
ai-hands-on
A group of notebooks and other files which can help you learn AI from scratch.
Stars: 978
A complete, hands-on guide to becoming an AI Engineer. This repository is designed to help you learn AI from first principles, build real neural networks, and understand modern LLM systems end-to-end. Progress through math, PyTorch, deep learning, transformers, RAG, and OCR with clean, intuitive Jupyter notebooks guiding you at every step. Suitable for beginners and engineers leveling up, providing clarity, structure, and intuition to build real AI systems.
README:
A complete, hands-on guide to becoming an AI Engineer.
This repository is designed to help you learn AI from first principles, build real neural networks, and understand modern LLM systems end-to-end. You'll progress through math, PyTorch, deep learning, transformers, RAG, and OCR — with clean, intuitive Jupyter notebooks guiding you at every step.
Whether you're a beginner or an engineer levelling up, this repo gives you the clarity, structure, and intuition needed to build real AI systems.
If you learn something useful, a star is appreciated.
- Math functions, derivatives, vectors, and gradients
- Matrix operations and linear algebra
- Probability and statistics
- Creating and manipulating tensors
- Matrix multiplication, transposing, and reshaping
- Indexing, slicing, and concatenating tensors
- Special tensor creation functions
- Building neurons, layers, and networks from scratch
- Normalization techniques (RMSNorm)
- Activation functions
- Optimizers (Adam, Muon) and learning rate decay
- Attention and self-attention mechanisms
- Multi-head attention
- Decoder-only transformer architecture
- Building RAG pipelines end to end
- Indexing, retrieval, chunking strategies
- Integrations with embedding models and vector stores
- OCR pipeline and utilities
- Preprocessing images and extracting text
Recommended reading to deepen your understanding (not included):
-
AI Engineeringby Chip Huyen -
Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlowby Aurélien Géron -
Deep Learningby Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville -
The Elements of Statistical Learningby Trevor Hastie, Robert Tibshirani, and Jerome Friedman -
Neural Networks and Deep Learningby Michael Nielsen -
SQL Cookbookby Anthony Molinaro
For more books in AI/ML, I have created another repo for this Check Here. I will be adding lot more in coming days/months. If you are interested to read book, go check this repo out.
For a recommended step-by-step progression through the materials, see the Learning Path:
Start_here/learning_path.md
Install dependencies with:
pip install -r requirements.txtSome subfolders (for example 5.RAG/ and 6.OCR/) include their own requirements.txt with additional dependencies.
Recommended workflow:
-
Open Jupyter in the project root:
jupyter lab # or jupyter notebook -
Work through notebooks in order:
1.Math/2.PyTorch/3.Neural-Network(NN)/4.Transformer/
-
Folder to run separately:
5.RAG/6.OCR/
-
Resources
-
Basic ML Model Implementation (Supervised + Un-supervised + RL)
1.Linear Regression2.Logistic Regression3.Decision Tree Model4.Naive Bayes Classification
| Tool | Category | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Scikit-learn | Traditional ML | https://scikit-learn.org/stable/ |
| XGBoost | Gradient Boosting | https://xgboost.ai/ |
| LightGBM | Gradient Boosting | https://lightgbm.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ |
| CatBoost | Gradient Boosting | https://catboost.ai/ |
Contributions are welcome!
Please ensure:
- Notebooks are clean (Restart & Run All before committing)
- Existing structure & naming conventions are followed
- PRs are focused, readable, and documented
- In folders like RAG and OCR, please maintain the cleaned structure part
- If you want to add something new folders, make it proper structure way.
- This project is licensed under the MIT License. See
LICENSEfor details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ai-hands-on
Similar Open Source Tools

ai-hands-on
A complete, hands-on guide to becoming an AI Engineer. This repository is designed to help you learn AI from first principles, build real neural networks, and understand modern LLM systems end-to-end. Progress through math, PyTorch, deep learning, transformers, RAG, and OCR with clean, intuitive Jupyter notebooks guiding you at every step. Suitable for beginners and engineers leveling up, providing clarity, structure, and intuition to build real AI systems.
