
nanolang
A tiny experimental language designed to be targeted by coding LLMs
Stars: 526
NanoLang is a minimal, LLM-friendly programming language that transpiles to C for native performance. It features mandatory testing, unambiguous syntax, automatic memory management, LLM-powered autonomous optimization, dual notation for operators, static typing, C interop, and native performance. The language supports variables, functions with mandatory tests, control flow, structs, enums, generic types, and provides a clean, modern syntax optimized for both human readability and AI code generation.
README:
A minimal, LLM-friendly programming language with mandatory testing and unambiguous syntax.
NanoLang transpiles to C for native performance while providing a clean, modern syntax optimized for both human readability and AI code generation.
→ User Guide ← - Start here! Comprehensive tutorial with executable examples
Additional Resources:
- Getting Started - 15-minute quick start
- Quick Reference - Syntax cheat sheet
- Language Specification - Complete language reference
- All Documentation - Full documentation index
# Clone and build
git clone https://github.com/jordanhubbard/nanolang.git
cd nanolang
make build
# Create hello.nano
cat > hello.nano << 'EOF'
fn greet(name: string) -> string {
return (+ "Hello, " name)
}
shadow greet {
assert (== (greet "World") "Hello, World")
}
fn main() -> int {
(println (greet "World"))
return 0
}
shadow main { assert true }
EOF
# Compile and run
./bin/nanoc hello.nano -o hello
./helloBSD users: Use gmake instead of make.
- Automatic Memory Management (ARC) ⭐ - Zero-overhead reference counting, no manual free() calls (v2.3.0)
- LLM-Powered Autonomous Optimization ⭐ - Continuous profiling and automatic optimization loop (v2.3.0)
-
Dual Notation - Both prefix
(+ a b)and infixa + boperators supported -
Mandatory Testing - Every function requires a
shadowtest block - Static Typing with type inference
- C Interop - Easy FFI via modules
- Native Performance - Transpiles to optimized C
# Variables (immutable by default)
let x: int = 42
let mut counter: int = 0
# Functions with mandatory tests
fn add(a: int, b: int) -> int {
return (+ a b)
}
shadow add {
assert (== (add 2 3) 5)
}
# Control flow
if (> x 0) {
(println "positive")
}
# Structs and enums
struct Point { x: int, y: int }
enum Status { Pending = 0, Active = 1 }
# Generic types
let numbers: List<int> = (List_int_new)
(List_int_push numbers 42)
make build # Build compiler (bin/nanoc)
make test # Run full test suite
make test-quick # Quick language tests only
make examples # Build all examplesWeb Playground (recommended for learning):
./bin/nanoc examples/playground/playground_server.nano -o bin/playground
./bin/playground # Open http://localhost:8080Examples Browser (requires SDL2):
cd examples && make launcherIndividual examples:
./bin/nanoc examples/language/nl_fibonacci.nano -o fib && ./fibSee examples/README.md for the complete catalog including games (Snake, Asteroids, Checkers) and graphics demos.
Fully supported:
- Ubuntu 22.04+ (x86_64, ARM64)
- macOS 14+ (Apple Silicon)
- FreeBSD
Windows: Use WSL2 with Ubuntu.
NanoLang is designed for AI code generation:
- MEMORY.md - LLM training reference with patterns and idioms
- spec.json - Formal language specification
See CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines.
Apache License 2.0 - See LICENSE for details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for nanolang
Similar Open Source Tools

nanolang
NanoLang is a minimal, LLM-friendly programming language that transpiles to C for native performance. It features mandatory testing, unambiguous syntax, automatic memory management, LLM-powered autonomous optimization, dual notation for operators, static typing, C interop, and native performance. The language supports variables, functions with mandatory tests, control flow, structs, enums, generic types, and provides a clean, modern syntax optimized for both human readability and AI code generation.

oh-my-pi
oh-my-pi is an AI coding agent for the terminal, providing tools for interactive coding, AI-powered git commits, Python code execution, LSP integration, time-traveling streamed rules, interactive code review, task management, interactive questioning, custom TypeScript slash commands, universal config discovery, MCP & plugin system, web search & fetch, SSH tool, Cursor provider integration, multi-credential support, image generation, TUI overhaul, edit fuzzy matching, and more. It offers a modern terminal interface with smart session management, supports multiple AI providers, and includes various tools for coding, task management, code review, and interactive questioning.
leetcode-py
A Python package to generate professional LeetCode practice environments. Features automated problem generation from LeetCode URLs, beautiful data structure visualizations (TreeNode, ListNode, GraphNode), and comprehensive testing with 10+ test cases per problem. Built with professional development practices including CI/CD, type hints, and quality gates. The tool provides a modern Python development environment with production-grade features such as linting, test coverage, logging, and CI/CD pipeline. It also offers enhanced data structure visualization for debugging complex structures, flexible notebook support, and a powerful CLI for generating problems anywhere.
