
model-catalog
A collection of standardized JSON descriptors for Large Language Model (LLM) files.
Stars: 779
model-catalog is a repository containing standardized JSON descriptors for Large Language Model (LLM) model files. Each model is described in a JSON file with details about the model, authors, additional resources, available model files, and providers. The format captures factors like model size, architecture, file format, and quantization format. A Github action merges individual JSON files from the `models/` directory into a `catalog.json` file, which is validated using a JSON schema. Contributors can help by adding new model JSON files following the contribution process.
README:
A collection of standardized JSON descriptors for Large Language Model (LLM) model files.
A single JSON file describes a model, its authors, additional resources (such as an academic paper) as well as available model files and their providers.
Version 0.0.1 of this format attempts to capture an informative set of factors including:
- model size (e.g.
7B,13B,30B, etc.) - model architecture (such as
Llama,MPT,Pythia, etc.) - model file format (e.g.
ggml) as well as quantization format (e.g.q4_0,q4_K_M, etc.)
See examples: guanaco-7b.json, samantha-1.1-llama-7b.json, Nous-Hermes-13b.json.
A Github action picks up .json files from the models/ directory and merges them into one catalog.json file.
The contents of each JSON file is validated by another Github action using a JSON schema.
You're invited to help catalog models and improve upon this description format.
- Fork this repo and create a new development branch.
- Create a new model JSON file and place it the
models/directory. - Validate your file against the expected JSON schema using the
validate.pytool or by runningcreateCatalog.py. - Open a PR with your change.
- Ensure all Github actions complete successfully.
Note: Do not modify catalog.json manually.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for model-catalog
Similar Open Source Tools

model-catalog
model-catalog is a repository containing standardized JSON descriptors for Large Language Model (LLM) model files. Each model is described in a JSON file with details about the model, authors, additional resources, available model files, and providers. The format captures factors like model size, architecture, file format, and quantization format. A Github action merges individual JSON files from the `models/` directory into a `catalog.json` file, which is validated using a JSON schema. Contributors can help by adding new model JSON files following the contribution process.
VulBench
This repository contains materials for the paper 'How Far Have We Gone in Vulnerability Detection Using Large Language Model'. It provides a tool for evaluating vulnerability detection models using datasets such as d2a, ctf, magma, big-vul, and devign. Users can query the model 'Llama-2-7b-chat-hf' and store results in a SQLite database for analysis. The tool supports binary and multiple classification tasks with concurrency settings. Additionally, users can evaluate the results and generate a CSV file with metrics for each dataset and prompt type.
turnkeyml
TurnkeyML is a tools framework that integrates models, toolchains, and hardware backends to simplify the evaluation and actuation of deep learning models. It supports use cases like exporting ONNX files, performance validation, functional coverage measurement, stress testing, and model insights analysis. The framework consists of analysis, build, runtime, reporting tools, and a models corpus, seamlessly integrated to provide comprehensive functionality with simple commands. Extensible through plugins, it offers support for various export and optimization tools and AI runtimes. The project is actively seeking collaborators and is licensed under Apache 2.0.
llm-ollama
LLM-ollama is a plugin that provides access to models running on an Ollama server. It allows users to query the Ollama server for a list of models, register them with LLM, and use them for prompting, chatting, and embedding. The plugin supports image attachments, embeddings, JSON schemas, async models, model aliases, and model options. Users can interact with Ollama models through the plugin in a seamless and efficient manner.
