multimodal-chat
A multimodal chat interface with many tools.
Stars: 117
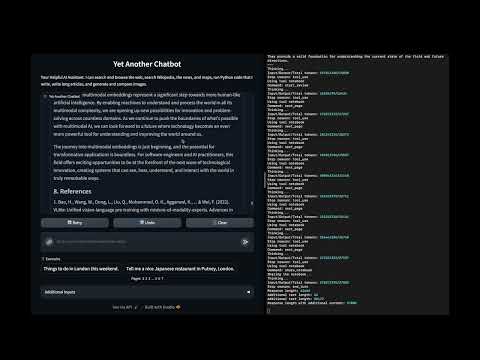
Yet Another Chatbot is a sophisticated multimodal chat interface powered by advanced AI models and equipped with a variety of tools. This chatbot can search and browse the web in real-time, query Wikipedia for information, perform news and map searches, execute Python code, compose long-form articles mixing text and images, generate, search, and compare images, analyze documents and images, search and download arXiv papers, save conversations as text and audio files, manage checklists, and track personal improvements. It offers tools for web interaction, Wikipedia search, Python scripting, content management, image handling, arXiv integration, conversation generation, file management, personal improvement, and checklist management.
README:
A multimodal chat interface with access to many tools.
YAIA is a sophisticated multimodal chat interface powered by advanced AI models and equipped with a variety of tools. It can:
- Search and browse the web in real-time
- Query Wikipedia for information
- Perform news searches
- Safely execute Python code that can produce text and images such as charts and diagrams
- Compose long-form articles mixing text and images
- Generate, search, and compare images
- Analyze documents and images
- Search and download arXiv papers
- Generate and save conversations as text and audio files
- Save files to the output directory
- Track personal improvements
- Manage checklists for task tracking
These are the main components:
- Gradio 5 for the web interface
- Amazon Bedrock to handle conversation and tool use
- Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet as main model
- Amazon Titan Text and Multimodal Embeddings models
- Amazon Titan Image Generator
- OpenSearch for text and multimodal indexes
- Amazon Polly for voices
- AWS Lambda for the code interpreter
Here are examples of how to use various tools:
-
Web Search: "Search the web for recent advancements in quantum computing."
-
Wikipedia: "Find Wikipedia articles about the history of artificial intelligence."
-
Python Scripting: "Create a Python script to generate a bar chart of global CO2 emissions by country."
-
Sketchbook: "Start a new sketchbook and write an introduction about how to compute Pi with numerical methods."
-
Image Generation: "Generate an image of a futuristic city with flying cars and tall skyscrapers."
-
Image Search: "Search the image catalog for pictures of endangered species."
-
arXiv Integration: "Search for recent research papers on deep learning in natural language processing."
-
Conversation Generation: "Create a conversation between three experts discussing how to set up multimodal RAG."
-
File Management: "Save a summary of our discussion about climate change to a file named 'climate_change_summary.txt'."
-
Personal Improvement: "Here's a suggestion to improve: to improve answers, search for official sources."
-
Checklist: "Start a new checklist to follow a list of tasks one by one."
