
latex2ai
LaTeX Plugin for Adobe Illustrator
Stars: 174
LaTeX2AI is a plugin for Adobe Illustrator that allows users to use editable text labels typeset in LaTeX inside an Illustrator document. It provides a seamless integration of LaTeX functionality within the Illustrator environment, enabling users to create and edit LaTeX labels, manage item scaling behavior, set global options, and save documents as PDF with included LaTeX labels. The tool simplifies the process of including LaTeX-generated content in Illustrator designs, ensuring accurate scaling and alignment with other elements in the document.
README:
LaTeX2AI is a plugin for Adobe Illustrator (MacOS and Windows) that enables the use of editable text labels typeset in LaTeX inside an Illustrator document.
LaTeX2AI is under the MIT license, see ./LICENSE. If you use LaTeX2AI to create figures for your work, please acknowledge it with a link to the GitHub repository. For example:
- Sketches in this work have been created using the Adobe Illustrator plug-in LaTeX2AI (https://github.com/isteinbrecher/latex2ai).
Feel free to leave a ⭐ on GitHub. You can also add your work to Work that uses LaTeX2AI.
The following software dependencies are required to run LaTeX2AI:
- A LaTeX compiler such as TeX Live or MiKTeX
- Ghost script
-
Download LaTeX2AI from the GitHub release page
-
Unzip the
.zipfile -
Copy the user interface folder
com.isteinbrecher.latex2ai- LaTeX2AI installation only for current user:
- Copy
com.isteinbrecher.latex2aitoC:\Users\<USERNAME>\AppData\Roaming\Adobe\CEP\extensions(the directory might have to be created)
- Copy
- LaTeX2AI installation for all users (requires administrator privileges):
- Copy
com.isteinbrecher.latex2aitoC:\Program Files\Common Files\Adobe\CEP\extensions\
- Copy
- LaTeX2AI installation only for current user:
-
Copy the plugin
- LaTeX2AI installation only for current user:
- Copy
WIN/LaTeX2AI.aipto an arbitrary directory. This directory has to be set as the Adobe Illustrator Plugin directory viaEdit/Preferences/Plug-ins & Scratch Disks.../Additional Plug-ins Folder/
- Copy
- LaTeX2AI installation for all users (requires administrator privileges):
- Copy
WIN/LaTeX2AI.aiptoC:\Program Files\Adobe\Adobe Illustrator <YOUR VERSION>\Plug-ins\
- Copy
- LaTeX2AI installation only for current user:
-
After a restart of Adobe Illustrator, you can display the LaTeX2AI tools with
Window/Toolbars/Advanced.
To uninstall LaTeX2AI, delete the files you copied.
-
Download LaTeX2AI from the GitHub release page
-
Unzip the file
-
Copy the user interface folder
com.isteinbrecher.latex2ai- LaTeX2AI installation only for current user:
- Copy
com.isteinbrecher.latex2aito~/Library/Application Support/Adobe/CEP/extensions/
- Copy
- LaTeX2AI installation for all users (requires administrator privileges):
- Copy
com.isteinbrecher.latex2aito/Library/Application Support/Adobe/CEP/extensions/
- Copy
- LaTeX2AI installation only for current user:
-
Copy the plugin
- LaTeX2AI installation only for current user:
- Copy
macOS/LaTeX2AI.aipto an arbitrary directory. This directory has to be set as the Adobe Illustrator Plugin directory viaEdit/Preferences/Plug-ins & Scratch Disks.../Additional Plug-ins Folder/
- Copy
- LaTeX2AI installation for all users (requires administrator privileges):
- Copy
macOS/LaTeX2AI.aipto/Applications/Adobe Illustrator <YOUR VERSION>/Plug-ins/
- Copy
- LaTeX2AI installation only for current user:
-
After a restart of Adobe Illustrator, you can display the LaTeX2AI tools with
Window/Toolbars/Advanced.Depending on your system settings you might get the following error message when starting Illustrator

This can be resolved by explicitly allowing the gatekeeper to run LaTeX2AI (see also this thread). To do so, open the terminal and type:
xattr -d com.apple.quarantine <PATH TO LaTeXAI.aip>
If you have installed LaTeX2AI for all users you need to run this command with administrator privileges:
sudo xattr -d com.apple.quarantine <PATH TO LaTeXAI.aip>
To uninstall LaTeX2AI, delete the files you copied.
