leetcode-py
Python LeetCode practice environment with automated problem generation, data structure visualizations, and comprehensive testing. Includes all Grind 75, partial Blind, Neetcode and Algomaster problems with enhanced TreeNode/ListNode helpers, CI/CD pipeline, and LLM-assisted problem creation.
Stars: 101
A Python package to generate professional LeetCode practice environments. Features automated problem generation from LeetCode URLs, beautiful data structure visualizations (TreeNode, ListNode, GraphNode), and comprehensive testing with 10+ test cases per problem. Built with professional development practices including CI/CD, type hints, and quality gates. The tool provides a modern Python development environment with production-grade features such as linting, test coverage, logging, and CI/CD pipeline. It also offers enhanced data structure visualization for debugging complex structures, flexible notebook support, and a powerful CLI for generating problems anywhere.
README:
A Python package to generate professional LeetCode practice environments. Features automated problem generation from LeetCode URLs, beautiful data structure visualizations (TreeNode, ListNode, GraphNode), and comprehensive testing with 10+ test cases per problem. Built with professional development practices including CI/CD, type hints, and quality gates.
- What's Included
- Quick Start
- Problem Structure
- Key Features
- Usage Patterns
- Development Setup
- Helper Classes
- Commands
- Architecture
- Quality Metrics
What makes this different:
- 🤖 LLM-Assisted Workflow: Generate new problems instantly with AI assistance