AI-For-Beginners
AI-For-Beginners is a comprehensive 12-week, 24-lesson curriculum designed by experts at Microsoft to introduce beginners to the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The curriculum covers various topics such as Symbolic AI, Neural Networks, Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, Genetic Algorithms, and Multi-Agent Systems. It includes hands-on lessons, quizzes, and labs using popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. The focus is on providing a foundational understanding of AI concepts and principles, making it an ideal starting point for individuals interested in AI.
ai4chem_course
The AI4Chemistry course is a hands-on course focusing on Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Chemistry. It covers topics such as Python programming, machine learning, cheminformatics toolkits, data science, deep learning for chemistry, and advanced AI topics. The course includes exercises using Google Colab and covers supervised and unsupervised machine learning, property prediction models, Bayesian optimization, and more. The course is created by the LIAC team and references open-source community examples. It aims to be accessible to learners with varying levels of experience in Python and ML.
generative-ai-with-javascript
The 'Generative AI with JavaScript' repository is a comprehensive resource hub for JavaScript developers interested in delving into the world of Generative AI. It provides code samples, tutorials, and resources from a video series, offering best practices and tips to enhance AI skills. The repository covers the basics of generative AI, guides on building AI applications using JavaScript, from local development to deployment on Azure, and scaling AI models. It is a living repository with continuous updates, making it a valuable resource for both beginners and experienced developers looking to explore AI with JavaScript.
MiniCPM-V-CookBook
MiniCPM-V & o Cookbook is a comprehensive repository for building multimodal AI applications effortlessly. It provides easy-to-use documentation, supports a wide range of users, and offers versatile deployment scenarios. The repository includes live demonstrations, inference recipes for vision and audio capabilities, fine-tuning recipes, serving recipes, quantization recipes, and a framework support matrix. Users can customize models, deploy them efficiently, and compress models to improve efficiency. The repository also showcases awesome works using MiniCPM-V & o and encourages community contributions.
generative-ai-for-beginners
This course has 18 lessons. Each lesson covers its own topic so start wherever you like! Lessons are labeled either "Learn" lessons explaining a Generative AI concept or "Build" lessons that explain a concept and code examples in both **Python** and **TypeScript** when possible. Each lesson also includes a "Keep Learning" section with additional learning tools. **What You Need** * Access to the Azure OpenAI Service **OR** OpenAI API - _Only required to complete coding lessons_ * Basic knowledge of Python or Typescript is helpful - *For absolute beginners check out these Python and TypeScript courses. * A Github account to fork this entire repo to your own GitHub account We have created a **Course Setup** lesson to help you with setting up your development environment. Don't