-
Web Interaction:
- DuckDuckGo Text Search: Performs web searches
- DuckDuckGo News Search: Searches for recent news articles
- DuckDuckGo Images Search: Searches for publicly available images
- Web Browser: Browses websites and retrieves their content
-
Wikipedia Tools:
- Wikipedia Search: Finds relevant Wikipedia pages
- Wikipedia Geodata Search: Locates Wikipedia articles by geographic location
- Wikipedia Page Retriever: Fetches full Wikipedia page content
-
Python Scripting:
- Runs Python scripts for computations, testing, and output generation, including text and images
- Python modules can be added to the Python interpreter
- Python code is run in a secure environment provided by AWS Lambda
-
Content Management:
- Personal Archive: Stores and retrieves text, Markdown, or HTML content, using a semantic database
- Sketchbook: Manages a multi-page sketchbook for writing and reviewing long-form content. Supports multiple output formats:
- Markdown (.md): For easy reading and editing
- Word Document (.docx): For document editing
-
Image Handling:
- Image Generation: Creates images based on text prompts
- Image Catalog Search: Searches images by description
- Image Similarity Search: Finds similar images based on a reference image
- Random Images: Retrieves random images from the catalog
- Get Image by ID: Retrieves a specific image from the catalog using its ID
- Image Catalog Count: Returns the total number of images in the catalog
- Download Image: Adds images from URLs to the catalog
-
arXiv Integration:
- Search and download arXiv papers
- Store paper content in the archive for easy retrieval
-
Conversation Generation:
- Transform content into a conversation between two to four people
- Generate audio files for the conversation using text-to-speech
-
File Management:
- Save File: Allows saving text content to a file with a specified name in the output directory
-
Personal Improvement:
- Track suggestions and mistakes for future enhancements
-
Checklist:
- Manage task lists with the ability to add items, mark them as completed, and review progress
For a comprehensive list of available tools and their usage, refer to ./Config/tools.json.
- A container tool: Docker or Finch (to install Finch, follow the instructions here)
- Python 3.12 or newer
- AWS account with appropriate permissions to access Amazon Bedrock, AWS Lambda, and Amazon ECR
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/danilop/multimodal-chat cd multimodal-chat -
Create and activate a virtual environment (optional but recommended):
python -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate # On Windows, use `venv\Scripts\activate` -
Install the required packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt -
Set up the AWS Lambda function for code execution:
cd LambdaFunction ./deploy_lambda_function.sh cd .. -
To use Selenium for web browsing, install ChromeDriver. Using Homebrew:
brew install --cask chromedriver -
To output audio, install
ffmpeg. Using Homebrew:brew install ffmpeg
You can either use a local OpenSearch instance or connect to a remote server. For local setup:
-
Navigate to the OpenSearch directory:
cd OpenSearch/ -
Set the admin password (first-time setup), this step will create the
.envfile and theopensearch_env.shfiles:./set_password.sh -
Start OpenSearch locally (it needs access to the
.envfile):./opensearch_start.sh -
Ensure OpenSearch (2 nodes + dashboard) starts correctly by checking the output
-
To update OpenSearch, download the new container images using this script:
./opensearch_update.sh
For remote server setup, update the client creation code in the main script.
To change password, you need to delete the container using finch or docker and then set a new password.
Default models for text, images, and embeddings are in the Config/config.ini file. The models to use are specified using Amazon Bedrock model IDs or cross-region inference profile IDs. You need permissions and access to these models as described in Access foundation models.
This section assumes OpenSearch is running locally in another terminal window as described before.
-
Load the OpenSearch admin password into the environment:
source OpenSearch/opensearch_env.sh -
Run the application:
python multimodal_chat.py -
To reset the text and multimodal indexes (note: this doesn't delete images in
./Images/):python multimodal_chat.py --reset-index -
Open a web browser and navigate to http://127.0.0.1:7860/ to start chatting.
Here are a few examples of what you can do this application.
