
generative-ai-application-builder-on-aws
Generative AI Application Builder on AWS facilitates the development, rapid experimentation, and deployment of generative artificial intelligence (AI) applications without requiring deep experience in AI. The solution includes integrations with Amazon Bedrock and its included LLMs, such as Amazon Titan, and pre-built connectors for 3rd-party LLMs.
Stars: 143
The Generative AI Application Builder on AWS (GAAB) is a solution that provides a web-based management dashboard for deploying customizable Generative AI (Gen AI) use cases. Users can experiment with and compare different combinations of Large Language Model (LLM) use cases, configure and optimize their use cases, and integrate them into their applications for production. The solution is targeted at novice to experienced users who want to experiment and productionize different Gen AI use cases. It uses LangChain open-source software to configure connections to Large Language Models (LLMs) for various use cases, with the ability to deploy chat use cases that allow querying over users' enterprise data in a chatbot-style User Interface (UI) and support custom end-user implementations through an API.
README:
| ✨ Generative AI Application Builder on AWS | 🚧 Feature request | 🐛 Bug Report | 📖 Implementation Guide |
NOTE:
- If you want to use the solution without any custom changes, navigate to Solution Landing Page and click the "Launch in the AWS Console" in the Deployment options for a 1-click deployment into your AWS Console.
- If you are upgrading from v1.4.x to the current version, please follow the steps in this section of the implementation guide.
The Generative AI Application Builder on AWS solution (GAAB) provides a web-based management dashboard to deploy customizable Generative AI (Gen AI) use cases. This Deployment dashboard allows customers to deploy, experiment with, and compare different combinations of Large Language Model (LLM) use cases. Once customers have successfully configured and optimized their use case, they can take their deployment into production and integrate it within their applications.
The Generative AI Application Builder is published under an Apache 2.0 license and is targeted for novice to experienced users who want to experiment and productionize different Gen AI use cases. The solution uses LangChain open-source software (OSS) to configure connections to your choice of Large Language Models (LLMs) for different use cases. The first release of GAAB allows users to deploy chat use cases which allow the ability to query over users' enterprise data in a chatbot-style User Interface (UI), along with an API to support custom end-user implementations.
Some of the features of GAAB are:
- Rapid experimentation with ability to productionize at scale
- Extendable and modularized architecture using nested Amazon CloudFormation stacks
- Enterprise ready for company-specific data to tackle real-world business problems
- Integration with Amazon Bedrock and Amazon SageMaker as LLM providers
- Multi-LLM comparison and experimentation with metric tracking using Amazon CloudWatch dashboards
- Growing list of model providers and Gen AI use cases
For a detailed solution implementation guide, refer to The Generative AI Application Builder on AWS
- Architecture Overview
- Deployment
- Source code
- SageMaker Model Input Documentation
- Creating a custom build
There are 3 unique user personas that are referred to in the solution walkthrough below:
- The DevOps user is responsible for deploying the solution within the AWS account and for managing the infrastructure, updating the solution, monitoring performance, and maintaining the overall health and lifecycle of the solution.
- The admin users are responsible for managing the content contained within the deployment. These users gets access to the Deployment dashboard UI and is primarily responsible for curating the business user experience. This is our primary target customer.
- The business users represents the individuals who the use case has been deployed for. They are the consumers of the knowledge base and the customer responsible for evaluating and experimenting with the LLMs.
NOTE:
- You have the option of deploying the solution as a VPC enabled configuration. With a VPC enabled configuration, you can choose
- if the solution should build the VPC for this deployment.
- if you would like to deploy the solution in a VPC existing in your AWS account.
- To see the VPC related architecture diagrams, please visit the implementation guide.
When the DevOps user deploys the Deployment Dashboard, the following components are deployed in the AWS account:
- The admin users can log in to the deployed Deployment Dashboard UI.
- Amazon CloudFront delivers the web UI which is hosted in an Amazon S3 bucket.
- AWS WAF protects the APIs from attacks. This solution configures a set of rules called a web access control list (web ACL) that allows, blocks, or counts web requests based on configurable, user-defined web security rules and conditions.
- The web UI leverages a set of REST APIs that are exposed using Amazon API Gateway.
- Amazon Cognito authenticates users and backs both the Cloudfront web UI and API Gateway. An Amazon DynamoDB table is used to store the AWS IAM policy of authorized users.