- 🎨 Visual Debugging: Interactive tree/graph rendering with Graphviz and anytree
- 🧪 Production Testing: Comprehensive test suites with edge cases and reproducibility verification
- 🚀 Modern Python: PEP 585/604 type hints, uv, and professional tooling
- 📊 Quality Assurance: 95%+ test coverage, security scanning, automated linting
- ⚡ Powerful CLI: Generate problems anywhere with
lcpycommand
Current Problem Sets:
- grind-75 - Essential coding interview questions from Grind 75 ✅ Complete
- grind - Extended Grind collection including all Grind 75 plus additional problems 🚧 Partial
- blind-75 - Original Blind 75 curated list ✅ Complete
- neetcode-150 - Comprehensive NeetCode 150 problem set 🚧 Partial
- algo-master-75 - Curated algorithmic mastery problems 🚧 Partial
Coverage: 130+ unique problems across all major coding interview topics and difficulty levels.
Note: Some problem sets are partially covered. We're actively working to complete all collections. Contributions welcome!
- Python 3.10+ - Python runtime
- Graphviz - Graph visualization library (install guide)
# Install the package
pip install leetcode-py-sdk
# Generate problems anywhere
lcpy gen -n 1 # Generate Two Sum
lcpy gen -t grind-75 # Generate all Grind 75 problems
lcpy gen -t neetcode-150 # Generate NeetCode 150 problems
lcpy list -t grind-75 # List Grind 75 problems
lcpy list -t blind-75 # List Blind 75 problems
# Start practicing
cd leetcode/two_sum
python -m pytest test_solution.py # Run tests
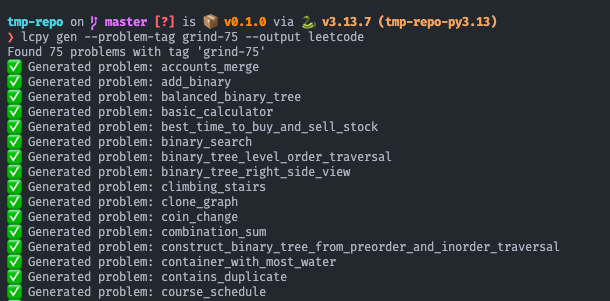
