terraform-provider-castai
Terraform provider for CAST AI platform
Stars: 52
Terraform Provider for CAST AI is a tool that allows users to manage their CAST AI resources using Terraform. It provides a seamless integration between Terraform and CAST AI platform, enabling users to define and manage their infrastructure as code. The provider supports various features such as setting up cluster configurations, managing node templates, and configuring autoscaler policies. Users can easily install the provider, pass API keys, and leverage the provider's functionalities to automate the deployment and management of their CAST AI resources.
README:
Website: https://www.cast.ai
To install this provider, put the following code into your Terraform configuration. Then, run terraform init.
terraform {
required_providers {
castai = {
source = "castai/castai"
version = "2.0.0" # can be omitted for the latest version
}
}
required_version = ">= 0.13"
}
provider "castai" {
api_token = "<<your-castai-api-key>>"
}Alternatively, you can pass api key via environment variable:
$ CASTAI_API_TOKEN=<<your-castai-api-key>> terraform planFor more logs use the log level flag:
$ TF_LOG=DEBUG terraform planMore examples can be found here.
Learn why required_providers block is required
in terraform 0.13 upgrade guide
.
Version 1.x.x no longer supports setting cluster configuration directly and castai_node_configuration resource should
be used. This applies to all castai_*_cluster resources.
Additionally, in case of castai_eks_cluster access_key_id and secret_access_key was removed in favor of assume_role_arn.
Having old configuration:
resource "castai_eks_cluster" "this" {
account_id = data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id
region = var.cluster_region
name = var.cluster_name
access_key_id = var.aws_access_key_id
secret_access_key = var.aws_secret_access_key
subnets = module.vpc.private_subnets
dns_cluster_ip = "10.100.0.10"
instance_profile_arn = var.instance_profile_arn
security_groups = [aws_security_group.test.id]
}New configuration will look like:
resource "castai_eks_cluster" "this" {
account_id = data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id
region = var.cluster_region
name = var.cluster_name
assume_role_arn = var.assume_role_arn
}
resource "castai_node_configuration" "test" {
name = "default"
cluster_id = castai_eks_cluster.this.id
subnets = module.vpc.private_subnets
eks {
instance_profile_arn = var.instance_profile_arn
dns_cluster_ip = "10.100.0.10"
security_groups = [aws_security_group.test.id]
}
}
resource "castai_node_configuration_default" "test" {
cluster_id = castai_eks_cluster.test.id
configuration_id = castai_node_configuration.test.id
}If you have used castai-eks-cluster module follow:
https://github.com/castai/terraform-castai-eks-cluster/blob/main/README.md#migrating-from-2xx-to-3xx
Version 4.x.x changed:
-
castai_eks_clusteridtype from data source to resource
Having old configuration:
data "castai_eks_clusterid" "cluster_id" {
account_id = data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id
region = var.cluster_region
cluster_name = var.cluster_name
}and usage data.castai_eks_clusterid.cluster_id.id
New configuration will look like:
resource "castai_eks_clusterid" "cluster_id" {
account_id = data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id
region = var.cluster_region
cluster_name = var.cluster_name
}
and usage castai_eks_clusterid.cluster_id.id
- removal of
castai_cluster_tokenresource in favour ofcluster_tokenincastai_eks_cluster
Having old configuration:
resource "castai_cluster_token" "this" {
cluster_id = castai_eks_cluster.this.id
}
resource "castai_eks_cluster" "this" {
account_id = data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id
region = var.cluster_region
name = var.cluster_name
}
and usage castai_cluster_token.this.cluster_token
New configuration will look like:
resource "castai_eks_cluster" "this" {
account_id = data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id
region = var.cluster_region
name = var.cluster_name
}and usage castai_eks_cluster.this.cluster_token
- default value for