In this demo:
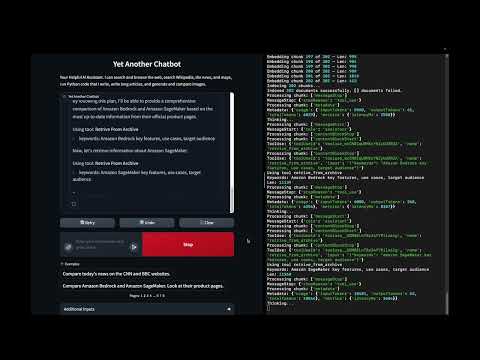
- Browse websites using Selenium and specific tools for DuckDuckGo (search, news, geosearch) and Wikipedia
- Use the semantic text archive tool to archive documents and retrieve by keywords
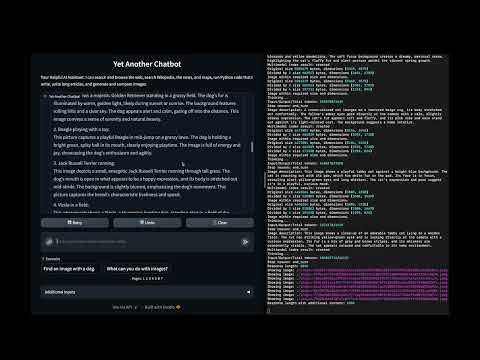
In this demo:
- Using a multimodal index and the local file system to manage an image catalog
- Store images with a generated description
- Retrieve images by text description (semantic search)
- Retrieve images by similarity to another image
- Retrieve random images
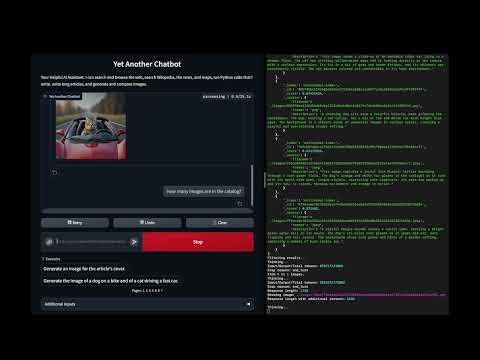
In this demo:
- Generate images from a textual description
- The text-to-image prompt is generated from chat instructions
- This approach allows to use the overall conversation to improve the prompt
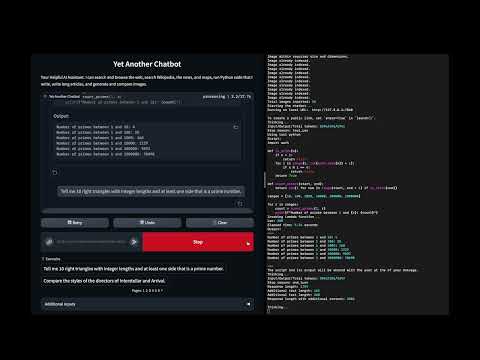
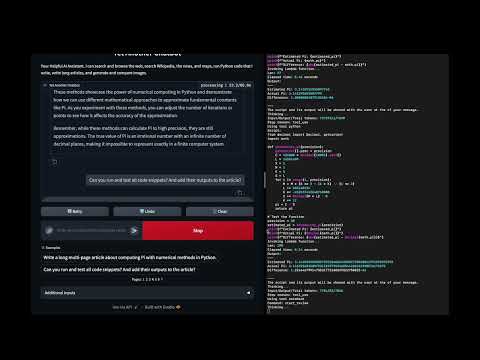
In this demo:
- Running AI generated code to solve problems
- Running for security in an AWS Lambda function with basic permissions
- Deployed via a container image to easily add Python modules
- Python only but easily extensible
In this demo:
- A tool to help write long forms of text such as articles and blog posts)
- Providing sequential access to text split in pages
- To mitigate the "asymmetry" between a model input and output sizes
In this demo:
- Best results use more than one tools together
- Start with a sketchbook to write a long article
- The article contains code snippets
- A review runs and tests all code snippets and updates each page fixing the code (if needed) and adding actual results
- If you encounter issues with OpenSearch, check the connection settings and ensure the service is running
- For AWS Lambda function errors, verify your AWS credentials and permissions
- If image processing fails, ensure you have the necessary libraries installed and check file permissions
Contributions to YAIA are welcome! Please refer to the contributing guidelines for more information on how to submit pull requests, report issues, or request features.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
- Combine multiple tools for complex tasks. For example, use the web search to find information, then use the sketchbook to write a summary, and finally generate a conversation about the topic.
- When working with images, you can generate new images, search for existing ones, or download images from the web to add to your catalog.
- Use the arXiv integration to stay up-to-date with the latest research in your field of interest.
- The conversation generation tool is great for creating engaging content or preparing for presentations.
- Regularly check and update your personal improvements to track your progress and areas for growth.