- AWS Lambda is used to provide the business logic for the REST endpoints. This Backing Lambda will manage and create the necessary resources to perform use case deployments using AWS Cloudformation.
- Amazon DynamoDB is used to store the list of deployments.
- When a new use case is created by the admin user, the Backing Lambda will initiate a CloudFormation stack creation event for the requested use case.
- All of the LLM configuration options provided by the admin user in the deployment wizard are saved in DynamoDB. The deployment uses this DynamoDB table to configure the LLM at runtime.
- Using Amazon Cloudwatch, this solution collects operational metrics from various services to generate custom dashboards that allow you to monitor the solution's performance and operational health.
Note: Although the Deployment dashboard can be launched in most AWS regions, the deployed use cases have some restrictions based on service availability. See Supported AWS Regions in the Implementation Guide for more details.
Once the Deployment Dashboard is deployed, the admin user can then deploy multiple use case stacks. When a use case stack is deployed by the admin user, the following components are deployed in the AWS account:
- Admin users deploy the use case using the Deployment dashboard. Business users log in to the use case UI.
- Amazon CloudFront delivers the web UI which is hosted in an Amazon S3 bucket.
- The web UI leverages a WebSocket integration built using Amazon API Gateway. The API Gateway is backed by a custom Lambda Authorizer function, which returns the appropriate AWS IAM policy based on the Amazon Cognito group the authenticating user is part of. The policy is stored in Amazon DynamoDB.
- Amazon Cognito authenticates users and backs both the Cloudfront web UI and API Gateway.
- Incoming requests from the business user are passed from API Gateway to an Amazon SQS queue and then to the LangChain Orchestrator. The LangChain Orchestrator is a collection of Lambda functions and layers that provide the business logic for fulfilling requests coming from the business user. The queue enables the asynchronous operation of the API Gateway to Lambda integration. The queue passes connection information to the Lambda functions which will then post results directly back to the API Gateway websocket connection to support long running inference calls.
- The LangChain Orchestrator uses Amazon DynamoDB to get the configured LLM options and necessary session information (such as the chat history).
- If the deployment has a knowledge base configured, then the LangChain Orchestrator leverages Amazon Kendra or Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrock to run a search query to retrieve document excerpts.
- Using the chat history, query, and context from the knowledge base, the LangChain Orchestrator creates the final prompt and sends the request to the LLM hosted on Amazon Bedrock or Amazon SageMaker.
- When the response comes back from the LLM, the LangChain Orchestrator streams the response back through the API Gateway WebSocket to be consumed by the client application.
- Using Amazon CloudWatch, this solution collects operational metrics from various services to generate custom dashboards that allow you to monitor the deployment’s performance and operational health.
NOTE:
- To use Amazon Bedrock, you must request access to models before they are available for use. Refer to Model access in the Amazon Bedrock User Guide for more details.
- You can also test the UI project locally by deploying the API endpoints and the rest of the infrastructure. To do so, follow either of the below two options and then refer Deployment Dashboard and Chat UI project for details.
There are two options for deployment into your AWS account:
Following are pre-requisites to build and deploy locally:
- Docker
- Nodejs 20.x
- CDK v2.118.0
-
Python >= 3.11, <=3.12.1
- Note: normal python installations should include support for
ensurepipandpip; however, if running in an environment without these packages you will need to manually install them (e.g. a minimal docker image). See pip's installation guide for details.
- Note: normal python installations should include support for
- AWS CLI
- jq
Note: Configure the AWS CLI with your AWS credentials or have them exported in the CLI terminal environment. In case the credentials are invalid or expired, running cdk deploy produces an error.
Also, if you have not run cdk bootstrap in this account and region, please follow the instructions here to execute cdk bootstrap as a one time process before proceeding with the below steps.