forget to star (🌟) this repo to find it easier later. ## 🧠 Ready to Deploy? If you are looking for more advanced code samples, check out our collection of Generative AI Code Samples in both **Python** and **TypeScript**. ## 🗣️ Meet Other Learners, Get Support Join our official AI Discord server to meet and network with other learners taking this course and get support. ## 🚀 Building a Startup? Sign up for Microsoft for Startups Founders Hub to receive **free OpenAI credits** and up to **$150k towards Azure credits to access OpenAI models through Azure OpenAI Services**. ## 🙏 Want to help? Do you have suggestions or found spelling or code errors? Raise an issue or Create a pull request ## 📂 Each lesson includes: * A short video introduction to the topic * A written lesson located in the README * Python and TypeScript code samples supporting Azure OpenAI and OpenAI API * Links to extra resources to continue your learning ## 🗃️ Lessons | | Lesson Link | Description | Additional Learning | | :-: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | | 00 | Course Setup | **Learn:** How to Setup Your Development Environment | Learn More | | 01 | Introduction to Generative AI and LLMs | **Learn:** Understanding what Generative AI is and how Large Language Models (LLMs) work. | Learn More | | 02 | Exploring and comparing different LLMs | **Learn:** How to select the right model for your use case | Learn More | | 03 | Using Generative AI Responsibly | **Learn:** How to build Generative AI Applications responsibly | Learn More | | 04 | Understanding Prompt Engineering Fundamentals | **Learn:** Hands-on Prompt Engineering Best Practices | Learn More | | 05 | Creating Advanced Prompts | **Learn:** How to apply prompt engineering techniques that improve the outcome of your prompts. | Learn More | | 06 | Building Text Generation Applications | **Build:** A text generation app using Azure OpenAI | Learn More | | 07 | Building Chat Applications | **Build:** Techniques for efficiently building and integrating chat applications. | Learn More | | 08 | Building Search Apps Vector Databases | **Build:** A search application that uses Embeddings to search for data. | Learn More | | 09 | Building Image Generation Applications | **Build:** A image generation application | Learn More | | 10 | Building Low Code AI Applications | **Build:** A Generative AI application using Low Code tools | Learn More | | 11 | Integrating External Applications with Function Calling | **Build:** What is function calling and its use cases for applications | Learn More | | 12 | Designing UX for AI Applications | **Learn:** How to apply UX design principles when developing Generative AI Applications | Learn More | | 13 | Securing Your Generative AI Applications | **Learn:** The threats and risks to AI systems and methods to secure these systems. | Learn More | | 14 | The Generative AI Application Lifecycle | **Learn:** The tools and metrics to manage the LLM Lifecycle and LLMOps | Learn More | | 15 | Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Vector Databases | **Build:** An application using a RAG Framework to retrieve embeddings from a Vector Databases | Learn More | | 16 | Open Source Models and Hugging Face | **Build:** An application using open source models available on Hugging Face | Learn More | | 17 | AI Agents | **Build:** An application using an AI Agent Framework | Learn More | | 18 | Fine-Tuning LLMs | **Learn:** The what, why and how of fine-tuning LLMs | Learn More |