LaTeX2AI adds four buttons to the main toolbar:
-
 Create / Edit: Edit an existing label by clicking on it, or creating a new one by clicking somewhere in the document.
Create / Edit: Edit an existing label by clicking on it, or creating a new one by clicking somewhere in the document. -
 Redo LaTeX2AI labels: This allows for the LaTeX recompilation and/or scaling reset of all existing LaTeX2AI labels.
Redo LaTeX2AI labels: This allows for the LaTeX recompilation and/or scaling reset of all existing LaTeX2AI labels. -
 LaTeX2AI options: Open a form where the global LaTeX2AI options can be set. Also the LaTeX header can be opened in an external application.
LaTeX2AI options: Open a form where the global LaTeX2AI options can be set. Also the LaTeX header can be opened in an external application. -
 Save as PDF: Save the current
Save as PDF: Save the current .aidocument as a.pdfdocument with the same name. The LaTeX2AI labels are included into the created.pdfdocument.
These buttons are the main way of interacting with LaTeX2AI. Additionally, double clicking on a LaTeX2AI label will enable the edit mode for that label.
The following form appears when creating or editing LaTeX2AI labels:
This option defines how a label behaves when it its size changes.
Take for example the well-known formula $\sum_{k=0}^{\infty}\frac{x^k}{k!}$ which is placed inside a rectangle:
The green box indicates the size of the LaTeX2I label and the dot describes the placement of the label. If the size changes due to a change in the LaTeX code, the position of this dot relative to the label will stay the same.
If the previous label is now changed to \displaystyle we get the following result:
The size of the label changed due to a change in the underlying LaTeX code, but the position (the indicated dot) stayed the same.
Additionally, there is the possibility of a baseline placement. This will result in a label where the baseline is exactly in the vertical center of the label. This label can now be easily adjusted and snapped to align with another baseline label or Illustrator text:
Per default, LaTeX2AI places the LaTeX labels inside Illustrator with a scale of 1:1, i.e., 1pt in the LaTeX label is 1pt in the Illustrator document. For example, if the LaTeX item is created with a font size of 12pt the font will match Illustrator text with 12pt. The user can resize the labels like any other Illustrator object, however, be aware that every time the LaTeX code of a label changes, the scale is reset to 1:1.
The recommended way of using LaTeX2AI is to always have items at a scale of 1:1.
By doing so, the exported Illustrator document can be simply included into a LaTeX document with the \includegraphics option scale=1, and the font size of the labels in the figures will exactly match the font size of the document (assuming that the header options are the same).
With the LaTeX2AI tool Redo items, one can easily reset the scaling of all LaTeX2AI items in the document.
LaTeX2AI assumed that all Illustrator files in the same directory use the same LaTeX header LaTeX2AI_header.tex (if no one exits in the directory, it will be created the first time it is needed).
This header can be edited to include packages and macros needed for the labels.
The .pdf files for the LaTeX labels are stored in the links subfolder of the document directory.
It is not required to keep track of the files in the links folder, LaTeX2AI manages and deletes unused label files.
LaTeX2AI currently does not work with Creative Cloud documents. However, if the document is stored in the Creative Cloud Files folder on the disk, LaTeX2AI should work as expected.
An incomplete list of work that uses LaTeX2AI
- Toenniessen, F.: Die Homotopie der Sphären - Eine Einführung in Spektralsequenzen, Lokalisierungen und Kohomologie-Operationen, Springer Verlag Heidelberg, 2023.
- Steinbrecher, I., Popp, A., Meier, C.: Consistent coupling of positions and rotations for embedding 1D Cosserat beams into 3D solid volumes. Comput Mech (2021), Open Access
- Steinbrecher, I., Mayr, M., Grill, M.J., Kremheller, J., Meier, C., Popp, A.: A mortar-type finite element approach for embedding 1D beams into 3D solid volumes, Comput Mech (2020), 66(6):1377-1398, Open Access
- Steinbrecher, I., Humer, A., Vu-Quoc, L.: On the numerical modeling of sliding beams: A comparison of different approaches, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 408:270-290, Open Access
If you are interested in contributing to LaTeX2AI, we welcome your collaboration. For general questions, feature request and bug reports please open an issue.
