
edge2ai-workshop
Edge2AI Workshop
Stars: 68
The edge2ai-workshop repository provides a hands-on workshop for building an IoT Predictive Maintenance workflow. It includes lab exercises for setting up components like NiFi, Streams Processing, Data Visualization, and more on a single host. The repository also covers use cases such as credit card fraud detection. Users can follow detailed instructions, prerequisites, and connectivity guidelines to connect to their cluster and explore various services. Additionally, troubleshooting tips are provided for common issues like MiNiFi not sending messages or CEM not picking up new NARs.
README:
= CDF Workshops
== Introduction
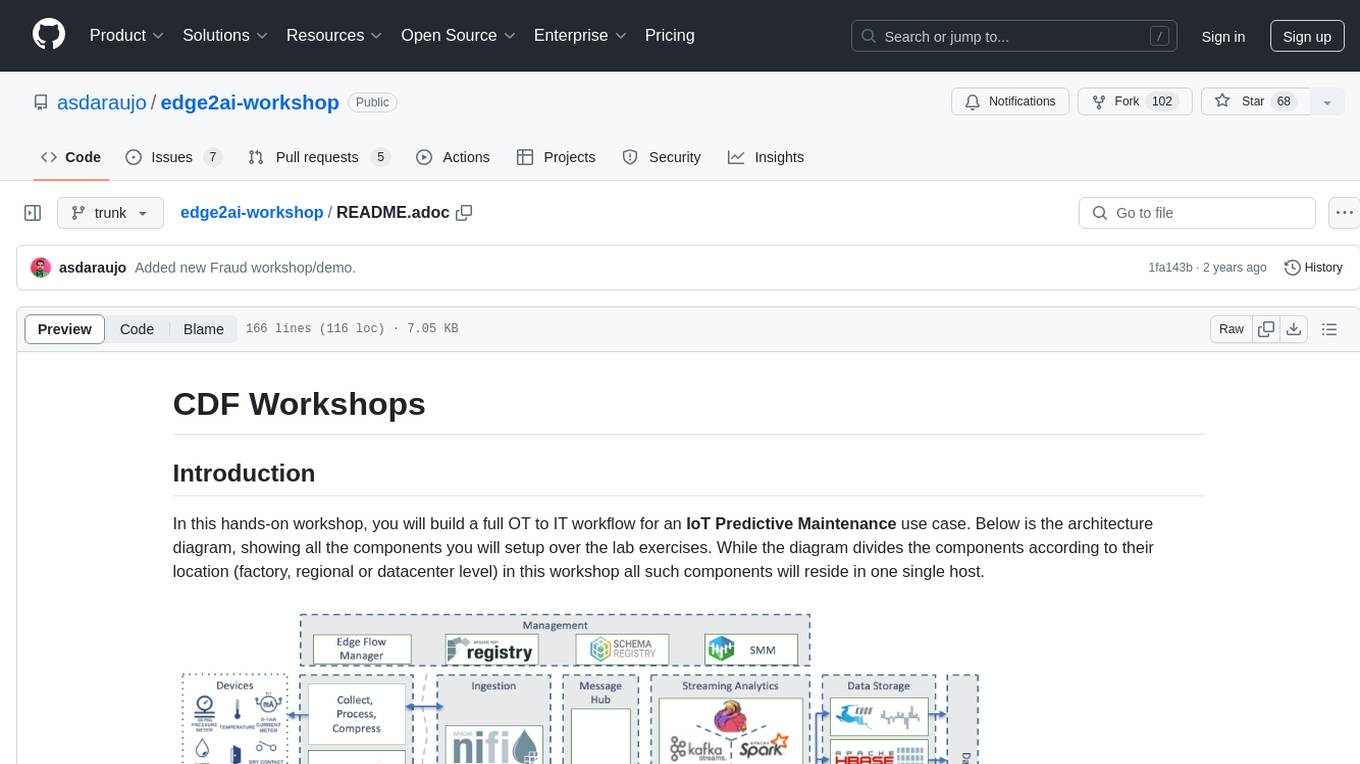
In this hands-on workshop, you will build a full OT to IT workflow for an IoT Predictive Maintenance use case. Below is the architecture diagram, showing all the components you will setup over the lab exercises. While the diagram divides the components according to their location (factory, regional or datacenter level) in this workshop all such components will reside in one single host.
image::images/iot-architecture.png[width=800]
=== Workshops
IMPORTANT: If this is your first time going through this content, please read the rest of this README introduction before jumping to the Labs.