After cloning the repo from GitHub, complete the following steps:
NOTE:
- Please update the
cdk-asset-bucketproperty insource/infrastructure/cdk.json. The value of this property should be the bucket name thatcdk bootstrapprocess created. Unless a bucket name is configured, thecdk bootstrapprocess creates a bucket in the following format:cdk-hnb659fds-assets-<aws-account-number>-<region>(where is the AWS Account ID where the solution is being deployed in the specific ). The repo currently has the value set as the following:
If deployed with this default value, the use case creation from deployment dashboards would fail."cdk-asset-bucket": "cdk-hnb659fds-assets-123456789012-us-east-1"
cd <project-directory>/source/infrastructure
npm install
npm run build
cdk synth
cdk deploy DeploymentPlatformStack --parameters AdminUserEmail=<replace with admin user's email>
Note: Because cdk deploy is executed with a stack name, it does not synthesize the other CloudFormation stacks in the infrastructure folder. To ensure all stacks are synthesized based on the infrastructure code changes, please ensure to cdk synth. For a complete list of cdk commands that can be run, see Toolkit commands
For the deployment dashboard to deploy LLM chat use cases, you would additionally need to stage synthesized CDK assets (such as lambdas, synthesized CloudFormation templates, etc.) from the source/infrastructure/cdk.out directory to a configured S3 bucket in your account from where these resources will be pulled from at the time of deployment. To make it easy to stage these assets, you can use the source/stage-assets.sh script. This script should be run from the source directory.
cd <project-directory>/source
./stage-assets.sh
When run, the script looks like this:
>>> ./stage-assets.sh
This script should be run from the 'source' folder
The region to upload CDK artifacts to (default:us-east-1)?
>>> us-west-2
>>> All assets will be uploaded to cdk-hnb659fds-assets-123456789-us-west-2
>>> Do you want to proceed? (y/n) y
You must provide the full region name as the first input to the script as shown in the above example.
Note: Assets must be staged every time there is a change in the codebase to have the most up-to-date staged assets. It is also recommend to run cdk synth before staging.
Refer section Creating a custom build
├── CHANGELOG.md
├── CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
├── CONTRIBUTING.md
├── Config
├── LICENSE.txt
├── NOTICE.txt
├── README.md
├── buildspec.yml
├── deployment
│ ├── build-open-source-dist.sh
│ ├── build-s3-dist.sh
│ ├── cdk-solution-helper
│ ├── clean-for-scan.sh
│ ├── get-cdk-version.js
│ └── manifest.yaml
| ├── run-unit-tests.sh [shell script that can run unit tests for the entire project]
├── pyproject.toml
├── pytest.ini
├── sonar-project.properties
└── source
├── images
├── infrastructure [CDK infrastructure]
├── lambda [Lambda functions for the application]
├── pre-build-lambda-layers.sh [pre-builds lambda layers for the project]
├── scripts [standalone utility scripts]
├── stage-assets.sh
├── test
├── ui-chat [Web App project for chat UI]
└── ui-deployment [Web App project for deployment dashboard UI]
└── docs
The project provides a docs folder which gives you access to sample SageMaker inputs. As SageMaker models can take in and output a variety of input and output schemas, respectively, the solution requests these values from the users to allow correct model invocation. This allows the solution to support a wide set of SageMaker models.
The input schemas are essentially your model's payload, with placeholders for the actual values. The placeholders enable replacing the actual model values at run-time and are represented by a keyword enclosed in angle brackets like: <<prompt>>. Note that <<prompt>> and <<temperature>> are reserved placeholders for the model prompt and temperatures respectively.
The model's output JSONPath provides the solution a path to retrieve the LLM's textual response from the model response.
Please always refer to model documentation and SageMaker JumpStart jupyter notebook samples to see the most up-to-date model payloads and supported parameters.
Run the following command:
git clone https://github.com/aws-solutions/<repository_name>
- Install the dependencies:
cd <rootDir>/source/infrastructure
npm install
- (Optional) Run the unit tests:
Note: To run the unit tests, docker must be installed and running, and valid AWS credentials must be configured.
cd <rootDir>/deployment
chmod +x ./run-unit-tests.sh
./run-unit-tests.sh
- Configure the bucket name of your target Amazon S3 distribution bucket:
export DIST_OUTPUT_BUCKET=my-bucket-name
export VERSION=my-version
- Build the distributable:
cd <rootDir>/deployment
chmod +x ./build-s3-dist.sh
./build-s3-dist.sh $DIST_OUTPUT_BUCKET $SOLUTION_NAME $VERSION $CF_TEMPLATE_BUCKET_NAME
Parameter details:
$DIST_OUTPUT_BUCKET - This is the global name of the distribution. For the bucket name, the AWS Region is added to the global name (example: 'my-bucket-name-us-east-1') to create a regional bucket. The lambda
artifacts should be uploaded to the regional buckets for the CloudFormation template to pick it up for deployment.
$SOLUTION_NAME - The name of This solution (example: generative-ai-application-builder-on-aws)
$VERSION - The version number of the change
$CF_TEMPLATE_BUCKET_NAME - The name of the S3 bucket where the CloudFormation templates should be uploaded
When you create and use buckets, we recommended that you:
- Use randomized names or uuid as part of your bucket naming strategy.