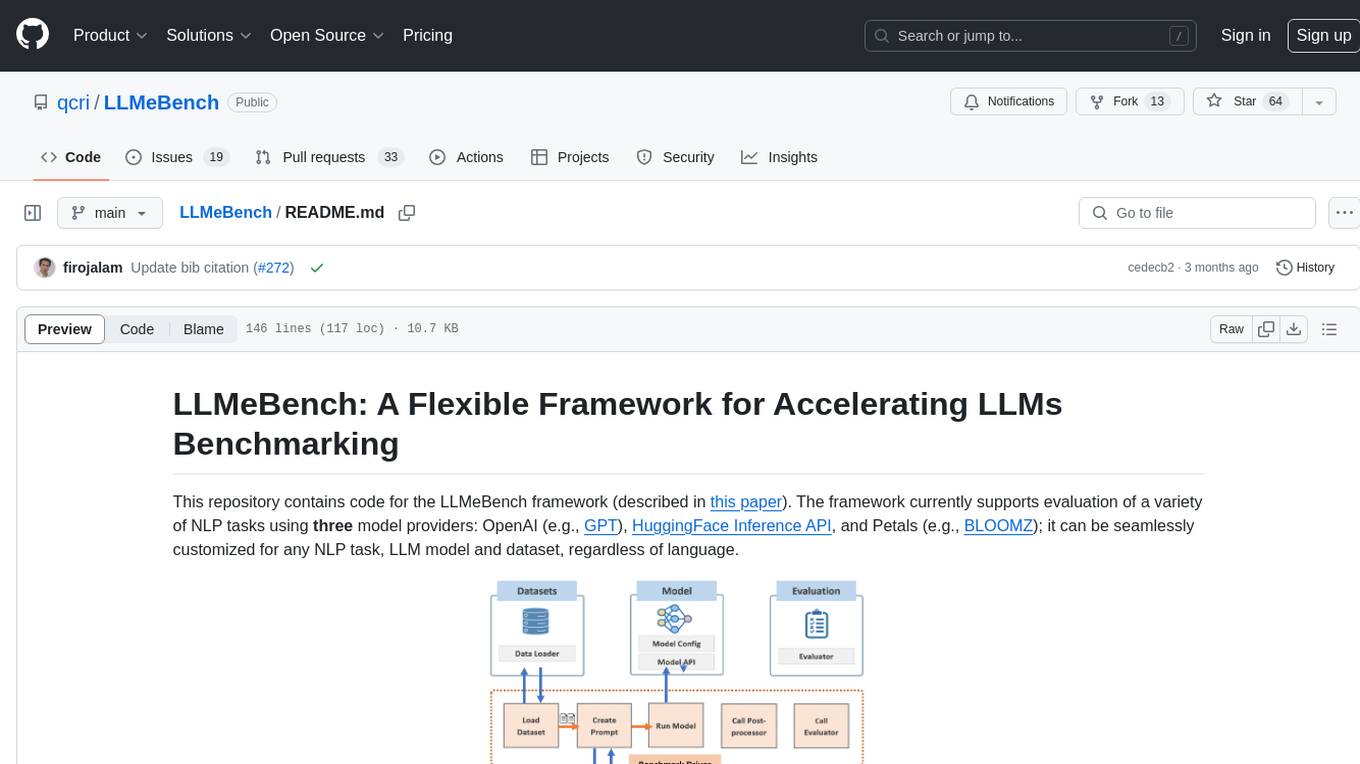
LLMeBench
LLMeBench is a flexible framework designed for accelerating benchmarking of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP). It supports evaluation of various NLP tasks using model providers like OpenAI, HuggingFace Inference API, and Petals. The framework is customizable for different NLP tasks, LLM models, and datasets across multiple languages. It features extensive caching capabilities, supports zero- and few-shot learning paradigms, and allows on-the-fly dataset download and caching. LLMeBench is open-source and continuously expanding to support new models accessible through APIs.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
debug-gym
debug-gym is a text-based interactive debugging framework designed for debugging Python programs. It provides an environment where agents can interact with code repositories, use various tools like pdb and grep to investigate and fix bugs, and propose code patches. The framework supports different LLM backends such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Anthropic. Users can customize tools, manage environment states, and run agents to debug code effectively. debug-gym is modular, extensible, and suitable for interactive debugging tasks in a text-based environment.
nextjs-openai-doc-search
This starter project is designed to process `.mdx` files in the `pages` directory to use as custom context within OpenAI Text Completion prompts. It involves building a custom ChatGPT style doc search powered by Next.js, OpenAI, and Supabase. The project includes steps for pre-processing knowledge base, storing embeddings in Postgres, performing vector similarity search, and injecting content into OpenAI GPT-3 text completion prompt.