lighteval
LightEval is a lightweight LLM evaluation suite that Hugging Face has been using internally with the recently released LLM data processing library datatrove and LLM training library nanotron. We're releasing it with the community in the spirit of building in the open. Note that it is still very much early so don't expect 100% stability ^^' In case of problems or question, feel free to open an issue!
alphora
Alphora is a full-stack framework for building production AI agents, providing agent orchestration, prompt engineering, tool execution, memory management, streaming, and deployment with an async-first, OpenAI-compatible design. It offers features like agent derivation, reasoning-action loop, async streaming, visual debugger, OpenAI compatibility, multimodal support, tool system with zero-config tools and type safety, prompt engine with dynamic prompts, memory and storage management, sandbox for secure execution, deployment as API, and more. Alphora allows users to build sophisticated AI agents easily and efficiently.
polyfire-js
Polyfire is an all-in-one managed backend for AI apps that allows users to build AI apps directly from the frontend, eliminating the need for a separate backend. It simplifies the process by providing most backend services in just a few lines of code. With Polyfire, users can easily create chatbots, transcribe audio files to text, generate simple text, create a long-term memory, and generate images with Dall-E. The tool also offers starter guides and tutorials to help users get started quickly and efficiently.
rkllama
RKLLama is a server and client tool designed for running and interacting with LLM models optimized for Rockchip RK3588(S) and RK3576 platforms. It allows models to run on the NPU, with features such as running models on NPU, partial Ollama API compatibility, pulling models from Huggingface, API REST with documentation, dynamic loading/unloading of models, inference requests with streaming modes, simplified model naming, CPU model auto-detection, and optional debug mode. The tool supports Python 3.8 to 3.12 and has been tested on Orange Pi 5 Pro and Orange Pi 5 Plus with specific OS versions.
executorch
ExecuTorch is an end-to-end solution for enabling on-device inference capabilities across mobile and edge devices including wearables, embedded devices and microcontrollers. It is part of the PyTorch Edge ecosystem and enables efficient deployment of PyTorch models to edge devices. Key value propositions of ExecuTorch are: * **Portability:** Compatibility with a wide variety of computing platforms, from high-end mobile phones to highly constrained embedded systems and microcontrollers. * **Productivity:** Enabling developers to use the same toolchains and SDK from PyTorch model authoring and conversion, to debugging and deployment to a wide variety of platforms. * **Performance:** Providing end users with a seamless and high-performance experience due to a lightweight runtime and utilizing full hardware capabilities such as CPUs, NPUs, and DSPs.
BrowserAI
BrowserAI is a tool that allows users to run large language models (LLMs) directly in the browser, providing a simple, fast, and open-source solution. It prioritizes privacy by processing data locally, is cost-effective with no server costs, works offline after initial download, and offers WebGPU acceleration for high performance. It is developer-friendly with a simple API, supports multiple engines, and comes with pre-configured models for easy use. Ideal for web developers, companies needing privacy-conscious AI solutions, researchers experimenting with browser-based AI, and hobbyists exploring AI without infrastructure overhead.
Llamatik
Llamatik is a Kotlin Multiplatform library that enables running large language models locally using llama.cpp with optional remote inference through a unified Kotlin API. It is designed for privacy-first, offline-capable, and cross-platform AI applications, allowing on-device and private inference, Kotlin Multiplatform support, LLM capabilities like text generation and embeddings, hybrid and remote inference options, and seamless switching between local and remote modes. The library provides a shared Kotlin API across Android, iOS, and Desktop platforms, with native performance via Kotlin/Native + C++ and a lightweight, dependency-free runtime.
agentfield
AgentField is an open-source control plane designed for autonomous AI agents, providing infrastructure for agents to make decisions beyond chatbots. It offers features like scaling infrastructure, routing & discovery, async execution, durable state, observability, trust infrastructure with cryptographic identity, verifiable credentials, and policy enforcement. Users can write agents in Python, Go, TypeScript, or interact via REST APIs. The tool enables the creation of AI backends that reason autonomously within defined boundaries, offering predictability and flexibility. AgentField aims to bridge the gap between AI frameworks and production-ready infrastructure for AI agents.