If you already familiar with the instructions in the README, time to start working and see some interesting stuff! Pick your lab and let's get started!
- link:workshop_edge.adoc[Ingesting data from the edge]
- link:workshop_nifi.adoc[NiFi and Streams Processing]
- link:workshop_dataviz.adoc[Creating Dashboards with Cloudera Data Viz]
- link:workshop_ssb.adoc[Querying streams with SQL]
- link:workshop_cdc.adoc[Change Data Capture (CDC) with Flink/SSB]
- link:streams_replication.adoc[Streams Replication]
- link:spark_analytics.adoc[Spark and Fast Analytics with Kudu]
- link:datascience.adoc[CDSW Experiments and Models]
Use cases:
- link:workshop_fraud.adoc[Credit card fraud detection]
=== Before you start
- Everything is Case-Sensitive.
- Check all your connections and spellings
- If you hit any problems like, for example, MiNiFi Not Sending Messages, check for clues in the <> section below.
=== Pre-requisites
- Laptop with a supported OS (Windows 7 not supported).
- A modern browser like Google Chrome or Firefox (IE not supported).
=== Connecting to your cluster
You instructor will give access to a registration link where you can request a cluster. You should have 2 addresses for you one-node cluster: the public DNS name and the public IP address. With those addresses you can test the following connectivity to your cluster:
NOTE: The credentials for all the services below that require authentication are admin/Supersecret1 (capital "S").
. Ensure you can connect to the following service using your browser:
+
[%autowidth,options="header"]
|===
|Service|URL|Comments
|Cloudera Manager|http://<public_dns>:7180/|Port 7183 when TLS is enabled
|Atlas|http://<public_dns>:31000/|Port 31443 when TLS is enabled
|CDSW|http://cdsw.<public_IP>.nip.io/|admin/Supersecret1
|CDP Data Visualization|http://viz.cdsw.<public_IP>.nip.io/|
|Edge Flow Manager|http://<public_dns>:10088/efm/ui/|
|Flink Dashboard|http://<public_dns>:8078/|
|Hue|http://<public_dns>:8889/|
|Knox|https://<public_dns>:9443/gateway/homepage/home/|Only when security is enabled
|NiFi|http://<public_dns>:8080/nifi/|Port 8443 when TLS is enabled
|NiFi Registry|http://<public_dns>:18080/nifi-registry/|Port 18433 when TLS is enabled
|Ranger|https://<public_dns>:6182/|Only when security is enabled
|Schema Registry|http://<public_dns>:7788/|Port 7790 when TLS is enabled
|SMM|http://<public_dns>:9991/|
|SQL Stream Builder (SSB)|http://<public_dns>:18121/|For SSB versions older than 1.7 use this instead: http://<public_dns>:18121/
|===
. Login into Cloudera Manager and familiarize yourself with the services installed
. Login into Hue. As you are the first user to login into Hue, you are granted admin privileges. At this point, you won't need to do anything on Hue, but by logging in, CDH has created your HDFS user and folder, which you will need for the next lab.
Below a screenshot of Chrome open with 8 tabs, one for each service.
image::images/browser.png[width=800]
=== (Optional) SSH access
This access is not required for the workshop labs. You can skip this section.
SSH access is only required if you need to troubleshoot issues or want to poke around your clusters. The procedure to connect via SSH depends on the type of computer you're using:
==== SSH into the cluster from the Web UI
From the registration link, you can click on the link at the right side to connect to the cluster from a web based SSH client with the credential centos/Supersecret1.