For more detailed information on specific components or advanced usage, please refer to the inline documentation in the source code.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for multimodal-chat
Similar Open Source Tools

multimodal-chat
Yet Another Chatbot is a sophisticated multimodal chat interface powered by advanced AI models and equipped with a variety of tools. This chatbot can search and browse the web in real-time, query Wikipedia for information, perform news and map searches, execute Python code, compose long-form articles mixing text and images, generate, search, and compare images, analyze documents and images, search and download arXiv papers, save conversations as text and audio files, manage checklists, and track personal improvements. It offers tools for web interaction, Wikipedia search, Python scripting, content management, image handling, arXiv integration, conversation generation, file management, personal improvement, and checklist management.

CLIPPyX
CLIPPyX is a powerful system-wide image search and management tool that offers versatile search options to find images based on their content, text, and visual similarity. With advanced features, users can effortlessly locate desired images across their entire computer's disk(s), regardless of their location or file names. The tool utilizes OpenAI's CLIP for image embeddings and text-based search, along with OCR for extracting text from images. It also employs Voidtools Everything SDK to list paths of all images on the system. CLIPPyX server receives search queries and queries collections of image embeddings and text embeddings to return relevant images.
Twitter-Insight-LLM
This project enables you to fetch liked tweets from Twitter (using Selenium), save it to JSON and Excel files, and perform initial data analysis and image captions. This is part of the initial steps for a larger personal project involving Large Language Models (LLMs).
chroma
Chroma is an open-source embedding database that provides a simple, scalable, and feature-rich way to build Python or JavaScript LLM apps with memory. It offers a fully-typed, fully-tested, and fully-documented API that makes it easy to get started and scale your applications. Chroma also integrates with popular tools like LangChain and LlamaIndex, and supports a variety of embedding models, including Sentence Transformers, OpenAI embeddings, and Cohere embeddings. With Chroma, you can easily add documents to your database, query relevant documents with natural language, and compose documents into the context window of an LLM like GPT3 for additional summarization or analysis.
leettools
LeetTools is an AI search assistant that can perform highly customizable search workflows and generate customized format results based on both web and local knowledge bases. It provides an automated document pipeline for data ingestion, indexing, and storage, allowing users to focus on implementing workflows without worrying about infrastructure. LeetTools can run with minimal resource requirements on the command line with configurable LLM settings and supports different databases for various functions. Users can configure different functions in the same workflow to use different LLM providers and models.
AntSK
AntSK is an AI knowledge base/agent built with .Net8+Blazor+SemanticKernel. It features a semantic kernel for accurate natural language processing, a memory kernel for continuous learning and knowledge storage, a knowledge base for importing and querying knowledge from various document formats, a text-to-image generator integrated with StableDiffusion, GPTs generation for creating personalized GPT models, API interfaces for integrating AntSK into other applications, an open API plugin system for extending functionality, a .Net plugin system for integrating business functions, real-time information retrieval from the internet, model management for adapting and managing different models from different vendors, support for domestic models and databases for operation in a trusted environment, and planned model fine-tuning based on llamafactory.
llm-memorization
The 'llm-memorization' project is a tool designed to index, archive, and search conversations with a local LLM using a SQLite database enriched with automatically extracted keywords. It aims to provide personalized context at the start of a conversation by adding memory information to the initial prompt. The tool automates queries from local LLM conversational management libraries, offers a hybrid search function, enhances prompts based on posed questions, and provides an all-in-one graphical user interface for data visualization. It supports both French and English conversations and prompts for bilingual use.
ChatData
ChatData is a robust chat-with-documents application designed to extract information and provide answers by querying the MyScale free knowledge base or uploaded documents. It leverages the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) framework, millions of Wikipedia pages, and arXiv papers. Features include self-querying retriever, VectorSQL, session management, and building a personalized knowledge base. Users can effortlessly navigate vast data, explore academic papers, and research documents. ChatData empowers researchers, students, and knowledge enthusiasts to unlock the true potential of information retrieval.
