
stride-gpt
An AI-powered threat modeling tool that leverages OpenAI's GPT models to generate threat models for a given application based on the STRIDE methodology.
Stars: 454
STRIDE GPT is an AI-powered threat modelling tool that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate threat models and attack trees for a given application based on the STRIDE methodology. Users provide application details, such as the application type, authentication methods, and whether the application is internet-facing or processes sensitive data. The model then generates its output based on the provided information. It features a simple and user-friendly interface, supports multi-modal threat modelling, generates attack trees, suggests possible mitigations for identified threats, and does not store application details. STRIDE GPT can be accessed via OpenAI API, Azure OpenAI Service, Google AI API, or Mistral API. It is available as a Docker container image for easy deployment.
README:
STRIDE GPT is an AI-powered threat modelling tool that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate threat models and attack trees for a given application based on the STRIDE methodology. Users provide application details, such as the application type, authentication methods, and whether the application is internet-facing or processes sensitive data. The model then generates its output based on the provided information.
- Star the Repo
- Features
- Roadmap
- Talk at Open Security Summit
- Changelog
- Installation
- Usage
- Contributing
- License
If you find STRIDE GPT useful, please consider starring the repository on GitHub. This helps more people discover the tool. Your support is greatly appreciated! ⭐
- Simple and user-friendly interface
- Generates threat models based on the STRIDE methodology
- Multi-modal: Use architecture diagrams, flowcharts, etc. as inputs for threat modelling
- Generates attack trees to enumerate possible attack paths
- Suggests possible mitigations for identified threats
- Supports DREAD risk scoring for identified threats
- Generates Gherkin test cases based on identified threats
- 🆕 GitHub repository analysis for comprehensive threat modelling
- No data storage; application details are not saved
- Supports models accessed via OpenAI API, Azure OpenAI Service, Google AI API, Mistral API, or 🆕 locally hosted models via Ollama
- Available as a Docker container image for easy deployment
- 🆕 Environment variable support for secure configuration
- [x] Add support for multi-modal threat modelling
- [x] Autogenerate application descriptions based on README files in GitHub repositories
- [ ] Customisable and exportable reports (e.g. PDF, Word) that include the generated threat model, attack tree, and mitigations
- [ ] Add a helper tool to guide users to create effective application descriptions before generating threat models
- [ ] Update UI to support multiple languages
In January 2024 I gave a talk about STRIDE GPT at the Open Security Summit. During the talk, I discussed the project's inception, its core functionalities, recent updates, and some future plans. You can watch the full presentation below:
This video is an excellent resource for anyone interested in understanding how STRIDE GPT works and how it can be used to improve threat modelling.
- GitHub Repository Analysis: STRIDE GPT now supports automatic analysis of GitHub repositories. Users can provide a GitHub repository URL, and the tool will analyse the README and key files to generate a more comprehensive threat model.
- Environment Variable Support: Added support for loading API keys and other configuration from environment variables, improving security and ease of deployment.
- Improved Error Handling: Enhanced error handling and retry mechanisms for API calls to improve reliability.
- UI Enhancements: Updated the user interface to accommodate new features and improve overall user experience.
Release highlights:
- Local Model Hosting: STRIDE GPT now supports the use of locally hosted LLMs via an integration with Ollama. This feature is particularly useful for organisations with strict data privacy requirements or those who prefer to keep their data on-premises. Please note that this feature is not available for users of the STRIDE GPT version hosted on Streamlit Community Cloud at https://stridegpt.streamlit.app
- Mistral Client v1.0: STRIDE GPT now uses v1.0 of the Mistral Client, which resolves the breaking changes introduced in the latest version of the Mistral API. This ensures that STRIDE GPT users can continue to leverage the Mistral API for threat modelling tasks.
This release added support for the following models:
-
GPT4o mini: I've added support for OpenAI's recently released GPT4o mini model. GPT4o mini is a cost-efficient small model that still provides high-quality responses for threat modelling tasks.
-
Gemini 1.5 Pro (stable): Users can now choose from either the stable or preview versions of the Gemini 1.5 Pro model.
Click to view release notes for earlier versions.
Release highlights:
-
DREAD Risk Scoring: STRIDE GPT now supports DREAD risk scoring, allowing users to assign risk scores to identified threats based on the DREAD model. This feature provides a more comprehensive threat assessment and helps prioritise mitigation efforts.