imds_v1was change totrue, in case that your configuration didn't had this specified please explicitly set this value tofalse
Version 5.x.x changed:
- Terraform provider adopts default node template concept
- Removed
spotInstancesfield fromautoscaler_policies_jsonattribute incastai_autoscaler_policiesresource - Removed
customInstancesEnabledfield fromautoscaler_policies_jsonattribute incastai_autoscaler_policiesresource - Removed
nodeConstraintsfield fromautoscaler_policies_jsonattribute incastai_autoscaler_policiesresource - All valid fields which were removed from
autoscaler_policies_jsonhave mapping incastai_node_templateresource
Old configuration:
resource "castai_autoscaler" "castai_autoscaler_policies" {
cluster_id = data.castai_eks_clusterid.cluster_id.id // or other reference
autoscaler_policies_json = <<-EOT
{
"enabled": true,
"unschedulablePods": {
"enabled": true,
"customInstancesEnabled": true,
"nodeConstraints": {
"enabled": true,
"minCpuCores": 2,
"maxCpuCores": 4,
"minRamMib": 3814,
"maxRamMib": 16384
}
},
"spotInstances": {
"enabled": true,
"clouds": ["gcp"],
"spotBackups": {
"enabled": true
}
},
"nodeDownscaler": {
"enabled": true,
"emptyNodes": {
"enabled": true
},
"evictor": {
"aggressiveMode": true,
"cycleInterval": "5m10s",
"dryRun": false,
"enabled": true,
"nodeGracePeriodMinutes": 10,
"scopedMode": false
}
}
}
EOT
}New configuration:
resource "castai_autoscaler" "castai_autoscaler_policies" {
cluster_id = data.castai_eks_clusterid.cluster_id.id // or other reference
autoscaler_policies_json = <<-EOT
{
"enabled": true,
"unschedulablePods": {
"enabled": true
},
"nodeDownscaler": {
"enabled": true,
"emptyNodes": {
"enabled": true
},
"evictor": {
"aggressiveMode": true,
"cycleInterval": "5m10s",
"dryRun": false,
"enabled": true,
"nodeGracePeriodMinutes": 10,
"scopedMode": false
}
}
}
EOT
}
resource "castai_node_template" "default_by_castai" {
cluster_id = data.castai_eks_clusterid.cluster_id.id // or other reference
name = "default-by-castai"
configuration_id = castai_node_configuration.default.id // or other reference
is_default = true
should_taint = false
custom_instances_enabled = true
constraints {
architectures = [
"amd64",
"arm64",
]
on_demand = true
spot = true
use_spot_fallbacks = true
min_cpu = 2
max_cpu = 4
min_memory = 3814
max_memory = 16384
}
depends_on = [ castai_autoscaler.castai_autoscaler_policies ]
}If you have used castai-eks-cluster or other modules follow:
https://github.com/castai/terraform-castai-eks-cluster/blob/main/README.md#migrating-from-5xx-to-6xx
Note: default-by-castai default node template is created in background by CAST.ai, when creating managed resource
in Terraform the provider will handle create as update. Importing default-by-castai default node template into Terraform
state is not needed if you follow the migration guide. Despite not being needed it can be performed and everything
will work correctly.
Example of node template import:
terraform import castai_node_template.default_by_castai 105e6fa3-20b1-424e-v589-9a64d1eeabea/default-by-castaiVersion 6.x.x changed:
- Removed
custom_labelattribute incastai_node_templateresource. Usecustom_labelsinstead.
Old configuration:
module "castai-aks-cluster" {
node_templates = {
spot_tmpl = {
custom_label = {
key = "custom-label-key-1"
value = "custom-label-value-1"
}
}
}
}New configuration:
module "castai-aks-cluster" {
node_templates = {
spot_tmpl = {
custom_labels = {
custom-label-key-1 = "custom-label-value-1"
}
}
}
}For more information for castai-aks-cluster module follow:
https://github.com/castai/terraform-castai-aks/blob/main/README.md#migrating-from-2xx-to-3xx
If you have used castai-eks-cluster or other modules follow:
https://github.com/castai/terraform-castai-eks-cluster/blob/main/README.md#migrating-from-6xx-to-7xx
If you have used castai-gke-cluster or other modules follow:
https://github.com/castai/terraform-castai-gke-cluster/blob/main/README.md#migrating-from-3xx-to-4xx
Version 7.x.x changed:
- Removed
compute_optimizedandstorage_optimizedattributes incastai_node_templateresource,constraintsobject. Usecompute_optimized_stateandstorage_optimized_stateinstead.