- Ensure that buckets aren't public.
- Verify bucket ownership prior to uploading templates or code artifacts.
- Deploy the distributable to an Amazon S3 bucket in your account.
Note: You must have the AWS CLI installed.
aws s3 cp ./global-s3-assets/ s3://my-bucket-name-<aws_region>/generative-ai-application-builder-on-aws/<my-version>/ --recursive --acl bucket-owner-full-control --profile aws-cred-profile-name
aws s3 cp ./regional-s3-assets/ s3://my-bucket-name-<aws_region>/generative-ai-application-builder-on-aws/<my-version>/ --recursive --acl bucket-owner-full-control --profile aws-cred-profile-name
The solution includes two separate React-based web applications: the Deployment Dashboard UI and the Chat UI. Both user interfaces are built using Vite, a modern and fast build tool for modern web projects.
- Node.js (version 16 or later)
- npm (usually included with Node.js)
-
Open a Terminal
- On Windows, you can use the built-in Command Prompt, PowerShell, or a terminal emulator like Git Bash.
- On macOS or Linux, open the default terminal application.
-
Navigate to the Source Directory
- Change to the
sourcedirectory within the project root:cd <project-directory>/source
- Change to the
-
Fetch and Update Runtime Config
-
Run the provided
setup_local_dev_server.pyscript with the appropriate arguments:python setup_local_dev_server.py --ui-project-type <ui_project_name> --website <website_url>- Replace
<ui_project_name>with eitherui-chatorui-deploymentdepending on which UI project you want to set up. - Replace
<website_url>with the URL of the website where the solution is deployed (e.g.,https://example.com).
- Replace
-
The script will fetch the runtime configuration used to configure AWS Amplify, which the project uses. It will also update the Cognito app client by adding the localhost address to the callbackurls and logouturls list, so it works with the Cognito hosted domain.
-
For example, to update the UI Chat project:
python setup_local_dev_server.py --ui-project-type ui-chat --website https://example.comor
python setup_local_dev_server.py -t ui-chat -w https://example.com -
To update the UI Deployment project:
python setup_local_dev_server.py --ui-project-type ui-deployment --website https://example.comor
python setup_local_dev_server.py -t ui-deployment -w https://example.com
-
-
Navigate to the UI Project Directory
-
Change to the directory of the UI project you want to work with:
cd ui-chator
cd ui-deployment
-
-
Install Dependencies
-
Install the required Node.js dependencies by running the following command in the project directory:
npm install
-
-
Start the Local Development Server
-
In the project directory, run the following command to start the local Vite development server:
npm start -
The Deployment Dashboard UI development server will start at
http://localhost:5177, and the Chat UI development server will start athttp://localhost:5178. -
If these ports are already in use on your machine, you can customize the
setup_local_dev_server.pyscript to use different ports.
-
With the local development environment set up, you can now customize the React components and functionality of the UI projects according to your requirements. The source code for the Deployment Dashboard UI is located in the source/ui-deployment directory, and the source code for the Chat UI is located in the source/ui-chat directory.
Follow the standard React development workflow to make changes to the code, and use the local Vite development server to preview your changes in real-time.
When you're ready to deploy your customized UI projects, follow the instructions in the main README file for building and deploying the solution using the AWS CDK.
This solution collects anonymized operational metrics to help AWS improve the quality and features of the solution. For more information, including how to disable this capability, please see the implementation guide.
Copyright Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
A script is included to migrate use cases created by v1.X to an upgraded v2.X deployment. See the documentation
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for generative-ai-application-builder-on-aws
Similar Open Source Tools

generative-ai-application-builder-on-aws
The Generative AI Application Builder on AWS (GAAB) is a solution that provides a web-based management dashboard for deploying customizable Generative AI (Gen AI) use cases. Users can experiment with and compare different combinations of Large Language Model (LLM) use cases, configure and optimize their use cases, and integrate them into their applications for production. The solution is targeted at novice to experienced users who want to experiment and productionize different Gen AI use cases. It uses LangChain open-source software to configure connections to Large Language Models (LLMs) for various use cases, with the ability to deploy chat use cases that allow querying over users' enterprise data in a chatbot-style User Interface (UI) and support custom end-user implementations through an API.
serverless-pdf-chat
The serverless-pdf-chat repository contains a sample application that allows users to ask natural language questions of any PDF document they upload. It leverages serverless services like Amazon Bedrock, AWS Lambda, and Amazon DynamoDB to provide text generation and analysis capabilities. The application architecture involves uploading a PDF document to an S3 bucket, extracting metadata, converting text to vectors, and using a LangChain to search for information related to user prompts. The application is not intended for production use and serves as a demonstration and educational tool.