human
AI-powered 3D Face Detection & Rotation Tracking, Face Description & Recognition, Body Pose Tracking, 3D Hand & Finger Tracking, Iris Analysis, Age & Gender & Emotion Prediction, Gaze Tracking, Gesture Recognition, Body Segmentation

TrustEval-toolkit
TrustEval-toolkit is a dynamic and comprehensive framework for evaluating the trustworthiness of Generative Foundation Models (GenFMs) across dimensions such as safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and more. It offers features like dynamic dataset generation, multi-model compatibility, customizable metrics, metadata-driven pipelines, comprehensive evaluation dimensions, optimized inference, and detailed reports.
trpc-agent-go
A powerful Go framework for building intelligent agent systems with large language models (LLMs), hierarchical planners, memory, telemetry, and a rich tool ecosystem. tRPC-Agent-Go enables the creation of autonomous or semi-autonomous agents that reason, call tools, collaborate with sub-agents, and maintain long-term state. The framework provides detailed documentation, examples, and tools for accelerating the development of AI applications.
kiss_ai
KISS AI is a lightweight and powerful multi-agent evolutionary framework that simplifies building AI agents. It uses native function calling for efficiency and accuracy, making building AI agents as straightforward as possible. The framework includes features like multi-agent orchestration, agent evolution and optimization, relentless coding agent for long-running tasks, output formatting, trajectory saving and visualization, GEPA for prompt optimization, KISSEvolve for algorithm discovery, self-evolving multi-agent, Docker integration, multiprocessing support, and support for various models from OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Together AI, and OpenRouter.
ChordMiniApp
ChordMini is an advanced music analysis platform with AI-powered chord recognition, beat detection, and synchronized lyrics. It features a clean and intuitive interface for YouTube search, chord progression visualization, interactive guitar diagrams with accurate fingering patterns, lead sheet with AI assistant for synchronized lyrics transcription, and various add-on features like Roman Numeral Analysis, Key Modulation Signals, Simplified Chord Notation, and Enhanced Chord Correction. The tool requires Node.js, Python 3.9+, and a Firebase account for setup. It offers a hybrid backend architecture for local development and production deployments, with features like beat detection, chord recognition, lyrics processing, rate limiting, and audio processing supporting MP3, WAV, and FLAC formats. ChordMini provides a comprehensive music analysis workflow from user input to visualization, including dual input support, environment-aware processing, intelligent caching, advanced ML pipeline, and rich visualization options.
For similar tasks

nanolang
NanoLang is a minimal, LLM-friendly programming language that transpiles to C for native performance. It features mandatory testing, unambiguous syntax, automatic memory management, LLM-powered autonomous optimization, dual notation for operators, static typing, C interop, and native performance. The language supports variables, functions with mandatory tests, control flow, structs, enums, generic types, and provides a clean, modern syntax optimized for both human readability and AI code generation.
Awesome-CS-Books
Awesome CS Books is a curated list of books on computer science and technology. The books are organized by topic, including programming languages, software engineering, computer networks, operating systems, databases, data structures and algorithms, big data, architecture, and interviews. The books are available in PDF format and can be downloaded for free. The repository also includes links to free online courses and other resources.
Awesome-Books-Notes
Awesome CS Books is a repository that archives excellent books related to computer science and technology, named in the format of {year}-{author}-{title}-{version}. It includes reading notes for each book, with PDF links provided at the beginning of the notes. The repository focuses on IT CS-related books, valuable open courses, and aims to provide a systematic way of learning to alleviate fragmented skills and one-sidedness. It respects the original authors by linking to official/copyright websites and emphasizes non-commercial use of the documents.

TutoriaLLM
TutoriaLLM is a self-hosted programming learning platform for K-12 Education that can be used on the web. It is designed for those who create educational content and those who learn from it. The platform provides a community for English and Japanese speakers, along with documentation and opportunities for contribution. Users can access a demo video showcasing TutoriaLLM in action.