-
Gherkin Test Cases: Users can now generate Gherkin test cases based on the identified threats. This feature helps bridge the gap between threat modelling and testing, ensuring that security considerations are integrated into the testing process.
-
UI Enhancements: I've refreshed the user interface making it easier to navigate and interact with the application and its features.
Release highlights:
- Multi-Modal Threat Modelling: STRIDE GPT now supports multi-modal threat modelling using OpenAI's GPT-4o and GPT-4-Turbo models. Users can provide an image of an architecture diagram, flowchart, or other visual representations of their application to enhance the threat modelling process.
- Google AI Integration: I've added support for Gemini 1.5 Pro via the Google AI API. Please note that Gemini doesn't consistently generate JSON output so you may need to retry some requests. In addition, Attack Trees can't be generated using Google AI models because of Google's safety restrictions.
- Refactored Codebase: I've refactored some parts of the codebase to improve maintainability and readability. This should make it easier to add new features and enhancements in future releases.
- Bug Fixes: Minor bug fixes and error handling improvements.
Release highlights:
-
Mistral API Integration: Users can now choose to use LLMs provided by Mistral AI to generate threat models, attack trees and mitigation suggestions. This provides an alternative to OpenAI's GPT models, offering greater flexibility and choice for users.
-
Refined Prompts: With more people using STRIDE GPT for work, I've updated the threat model prompt templates to encourage the LLMs to generate more comprehensive outputs. Users should now see multiple threats identified within each STRIDE category.
-
Public Roadmap: I've created a public roadmap to provide visibility into upcoming features and improvements.
-
UI Enhancements: I've made some minor updates to the UI to accommodate the new Mistral API integration and improve the overall user experience.
Release highlights:
- Azure OpenAI Service Integration: Users can now opt to use OpenAI 1106-preview models hosted on the Azure OpenAI Service, in addition to the standard OpenAI API.
- Docker Container Image: To make it easier to deploy STRIDE GPT on public and private clouds, the tool is now available as a Docker container image on Docker Hub.
Release highlights:
- Integration of New GPT Models: The application now supports the latest "gpt-4-1106-preview" and "gpt-3.5-turbo-1106" models, offering advanced capabilities and more accurate responses for threat modelling and attack tree generation.
- Direct OpenAI API Calls: STRIDE GPT now makes direct calls to the OpenAI API in order to take advantage of the recently introduced JSON Mode. This should greatly reduce the reduce the likelihood of syntax errors when generating threat models.
- Refined Attack Tree Generation: The process for generating attack trees has been overhauled to be more reliable, minimising syntax errors when generating Mermaid diagrams and improving the overall quality of the visualisations.
- New Logo and Color Scheme: A refreshed colour scheme and new logo (generated by DALL·E 3).
- Continued Bug Fixes and Performance Improvements: I've made a small number of additional updates to address existing bugs and optimise the application for better performance, ensuring a smoother and more efficient user experience.
Release highlights:
- Threat Mitigations: STRIDE GPT can now suggest potential mitigations for the threats identified in the threat modelling phase. This helps users develop strategies to prevent or minimise the impact of the identified threats.
- Downloadable Output: Users can now download the generated threat model, attack tree, and mitigations as Markdown files directly from the application. This makes it easy to share and document the generated outputs.
- Improved User Interface: I've further refined the user interface to provide a smoother and more intuitive user experience. The application layout has been optimised for better readability and usability.
- Updated GPT Models: STRIDE GPT now supports the latest 0613 versions of the GPT-3.5-turbo and GPT-4 models. These updated models provide improved performance and increased control over the generated output.
- Bug Fixes and Performance Enhancements: I've addressed several bugs and made performance improvements to ensure a more stable and responsive application.
Release highlights:
- Attack Tree Generation: In addition to generating threat models, STRIDE GPT can now generate attack trees for your applications based on the provided details. This helps users better understand potential attack paths for their applications.
- Attack Tree Visualisation: This is an experimental feature that allows users to visualise the generated attack tree directly in the app using Mermaid.js. This provides a more interactive experience within the STRIDE GPT interface.
- GPT-4 Model Support: STRIDE GPT now supports the use of OpenAI's GPT-4 model, provided the user has access to the GPT-4 API. This allows users to leverage the latest advancements in GPT technology to generate more accurate and comprehensive threat models and attack trees.