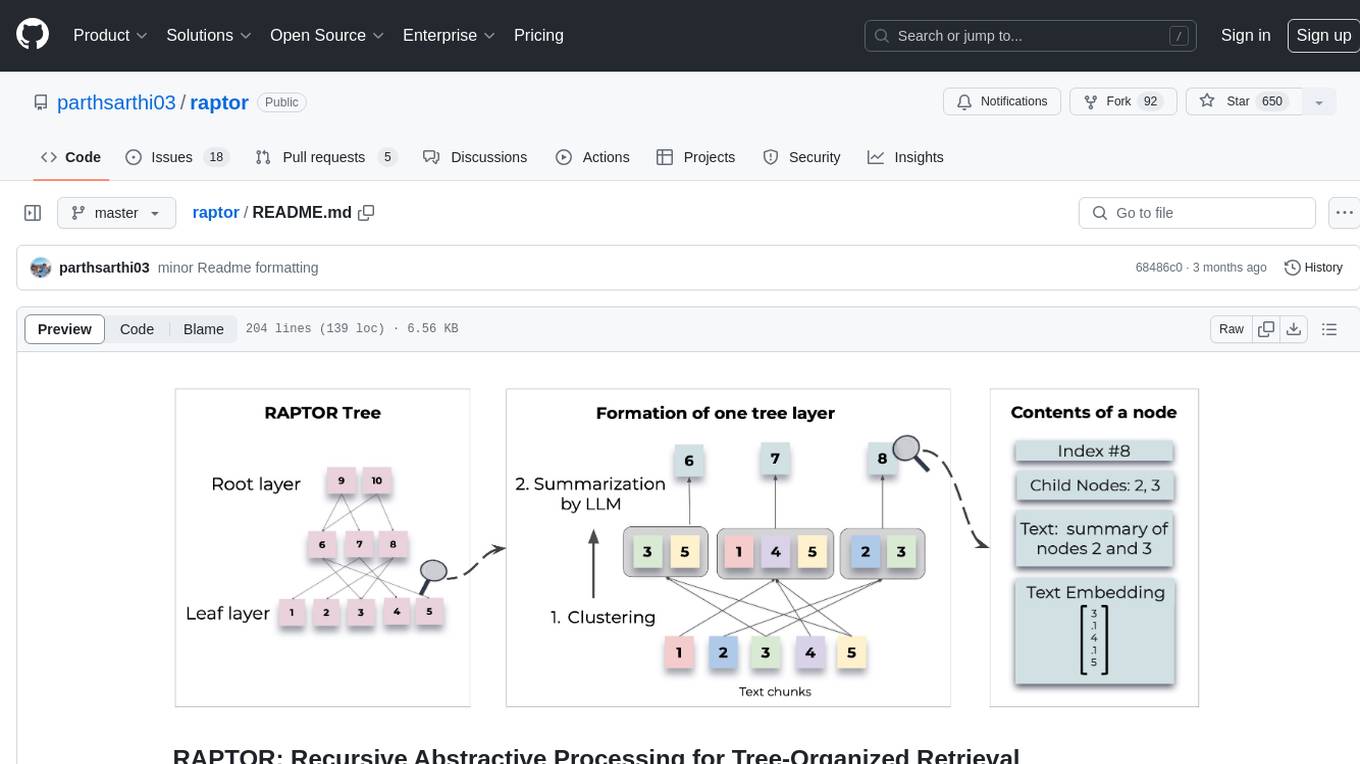
raptor
RAPTOR introduces a novel approach to retrieval-augmented language models by constructing a recursive tree structure from documents. This allows for more efficient and context-aware information retrieval across large texts, addressing common limitations in traditional language models. Users can add documents to the tree, answer questions based on indexed documents, save and load the tree, and extend RAPTOR with custom summarization, question-answering, and embedding models. The tool is designed to be flexible and customizable for various NLP tasks.
monitors4codegen
This repository hosts the official code and data artifact for the paper 'Monitor-Guided Decoding of Code LMs with Static Analysis of Repository Context'. It introduces Monitor-Guided Decoding (MGD) for code generation using Language Models, where a monitor uses static analysis to guide the decoding. The repository contains datasets, evaluation scripts, inference results, a language server client 'multilspy' for static analyses, and implementation of various monitors monitoring for different properties in 3 programming languages. The monitors guide Language Models to adhere to properties like valid identifier dereferences, correct number of arguments to method calls, typestate validity of method call sequences, and more.
py-vectara-agentic
The `vectara-agentic` Python library is designed for developing powerful AI assistants using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It supports various agent types, includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal, and enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents. The library provides tools for summarizing text, rephrasing text, legal tasks like summarizing legal text and critiquing as a judge, financial tasks like analyzing balance sheets and income statements, and database tools for inspecting and querying databases. It also supports observability via LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix integration.
verifiers
Verifiers is a library of modular components for creating RL environments and training LLM agents. It includes an async GRPO implementation built around the `transformers` Trainer, is supported by `prime-rl` for large-scale FSDP training, and can easily be integrated into any RL framework which exposes an OpenAI-compatible inference client. The library provides tools for creating and evaluating RL environments, training LLM agents, and leveraging OpenAI-compatible models for various tasks. Verifiers aims to be a reliable toolkit for building on top of, minimizing fork proliferation in the RL infrastructure ecosystem.
vectorflow
VectorFlow is an open source, high throughput, fault tolerant vector embedding pipeline. It provides a simple API endpoint for ingesting large volumes of raw data, processing, and storing or returning the vectors quickly and reliably. The tool supports text-based files like TXT, PDF, HTML, and DOCX, and can be run locally with Kubernetes in production. VectorFlow offers functionalities like embedding documents, running chunking schemas, custom chunking, and integrating with vector databases like Pinecone, Qdrant, and Weaviate. It enforces a standardized schema for uploading data to a vector store and supports features like raw embeddings webhook, chunk validation webhook, S3 endpoint, and telemetry. The tool can be used with the Python client and provides detailed instructions for running and testing the functionalities.