==== SSH into the cluster from Linux/Macos
From the registration link, download the PEM key required to access to your cluster with SSH. Run the following command:
==== SSH into the cluster from Windows
From the registration link, download the PEM key required to access to your cluster with SSH. We will use link:https://www.putty.org/[PuTTY] to connect to the cluster. However, Putty doesn't accept PEM key. Follow these instructions to convert your PEM key into a PPK key and connect to the cluster
Convert your key with PuTTYgen:
. Use PuTTYgen to convert .PEM file to .PPK file. . Start PuTTYgen and select “Load” . Select your .PEM file. . Putty will convert the .PEM format to .PPK format. . Select “Save Private Key” A passphrase is not required but can be used if additional security is required.
Connect with PuTTY:
. Launch PuTTY and enter the host IP address. . Navigate to Connection/SSH/Auth . Click “Browse” and select the .PPK file you exported from PuTTYgen. . Click “Open.”
== Resources
-
link:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/building-an-iiot-system-using-apache-nifi-mqtt-and-raspberry-pi-ce1d6ed565bc[Original blog by Abdelkrim Hadjidj]
-
This workshop is based on the following work by Fabio Ghirardello: ** https://github.com/fabiog1901/IoT-predictive-maintenance ** https://github.com/fabiog1901/OneNodeCDHCluster
-
link:https://www.cloudera.com/documentation.html[Cloudera Documentation]
[[troubleshooting, Troubleshooting]] == Troubleshooting
==== General
- Everything is Case-Sensitive.
- Check all your connections and spellings
==== MiNiFi Not Sending Messages
- Make sure you pick HTTP, not RAW, in Cloud Connection to NiFi
- Make sure there are no spaces before or after Destination ID, URL, Names, Topics, Brokers, etc...
- Make sure there are no spaces anywhere!
- Everything is Case-Sensitive. For example, the bucket name in NiFi Registry is
IoT, notiot. - Check /opt/cloudera/cem/minifi/logs/minifi-app.log if you can't find an issue
- You must have HDFS User Created via HUE, Go there First
==== CEM doesn't pick up new NARs
. Delete the agent manifest manually using the EFM API:
http://hostname:10088/efm/api/agent-classes [{"name":"iot1","agentManifests":["agent-manifest-id"]},{"name":"iot4","agentManifests":["agent-manifest-id"]}]
http://hostname:10088/efm/api/agent-manifests?class=iot4 [{"identifier":"agent-manifest-id","agentType":"minifi-java","version":"1","buildInfo":{"timestamp":1556628651811,"compiler":"JDK 8"},"bundles":[{"group":"default","artifact":"system","version":"unversioned","componentManifest":{"controllerServices":[],"processors":
. Hit the DELETE - Delete the agent manifest specified by id button, and in the id field, enter `agent-manifest-id
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for edge2ai-workshop
Similar Open Source Tools

edge2ai-workshop
The edge2ai-workshop repository provides a hands-on workshop for building an IoT Predictive Maintenance workflow. It includes lab exercises for setting up components like NiFi, Streams Processing, Data Visualization, and more on a single host. The repository also covers use cases such as credit card fraud detection. Users can follow detailed instructions, prerequisites, and connectivity guidelines to connect to their cluster and explore various services. Additionally, troubleshooting tips are provided for common issues like MiNiFi not sending messages or CEM not picking up new NARs.
bedrock-claude-chatbot
Bedrock Claude ChatBot is a Streamlit application that provides a conversational interface for users to interact with various Large Language Models (LLMs) on Amazon Bedrock. Users can ask questions, upload documents, and receive responses from the AI assistant. The app features conversational UI, document upload, caching, chat history storage, session management, model selection, cost tracking, logging, and advanced data analytics tool integration. It can be customized using a config file and is extensible for implementing specialized tools using Docker containers and AWS Lambda. The app requires access to Amazon Bedrock Anthropic Claude Model, S3 bucket, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Textract, and optionally Amazon Elastic Container Registry and Amazon Athena for advanced analytics features.