Old configuration:
module "castai-aks-cluster" {
node_templates = {
spot_tmpl = {
constraints = {
compute_optimized = false
storage_optimized = true
}
}
}
}New configuration:
module "castai-aks-cluster" {
node_templates = {
spot_tmpl = {
constraints = {
compute_optimized_state = "disabled"
storage_optimized_state = "enabled"
}
}
}
}- [v7.4.X] Deprecated
autoscaler_policies_jsonattribute incastai_autoscalerresource. Useautoscaler_settingsinstead.
Old configuration:
resource "castai_autoscaler" "castai_autoscaler_policies" {
cluster_id = data.castai_eks_clusterid.cluster_id.id // or other reference
autoscaler_policies_json = <<-EOT
{
"enabled": true,
"unschedulablePods": {
"enabled": true
},
"nodeDownscaler": {
"enabled": true,
"emptyNodes": {
"enabled": true
},
"evictor": {
"aggressiveMode": false,
"cycleInterval": "5m10s",
"dryRun": false,
"enabled": true,
"nodeGracePeriodMinutes": 10,
"scopedMode": false
}
},
"nodeTemplatesPartialMatchingEnabled": false,
"clusterLimits": {
"cpu": {
"maxCores": 20,
"minCores": 1
},
"enabled": true
}
}
EOT
}New configuration:
resource "castai_autoscaler" "castai_autoscaler_policies" {
cluster_id = data.castai_eks_clusterid.cluster_id.id // or other reference
autoscaler_settings {
enabled = true
node_templates_partial_matching_enabled = false
unschedulable_pods {
enabled = true
}
node_downscaler {
enabled = true
empty_nodes {
enabled = false
}
evictor {
aggressive_mode = false
cycle_interval = "5m10s"
dry_run = false
enabled = true
node_grace_period_minutes = 10
scoped_mode = false
}
}
cluster_limits {
enabled = true
cpu {
max_cores = 20
min_cores = 1
}
}
}
}For more information for castai-aks-cluster module follow:
https://github.com/castai/terraform-castai-aks/blob/main/README.md#migrating-from-3xx-to-4xx
If you have used castai-eks-cluster or other modules follow:
https://github.com/castai/terraform-castai-eks-cluster/blob/main/README.md#migrating-from-7xx-to-8xx
If you have used castai-gke-cluster or other modules follow:
https://github.com/castai/terraform-castai-gke-cluster/blob/main/README.md#migrating-from-4xx-to-5xx
Starting with version v7.9.3, several fields within the castai_autoscaler resource (specifically under the autoscaler_settings block) have been deprecated.
These fields are planned for removal in a future major version. Users are encouraged to update their configurations to use the new recommended approaches to ensure compatibility and leverage the latest features. Most of these functionalities have been consolidated into the castai_node_template resource (default template) for a more unified approach to node configuration.
Summary of Deprecated Fields and New Locations:
-
Headroom Configuration:
-
Deprecated:
autoscaler_settings.headroom,autoscaler_settings.headroom_spot. These configurations are deprecated. For managing cluster headroom, please refer to the CAST AI Autoscaler FAQ for recommended strategies, such as using low-priority placeholder deployments.
-
Deprecated:
-
Node Constraints for Unschedulable Pods:
-
Deprecated:
autoscaler_settings.unschedulable_pods.node_constraints(including its fields likemin_cpu_cores,max_cpu_cores,min_ram_mib,max_ram_mib). Use theconstraintsblock (with fields likemin_cpu,max_cpu,min_memory,max_memory) within the defaultcastai_node_templateresource. -
Deprecated:
autoscaler_settings.unschedulable_pods.node_constraints.custom_instances_enabled. Use the top-levelcustom_instances_enabledfield in the defaultcastai_node_templateresource.
-
Deprecated:
-
Spot Instance Configuration:
-
Deprecated: The entire
autoscaler_settings.spot_instancesblock.-
spot_instances.enabled: New Location: Useconstraints.spotin the defaultcastai_node_template. -
spot_instances.max_reclaim_rate: Note: This field is deprecated and has no direct replacement in the node template. Setting it will have no effect. -
spot_instances.spot_backups: New Location: Useconstraints.use_spot_fallbacksandconstraints.fallback_restore_rate_secondsin the defaultcastai_node_template.