If you contribute actual code, fork the repository and make the changes in a feature branch.
Depending on the topic and amount of changes you also might want to open an issue.
To merge your changes into the main LaTeX2AI repository, create a pull request to the develop branch (this branch will be merged into main with the next release).
A few things to keep in mind:
- Compile a debug build and run the framework tests in Illustrator
 .
You might also consider adding tests for your changes (
.
You might also consider adding tests for your changes (./src/tests). - Run the
python3script./scripts/check_license.pyto ensure that all added source files have the correct license header. - LaTeX2AI uses
clang-formatto format the C++ code. Make sure to apply clang format to the changed source files:- With the Visual Studio solution in the repository this can be done with
Crtl-Kfollowed byCtrl-D. - On macOS you can use the following command (run in the root directory of LaTeX2AI):
find src -iname '*.h' -o -iname '*.cpp' | xargs clang-format -i
- With the Visual Studio solution in the repository this can be done with
- Add a short description of your changes to the Changelog.
- Feel free to add yourself to the ./CONTRIBUTORS file.
Instructions on how to build LaTeX2AI from source can be found here
A detailed changelog can be found here
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for latex2ai
Similar Open Source Tools

latex2ai
LaTeX2AI is a plugin for Adobe Illustrator that allows users to use editable text labels typeset in LaTeX inside an Illustrator document. It provides a seamless integration of LaTeX functionality within the Illustrator environment, enabling users to create and edit LaTeX labels, manage item scaling behavior, set global options, and save documents as PDF with included LaTeX labels. The tool simplifies the process of including LaTeX-generated content in Illustrator designs, ensuring accurate scaling and alignment with other elements in the document.
aiyabot
AIYA is a Discord bot interface for Stable Diffusion, offering features like live preview, negative prompts, model swapping, image generation, image captioning, image resizing, and more. It supports various options and bonus features to enhance user experience. Users can set per-channel defaults, view stats, manage queues, upscale images, and perform various commands on images. AIYA requires setup with AUTOMATIC1111's Stable Diffusion AI Web UI or SD.Next, and can be deployed using Docker with additional configuration options. Credits go to AUTOMATIC1111, vladmandic, harubaru, and various contributors for their contributions to AIYA's development.
bedrock-claude-chatbot
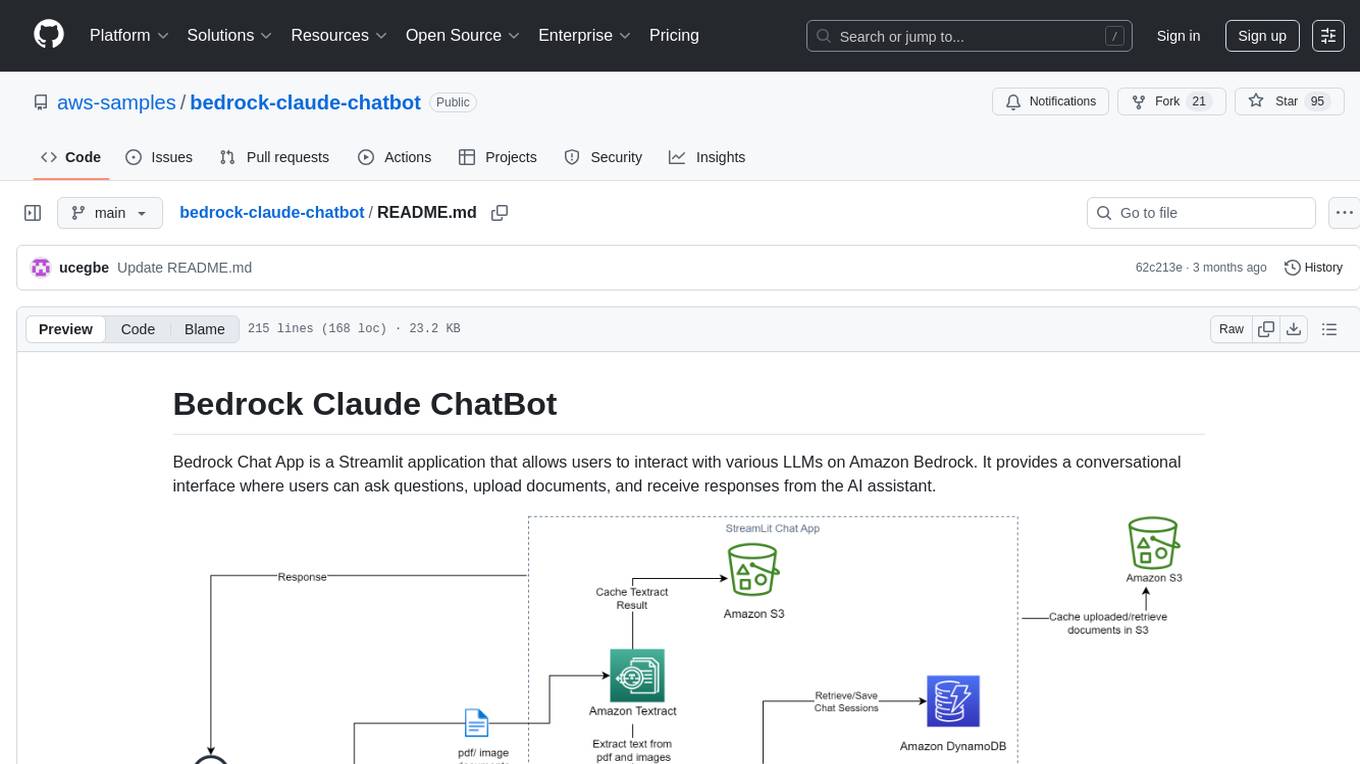