- Improved Layout and Organisation: I've restructured the app layout to make it easier to navigate and use. Key sections, such as Threat Model and Attack Tree, are now organised into collapsible sections for a cleaner and more intuitive user experience.
Initial release of the application.
-
Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/mrwadams/stride-gpt.git
-
Change to the cloned repository directory:
cd stride-gpt -
Install the required Python packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Set up environment variables:
a. Copy the
.env.examplefile to a new file named.env:cp .env.example .envb. Edit the
.envfile and add your API keys:GITHUB_API_KEY=your_actual_github_api_key OPENAI_API_KEY=your_actual_openai_api_key # ... add other API keys as needed
-
Pull the Docker image from Docker Hub:
docker pull mrwadams/stridegpt:latest
-
Create a
.envfile with your API keys as described in step 4 of Option 1.
-
Run the Streamlit app:
streamlit run main.py
-
Open the app in your web browser using the provided URL.
-
Follow the steps in the Streamlit interface to use STRIDE GPT.
-
Run the Docker container, mounting the
.envfile:docker run -p 8501:8501 --env-file .env mrwadams/stridegpt
This command will start the container, map port 8501 (default for Streamlit apps) from the container to your host machine, and load the environment variables from the
.envfile. -
Open a web browser and navigate to
http://localhost:8501to access the app running inside the container. -
Follow the steps in the Streamlit interface to use STRIDE GPT.
Note: When you run the application (either locally or via Docker), it will automatically load the environment variables you've set in the .env file. This will pre-fill the API keys in the application interface.
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for stride-gpt
Similar Open Source Tools

stride-gpt
STRIDE GPT is an AI-powered threat modelling tool that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate threat models and attack trees for a given application based on the STRIDE methodology. Users provide application details, such as the application type, authentication methods, and whether the application is internet-facing or processes sensitive data. The model then generates its output based on the provided information. It features a simple and user-friendly interface, supports multi-modal threat modelling, generates attack trees, suggests possible mitigations for identified threats, and does not store application details. STRIDE GPT can be accessed via OpenAI API, Azure OpenAI Service, Google AI API, or Mistral API. It is available as a Docker container image for easy deployment.
Local-Multimodal-AI-Chat
Local Multimodal AI Chat is a multimodal chat application that integrates various AI models to manage audio, images, and PDFs seamlessly within a single interface. It offers local model processing with Ollama for data privacy, integration with OpenAI API for broader AI capabilities, audio chatting with Whisper AI for accurate voice interpretation, and PDF chatting with Chroma DB for efficient PDF interactions. The application is designed for AI enthusiasts and developers seeking a comprehensive solution for multimodal AI technologies.
burpference
Burpference is an open-source extension designed to capture in-scope HTTP requests and responses from Burp's proxy history and send them to a remote LLM API in JSON format. It automates response capture, integrates with APIs, optimizes resource usage, provides color-coded findings visualization, offers comprehensive logging, supports native Burp reporting, and allows flexible configuration. Users can customize system prompts, API keys, and remote hosts, and host models locally to prevent high inference costs. The tool is ideal for offensive web application engagements to surface findings and vulnerabilities.
radicalbit-ai-monitoring
The Radicalbit AI Monitoring Platform provides a comprehensive solution for monitoring Machine Learning and Large Language models in production. It helps proactively identify and address potential performance issues by analyzing data quality, model quality, and model drift. The repository contains files and projects for running the platform, including UI, API, SDK, and Spark components. Installation using Docker compose is provided, allowing deployment with a K3s cluster and interaction with a k9s container. The platform documentation includes a step-by-step guide for installation and creating dashboards. Community engagement is encouraged through a Discord server. The roadmap includes adding functionalities for batch and real-time workloads, covering various model types and tasks.
fridon-ai
FridonAI is an open-source project offering AI-powered tools for cryptocurrency analysis and blockchain operations. It includes modules like FridonAnalytics for price analysis, FridonSearch for technical indicators, FridonNotifier for custom alerts, FridonBlockchain for blockchain operations, and FridonChat as a unified chat interface. The platform empowers users to create custom AI chatbots, access crypto tools, and interact effortlessly through chat. The core functionality is modular, with plugins, tools, and utilities for easy extension and development. FridonAI implements a scoring system to assess user interactions and incentivize engagement. The application uses Redis extensively for communication and includes a Nest.js backend for system operations.