-
-
Deprecated:
autoscaler_settings.spot_diversity_enabled. Useconstraints.enable_spot_diversityin the defaultcastai_node_template. -
Deprecated:
autoscaler_settings.spot_diversity_price_increase_limit. Useconstraints.spot_diversity_price_increase_limit_percentin the defaultcastai_node_template.
-
Deprecated: The entire
-
Spot Interruption Predictions:
-
Deprecated:
autoscaler_settings.spot_interruption_predictionsblock. Use the top-levelspot_interruption_predictions_enabledandspot_interruption_predictions_typefields in the defaultcastai_node_templateresource.
-
Deprecated:
Make sure you have Go installed on your machine (please check the requirements).
To build the provider locally:
$ git clone https://github.com/CastAI/terraform-provider-castai.git
$ cd terraform-provider-castai
$ make buildAfter you build the provider, you have to set the ~/.terraformrc configuration to let terraform know you want to use local provider:
provider_installation {
dev_overrides {
"castai/castai" = "<path-to-terraform-provider-castai-repository>"
}
direct {}
}make build builds the provider and install symlinks to that build for all terraform projects in examples/* dir.
Now you can work on examples/localdev.
Whenever you make changes to the provider re-run make build.
You'll need to run terraform init in your terraform project again since the binary has changed.
To run unit tests:
$ make testThis repository contains a github action to automatically build and publish assets for release when
tag is pushed with pattern v* (ie. v0.1.0).
Gorelaser is used to produce build artifacts matching the layout required to publish the provider in the Terraform Registry.
Releases will appear as drafts. Once marked as published on the GitHub Releases page, they will become available via the Terraform Registry.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for terraform-provider-castai
Similar Open Source Tools

terraform-provider-castai
Terraform Provider for CAST AI is a tool that allows users to manage their CAST AI resources using Terraform. It provides a seamless integration between Terraform and CAST AI platform, enabling users to define and manage their infrastructure as code. The provider supports various features such as setting up cluster configurations, managing node templates, and configuring autoscaler policies. Users can easily install the provider, pass API keys, and leverage the provider's functionalities to automate the deployment and management of their CAST AI resources.

clawlet
Clawlet is an ultra-lightweight and efficient personal AI assistant that comes as a single binary with no CGO, runtime, or dependencies. It features hybrid semantic memory search and is inspired by OpenClaw and nanobot. Users can easily download Clawlet from GitHub Releases and drop it on any machine to enable memory search functionality. The tool supports various LLM providers like OpenAI, OpenRouter, Anthropic, Gemini, and local endpoints. Users can configure Clawlet for memory search setup and chat app integrations for platforms like Telegram, WhatsApp, Discord, and Slack. Clawlet CLI provides commands for initializing workspace, running the agent, managing channels, scheduling jobs, and more.
crush
Crush is a versatile tool designed to enhance coding workflows in your terminal. It offers support for multiple LLMs, allows for flexible switching between models, and enables session-based work management. Crush is extensible through MCPs and works across various operating systems. It can be installed using package managers like Homebrew and NPM, or downloaded directly. Crush supports various APIs like Anthropic, OpenAI, Groq, and Google Gemini, and allows for customization through environment variables. The tool can be configured locally or globally, and supports LSPs for additional context. Crush also provides options for ignoring files, allowing tools, and configuring local models. It respects `.gitignore` files and offers logging capabilities for troubleshooting and debugging.
capsule
Capsule is a secure and durable runtime for AI agents, designed to coordinate tasks in isolated environments. It allows for long-running workflows, large-scale processing, autonomous decision-making, and multi-agent systems. Tasks run in WebAssembly sandboxes with isolated execution, resource limits, automatic retries, and lifecycle tracking. It enables safe execution of untrusted code within AI agent systems.
llm-metadata
LLM Metadata is a lightweight static API designed for discovering and integrating LLM metadata. It provides a high-throughput friendly, static-by-default interface that serves static JSON via GitHub Pages. The sources for the metadata include models.dev/api.json and contributions from the basellm community. The tool allows for easy rebuilding on change and offers various scripts for compiling TypeScript, building the API, and managing the project. It also supports internationalization for both documentation and API, enabling users to add new languages and localize capability labels and descriptions. The tool follows an auto-update policy based on a configuration file and allows for directory-based overrides for providers and models, facilitating customization and localization of metadata.