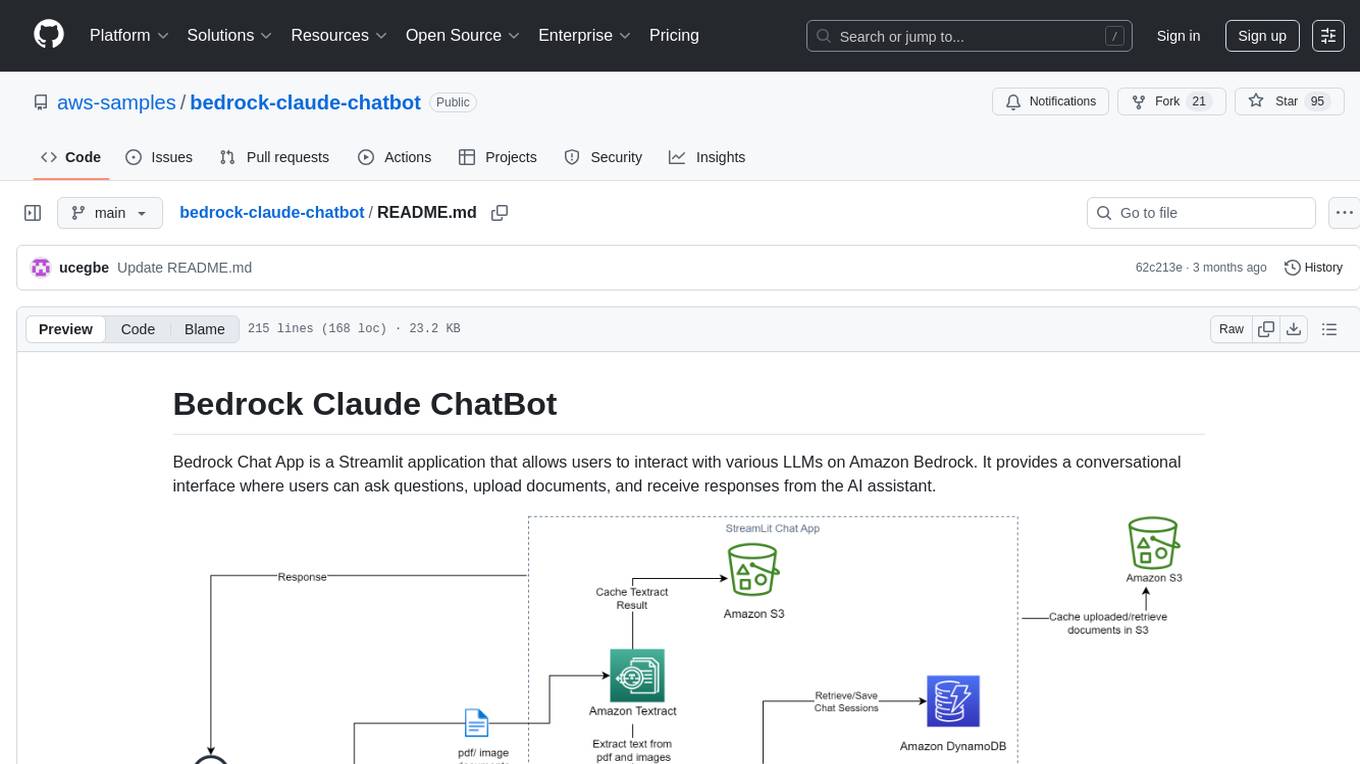
bedrock-claude-chatbot
Bedrock Claude ChatBot is a Streamlit application that provides a conversational interface for users to interact with various Large Language Models (LLMs) on Amazon Bedrock. Users can ask questions, upload documents, and receive responses from the AI assistant. The app features conversational UI, document upload, caching, chat history storage, session management, model selection, cost tracking, logging, and advanced data analytics tool integration. It can be customized using a config file and is extensible for implementing specialized tools using Docker containers and AWS Lambda. The app requires access to Amazon Bedrock Anthropic Claude Model, S3 bucket, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Textract, and optionally Amazon Elastic Container Registry and Amazon Athena for advanced analytics features.