TaskWeaver
TaskWeaver is a code-first agent framework designed for planning and executing data analytics tasks. It interprets user requests through code snippets, coordinates various plugins to execute tasks in a stateful manner, and preserves both chat history and code execution history. It supports rich data structures, customized algorithms, domain-specific knowledge incorporation, stateful execution, code verification, easy debugging, security considerations, and easy extension. TaskWeaver is easy to use with CLI and WebUI support, and it can be integrated as a library. It offers detailed documentation, demo examples, and citation guidelines.
AutoNode
AutoNode is a self-operating computer system designed to automate web interactions and data extraction processes. It leverages advanced technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), YOLO (You Only Look Once) models for object detection, and a custom site-graph to navigate and interact with web pages programmatically. Users can define objectives, create site-graphs, and utilize AutoNode via API to automate tasks on websites. The tool also supports training custom YOLO models for object detection and OCR for text recognition on web pages. AutoNode can be used for tasks such as extracting product details, automating web interactions, and more.
langdrive
LangDrive is an open-source AI library that simplifies training, deploying, and querying open-source large language models (LLMs) using private data. It supports data ingestion, fine-tuning, and deployment via a command-line interface, YAML file, or API, with a quick, easy setup. Users can build AI applications such as question/answering systems, chatbots, AI agents, and content generators. The library provides features like data connectors for ingestion, fine-tuning of LLMs, deployment to Hugging Face hub, inference querying, data utilities for CRUD operations, and APIs for model access. LangDrive is designed to streamline the process of working with LLMs and making AI development more accessible.

Sentient
Sentient is a personal, private, and interactive AI companion developed by Existence. The project aims to build a completely private AI companion that is deeply personalized and context-aware of the user. It utilizes automation and privacy to create a true companion for humans. The tool is designed to remember information about the user and use it to respond to queries and perform various actions. Sentient features a local and private environment, MBTI personality test, integrations with LinkedIn, Reddit, and more, self-managed graph memory, web search capabilities, multi-chat functionality, and auto-updates for the app. The project is built using technologies like ElectronJS, Next.js, TailwindCSS, FastAPI, Neo4j, and various APIs.
SunoApi
SunoAPI is an unofficial client for Suno AI, built on Python and Streamlit. It supports functions like generating music and obtaining music information. Users can set up multiple account information to be saved for use. The tool also features built-in maintenance and activation functions for tokens, eliminating concerns about token expiration. It supports multiple languages and allows users to upload pictures for generating songs based on image content analysis.
LlamaEdge
The LlamaEdge project makes it easy to run LLM inference apps and create OpenAI-compatible API services for the Llama2 series of LLMs locally. It provides a Rust+Wasm stack for fast, portable, and secure LLM inference on heterogeneous edge devices. The project includes source code for text generation, chatbot, and API server applications, supporting all LLMs based on the llama2 framework in the GGUF format. LlamaEdge is committed to continuously testing and validating new open-source models and offers a list of supported models with download links and startup commands. It is cross-platform, supporting various OSes, CPUs, and GPUs, and provides troubleshooting tips for common errors.
CyberScraper-2077
CyberScraper 2077 is an advanced web scraping tool powered by AI, designed to extract data from websites with precision and style. It offers a user-friendly interface, supports multiple data export formats, operates in stealth mode to avoid detection, and promises lightning-fast scraping. The tool respects ethical scraping practices, including robots.txt and site policies. With upcoming features like proxy support and page navigation, CyberScraper 2077 is a futuristic solution for data extraction in the digital realm.

verifAI
VerifAI is a document-based question-answering system that addresses hallucinations in generative large language models and search engines. It retrieves relevant documents, generates answers with references, and verifies answers for accuracy. The engine uses generative search technology and a verification model to ensure no misinformation. VerifAI supports various document formats and offers user registration with a React.js interface. It is open-source and designed to be user-friendly, making it accessible for anyone to use.