AntSK
AntSK is an AI knowledge base/agent built with .Net8+Blazor+SemanticKernel. It features a semantic kernel for accurate natural language processing, a memory kernel for continuous learning and knowledge storage, a knowledge base for importing and querying knowledge from various document formats, a text-to-image generator integrated with StableDiffusion, GPTs generation for creating personalized GPT models, API interfaces for integrating AntSK into other applications, an open API plugin system for extending functionality, a .Net plugin system for integrating business functions, real-time information retrieval from the internet, model management for adapting and managing different models from different vendors, support for domestic models and databases for operation in a trusted environment, and planned model fine-tuning based on llamafactory.
bionic-gpt
BionicGPT is an on-premise replacement for ChatGPT, offering the advantages of Generative AI while maintaining strict data confidentiality. BionicGPT can run on your laptop or scale into the data center.
graphrag-local-ollama
GraphRAG Local Ollama is a repository that offers an adaptation of Microsoft's GraphRAG, customized to support local models downloaded using Ollama. It enables users to leverage local models with Ollama for large language models (LLMs) and embeddings, eliminating the need for costly OpenAPI models. The repository provides a simple setup process and allows users to perform question answering over private text corpora by building a graph-based text index and generating community summaries for closely-related entities. GraphRAG Local Ollama aims to improve the comprehensiveness and diversity of generated answers for global sensemaking questions over datasets.
wandbot
Wandbot is a question-answering bot designed for Weights & Biases documentation. It employs Retrieval Augmented Generation with a ChromaDB backend for efficient responses. The bot features periodic data ingestion, integration with Discord and Slack, and performance monitoring through logging. It has a fallback mechanism for model selection and is evaluated based on retrieval accuracy and model-generated responses. The implementation includes creating document embeddings, constructing the Q&A RAGPipeline, model selection, deployment on FastAPI, Discord, and Slack, logging and analysis with Weights & Biases Tables, and performance evaluation.
nextpy
Nextpy is a cutting-edge software development framework optimized for AI-based code generation. It provides guardrails for defining AI system boundaries, structured outputs for prompt engineering, a powerful prompt engine for efficient processing, better AI generations with precise output control, modularity for multiplatform and extensible usage, developer-first approach for transferable knowledge, and containerized & scalable deployment options. It offers 4-10x faster performance compared to Streamlit apps, with a focus on cooperation within the open-source community and integration of key components from various projects.
GraphRAG-Local-UI
GraphRAG Local with Interactive UI is an adaptation of Microsoft's GraphRAG, tailored to support local models and featuring a comprehensive interactive user interface. It allows users to leverage local models for LLM and embeddings, visualize knowledge graphs in 2D or 3D, manage files, settings, and queries, and explore indexing outputs. The tool aims to be cost-effective by eliminating dependency on costly cloud-based models and offers flexible querying options for global, local, and direct chat queries.
llmesh
LLM Agentic Tool Mesh is a platform by HPE Athonet that democratizes Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) by enabling users to create tools and web applications using Gen AI with Low or No Coding. The platform simplifies the integration process, focuses on key user needs, and abstracts complex libraries into easy-to-understand services. It empowers both technical and non-technical teams to develop tools related to their expertise and provides orchestration capabilities through an agentic Reasoning Engine based on Large Language Models (LLMs) to ensure seamless tool integration and enhance organizational functionality and efficiency.
ComfyUI-Tara-LLM-Integration
Tara is a powerful node for ComfyUI that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance and automate workflow processes. With Tara, you can create complex, intelligent workflows that refine and generate content, manage API keys, and seamlessly integrate various LLMs into your projects. It comprises nodes for handling OpenAI-compatible APIs, saving and loading API keys, composing multiple texts, and using predefined templates for OpenAI and Groq. Tara supports OpenAI and Grok models with plans to expand support to together.ai and Replicate. Users can install Tara via Git URL or ComfyUI Manager and utilize it for tasks like input guidance, saving and loading API keys, and generating text suitable for chaining in workflows.