Open_Data_QnA
Open Data QnA is a Python library that allows users to interact with their PostgreSQL or BigQuery databases in a conversational manner, without needing to write SQL queries. The library leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to bridge the gap between human language and database queries, enabling users to ask questions in natural language and receive informative responses. It offers features such as conversational querying with multiturn support, table grouping, multi schema/dataset support, SQL generation, query refinement, natural language responses, visualizations, and extensibility. The library is built on a modular design and supports various components like Database Connectors, Vector Stores, and Agents for SQL generation, validation, debugging, descriptions, embeddings, responses, and visualizations.
geti-sdk
The Intel® Geti™ SDK is a python package that enables teams to rapidly develop AI models by easing the complexities of model development and enhancing collaboration between teams. It provides tools to interact with an Intel® Geti™ server via the REST API, allowing for project creation, downloading, uploading, deploying for local inference with OpenVINO, setting project and model configuration, launching and monitoring training jobs, and media upload and prediction. The SDK also includes tutorial-style Jupyter notebooks demonstrating its usage.
geti-sdk
The Intel® Geti™ SDK is a python package that enables teams to rapidly develop AI models by easing the complexities of model development and fostering collaboration. It provides tools to interact with an Intel® Geti™ server via the REST API, allowing for project creation, downloading, uploading, deploying for local inference with OpenVINO, configuration management, training job monitoring, media upload, and prediction. The repository also includes tutorial-style Jupyter notebooks demonstrating SDK usage.
holohub
Holohub is a central repository for the NVIDIA Holoscan AI sensor processing community to share reference applications, operators, tutorials, and benchmarks. It includes example applications, community components, package configurations, and tutorials. Users and developers of the Holoscan platform are invited to reuse and contribute to this repository. The repository provides detailed instructions on prerequisites, building, running applications, contributing, and glossary terms. It also offers a searchable catalog of available components on the Holoscan SDK User Guide website.
vector-vein
VectorVein is a no-code AI workflow software inspired by LangChain and langflow, aiming to combine the powerful capabilities of large language models and enable users to achieve intelligent and automated daily workflows through simple drag-and-drop actions. Users can create powerful workflows without the need for programming, automating all tasks with ease. The software allows users to define inputs, outputs, and processing methods to create customized workflow processes for various tasks such as translation, mind mapping, summarizing web articles, and automatic categorization of customer reviews.
genai-for-marketing
This repository provides a deployment guide for utilizing Google Cloud's Generative AI tools in marketing scenarios. It includes step-by-step instructions, examples of crafting marketing materials, and supplementary Jupyter notebooks. The demos cover marketing insights, audience analysis, trendspotting, content search, content generation, and workspace integration. Users can access and visualize marketing data, analyze trends, improve search experience, and generate compelling content. The repository structure includes backend APIs, frontend code, sample notebooks, templates, and installation scripts.

cognita
Cognita is an open-source framework to organize your RAG codebase along with a frontend to play around with different RAG customizations. It provides a simple way to organize your codebase so that it becomes easy to test it locally while also being able to deploy it in a production ready environment. The key issues that arise while productionizing RAG system from a Jupyter Notebook are: 1. **Chunking and Embedding Job** : The chunking and embedding code usually needs to be abstracted out and deployed as a job. Sometimes the job will need to run on a schedule or be trigerred via an event to keep the data updated. 2. **Query Service** : The code that generates the answer from the query needs to be wrapped up in a api server like FastAPI and should be deployed as a service. This service should be able to handle multiple queries at the same time and also autoscale with higher traffic. 3. **LLM / Embedding Model Deployment** : Often times, if we are using open-source models, we load the model in the Jupyter notebook. This will need to be hosted as a separate service in production and model will need to be called as an API. 4. **Vector DB deployment** : Most testing happens on vector DBs in memory or on disk. However, in production, the DBs need to be deployed in a more scalable and reliable way. Cognita makes it really easy to customize and experiment everything about a RAG system and still be able to deploy it in a good way. It also ships with a UI that makes it easier to try out different RAG configurations and see the results in real time. You can use it locally or with/without using any Truefoundry components. However, using Truefoundry components makes it easier to test different models and deploy the system in a scalable way. Cognita allows you to host multiple RAG systems using one app. ### Advantages of using Cognita are: 1. A central reusable repository of parsers, loaders, embedders and retrievers. 2. Ability for non-technical users to play with UI - Upload documents and perform QnA using modules built by the development team. 3. Fully API driven - which allows integration with other systems. > If you use Cognita with Truefoundry AI Gateway, you can get logging, metrics and feedback mechanism for your user queries. ### Features: 1. Support for multiple document retrievers that use `Similarity Search`, `Query Decompostion`, `Document Reranking`, etc 2. Support for SOTA OpenSource embeddings and reranking from `mixedbread-ai` 3. Support for using LLMs using `Ollama` 4. Support for incremental indexing that ingests entire documents in batches (reduces compute burden), keeps track of already indexed documents and prevents re-indexing of those docs.