Bedrock Claude ChatBot is a Streamlit application that provides a conversational interface for users to interact with various Large Language Models (LLMs) on Amazon Bedrock. Users can ask questions, upload documents, and receive responses from the AI assistant. The app features conversational UI, document upload, caching, chat history storage, session management, model selection, cost tracking, logging, and advanced data analytics tool integration. It can be customized using a config file and is extensible for implementing specialized tools using Docker containers and AWS Lambda. The app requires access to Amazon Bedrock Anthropic Claude Model, S3 bucket, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Textract, and optionally Amazon Elastic Container Registry and Amazon Athena for advanced analytics features.
geti-sdk
The Intel® Geti™ SDK is a python package that enables teams to rapidly develop AI models by easing the complexities of model development and fostering collaboration. It provides tools to interact with an Intel® Geti™ server via the REST API, allowing for project creation, downloading, uploading, deploying for local inference with OpenVINO, configuration management, training job monitoring, media upload, and prediction. The repository also includes tutorial-style Jupyter notebooks demonstrating SDK usage.
geti-sdk
The Intel® Geti™ SDK is a python package that enables teams to rapidly develop AI models by easing the complexities of model development and enhancing collaboration between teams. It provides tools to interact with an Intel® Geti™ server via the REST API, allowing for project creation, downloading, uploading, deploying for local inference with OpenVINO, setting project and model configuration, launching and monitoring training jobs, and media upload and prediction. The SDK also includes tutorial-style Jupyter notebooks demonstrating its usage.
llm-subtrans
LLM-Subtrans is an open source subtitle translator that utilizes LLMs as a translation service. It supports translating subtitles between any language pairs supported by the language model. The application offers multiple subtitle formats support through a pluggable system, including .srt, .ssa/.ass, and .vtt files. Users can choose to use the packaged release for easy usage or install from source for more control over the setup. The tool requires an active internet connection as subtitles are sent to translation service providers' servers for translation.

aider-composer
Aider Composer is a VSCode extension that integrates Aider into your development workflow. It allows users to easily add and remove files, toggle between read-only and editable modes, review code changes, use different chat modes, and reference files in the chat. The extension supports multiple models, code generation, code snippets, and settings customization. It has limitations such as lack of support for multiple workspaces, Git repository features, linting, testing, voice features, in-chat commands, and configuration options.