Perplexica
Perplexica is an open-source AI-powered search engine that utilizes advanced machine learning algorithms to provide clear answers with sources cited. It offers various modes like Copilot Mode, Normal Mode, and Focus Modes for specific types of questions. Perplexica ensures up-to-date information by using SearxNG metasearch engine. It also features image and video search capabilities and upcoming features include finalizing Copilot Mode and adding Discover and History Saving features.

cognita
Cognita is an open-source framework to organize your RAG codebase along with a frontend to play around with different RAG customizations. It provides a simple way to organize your codebase so that it becomes easy to test it locally while also being able to deploy it in a production ready environment. The key issues that arise while productionizing RAG system from a Jupyter Notebook are: 1. **Chunking and Embedding Job** : The chunking and embedding code usually needs to be abstracted out and deployed as a job. Sometimes the job will need to run on a schedule or be trigerred via an event to keep the data updated. 2. **Query Service** : The code that generates the answer from the query needs to be wrapped up in a api server like FastAPI and should be deployed as a service. This service should be able to handle multiple queries at the same time and also autoscale with higher traffic. 3. **LLM / Embedding Model Deployment** : Often times, if we are using open-source models, we load the model in the Jupyter notebook. This will need to be hosted as a separate service in production and model will need to be called as an API. 4. **Vector DB deployment** : Most testing happens on vector DBs in memory or on disk. However, in production, the DBs need to be deployed in a more scalable and reliable way. Cognita makes it really easy to customize and experiment everything about a RAG system and still be able to deploy it in a good way. It also ships with a UI that makes it easier to try out different RAG configurations and see the results in real time. You can use it locally or with/without using any Truefoundry components. However, using Truefoundry components makes it easier to test different models and deploy the system in a scalable way. Cognita allows you to host multiple RAG systems using one app. ### Advantages of using Cognita are: 1. A central reusable repository of parsers, loaders, embedders and retrievers. 2. Ability for non-technical users to play with UI - Upload documents and perform QnA using modules built by the development team. 3. Fully API driven - which allows integration with other systems. > If you use Cognita with Truefoundry AI Gateway, you can get logging, metrics and feedback mechanism for your user queries. ### Features: 1. Support for multiple document retrievers that use `Similarity Search`, `Query Decompostion`, `Document Reranking`, etc 2. Support for SOTA OpenSource embeddings and reranking from `mixedbread-ai` 3. Support for using LLMs using `Ollama` 4. Support for incremental indexing that ingests entire documents in batches (reduces compute burden), keeps track of already indexed documents and prevents re-indexing of those docs.
gpustack
GPUStack is an open-source GPU cluster manager designed for running large language models (LLMs). It supports a wide variety of hardware, scales with GPU inventory, offers lightweight Python package with minimal dependencies, provides OpenAI-compatible APIs, simplifies user and API key management, enables GPU metrics monitoring, and facilitates token usage and rate metrics tracking. The tool is suitable for managing GPU clusters efficiently and effectively.
mobile-use
Mobile-use is an open-source AI agent that controls Android or IOS devices using natural language. It understands commands to perform tasks like sending messages and navigating apps. Features include natural language control, UI-aware automation, data scraping, and extensibility. Users can automate their mobile experience by setting up environment variables, customizing LLM configurations, and launching the tool via Docker or manually for development. The tool supports physical Android phones, Android simulators, and iOS simulators. Contributions are welcome, and the project is licensed under MIT.
uni-api
uni-api is a project that unifies the management of large language model APIs, allowing you to call multiple backend services through a single unified API interface, converting them all to OpenAI format, and supporting load balancing. It supports various backend services such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Vertex, Azure, xai, Cohere, Groq, Cloudflare, OpenRouter, and more. The project offers features like no front-end, pure configuration file setup, unified management of multiple backend services, support for multiple standard OpenAI format interfaces, rate limiting, automatic retry, channel cooling, fine-grained model timeout settings, and fine-grained permission control.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
For similar tasks

edge2ai-workshop
The edge2ai-workshop repository provides a hands-on workshop for building an IoT Predictive Maintenance workflow. It includes lab exercises for setting up components like NiFi, Streams Processing, Data Visualization, and more on a single host. The repository also covers use cases such as credit card fraud detection. Users can follow detailed instructions, prerequisites, and connectivity guidelines to connect to their cluster and explore various services. Additionally, troubleshooting tips are provided for common issues like MiNiFi not sending messages or CEM not picking up new NARs.