serverless-chat-langchainjs
This sample shows how to build a serverless chat experience with Retrieval-Augmented Generation using LangChain.js and Azure. The application is hosted on Azure Static Web Apps and Azure Functions, with Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB vCore as the vector database. You can use it as a starting point for building more complex AI applications.
nx_open
The `nx_open` repository contains open-source components for the Network Optix Meta Platform, used to build products like Nx Witness Video Management System. It includes source code, specifications, and a Desktop Client. The repository is licensed under Mozilla Public License 2.0. Users can build the Desktop Client and customize it using a zip file. The build environment supports Windows, Linux, and macOS platforms with specific prerequisites. The repository provides scripts for building, signing executable files, and running the Desktop Client. Compatibility with VMS Server versions is crucial, and automatic VMS updates are disabled for the open-source Desktop Client.
burpference
Burpference is an open-source extension designed to capture in-scope HTTP requests and responses from Burp's proxy history and send them to a remote LLM API in JSON format. It automates response capture, integrates with APIs, optimizes resource usage, provides color-coded findings visualization, offers comprehensive logging, supports native Burp reporting, and allows flexible configuration. Users can customize system prompts, API keys, and remote hosts, and host models locally to prevent high inference costs. The tool is ideal for offensive web application engagements to surface findings and vulnerabilities.
leettools
LeetTools is an AI search assistant that can perform highly customizable search workflows and generate customized format results based on both web and local knowledge bases. It provides an automated document pipeline for data ingestion, indexing, and storage, allowing users to focus on implementing workflows without worrying about infrastructure. LeetTools can run with minimal resource requirements on the command line with configurable LLM settings and supports different databases for various functions. Users can configure different functions in the same workflow to use different LLM providers and models.

unitycatalog
Unity Catalog is an open and interoperable catalog for data and AI, supporting multi-format tables, unstructured data, and AI assets. It offers plugin support for extensibility and interoperates with Delta Sharing protocol. The catalog is fully open with OpenAPI spec and OSS implementation, providing unified governance for data and AI with asset-level access control enforced through REST APIs.

coral-cloud
Coral Cloud Resorts is a sample hospitality application that showcases Data Cloud, Agents, and Prompts. It provides highly personalized guest experiences through smart automation, content generation, and summarization. The app requires licenses for Data Cloud, Agents, Prompt Builder, and Einstein for Sales. Users can activate features, deploy metadata, assign permission sets, import sample data, and troubleshoot common issues. Additionally, the repository offers integration with modern web development tools like Prettier, ESLint, and pre-commit hooks for code formatting and linting.
For similar tasks

generative-ai-application-builder-on-aws
The Generative AI Application Builder on AWS (GAAB) is a solution that provides a web-based management dashboard for deploying customizable Generative AI (Gen AI) use cases. Users can experiment with and compare different combinations of Large Language Model (LLM) use cases, configure and optimize their use cases, and integrate them into their applications for production. The solution is targeted at novice to experienced users who want to experiment and productionize different Gen AI use cases. It uses LangChain open-source software to configure connections to Large Language Models (LLMs) for various use cases, with the ability to deploy chat use cases that allow querying over users' enterprise data in a chatbot-style User Interface (UI) and support custom end-user implementations through an API.
LLMinator
LLMinator is a Gradio-based tool with an integrated chatbot designed to locally run and test Language Model Models (LLMs) directly from HuggingFace. It provides an easy-to-use interface made with Gradio, LangChain, and Torch, offering features such as context-aware streaming chatbot, inbuilt code syntax highlighting, loading any LLM repo from HuggingFace, support for both CPU and CUDA modes, enabling LLM inference with llama.cpp, and model conversion capabilities.