# Edit solution.py, then rerun testslcpy gen --problem-tag grind-75 --output leetcode # Generate all Grind 75 problems
lcpy gen --problem-tag neetcode-150 --output leetcode # Generate NeetCode 150 problems
lcpy gen --problem-tag blind-75 --output leetcode # Generate Blind 75 problemsBulk generation output showing "Generated problem:" messages for all 75 Grind problems
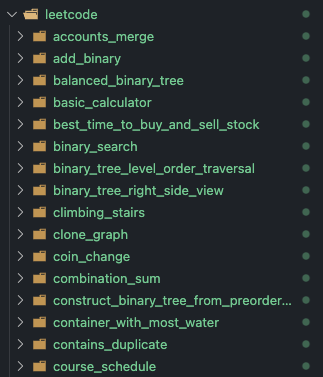
Generated folder structure showing all 75 problem directories after command execution
Each problem follows a consistent, production-ready template:
leetcode/two_sum/
├── README.md # Problem description with examples and constraints
├── solution.py # Implementation with type hints and TODO placeholder
├── test_solution.py # Comprehensive parametrized tests (10+ test cases)
├── helpers.py # Test helper functions
├── playground.py # Interactive debugging environment (converted from .ipynb)
└── __init__.py # Package marker
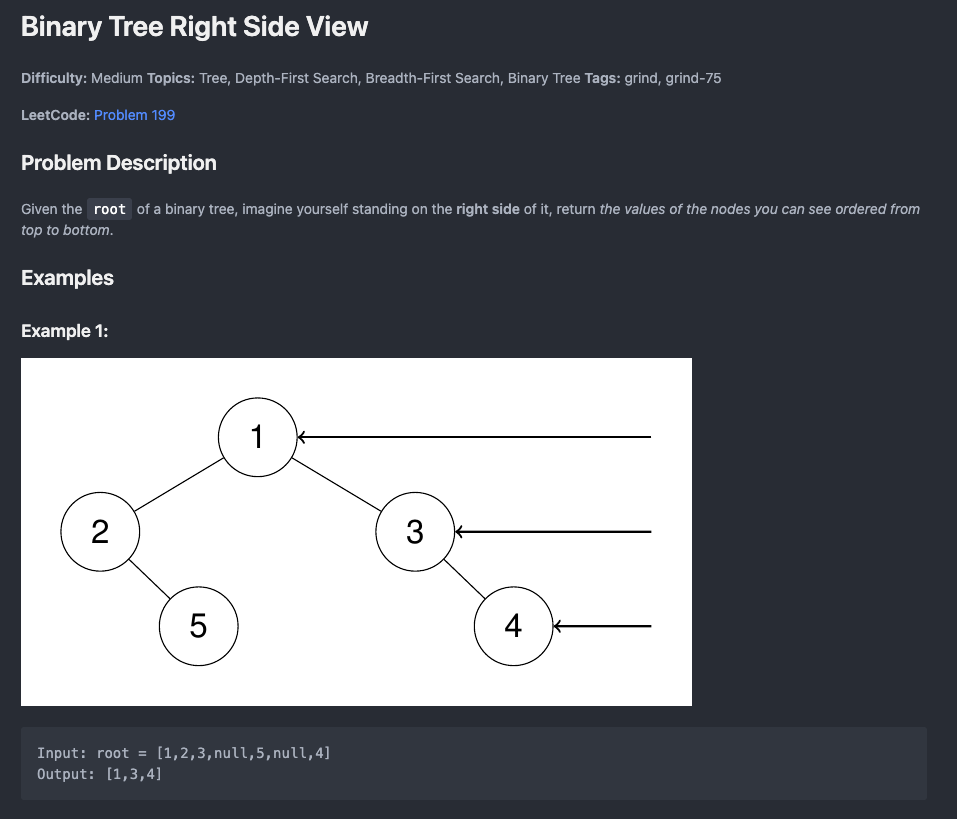
README format that mirrors LeetCode's problem description layout
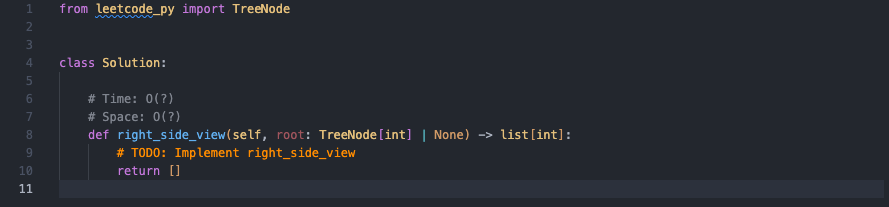
Solution boilerplate with type hints and TODO placeholder
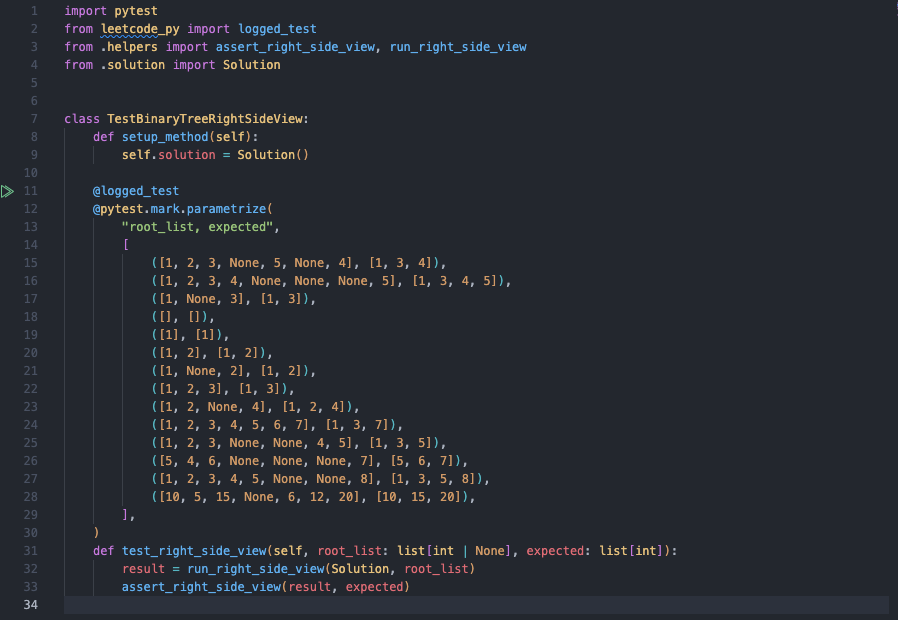
Comprehensive parametrized tests with 10+ test cases - executable and debuggable in local development environment
Beautiful colorful test output with loguru integration for enhanced debugging and test result visualization
- Modern Python: PEP 585/604 type hints, snake_case conventions
- Comprehensive Linting: black, isort, ruff, mypy with nbqa for notebooks
- High Test Coverage: 10+ test cases per problem including edge cases