For similar jobs
fluid
Fluid is an open source Kubernetes-native Distributed Dataset Orchestrator and Accelerator for data-intensive applications, such as big data and AI applications. It implements dataset abstraction, scalable cache runtime, automated data operations, elasticity and scheduling, and is runtime platform agnostic. Key concepts include Dataset and Runtime. Prerequisites include Kubernetes version > 1.16, Golang 1.18+, and Helm 3. The tool offers features like accelerating remote file accessing, machine learning, accelerating PVC, preloading dataset, and on-the-fly dataset cache scaling. Contributions are welcomed, and the project is under the Apache 2.0 license with a vendor-neutral approach.

edge2ai-workshop
The edge2ai-workshop repository provides a hands-on workshop for building an IoT Predictive Maintenance workflow. It includes lab exercises for setting up components like NiFi, Streams Processing, Data Visualization, and more on a single host. The repository also covers use cases such as credit card fraud detection. Users can follow detailed instructions, prerequisites, and connectivity guidelines to connect to their cluster and explore various services. Additionally, troubleshooting tips are provided for common issues like MiNiFi not sending messages or CEM not picking up new NARs.
sail
Sail is a tool designed to unify stream processing, batch processing, and compute-intensive workloads, serving as a drop-in replacement for Spark SQL and the Spark DataFrame API in single-process settings. It aims to streamline data processing tasks and facilitate AI workloads.
ShannonBase
ShannonBase is a HTAP database provided by Shannon Data AI, designed for big data and AI. It extends MySQL with native embedding support, machine learning capabilities, a JavaScript engine, and a columnar storage engine. ShannonBase supports multimodal data types and natively integrates LightGBM for training and prediction. It leverages embedding algorithms and vector data type for ML/RAG tasks, providing Zero Data Movement, Native Performance Optimization, and Seamless SQL Integration. The tool includes a lightweight JavaScript engine for writing stored procedures in SQL or JavaScript.
bigtop-manager
Apache Bigtop Manager is a modern, AI-driven web application designed to simplify the complexity of bigdata cluster management. It provides an easy deployment solution not only for Apache Bigtop components, but also other community version bigdata components. The platform aims to streamline the management of bigdata clusters by leveraging AI technology and user-friendly interfaces.
serverless-pdf-chat
The serverless-pdf-chat repository contains a sample application that allows users to ask natural language questions of any PDF document they upload. It leverages serverless services like Amazon Bedrock, AWS Lambda, and Amazon DynamoDB to provide text generation and analysis capabilities. The application architecture involves uploading a PDF document to an S3 bucket, extracting metadata, converting text to vectors, and using a LangChain to search for information related to user prompts. The application is not intended for production use and serves as a demonstration and educational tool.
generative-bi-using-rag
Generative BI using RAG on AWS is a comprehensive framework designed to enable Generative BI capabilities on customized data sources hosted on AWS. It offers features such as Text-to-SQL functionality for querying data sources using natural language, user-friendly interface for managing data sources, performance enhancement through historical question-answer ranking, and entity recognition. It also allows customization of business information, handling complex attribution analysis problems, and provides an intuitive question-answering UI with a conversational approach for complex queries.
azure-functions-openai-extension
Azure Functions OpenAI Extension is a project that adds support for OpenAI LLM (GPT-3.5-turbo, GPT-4) bindings in Azure Functions. It provides NuGet packages for various functionalities like text completions, chat completions, assistants, embeddings generators, and semantic search. The project requires .NET 6 SDK or greater, Azure Functions Core Tools v4.x, and specific settings in Azure Function or local settings for development. It offers features like text completions, chat completion, assistants with custom skills, embeddings generators for text relatedness, and semantic search using vector databases. The project also includes examples in C# and Python for different functionalities.