smithers
Smithers is a tool for declarative AI workflow orchestration using React components. It allows users to define complex multi-agent workflows as component trees, ensuring composability, durability, and error handling. The tool leverages React's re-rendering mechanism to persist outputs to SQLite, enabling crashed workflows to resume seamlessly. Users can define schemas for task outputs, create workflow instances, define agents, build workflow trees, and run workflows programmatically or via CLI. Smithers supports components for pipeline stages, structured output validation with Zod, MDX prompts, validation loops with Ralph, dynamic branching, and various built-in tools like read, edit, bash, grep, and write. The tool follows a clear workflow execution process involving defining, rendering, executing, re-rendering, and repeating tasks until completion, all while storing task results in SQLite for fault tolerance.
ogpt.nvim
OGPT.nvim is a Neovim plugin that enables users to interact with various language models (LLMs) such as Ollama, OpenAI, TextGenUI, and more. Users can engage in interactive question-and-answer sessions, have persona-based conversations, and execute customizable actions like grammar correction, translation, keyword generation, docstring creation, test addition, code optimization, summarization, bug fixing, code explanation, and code readability analysis. The plugin allows users to define custom actions using a JSON file or plugin configurations.
Webscout
Webscout is an all-in-one Python toolkit for web search, AI interaction, digital utilities, and more. It provides access to diverse search engines, cutting-edge AI models, temporary communication tools, media utilities, developer helpers, and powerful CLI interfaces through a unified library. With features like comprehensive search leveraging Google and DuckDuckGo, AI powerhouse for accessing various AI models, YouTube toolkit for video and transcript management, GitAPI for GitHub data extraction, Tempmail & Temp Number for privacy, Text-to-Speech conversion, GGUF conversion & quantization, SwiftCLI for CLI interfaces, LitPrinter for styled console output, LitLogger for logging, LitAgent for user agent generation, Text-to-Image generation, Scout for web parsing and crawling, Awesome Prompts for specialized tasks, Weather Toolkit, and AI Search Providers.
Webscout
WebScout is a versatile tool that allows users to search for anything using Google, DuckDuckGo, and phind.com. It contains AI models, can transcribe YouTube videos, generate temporary email and phone numbers, has TTS support, webai (terminal GPT and open interpreter), and offline LLMs. It also supports features like weather forecasting, YT video downloading, temp mail and number generation, text-to-speech, advanced web searches, and more.
llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a plugin for Neovim that enables code completion using LLM models. It supports 'ghost-text' code completion similar to Copilot and allows users to choose their model for code generation via HTTP requests. The plugin interfaces with multiple backends like Hugging Face, Ollama, Open AI, and TGI, providing flexibility in model selection and configuration. Users can customize the behavior of suggestions, tokenization, and model parameters to enhance their coding experience. llm.nvim also includes commands for toggling auto-suggestions and manually requesting suggestions, making it a versatile tool for developers using Neovim.
nexus
Nexus is a tool that acts as a unified gateway for multiple LLM providers and MCP servers. It allows users to aggregate, govern, and control their AI stack by connecting multiple servers and providers through a single endpoint. Nexus provides features like MCP Server Aggregation, LLM Provider Routing, Context-Aware Tool Search, Protocol Support, Flexible Configuration, Security features, Rate Limiting, and Docker readiness. It supports tool calling, tool discovery, and error handling for STDIO servers. Nexus also integrates with AI assistants, Cursor, Claude Code, and LangChain for seamless usage.

ollama-ex
Ollama is a powerful tool for running large language models locally or on your own infrastructure. It provides a full implementation of the Ollama API, support for streaming requests, and tool use capability. Users can interact with Ollama in Elixir to generate completions, chat messages, and perform streaming requests. The tool also supports function calling on compatible models, allowing users to define tools with clear descriptions and arguments. Ollama is designed to facilitate natural language processing tasks and enhance user interactions with language models.
mistreevous
Mistreevous is a library written in TypeScript for Node and browsers, used to declaratively define, build, and execute behaviour trees for creating complex AI. It allows defining trees with JSON or a minimal DSL, providing in-browser editor and visualizer. The tool offers methods for tree state, stepping, resetting, and getting node details, along with various composite, decorator, leaf nodes, callbacks, guards, and global functions/subtrees. Version history includes updates for node types, callbacks, global functions, and TypeScript conversion.