blinkid-android
The BlinkID Android SDK is a comprehensive solution for implementing secure document scanning and extraction. It offers powerful capabilities for extracting data from a wide range of identification documents. The SDK provides features for integrating document scanning into Android apps, including camera requirements, SDK resource pre-bundling, customizing the UX, changing default strings and localization, troubleshooting integration difficulties, and using the SDK through various methods. It also offers options for completely custom UX with low-level API integration. The SDK size is optimized for different processor architectures, and API documentation is available for reference. For any questions or support, users can contact the Microblink team at help.microblink.com.
ai2-scholarqa-lib
Ai2 Scholar QA is a system for answering scientific queries and literature review by gathering evidence from multiple documents across a corpus and synthesizing an organized report with evidence for each claim. It consists of a retrieval component and a three-step generator pipeline. The retrieval component fetches relevant evidence passages using the Semantic Scholar public API and reranks them. The generator pipeline includes quote extraction, planning and clustering, and summary generation. The system is powered by the ScholarQA class, which includes components like PaperFinder and MultiStepQAPipeline. It requires environment variables for Semantic Scholar API and LLMs, and can be run as local docker containers or embedded into another application as a Python package.
codespin
CodeSpin.AI is a set of open-source code generation tools that leverage large language models (LLMs) to automate coding tasks. With CodeSpin, you can generate code in various programming languages, including Python, JavaScript, Java, and C++, by providing natural language prompts. CodeSpin offers a range of features to enhance code generation, such as custom templates, inline prompting, and the ability to use ChatGPT as an alternative to API keys. Additionally, CodeSpin provides options for regenerating code, executing code in prompt files, and piping data into the LLM for processing. By utilizing CodeSpin, developers can save time and effort in coding tasks, improve code quality, and explore new possibilities in code generation.
For similar tasks

model-catalog
model-catalog is a repository containing standardized JSON descriptors for Large Language Model (LLM) model files. Each model is described in a JSON file with details about the model, authors, additional resources, available model files, and providers. The format captures factors like model size, architecture, file format, and quantization format. A Github action merges individual JSON files from the `models/` directory into a `catalog.json` file, which is validated using a JSON schema. Contributors can help by adding new model JSON files following the contribution process.
NewEraAI-Papers
The NewEraAI-Papers repository provides links to collections of influential and interesting research papers from top AI conferences, along with open-source code to promote reproducibility and provide detailed implementation insights beyond the scope of the article. Users can stay up to date with the latest advances in AI research by exploring this repository. Contributions to improve the completeness of the list are welcomed, and users can create pull requests, open issues, or contact the repository owner via email to enhance the repository further.
Awesome_Mamba
Awesome Mamba is a curated collection of groundbreaking research papers and articles on Mamba Architecture, a pioneering framework in deep learning known for its selective state spaces and efficiency in processing complex data structures. The repository offers a comprehensive exploration of Mamba architecture through categorized research papers covering various domains like visual recognition, speech processing, remote sensing, video processing, activity recognition, image enhancement, medical imaging, reinforcement learning, natural language processing, 3D recognition, multi-modal understanding, time series analysis, graph neural networks, point cloud analysis, and tabular data handling.
OnAIR
The On-board Artificial Intelligence Research (OnAIR) Platform is a framework that enables AI algorithms written in Python to interact with NASA's cFS. It is intended to explore research concepts in autonomous operations in a simulated environment. The platform provides tools for generating environments, handling telemetry data through Redis, running unit tests, and contributing to the repository. Users can set up a conda environment, configure telemetry and Redis examples, run simulations, and conduct unit tests to ensure the functionality of their AI algorithms. The platform also includes guidelines for licensing, copyright, and contributions to the repository.
22AIE111-Object-Oriented-Programming-in-Java-S2-2025
The 'Object Oriented Programming in Java' repository provides notes and code examples organized into units to help users understand and practice Java concepts step-by-step. It includes theoretical notes, practical Java examples, setup files for Visual Studio Code and IntelliJ IDEA, instructions on setting up Java, running Java programs from the command line, and loading projects in VS Code or IntelliJ IDEA. Users can contribute by opening issues or submitting pull requests. The repository is intended for educational purposes, allowing forking and modification for personal study or classroom use.
support-genAI-book
This repository serves as a support page for the book 'Deciphering Generative AI from Original Papers' released by Gijutsu-Hyohron Co., Ltd. It includes answers to exercises and errata from the book. The exercises are provided in chapter-specific .md files in the 'exercises' directory. Please note that there may be some rendering issues with GitHub's math rendering, and the answers are just examples for reference. Contributions to this repository can be made by following the guidelines in CONTRIBUTING.md.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