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
GenAIComps
GenAIComps is an initiative aimed at building enterprise-grade Generative AI applications using a microservice architecture. It simplifies the scaling and deployment process for production, abstracting away infrastructure complexities. GenAIComps provides a suite of containerized microservices that can be assembled into a mega-service tailored for real-world Enterprise AI applications. The modular approach of microservices allows for independent development, deployment, and scaling of individual components, promoting modularity, flexibility, and scalability. The mega-service orchestrates multiple microservices to deliver comprehensive solutions, encapsulating complex business logic and workflow orchestration. The gateway serves as the interface for users to access the mega-service, providing customized access based on user requirements.
dl_model_infer
This project is a c++ version of the AI reasoning library that supports the reasoning of tensorrt models. It provides accelerated deployment cases of deep learning CV popular models and supports dynamic-batch image processing, inference, decode, and NMS. The project has been updated with various models and provides tutorials for model exports. It also includes a producer-consumer inference model for specific tasks. The project directory includes implementations for model inference applications, backend reasoning classes, post-processing, pre-processing, and target detection and tracking. Speed tests have been conducted on various models, and onnx downloads are available for different models.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
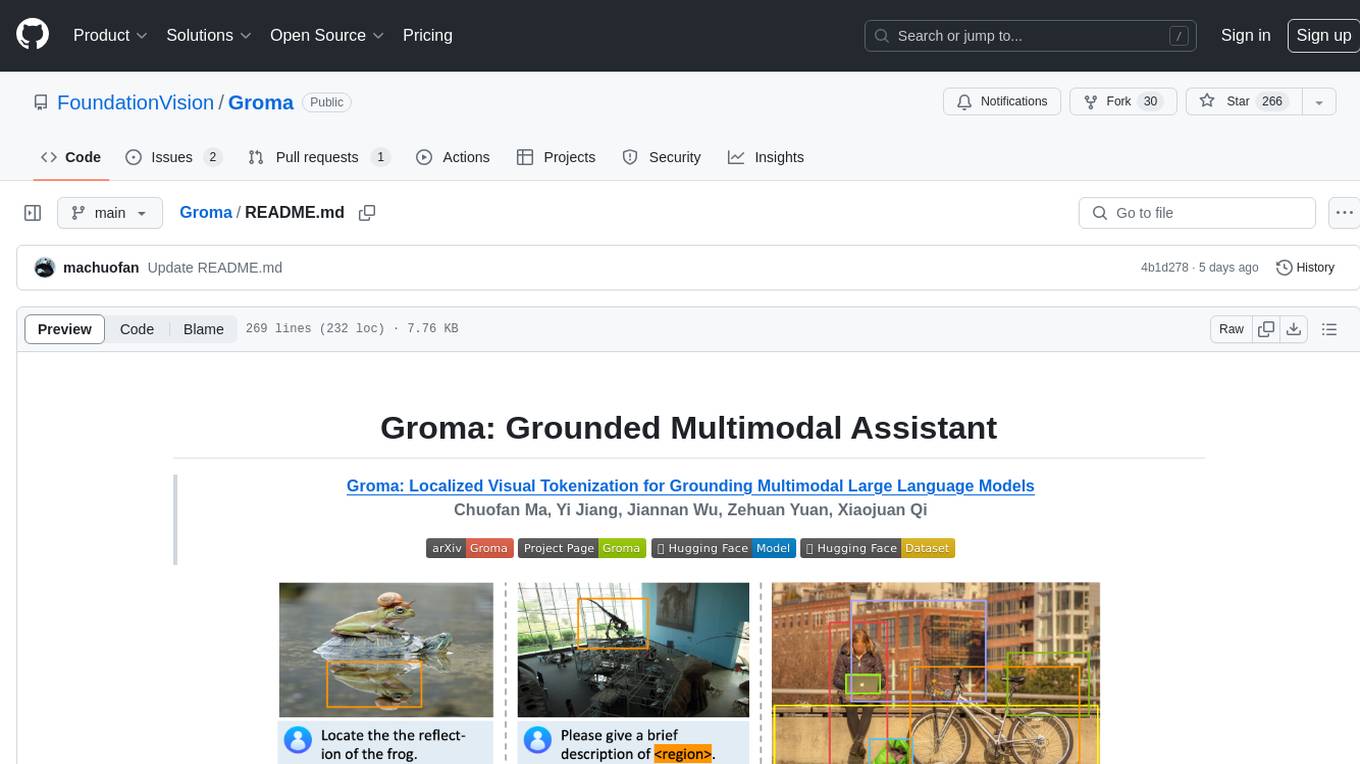
Groma
Groma is a grounded multimodal assistant that excels in region understanding and visual grounding. It can process user-defined region inputs and generate contextually grounded long-form responses. The tool presents a unique paradigm for multimodal large language models, focusing on visual tokenization for localization. Groma achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension benchmarks. The tool provides pretrained model weights and instructions for data preparation, training, inference, and evaluation. Users can customize training by starting from intermediate checkpoints. Groma is designed to handle tasks related to detection pretraining, alignment pretraining, instruction finetuning, instruction following, and more.
amber-train
Amber is the first model in the LLM360 family, an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs. It is a 7B English language model with the LLaMA architecture. The model type is a language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B. It is licensed under Apache 2.0. The resources available include training code, data preparation, metrics, and fully processed Amber pretraining data. The model has been trained on various datasets like Arxiv, Book, C4, Refined-Web, StarCoder, StackExchange, and Wikipedia. The hyperparameters include a total of 6.7B parameters, hidden size of 4096, intermediate size of 11008, 32 attention heads, 32 hidden layers, RMSNorm ε of 1e^-6, max sequence length of 2048, and a vocabulary size of 32000.