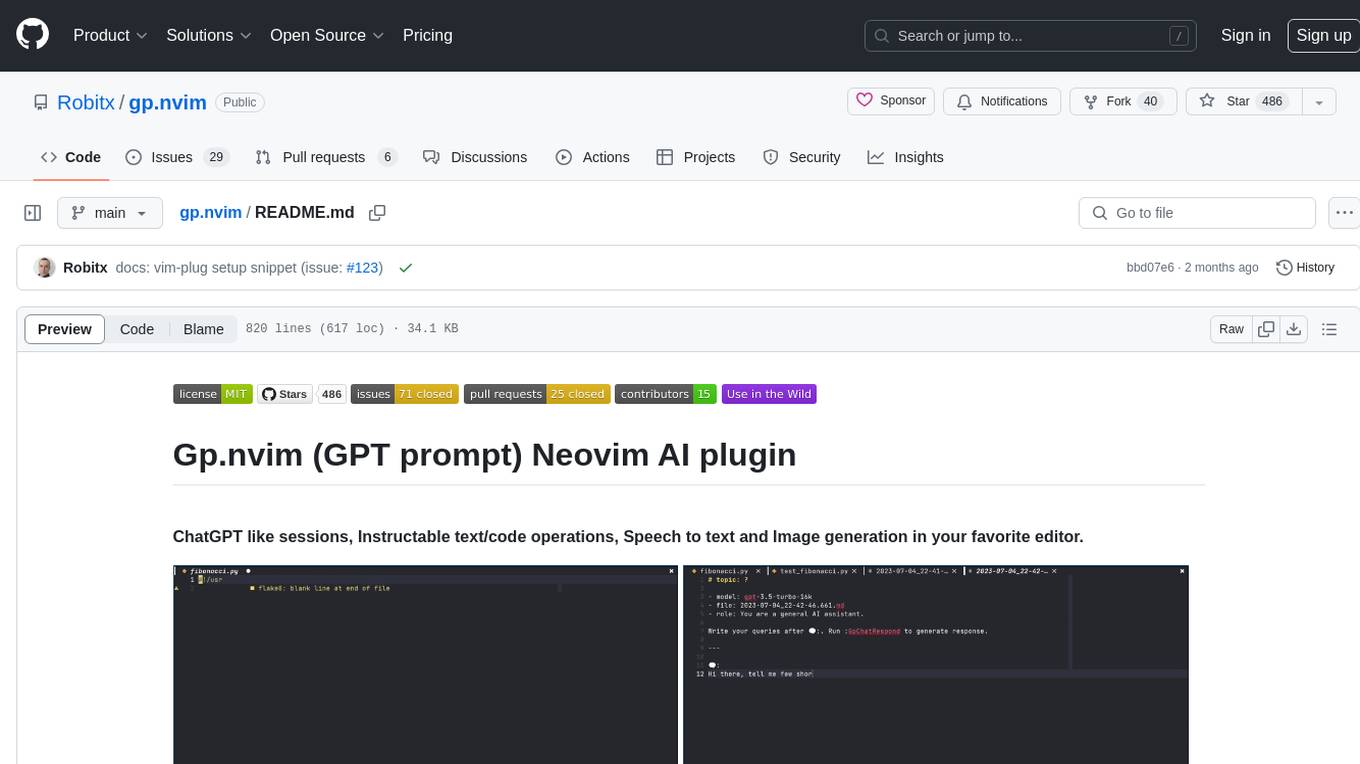
gp.nvim
Gp.nvim (GPT prompt) Neovim AI plugin provides a seamless integration of GPT models into Neovim, offering features like streaming responses, extensibility via hook functions, minimal dependencies, ChatGPT-like sessions, instructable text/code operations, speech-to-text support, and image generation directly within Neovim. The plugin aims to enhance the Neovim experience by leveraging the power of AI models in a user-friendly and native way.
python-utcp
The Universal Tool Calling Protocol (UTCP) is a secure and scalable standard for defining and interacting with tools across various communication protocols. UTCP emphasizes scalability, extensibility, interoperability, and ease of use. It offers a modular core with a plugin-based architecture, making it extensible, testable, and easy to package. The repository contains the complete UTCP Python implementation with core components and protocol-specific plugins for HTTP, CLI, Model Context Protocol, file-based tools, and more.