- Beautiful Logging: loguru integration for enhanced test debugging
- CI/CD Pipeline: Automated testing, security scanning, and quality gates
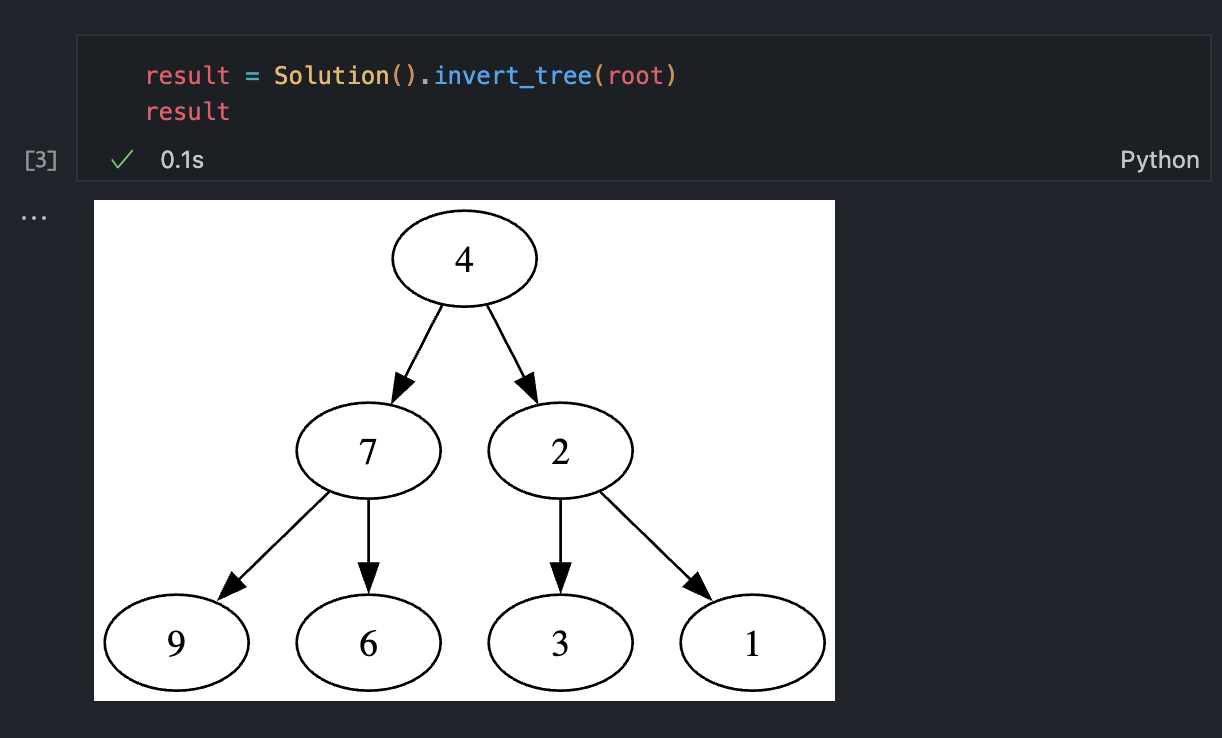
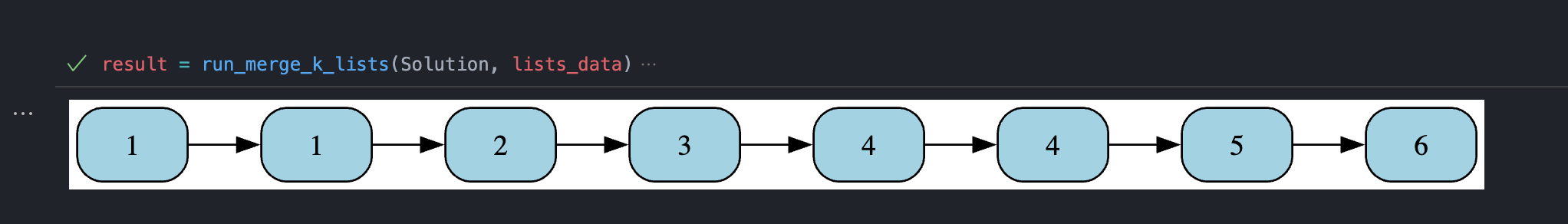
Professional-grade visualization for debugging complex data structures with dual rendering modes:
- TreeNode: Beautiful tree rendering with anytree and Graphviz integration
- ListNode: Clean arrow-based visualization with cycle detection
- GraphNode: Interactive graph rendering for adjacency list problems
- DictTree: Box-drawing character trees perfect for Trie implementations
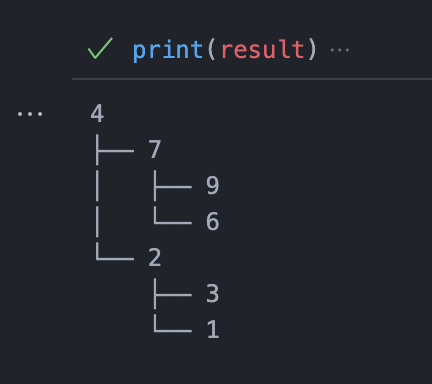
Interactive tree visualization using Graphviz SVG rendering in Jupyter notebooks
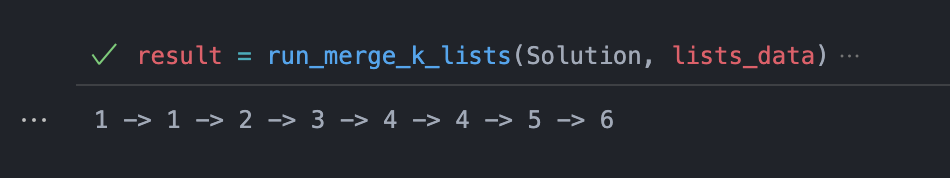
Professional linked list visualization with Graphviz in Jupyter environment
Clean ASCII tree rendering using anytree for terminal debugging and logging
Simple arrow-based list representation for console output and test debugging
-
Template Generation: Creates Jupyter notebooks (
.ipynb) by default with rich data structure rendering -
User Choice: Use
jupytextto convert notebooks to Python files, or keep as.ipynbfor interactive exploration -
Repository State: This repo converts them to Python files (
.py) for better version control - Dual Rendering: Automatic HTML visualization in notebooks, clean string output in terminals
Interactive multi-cell playground with rich data structure visualization for each problem
Perfect for quick problem generation anywhere. See the 📖 Complete CLI Usage Guide for detailed documentation with all options and examples.