pytorch-grad-cam
This repository provides advanced AI explainability for PyTorch, offering state-of-the-art methods for Explainable AI in computer vision. It includes a comprehensive collection of Pixel Attribution methods for various tasks like Classification, Object Detection, Semantic Segmentation, and more. The package supports high performance with full batch image support and includes metrics for evaluating and tuning explanations. Users can visualize and interpret model predictions, making it suitable for both production and model development scenarios.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

MNN
MNN is a highly efficient and lightweight deep learning framework that supports inference and training of deep learning models. It has industry-leading performance for on-device inference and training. MNN has been integrated into various Alibaba Inc. apps and is used in scenarios like live broadcast, short video capture, search recommendation, and product searching by image. It is also utilized on embedded devices such as IoT. MNN-LLM and MNN-Diffusion are specific runtime solutions developed based on the MNN engine for deploying language models and diffusion models locally on different platforms. The framework is optimized for devices, supports various neural networks, and offers high performance with optimized assembly code and GPU support. MNN is versatile, easy to use, and supports hybrid computing on multiple devices.
For similar tasks

cl-waffe2
cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.
xlang
XLang™ is a cutting-edge language designed for AI and IoT applications, offering exceptional dynamic and high-performance capabilities. It excels in distributed computing and seamless integration with popular languages like C++, Python, and JavaScript. Notably efficient, running 3 to 5 times faster than Python in AI and deep learning contexts. Features optimized tensor computing architecture for constructing neural networks through tensor expressions. Automates tensor data flow graph generation and compilation for specific targets, enhancing GPU performance by 6 to 10 times in CUDA environments.
AI-resources
AI-resources is a repository containing links to various resources for learning Artificial Intelligence. It includes video lectures, courses, tutorials, and open-source libraries related to deep learning, reinforcement learning, machine learning, and more. The repository categorizes resources for beginners, average users, and advanced users/researchers, providing a comprehensive collection of materials to enhance knowledge and skills in AI.

ai-hands-on
A complete, hands-on guide to becoming an AI Engineer. This repository is designed to help you learn AI from first principles, build real neural networks, and understand modern LLM systems end-to-end. Progress through math, PyTorch, deep learning, transformers, RAG, and OCR with clean, intuitive Jupyter notebooks guiding you at every step. Suitable for beginners and engineers leveling up, providing clarity, structure, and intuition to build real AI systems.
ByteMLPerf
ByteMLPerf is an AI Accelerator Benchmark that focuses on evaluating AI Accelerators from a practical production perspective, including the ease of use and versatility of software and hardware. Byte MLPerf has the following characteristics: - Models and runtime environments are more closely aligned with practical business use cases. - For ASIC hardware evaluation, besides evaluate performance and accuracy, it also measure metrics like compiler usability and coverage. - Performance and accuracy results obtained from testing on the open Model Zoo serve as reference metrics for evaluating ASIC hardware integration.
AIFoundation
AIFoundation focuses on AI Foundation, large model systems. Large models optimize the performance of full-stack hardware and software based on AI clusters. The training process requires distributed parallelism, cluster communication algorithms, and continuous evolution in the field of large models such as intelligent agents. The course covers modules like AI chip principles, communication & storage, AI clusters, computing architecture, communication architecture, large model algorithms, training, inference, and analysis of hot technologies in the large model field.
LightRAG
LightRAG is a repository hosting the code for LightRAG, a system that supports seamless integration of custom knowledge graphs, Oracle Database 23ai, Neo4J for storage, and multiple file types. It includes features like entity deletion, batch insert, incremental insert, and graph visualization. LightRAG provides an API server implementation for RESTful API access to RAG operations, allowing users to interact with it through HTTP requests. The repository also includes evaluation scripts, code for reproducing results, and a comprehensive code structure.
aistore
AIStore is a lightweight object storage system designed for AI applications. It is highly scalable, reliable, and easy to use. AIStore can be deployed on any commodity hardware, and it can be used to store and manage large datasets for deep learning and other AI applications.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.