persian-license-plate-recognition
The Persian License Plate Recognition (PLPR) system is a state-of-the-art solution designed for detecting and recognizing Persian license plates in images and video streams. Leveraging advanced deep learning models and a user-friendly interface, it ensures reliable performance across different scenarios. The system offers advanced detection using YOLOv5 models, precise recognition of Persian characters, real-time processing capabilities, and a user-friendly GUI. It is well-suited for applications in traffic monitoring, automated vehicle identification, and similar fields. The system's architecture includes modules for resident management, entrance management, and a detailed flowchart explaining the process from system initialization to displaying results in the GUI. Hardware requirements include an Intel Core i5 processor, 8 GB RAM, a dedicated GPU with at least 4 GB VRAM, and an SSD with 20 GB of free space. The system can be installed by cloning the repository and installing required Python packages. Users can customize the video source for processing and run the application to upload and process images or video streams. The system's GUI allows for parameter adjustments to optimize performance, and the Wiki provides in-depth information on the system's architecture and model training.
reductstore
ReductStore is a high-performance time series database designed for storing and managing large amounts of unstructured blob data. It offers features such as real-time querying, batching data, and HTTP(S) API for edge computing, computer vision, and IoT applications. The database ensures data integrity, implements retention policies, and provides efficient data access, making it a cost-effective solution for applications requiring unstructured data storage and access at specific time intervals.
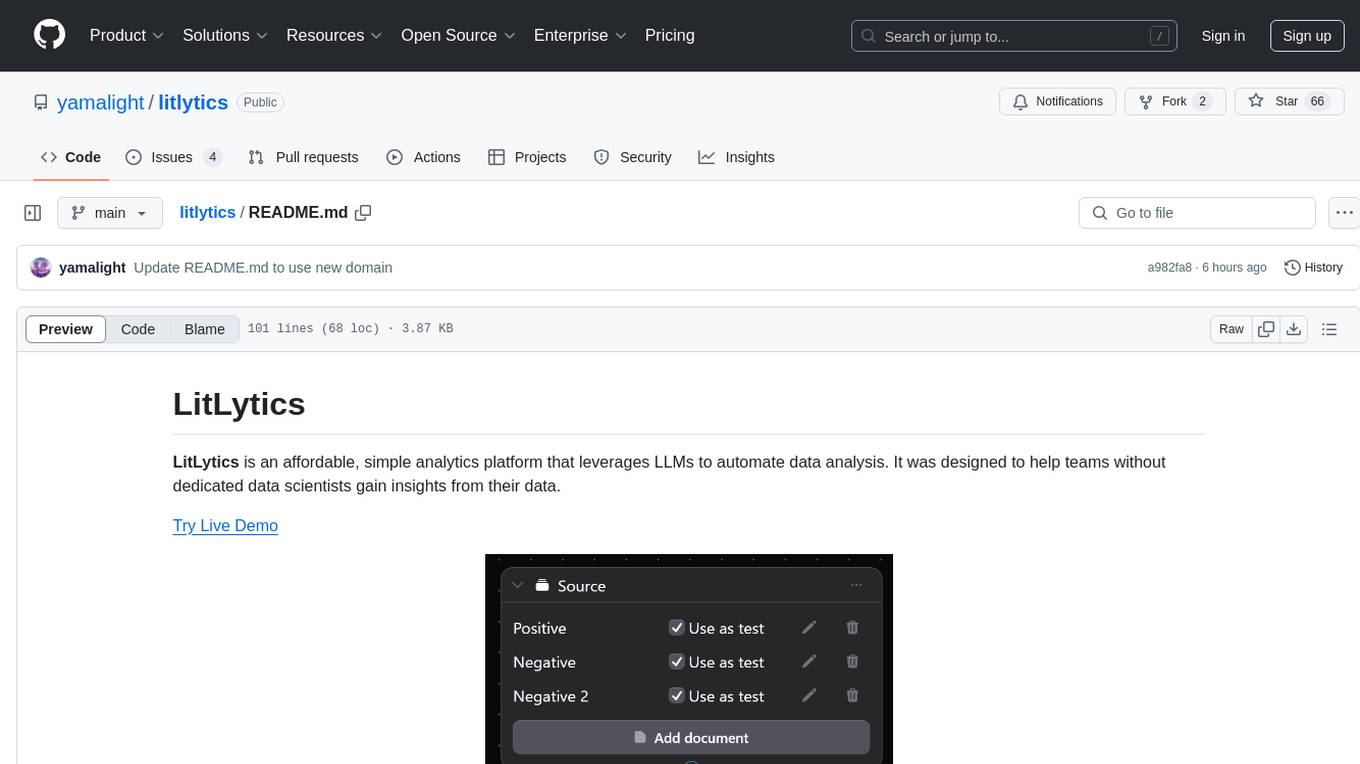
litlytics
LitLytics is an affordable analytics platform leveraging LLMs for automated data analysis. It simplifies analytics for teams without data scientists, generates custom pipelines, and allows customization. Cost-efficient with low data processing costs. Scalable and flexible, works with CSV, PDF, and plain text data formats.