For working within this repository to generate additional LeetCode problems using LLM assistance:
- Python 3.10+ - Modern Python runtime with latest type system features
- uv - Fast Python package manager
- Bake - Modern task runner (uses typer for CLI)
- Git - Version control system
- Graphviz - Graph visualization library (install guide)
# Clone repository for development
git clone https://github.com/wislertt/leetcode-py.git
cd leetcode-py
uv sync
# Generate problems from JSON templates
bake p-gen -p problem_name
bake p-test -p problem_name
# Regenerate all existing problems
bake gen-all-problemsTo extend the problem collection beyond the current catalog, leverage an LLM assistant within your IDE (Cursor, GitHub Copilot Chat, Amazon Q, etc.).
📖 Complete LLM-Assisted Problem Creation Guide - Comprehensive guide with screenshots and detailed workflow.
Quick Start:
# Problem generation commands:
"Add problem 198. House Robber"
"Add problem 198. House Robber. tag: grind"
# Test enhancement commands:
"Enhance test cases for two_sum problem"
"Fix test reproducibility for binary_tree_inorder_traversal"Required LLM Context: Include these rule files in your LLM context for automated problem generation and test enhancement:
-
.claude/commands/problem-creation.md- Complete problem generation workflow -
.claude/commands/test-quality-assurance.md- Test enhancement and reproducibility verification
Manual Check: Find problems needing more test cases:
uv run python -m leetcode_py.tools.check_test_cases --threshold=10-
TreeNode:
from leetcode_py import TreeNode- Array ↔ tree conversion:
TreeNode.from_list([1,2,3]),tree.to_list() - Beautiful anytree text rendering and Graphviz SVG for Jupyter
- Node search:
tree.find_node(value) - Generic type support:
TreeNode[int],TreeNode[str]
- Array ↔ tree conversion:
-
ListNode:
from leetcode_py import ListNode- Array ↔ list conversion:
ListNode.from_list([1,2,3]),node.to_list() - Cycle detection with Floyd's algorithm
- Graphviz visualization for Jupyter notebooks
- Generic type support:
ListNode[int],ListNode[str]
- Array ↔ list conversion:
-
GraphNode:
from leetcode_py import GraphNode- Adjacency list conversion:
GraphNode.from_adjacency_list([[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]) - Clone detection:
original.is_clone(cloned) - Graphviz visualization for undirected graphs
- DFS traversal utilities
- Adjacency list conversion:
-
DictTree:
from leetcode_py.data_structures import DictTree- Perfect for Trie implementations:
DictTree[str]() - Beautiful tree rendering with box-drawing characters
- Graphviz visualization for Jupyter notebooks
- Generic key type support
- Perfect for Trie implementations:
📖 Complete CLI Usage Guide - Detailed documentation with all options and examples.
# Generate problems
lcpy gen -n 1 # Single problem by number
lcpy gen -s two-sum # Single problem by slug
lcpy gen -t grind-75 # Bulk generation by tag
lcpy gen -t neetcode-150 # Generate NeetCode 150 problems
lcpy gen -n 1 -n 2 -n 3 # Multiple problems
lcpy gen -t grind-75 -d Easy # Filter by difficulty
lcpy gen -n 1 -o my-problems # Custom output directory
# List problems
lcpy list # All available problems
lcpy list -t grind-75 # Filter by Grind 75 tag
lcpy list -t blind-75 # Filter by Blind 75 tag
lcpy list -t neetcode-150 # Filter by NeetCode 150 tag
lcpy list -d Medium # Filter by difficulty
# Scrape problem data
lcpy scrape -n 1 # Fetch by number
lcpy scrape -s two-sum # Fetch by slug# Problem-specific operations
bake p-test -p problem_name # Test specific problem
bake p-gen -p problem_name # Generate problem from JSON template
bake p-gen -p problem_name -f # Force regenerate (overwrite existing files)
# Bulk operations
bake test # Run all tests
bake lint # Lint entire codebase
bake gen-all-problems # Regenerate all problems (destructive)
bake gen-all-problems -f # Force regenerate all problems-
Template-Driven: JSON templates in
leetcode_py/cli/resources/leetcode/json/problems/drive code generation -
Cookiecutter Integration: Uses
leetcode_py/cli/resources/leetcode/{{cookiecutter.problem_name}}/template for consistent file structure - Automated Scraping: LLM-assisted problem data extraction from LeetCode
- Version Control Friendly: Python files by default, optional notebook support
- Test Coverage: 95%+ with comprehensive edge case testing (Codecov integration)
- Security: SonarCloud quality gates, Trivy dependency scanning, Gitleaks secret detection
- Code Quality: Automated linting with black, isort, ruff, mypy
- Test Reproducibility: Automated verification that problems can be regenerated consistently
- CI/CD: GitHub Actions for testing, security, pre-commit hooks, and release automation
Perfect for systematic coding interview preparation with professional development practices and enhanced debugging capabilities.