cognita
Cognita is an open-source framework to organize your RAG codebase along with a frontend to play around with different RAG customizations. It provides a simple way to organize your codebase so that it becomes easy to test it locally while also being able to deploy it in a production ready environment. The key issues that arise while productionizing RAG system from a Jupyter Notebook are: 1. **Chunking and Embedding Job** : The chunking and embedding code usually needs to be abstracted out and deployed as a job. Sometimes the job will need to run on a schedule or be trigerred via an event to keep the data updated. 2. **Query Service** : The code that generates the answer from the query needs to be wrapped up in a api server like FastAPI and should be deployed as a service. This service should be able to handle multiple queries at the same time and also autoscale with higher traffic. 3. **LLM / Embedding Model Deployment** : Often times, if we are using open-source models, we load the model in the Jupyter notebook. This will need to be hosted as a separate service in production and model will need to be called as an API. 4. **Vector DB deployment** : Most testing happens on vector DBs in memory or on disk. However, in production, the DBs need to be deployed in a more scalable and reliable way. Cognita makes it really easy to customize and experiment everything about a RAG system and still be able to deploy it in a good way. It also ships with a UI that makes it easier to try out different RAG configurations and see the results in real time. You can use it locally or with/without using any Truefoundry components. However, using Truefoundry components makes it easier to test different models and deploy the system in a scalable way. Cognita allows you to host multiple RAG systems using one app. ### Advantages of using Cognita are: 1. A central reusable repository of parsers, loaders, embedders and retrievers. 2. Ability for non-technical users to play with UI - Upload documents and perform QnA using modules built by the development team. 3. Fully API driven - which allows integration with other systems. > If you use Cognita with Truefoundry AI Gateway, you can get logging, metrics and feedback mechanism for your user queries. ### Features: 1. Support for multiple document retrievers that use `Similarity Search`, `Query Decompostion`, `Document Reranking`, etc 2. Support for SOTA OpenSource embeddings and reranking from `mixedbread-ai` 3. Support for using LLMs using `Ollama` 4. Support for incremental indexing that ingests entire documents in batches (reduces compute burden), keeps track of already indexed documents and prevents re-indexing of those docs.
bia-bob
BIA `bob` is a Jupyter-based assistant for interacting with data using large language models to generate Python code. It can utilize OpenAI's chatGPT, Google's Gemini, Helmholtz' blablador, and Ollama. Users need respective accounts to access these services. Bob can assist in code generation, bug fixing, code documentation, GPU-acceleration, and offers a no-code custom Jupyter Kernel. It provides example notebooks for various tasks like bio-image analysis, model selection, and bug fixing. Installation is recommended via conda/mamba environment. Custom endpoints like blablador and ollama can be used. Google Cloud AI API integration is also supported. The tool is extensible for Python libraries to enhance Bob's functionality.
AI-on-the-edge-device-docs
This repository contains documentation for the AI on the Edge Device Project. Users can edit Markdown documents in the 'docs' folder, create Pull Requests to merge changes, and Github Actions will regenerate the documentation on the 'gh-pages' branch. The documentation includes parameter documentation, template generation for new parameters, formatting options like boxes using the admonition extension, and local testing instructions using MkDocs.
gpt-subtrans
GPT-Subtrans is an open-source subtitle translator that utilizes large language models (LLMs) as translation services. It supports translation between any language pairs that the language model supports. Note that GPT-Subtrans requires an active internet connection, as subtitles are sent to the provider's servers for translation, and their privacy policy applies.
LARS
LARS is an application that enables users to run Large Language Models (LLMs) locally on their devices, upload their own documents, and engage in conversations where the LLM grounds its responses with the uploaded content. The application focuses on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to increase accuracy and reduce AI-generated inaccuracies. LARS provides advanced citations, supports various file formats, allows follow-up questions, provides full chat history, and offers customization options for LLM settings. Users can force enable or disable RAG, change system prompts, and tweak advanced LLM settings. The application also supports GPU-accelerated inferencing, multiple embedding models, and text extraction methods. LARS is open-source and aims to be the ultimate RAG-centric LLM application.