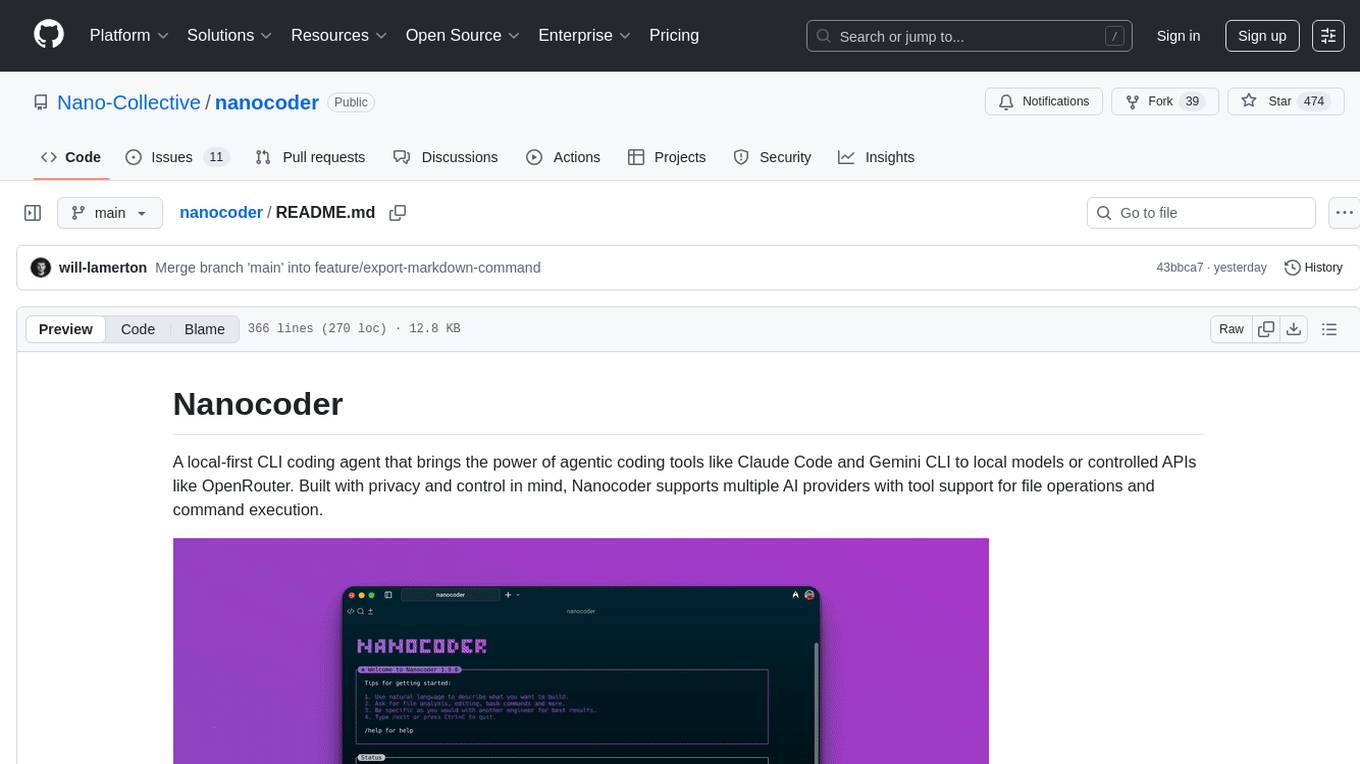
nanocoder
Nanocoder is a versatile code editor designed for beginners and experienced programmers alike. It provides a user-friendly interface with features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, and error checking. With Nanocoder, you can easily write and debug code in various programming languages, making it an ideal tool for learning, practicing, and developing software projects. Whether you are a student, hobbyist, or professional developer, Nanocoder offers a seamless coding experience to boost your productivity and creativity.
agentfactory
The AI Agent Factory is a spec-driven blueprint for building and monetizing digital FTEs. It empowers developers, entrepreneurs, and organizations to learn, build, and monetize intelligent AI agents, creating reliable digital FTEs that can be trusted, deployed, and scaled. The tool focuses on co-learning between humans and machines, emphasizing collaboration, clear specifications, and evolving together. It covers AI-assisted, AI-driven, and AI-native development approaches, guiding users through the AI development spectrum and organizational AI maturity levels. The core philosophy revolves around treating AI as a collaborative partner, using specification-first methodology, bilingual development, learning by doing, and ensuring transparency and reproducibility. The tool is suitable for beginners, professional developers, entrepreneurs, product leaders, educators, and tech leaders.
scalene
Scalene is a high-performance CPU, GPU, and memory profiler for Python that provides detailed information and runs faster than many other profilers. It incorporates AI-powered proposed optimizations, allowing users to generate optimization suggestions by clicking on specific lines or regions of code. Scalene separates time spent in Python from native code, highlights hotspots, and identifies memory usage per line. It supports GPU profiling on NVIDIA-based systems and detects memory leaks. Users can generate reduced profiles, profile specific functions using decorators, and suspend/resume profiling for background processes. Scalene is available as a pip or conda package and works on various platforms. It offers features like profiling at the line level, memory trends, copy volume reporting, and leak detection.
sourcery
Sourcery is an automated code reviewer tool that provides instant feedback on pull requests, helping to speed up the code review process, improve code quality, and accelerate development velocity. It offers high-level feedback, line-by-line suggestions, and aims to mimic the type of code review one would expect from a colleague. Sourcery can also be used as an IDE coding assistant to understand existing code, add unit tests, optimize code, and improve code quality with instant suggestions. It is free for public repos/open source projects and offers a 14-day trial for private repos.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

