easily switch between different assistants, define custom assistants, and configure model parameters and API keys in a YAML file for easy customization and management.

airbyte_serverless
AirbyteServerless is a lightweight tool designed to simplify the management of Airbyte connectors. It offers a serverless mode for running connectors, allowing users to easily move data from any source to their data warehouse. Unlike the full Airbyte-Open-Source-Platform, AirbyteServerless focuses solely on the Extract-Load process without a UI, database, or transform layer. It provides a CLI tool, 'abs', for managing connectors, creating connections, running jobs, selecting specific data streams, handling secrets securely, and scheduling remote runs. The tool is scalable, allowing independent deployment of multiple connectors. It aims to streamline the connector management process and provide a more agile alternative to the comprehensive Airbyte platform.
vidai
vidai is a CLI tool for RunwayML that generates videos using AI. It supports Gen3 and Gen3 Turbo models, allowing users to create videos directly from the command line using text or image prompts. Users can also extend videos, edit videos, and explore unlimited generations. The tool requires a RunwayML account and ffmpeg for extended videos.
genai-toolbox
Gen AI Toolbox for Databases is an open source server that simplifies building Gen AI tools for interacting with databases. It handles complexities like connection pooling, authentication, and more, enabling easier, faster, and more secure tool development. The toolbox sits between the application's orchestration framework and the database, providing a control plane to modify, distribute, or invoke tools. It offers simplified development, better performance, enhanced security, and end-to-end observability. Users can install the toolbox as a binary, container image, or compile from source. Configuration is done through a 'tools.yaml' file, defining sources, tools, and toolsets. The project follows semantic versioning and welcomes contributions.
geti-sdk
The Intel® Geti™ SDK is a python package that enables teams to rapidly develop AI models by easing the complexities of model development and fostering collaboration. It provides tools to interact with an Intel® Geti™ server via the REST API, allowing for project creation, downloading, uploading, deploying for local inference with OpenVINO, configuration management, training job monitoring, media upload, and prediction. The repository also includes tutorial-style Jupyter notebooks demonstrating SDK usage.
AgentIQ
AgentIQ is a flexible library designed to seamlessly integrate enterprise agents with various data sources and tools. It enables true composability by treating agents, tools, and workflows as simple function calls. With features like framework agnosticism, reusability, rapid development, profiling, observability, evaluation system, user interface, and MCP compatibility, AgentIQ empowers developers to move quickly, experiment freely, and ensure reliability across agent-driven projects.
geti-sdk
The Intel® Geti™ SDK is a python package that enables teams to rapidly develop AI models by easing the complexities of model development and enhancing collaboration between teams. It provides tools to interact with an Intel® Geti™ server via the REST API, allowing for project creation, downloading, uploading, deploying for local inference with OpenVINO, setting project and model configuration, launching and monitoring training jobs, and media upload and prediction. The SDK also includes tutorial-style Jupyter notebooks demonstrating its usage.
holohub
Holohub is a central repository for the NVIDIA Holoscan AI sensor processing community to share reference applications, operators, tutorials, and benchmarks. It includes example applications, community components, package configurations, and tutorials. Users and developers of the Holoscan platform are invited to reuse and contribute to this repository. The repository provides detailed instructions on prerequisites, building, running applications, contributing, and glossary terms. It also offers a searchable catalog of available components on the Holoscan SDK User Guide website.
artkit
ARTKIT is a Python framework developed by BCG X for automating prompt-based testing and evaluation of Gen AI applications. It allows users to develop automated end-to-end testing and evaluation pipelines for Gen AI systems, supporting multi-turn conversations and various testing scenarios like Q&A accuracy, brand values, equitability, safety, and security. The framework provides a simple API, asynchronous processing, caching, model agnostic support, end-to-end pipelines, multi-turn conversations, robust data flows, and visualizations. ARTKIT is designed for customization by data scientists and engineers to enhance human-in-the-loop testing and evaluation, emphasizing the importance of tailored testing for each Gen AI use case.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)
vulnerability-analysis
The NVIDIA AI Blueprint for Vulnerability Analysis for Container Security showcases accelerated analysis on common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) at an enterprise scale, reducing mitigation time from days to seconds. It enables security analysts to determine software package vulnerabilities using large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). The blueprint is designed for security analysts, IT engineers, and AI practitioners in cybersecurity. It requires NVAIE developer license and API keys for vulnerability databases, search engines, and LLM model services. Hardware requirements include L40 GPU for pipeline operation and optional LLM NIM and Embedding NIM. The workflow involves LLM pipeline for CVE impact analysis, utilizing LLM planner, agent, and summarization nodes. The blueprint uses NVIDIA NIM microservices and Morpheus Cybersecurity AI SDK for vulnerability analysis.
warc-gpt
WARC-GPT is an experimental retrieval augmented generation pipeline for web archive collections. It allows users to interact with WARC files, extract text, generate text embeddings, visualize embeddings, and interact with a web UI and API. The tool is highly customizable, supporting various LLMs, providers, and embedding models. Users can configure the application using environment variables, ingest WARC files, start the server, and interact with the web UI and API to search for content and generate text completions. WARC-GPT is designed for exploration and experimentation in exploring web archives using AI.
For similar tasks

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

ray
Ray is a unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications. It consists of a core distributed runtime and a set of AI libraries for simplifying ML compute, including Data, Train, Tune, RLlib, and Serve. Ray runs on any machine, cluster, cloud provider, and Kubernetes, and features a growing ecosystem of community integrations. With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster, making it easy to meet the compute-intensive demands of modern ML workloads.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.

djl
Deep Java Library (DJL) is an open-source, high-level, engine-agnostic Java framework for deep learning. It is designed to be easy to get started with and simple to use for Java developers. DJL provides a native Java development experience and allows users to integrate machine learning and deep learning models with their Java applications. The framework is deep learning engine agnostic, enabling users to switch engines at any point for optimal performance. DJL's ergonomic API interface guides users with best practices to accomplish deep learning tasks, such as running inference and training neural networks.

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking
tt-metal
TT-NN is a python & C++ Neural Network OP library. It provides a low-level programming model, TT-Metalium, enabling kernel development for Tenstorrent hardware.
burn
Burn is a new comprehensive dynamic Deep Learning Framework built using Rust with extreme flexibility, compute efficiency and portability as its primary goals.
awsome-distributed-training
This repository contains reference architectures and test cases for distributed model training with Amazon SageMaker Hyperpod, AWS ParallelCluster, AWS Batch, and Amazon EKS. The test cases cover different types and sizes of models as well as different frameworks and parallel optimizations (Pytorch DDP/FSDP, MegatronLM, NemoMegatron...).
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