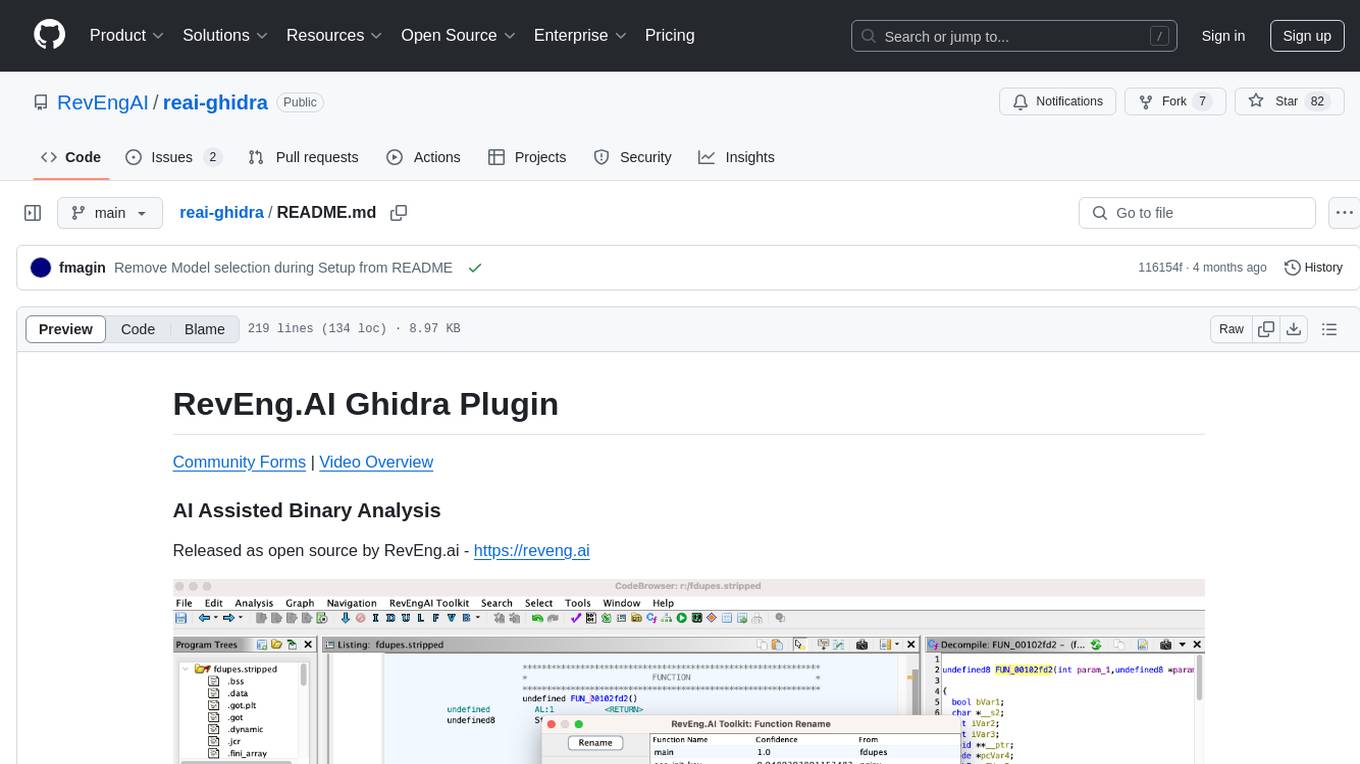
reai-ghidra
The RevEng.AI Ghidra Plugin by RevEng.ai allows users to interact with their API within Ghidra for Binary Code Similarity analysis to aid in Reverse Engineering stripped binaries. Users can upload binaries, rename functions above a confidence threshold, and view similar functions for a selected function.
warc-gpt
WARC-GPT is an experimental retrieval augmented generation pipeline for web archive collections. It allows users to interact with WARC files, extract text, generate text embeddings, visualize embeddings, and interact with a web UI and API. The tool is highly customizable, supporting various LLMs, providers, and embedding models. Users can configure the application using environment variables, ingest WARC files, start the server, and interact with the web UI and API to search for content and generate text completions. WARC-GPT is designed for exploration and experimentation in exploring web archives using AI.
docker-h5ai
docker-h5ai is a Docker image that provides a modern file indexer for HTTP web servers, enhancing file browsing with different views, a breadcrumb, and a tree overview. It is built on Alpine Linux with Nginx and PHP, supporting h5ai 0.30.0 and enabling PHP 8 JIT compiler. The image supports multiple architectures and can be used to host shared files with customizable configurations. Users can set up authentication using htpasswd and run the image as a real-time service. It is recommended to use HTTPS for data encryption when deploying the service.
agentok
Agentok Studio is a visual tool built for AutoGen, a cutting-edge agent framework from Microsoft and various contributors. It offers intuitive visual tools to simplify the construction and management of complex agent-based workflows. Users can create workflows visually as graphs, chat with agents, and share flow templates. The tool is designed to streamline the development process for creators and developers working on next-generation Multi-Agent Applications.