If you find this project helpful, please consider starring the repo ⭐ or sponsoring my work 💖. Your support helps me maintain and improve this project. Thank you!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for leetcode-py
Similar Open Source Tools
For similar tasks
leetcode-py
A Python package to generate professional LeetCode practice environments. Features automated problem generation from LeetCode URLs, beautiful data structure visualizations (TreeNode, ListNode, GraphNode), and comprehensive testing with 10+ test cases per problem. Built with professional development practices including CI/CD, type hints, and quality gates. The tool provides a modern Python development environment with production-grade features such as linting, test coverage, logging, and CI/CD pipeline. It also offers enhanced data structure visualization for debugging complex structures, flexible notebook support, and a powerful CLI for generating problems anywhere.
commanddash
Dash AI is an open-source coding assistant for Flutter developers. It is designed to not only write code but also run and debug it, allowing it to assist beyond code completion and automate routine tasks. Dash AI is powered by Gemini, integrated with the Dart Analyzer, and specifically tailored for Flutter engineers. The vision for Dash AI is to create a single-command assistant that can automate tedious development tasks, enabling developers to focus on creativity and innovation. It aims to assist with the entire process of engineering a feature for an app, from breaking down the task into steps to generating exploratory tests and iterating on the code until the feature is complete. To achieve this vision, Dash AI is working on providing LLMs with the same access and information that human developers have, including full contextual knowledge, the latest syntax and dependencies data, and the ability to write, run, and debug code. Dash AI welcomes contributions from the community, including feature requests, issue fixes, and participation in discussions. The project is committed to building a coding assistant that empowers all Flutter developers.
ollama4j
Ollama4j is a Java library that serves as a wrapper or binding for the Ollama server. It facilitates communication with the Ollama server and provides models for deployment. The tool requires Java 11 or higher and can be installed locally or via Docker. Users can integrate Ollama4j into Maven projects by adding the specified dependency. The tool offers API specifications and supports various development tasks such as building, running unit tests, and integration tests. Releases are automated through GitHub Actions CI workflow. Areas of improvement include adhering to Java naming conventions, updating deprecated code, implementing logging, using lombok, and enhancing request body creation. Contributions to the project are encouraged, whether reporting bugs, suggesting enhancements, or contributing code.
crewAI-tools
The crewAI Tools repository provides a guide for setting up tools for crewAI agents, enabling the creation of custom tools to enhance AI solutions. Tools play a crucial role in improving agent functionality. The guide explains how to equip agents with a range of tools and how to create new tools. Tools are designed to return strings for generating responses. There are two main methods for creating tools: subclassing BaseTool and using the tool decorator. Contributions to the toolset are encouraged, and the development setup includes steps for installing dependencies, activating the virtual environment, setting up pre-commit hooks, running tests, static type checking, packaging, and local installation. Enhance AI agent capabilities with advanced tooling.
lightning-lab
Lightning Lab is a public template for artificial intelligence and machine learning research projects using Lightning AI's PyTorch Lightning. It provides a structured project layout with modules for command line interface, experiment utilities, Lightning Module and Trainer, data acquisition and preprocessing, model serving APIs, project configurations, training checkpoints, technical documentation, logs, notebooks for data analysis, requirements management, testing, and packaging. The template simplifies the setup of deep learning projects and offers extras for different domains like vision, text, audio, reinforcement learning, and forecasting.