For similar tasks

stride-gpt
STRIDE GPT is an AI-powered threat modelling tool that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate threat models and attack trees for a given application based on the STRIDE methodology. Users provide application details, such as the application type, authentication methods, and whether the application is internet-facing or processes sensitive data. The model then generates its output based on the provided information. It features a simple and user-friendly interface, supports multi-modal threat modelling, generates attack trees, suggests possible mitigations for identified threats, and does not store application details. STRIDE GPT can be accessed via OpenAI API, Azure OpenAI Service, Google AI API, or Mistral API. It is available as a Docker container image for easy deployment.
For similar jobs
ciso-assistant-community
CISO Assistant is a tool that helps organizations manage their cybersecurity posture and compliance. It provides a centralized platform for managing security controls, threats, and risks. CISO Assistant also includes a library of pre-built frameworks and tools to help organizations quickly and easily implement best practices.
PurpleLlama
Purple Llama is an umbrella project that aims to provide tools and evaluations to support responsible development and usage of generative AI models. It encompasses components for cybersecurity and input/output safeguards, with plans to expand in the future. The project emphasizes a collaborative approach, borrowing the concept of purple teaming from cybersecurity, to address potential risks and challenges posed by generative AI. Components within Purple Llama are licensed permissively to foster community collaboration and standardize the development of trust and safety tools for generative AI.
vpnfast.github.io
VPNFast is a lightweight and fast VPN service provider that offers secure and private internet access. With VPNFast, users can protect their online privacy, bypass geo-restrictions, and secure their internet connection from hackers and snoopers. The service provides high-speed servers in multiple locations worldwide, ensuring a reliable and seamless VPN experience for users. VPNFast is easy to use, with a user-friendly interface and simple setup process. Whether you're browsing the web, streaming content, or accessing sensitive information, VPNFast helps you stay safe and anonymous online.
taranis-ai
Taranis AI is an advanced Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) tool that leverages Artificial Intelligence to revolutionize information gathering and situational analysis. It navigates through diverse data sources like websites to collect unstructured news articles, utilizing Natural Language Processing and Artificial Intelligence to enhance content quality. Analysts then refine these AI-augmented articles into structured reports that serve as the foundation for deliverables such as PDF files, which are ultimately published.
NightshadeAntidote
Nightshade Antidote is an image forensics tool used to analyze digital images for signs of manipulation or forgery. It implements several common techniques used in image forensics including metadata analysis, copy-move forgery detection, frequency domain analysis, and JPEG compression artifacts analysis. The tool takes an input image, performs analysis using the above techniques, and outputs a report summarizing the findings.
h4cker
This repository is a comprehensive collection of cybersecurity-related references, scripts, tools, code, and other resources. It is carefully curated and maintained by Omar Santos. The repository serves as a supplemental material provider to several books, video courses, and live training created by Omar Santos. It encompasses over 10,000 references that are instrumental for both offensive and defensive security professionals in honing their skills.
AIMr
AIMr is an AI aimbot tool written in Python that leverages modern technologies to achieve an undetected system with a pleasing appearance. It works on any game that uses human-shaped models. To optimize its performance, users should build OpenCV with CUDA. For Valorant, additional perks in the Discord and an Arduino Leonardo R3 are required.
admyral
Admyral is an open-source Cybersecurity Automation & Investigation Assistant that provides a unified console for investigations and incident handling, workflow automation creation, automatic alert investigation, and next step suggestions for analysts. It aims to tackle alert fatigue and automate security workflows effectively by offering features like workflow actions, AI actions, case management, alert handling, and more. Admyral combines security automation and case management to streamline incident response processes and improve overall security posture. The tool is open-source, transparent, and community-driven, allowing users to self-host, contribute, and collaborate on integrations and features.