vector-vein
VectorVein is a no-code AI workflow software inspired by LangChain and langflow, aiming to combine the powerful capabilities of large language models and enable users to achieve intelligent and automated daily workflows through simple drag-and-drop actions. Users can create powerful workflows without the need for programming, automating all tasks with ease. The software allows users to define inputs, outputs, and processing methods to create customized workflow processes for various tasks such as translation, mind mapping, summarizing web articles, and automatic categorization of customer reviews.
graphrag-local-ollama
GraphRAG Local Ollama is a repository that offers an adaptation of Microsoft's GraphRAG, customized to support local models downloaded using Ollama. It enables users to leverage local models with Ollama for large language models (LLMs) and embeddings, eliminating the need for costly OpenAPI models. The repository provides a simple setup process and allows users to perform question answering over private text corpora by building a graph-based text index and generating community summaries for closely-related entities. GraphRAG Local Ollama aims to improve the comprehensiveness and diversity of generated answers for global sensemaking questions over datasets.
easy-web-summarizer
A Python script leveraging advanced language models to summarize webpages and youtube videos directly from URLs. It integrates with LangChain and ChatOllama for state-of-the-art summarization, providing detailed summaries for quick understanding of web-based documents. The tool offers a command-line interface for easy use and integration into workflows, with plans to add support for translating to different languages and streaming text output on gradio. It can also be used via a web UI using the gradio app. The script is dockerized for easy deployment and is open for contributions to enhance functionality and capabilities.
AutoNode
AutoNode is a self-operating computer system designed to automate web interactions and data extraction processes. It leverages advanced technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), YOLO (You Only Look Once) models for object detection, and a custom site-graph to navigate and interact with web pages programmatically. Users can define objectives, create site-graphs, and utilize AutoNode via API to automate tasks on websites. The tool also supports training custom YOLO models for object detection and OCR for text recognition on web pages. AutoNode can be used for tasks such as extracting product details, automating web interactions, and more.
serverless-pdf-chat
The serverless-pdf-chat repository contains a sample application that allows users to ask natural language questions of any PDF document they upload. It leverages serverless services like Amazon Bedrock, AWS Lambda, and Amazon DynamoDB to provide text generation and analysis capabilities. The application architecture involves uploading a PDF document to an S3 bucket, extracting metadata, converting text to vectors, and using a LangChain to search for information related to user prompts. The application is not intended for production use and serves as a demonstration and educational tool.

FunClip
FunClip is an open-source, locally deployed automated video clipping tool that leverages Alibaba TONGYI speech lab's FunASR Paraformer series models for speech recognition on videos. Users can select text segments or speakers from recognition results to obtain corresponding video clips. It integrates industrial-grade models for accurate predictions and offers hotword customization and speaker recognition features. The tool is user-friendly with Gradio interaction, supporting multi-segment clipping and providing full video and target segment subtitles. FunClip is suitable for users looking to automate video clipping tasks with advanced AI capabilities.
burpference
Burpference is an open-source extension designed to capture in-scope HTTP requests and responses from Burp's proxy history and send them to a remote LLM API in JSON format. It automates response capture, integrates with APIs, optimizes resource usage, provides color-coded findings visualization, offers comprehensive logging, supports native Burp reporting, and allows flexible configuration. Users can customize system prompts, API keys, and remote hosts, and host models locally to prevent high inference costs. The tool is ideal for offensive web application engagements to surface findings and vulnerabilities.
FunClip
FunClip is an open-source, locally deployable automated video editing tool that utilizes the FunASR Paraformer series models from Alibaba DAMO Academy for speech recognition in videos. Users can select text segments or speakers from the recognition results and click the clip button to obtain the corresponding video segments. FunClip integrates advanced features such as the Paraformer-Large model for accurate Chinese ASR, SeACo-Paraformer for customized hotword recognition, CAM++ speaker recognition model, Gradio interactive interface for easy usage, support for multiple free edits with automatic SRT subtitles generation, and segment-specific SRT subtitles.