For similar tasks

latex2ai
LaTeX2AI is a plugin for Adobe Illustrator that allows users to use editable text labels typeset in LaTeX inside an Illustrator document. It provides a seamless integration of LaTeX functionality within the Illustrator environment, enabling users to create and edit LaTeX labels, manage item scaling behavior, set global options, and save documents as PDF with included LaTeX labels. The tool simplifies the process of including LaTeX-generated content in Illustrator designs, ensuring accurate scaling and alignment with other elements in the document.
For similar jobs
learnhouse
LearnHouse is an open-source platform that allows anyone to easily provide world-class educational content. It supports various content types, including dynamic pages, videos, and documents. The platform is still in early development and should not be used in production environments. However, it offers several features, such as dynamic Notion-like pages, ease of use, multi-organization support, support for uploading videos and documents, course collections, user management, quizzes, course progress tracking, and an AI-powered assistant for teachers and students. LearnHouse is built using various open-source projects, including Next.js, TailwindCSS, Radix UI, Tiptap, FastAPI, YJS, PostgreSQL, LangChain, and React.
languagemodels
Language Models is a Python package that provides building blocks to explore large language models with as little as 512MB of RAM. It simplifies the usage of large language models from Python, ensuring all inference is performed locally to keep data private. The package includes features such as text completions, chat capabilities, code completions, external text retrieval, semantic search, and more. It outperforms Hugging Face transformers for CPU inference and offers sensible default models with varying parameters based on memory constraints. The package is suitable for learners and educators exploring the intersection of large language models with modern software development.
curriculum
The 'curriculum' repository is an open-source content repository by Enki, providing a community-driven curriculum for education. It follows a contributor covenant code of conduct to ensure a safe and engaging learning environment. The content is licensed under Creative Commons, allowing free use for non-commercial purposes with attribution to Enki and the author.
obsidian-arcana
Arcana is a plugin for Obsidian that offers a collection of AI-powered tools inspired by famous historical figures to enhance creativity and productivity. It includes tools for conversation, text-to-speech transcription, speech-to-text replies, metadata markup, text generation, file moving, flashcard generation, auto tagging, and note naming. Users can interact with these tools using the command palette and sidebar views, with an OpenAI API key required for usage. The plugin aims to assist users in various note-taking and knowledge management tasks within the Obsidian vault environment.
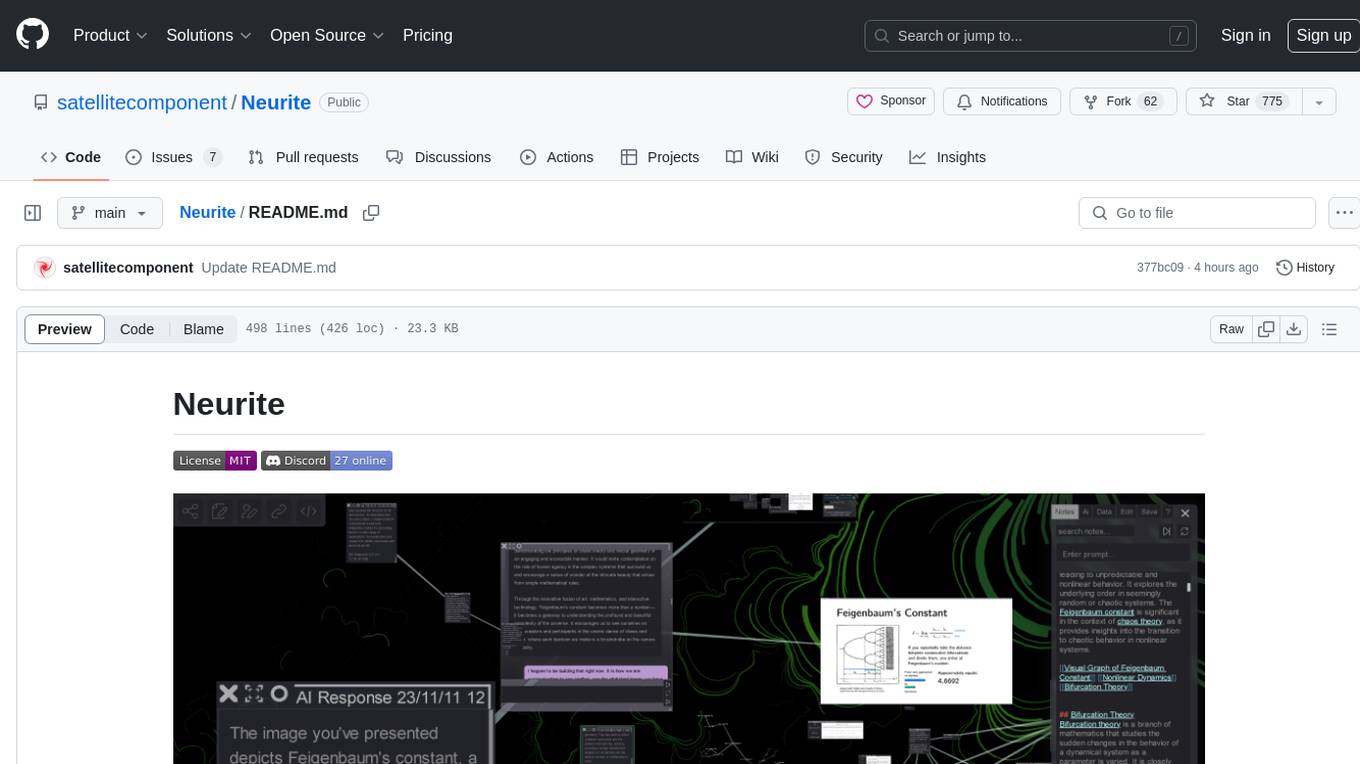
Neurite