AI-Scientist
The AI Scientist is a comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models to perform research independently. It aims to tackle the grand challenge of developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. The tool generates papers on various topics using Large Language Models (LLMs) and provides a platform for exploring new research ideas. Users can create their own templates for specific areas of study and run experiments to generate papers. However, caution is advised as the codebase executes LLM-written code, which may pose risks such as the use of potentially dangerous packages and web access.
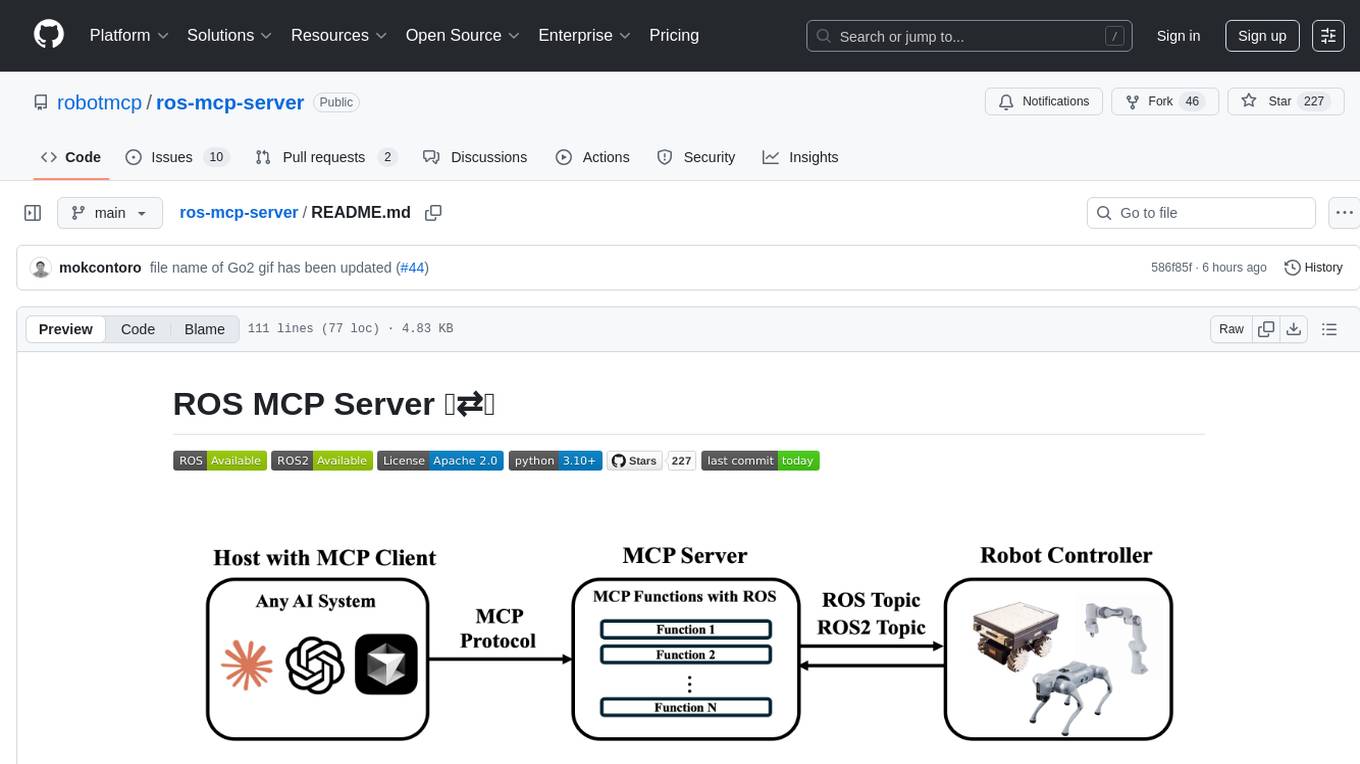
ros-mcp-server
The ros-mcp-server repository contains a ROS (Robot Operating System) package that provides a server for Multi-Contact Planning (MCP) in robotics. The server facilitates the planning of multiple contacts between a robot and its environment, enabling complex manipulation tasks. It includes functionalities for collision checking, motion planning, and contact stability analysis. This tool is designed to enhance the capabilities of robotic systems by enabling them to perform tasks that involve multiple points of contact with the environment. The repository includes documentation and examples to help users integrate the MCP server into their robotic applications.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