For similar tasks

terraform-provider-castai
Terraform Provider for CAST AI is a tool that allows users to manage their CAST AI resources using Terraform. It provides a seamless integration between Terraform and CAST AI platform, enabling users to define and manage their infrastructure as code. The provider supports various features such as setting up cluster configurations, managing node templates, and configuring autoscaler policies. Users can easily install the provider, pass API keys, and leverage the provider's functionalities to automate the deployment and management of their CAST AI resources.
For similar jobs

AirGo
AirGo is a front and rear end separation, multi user, multi protocol proxy service management system, simple and easy to use. It supports vless, vmess, shadowsocks, and hysteria2.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
llm-code-interpreter
The 'llm-code-interpreter' repository is a deprecated plugin that provides a code interpreter on steroids for ChatGPT by E2B. It gives ChatGPT access to a sandboxed cloud environment with capabilities like running any code, accessing Linux OS, installing programs, using filesystem, running processes, and accessing the internet. The plugin exposes commands to run shell commands, read files, and write files, enabling various possibilities such as running different languages, installing programs, starting servers, deploying websites, and more. It is powered by the E2B API and is designed for agents to freely experiment within a sandboxed environment.

pezzo
Pezzo is a fully cloud-native and open-source LLMOps platform that allows users to observe and monitor AI operations, troubleshoot issues, save costs and latency, collaborate, manage prompts, and deliver AI changes instantly. It supports various clients for prompt management, observability, and caching. Users can run the full Pezzo stack locally using Docker Compose, with prerequisites including Node.js 18+, Docker, and a GraphQL Language Feature Support VSCode Extension. Contributions are welcome, and the source code is available under the Apache 2.0 License.
learn-generative-ai
Learn Cloud Applied Generative AI Engineering (GenEng) is a course focusing on the application of generative AI technologies in various industries. The course covers topics such as the economic impact of generative AI, the role of developers in adopting and integrating generative AI technologies, and the future trends in generative AI. Students will learn about tools like OpenAI API, LangChain, and Pinecone, and how to build and deploy Large Language Models (LLMs) for different applications. The course also explores the convergence of generative AI with Web 3.0 and its potential implications for decentralized intelligence.
gcloud-aio
This repository contains shared codebase for two projects: gcloud-aio and gcloud-rest. gcloud-aio is built for Python 3's asyncio, while gcloud-rest is a threadsafe requests-based implementation. It provides clients for Google Cloud services like Auth, BigQuery, Datastore, KMS, PubSub, Storage, and Task Queue. Users can install the library using pip and refer to the documentation for usage details. Developers can contribute to the project by following the contribution guide.
fluid
Fluid is an open source Kubernetes-native Distributed Dataset Orchestrator and Accelerator for data-intensive applications, such as big data and AI applications. It implements dataset abstraction, scalable cache runtime, automated data operations, elasticity and scheduling, and is runtime platform agnostic. Key concepts include Dataset and Runtime. Prerequisites include Kubernetes version > 1.16, Golang 1.18+, and Helm 3. The tool offers features like accelerating remote file accessing, machine learning, accelerating PVC, preloading dataset, and on-the-fly dataset cache scaling. Contributions are welcomed, and the project is under the Apache 2.0 license with a vendor-neutral approach.
aiges
AIGES is a core component of the Athena Serving Framework, designed as a universal encapsulation tool for AI developers to deploy AI algorithm models and engines quickly. By integrating AIGES, you can deploy AI algorithm models and engines rapidly and host them on the Athena Serving Framework, utilizing supporting auxiliary systems for networking, distribution strategies, data processing, etc. The Athena Serving Framework aims to accelerate the cloud service of AI algorithm models and engines, providing multiple guarantees for cloud service stability through cloud-native architecture. You can efficiently and securely deploy, upgrade, scale, operate, and monitor models and engines without focusing on underlying infrastructure and service-related development, governance, and operations.