Magic_Words
Magic_Words is a repository containing code for the paper 'What's the Magic Word? A Control Theory of LLM Prompting'. It implements greedy back generation and greedy coordinate gradient (GCG) to find optimal control prompts (magic words). Users can set up a virtual environment, install the package and dependencies, and run example scripts for pointwise control and optimizing prompts for datasets. The repository provides scripts for finding optimal control prompts for question-answer pairs and dataset optimization using the GCG algorithm.
grafana-llm-app
This repository contains separate packages for Grafana LLM Plugin and the @grafana/llm package for interfacing with it. The packages are tightly coupled and developed together with identical dependencies. The repository provides instructions for developing the packages, including backend and frontend development, testing, and release processes.
crewAI-tools
This repository provides a guide for setting up tools for crewAI agents to enhance functionality. It offers steps to equip agents with ready-to-use tools and create custom ones. Tools are expected to return strings for generating responses. Users can create tools by subclassing BaseTool or using the tool decorator. Contributions are welcome to enrich the toolset, and guidelines are provided for contributing. The development setup includes installing dependencies, activating virtual environment, setting up pre-commit hooks, running tests, static type checking, packaging, and local installation. The goal is to empower AI solutions through advanced tooling.
For similar jobs
RLHF-Reward-Modeling
This repository, RLHF-Reward-Modeling, is dedicated to training reward models for DRL-based RLHF (PPO), Iterative SFT, and iterative DPO. It provides state-of-the-art performance in reward models with a base model size of up to 13B. The installation instructions involve setting up the environment and aligning the handbook. Dataset preparation requires preprocessing conversations into a standard format. The code can be run with Gemma-2b-it, and evaluation results can be obtained using provided datasets. The to-do list includes various reward models like Bradley-Terry, preference model, regression-based reward model, and multi-objective reward model. The repository is part of iterative rejection sampling fine-tuning and iterative DPO.
AIT
AIT is a repository focused on Algorithmic Information Theory, specifically utilizing Binary Lambda Calculus. It provides resources and tools for studying and implementing algorithms based on information theory principles. The repository aims to explore the relationship between algorithms and information theory through the lens of Binary Lambda Calculus, offering insights into computational complexity and data compression techniques.
AlgoListed
Algolisted is a pioneering platform dedicated to algorithmic problem-solving, offering a centralized hub for a diverse array of algorithmic challenges. It provides an immersive online environment for programmers to enhance their skills through Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) sheets, academic progress tracking, resume refinement with OpenAI integration, adaptive testing, and job opportunity listings. The project is built on the MERN stack, Flask, Beautiful Soup, and Selenium,GEN AI, and deployed on Firebase. Algolisted aims to be a reliable companion in the pursuit of coding knowledge and proficiency.
RAM
This repository, RAM, focuses on developing advanced algorithms and methods for Reasoning, Alignment, Memory. It contains projects related to these areas and is maintained by a team of individuals. The repository is licensed under the MIT License.
oat
Oat is a simple and efficient framework for running online LLM alignment algorithms. It implements a distributed Actor-Learner-Oracle architecture, with components optimized using state-of-the-art tools. Oat simplifies the experimental pipeline of LLM alignment by serving an Oracle online for preference data labeling and model evaluation. It provides a variety of oracles for simulating feedback and supports verifiable rewards. Oat's modular structure allows for easy inheritance and modification of classes, enabling rapid prototyping and experimentation with new algorithms. The framework implements cutting-edge online algorithms like PPO for math reasoning and various online exploration algorithms.

all-in-rag
All-in-RAG is a comprehensive repository for all things related to Randomized Algorithms and Graphs. It provides a wide range of resources, including implementations of various randomized algorithms, graph data structures, and visualization tools. The repository aims to serve as a one-stop solution for researchers, students, and enthusiasts interested in exploring the intersection of randomized algorithms and graph theory. Whether you are looking to study theoretical concepts, implement algorithms in practice, or visualize graph structures, All-in-RAG has got you covered.
leetcode-py
A Python package to generate professional LeetCode practice environments. Features automated problem generation from LeetCode URLs, beautiful data structure visualizations (TreeNode, ListNode, GraphNode), and comprehensive testing with 10+ test cases per problem. Built with professional development practices including CI/CD, type hints, and quality gates. The tool provides a modern Python development environment with production-grade features such as linting, test coverage, logging, and CI/CD pipeline. It also offers enhanced data structure visualization for debugging complex structures, flexible notebook support, and a powerful CLI for generating problems anywhere.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.