For similar tasks
document-ai-samples
The Google Cloud Document AI Samples repository contains code samples and Community Samples demonstrating how to analyze, classify, and search documents using Google Cloud Document AI. It includes various projects showcasing different functionalities such as integrating with Google Drive, processing documents using Python, content moderation with Dialogflow CX, fraud detection, language extraction, paper summarization, tax processing pipeline, and more. The repository also provides access to test document files stored in a publicly-accessible Google Cloud Storage Bucket. Additionally, there are codelabs available for optical character recognition (OCR), form parsing, specialized processors, and managing Document AI processors. Community samples, like the PDF Annotator Sample, are also included. Contributions are welcome, and users can seek help or report issues through the repository's issues page. Please note that this repository is not an officially supported Google product and is intended for demonstrative purposes only.
step-free-api
The StepChat Free service provides high-speed streaming output, multi-turn dialogue support, online search support, long document interpretation, and image parsing. It offers zero-configuration deployment, multi-token support, and automatic session trace cleaning. It is fully compatible with the ChatGPT interface. Additionally, it provides seven other free APIs for various services. The repository includes a disclaimer about using reverse APIs and encourages users to avoid commercial use to prevent service pressure on the official platform. It offers online testing links, showcases different demos, and provides deployment guides for Docker, Docker-compose, Render, Vercel, and native deployments. The repository also includes information on using multiple accounts, optimizing Nginx reverse proxy, and checking the liveliness of refresh tokens.
unilm
The 'unilm' repository is a collection of tools, models, and architectures for Foundation Models and General AI, focusing on tasks such as NLP, MT, Speech, Document AI, and Multimodal AI. It includes various pre-trained models, such as UniLM, InfoXLM, DeltaLM, MiniLM, AdaLM, BEiT, LayoutLM, WavLM, VALL-E, and more, designed for tasks like language understanding, generation, translation, vision, speech, and multimodal processing. The repository also features toolkits like s2s-ft for sequence-to-sequence fine-tuning and Aggressive Decoding for efficient sequence-to-sequence decoding. Additionally, it offers applications like TrOCR for OCR, LayoutReader for reading order detection, and XLM-T for multilingual NMT.
searchGPT
searchGPT is an open-source project that aims to build a search engine based on Large Language Model (LLM) technology to provide natural language answers. It supports web search with real-time results, file content search, and semantic search from sources like the Internet. The tool integrates LLM technologies such as OpenAI and GooseAI, and offers an easy-to-use frontend user interface. The project is designed to provide grounded answers by referencing real-time factual information, addressing the limitations of LLM's training data. Contributions, especially from frontend developers, are welcome under the MIT License.
LLMs-at-DoD
This repository contains tutorials for using Large Language Models (LLMs) in the U.S. Department of Defense. The tutorials utilize open-source frameworks and LLMs, allowing users to run them in their own cloud environments. The repository is maintained by the Defense Digital Service and welcomes contributions from users.
LARS
LARS is an application that enables users to run Large Language Models (LLMs) locally on their devices, upload their own documents, and engage in conversations where the LLM grounds its responses with the uploaded content. The application focuses on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to increase accuracy and reduce AI-generated inaccuracies. LARS provides advanced citations, supports various file formats, allows follow-up questions, provides full chat history, and offers customization options for LLM settings. Users can force enable or disable RAG, change system prompts, and tweak advanced LLM settings. The application also supports GPU-accelerated inferencing, multiple embedding models, and text extraction methods. LARS is open-source and aims to be the ultimate RAG-centric LLM application.

EAGLE
Eagle is a family of Vision-Centric High-Resolution Multimodal LLMs that enhance multimodal LLM perception using a mix of vision encoders and various input resolutions. The model features a channel-concatenation-based fusion for vision experts with different architectures and knowledge, supporting up to over 1K input resolution. It excels in resolution-sensitive tasks like optical character recognition and document understanding.
erag
ERAG is an advanced system that combines lexical, semantic, text, and knowledge graph searches with conversation context to provide accurate and contextually relevant responses. This tool processes various document types, creates embeddings, builds knowledge graphs, and uses this information to answer user queries intelligently. It includes modules for interacting with web content, GitHub repositories, and performing exploratory data analysis using various language models.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.