Neurite is an innovative project that combines chaos theory and graph theory to create a digital interface that explores hidden patterns and connections for creative thinking. It offers a unique workspace blending fractals with mind mapping techniques, allowing users to navigate the Mandelbrot set in real-time. Nodes in Neurite represent various content types like text, images, videos, code, and AI agents, enabling users to create personalized microcosms of thoughts and inspirations. The tool supports synchronized knowledge management through bi-directional synchronization between mind-mapping and text-based hyperlinking. Neurite also features FractalGPT for modular conversation with AI, local AI capabilities for multi-agent chat networks, and a Neural API for executing code and sequencing animations. The project is actively developed with plans for deeper fractal zoom, advanced control over node placement, and experimental features.
commonplace-bot
Commonplace Bot is a modern representation of the commonplace book, leveraging modern technological advancements in computation, data storage, machine learning, and networking. It aims to capture, engage, and share knowledge by providing a platform for users to collect ideas, quotes, and information, organize them efficiently, engage with the data through various strategies and triggers, and transform the data into new mediums for sharing. The tool utilizes embeddings and cached transformations for efficient data storage and retrieval, flips traditional engagement rules by engaging with the user, and enables users to alchemize raw data into new forms like art prompts. Commonplace Bot offers a unique approach to knowledge management and creative expression.
AI-Prompt-Genius
AI Prompt Genius is a Chrome extension that allows you to curate a custom library of AI prompts. It is built using React web app and Tailwind CSS with DaisyUI components. The extension enables users to create and manage AI prompts for various purposes. It provides a user-friendly interface for organizing and accessing AI prompts efficiently. AI Prompt Genius is designed to enhance productivity and creativity by offering a personalized collection of prompts tailored to individual needs. Users can easily install the extension from the Chrome Web Store and start using it to generate AI prompts for different tasks.
Advanced-GPTs
Nerority's Advanced GPT Suite is a collection of 33 GPTs that can be controlled with natural language prompts. The suite includes tools for various tasks such as strategic consulting, business analysis, career profile building, content creation, educational purposes, image-based tasks, knowledge engineering, marketing, persona creation, programming, prompt engineering, role-playing, simulations, and task management. Users can access links, usage instructions, and guides for each GPT on their respective pages. The suite is designed for public demonstration and usage, offering features like meta-sequence optimization, AI priming, prompt classification, and optimization. It also provides tools for generating articles, analyzing contracts, visualizing data, distilling knowledge, creating educational content, exploring topics, generating marketing copy, simulating scenarios, managing tasks, and more.




