
QuantaAlpha
QuantaAlpha transforms how you discover quantitative alpha factors by combining LLM intelligence with evolutionary strategies. Just describe your research direction, and watch as factors are automatically mined, evolved, and validated through self-evolving trajectories.
Stars: 351
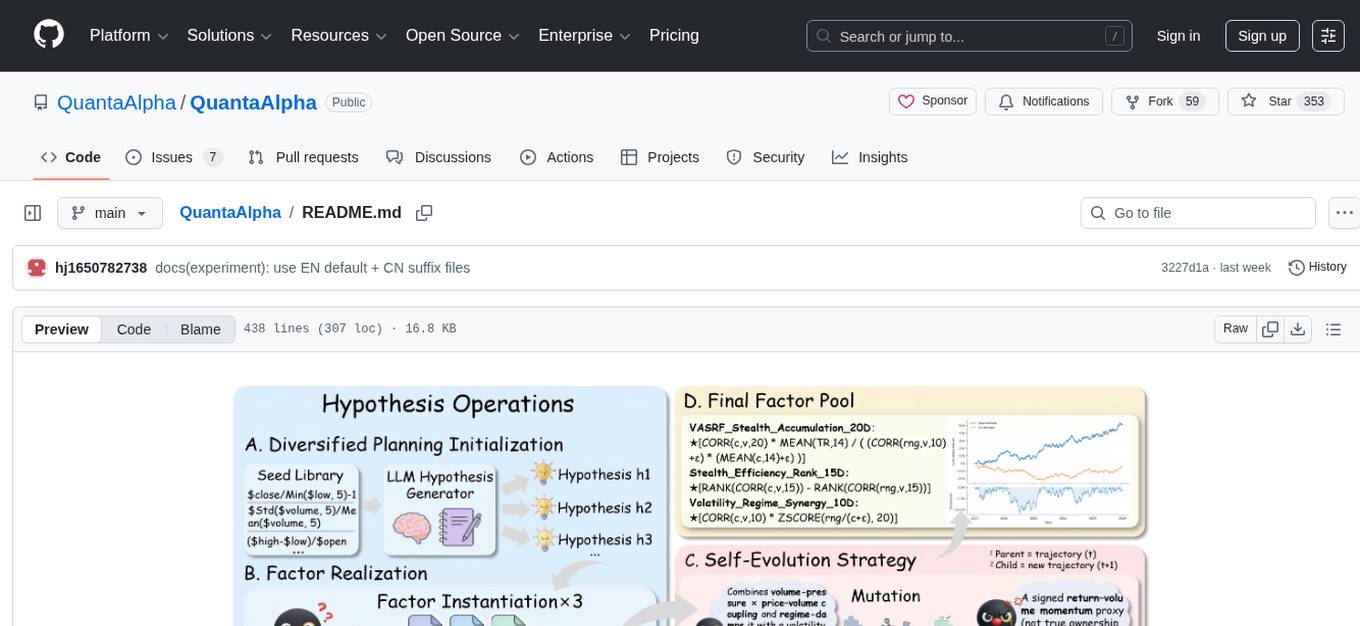
QuantaAlpha is a framework designed for factor mining in quantitative alpha research. It combines LLM intelligence with evolutionary strategies to automatically mine, evolve, and validate alpha factors through self-evolving trajectories. The framework provides a trajectory-based approach with diversified planning initialization and structured hypothesis-code constraint. Users can describe their research direction and observe the automatic factor mining process. QuantaAlpha aims to transform how quantitative alpha factors are discovered by leveraging advanced technologies and self-evolving methodologies.
README:
🧬 Achieving superior quantitative alpha through trajectory-based self-evolution with diversified planning initialization, trajectory-level evolution, and structured hypothesis-code constraint
QuantaAlpha transforms how you discover quantitative alpha factors by combining LLM intelligence with evolutionary strategies. Just describe your research direction, and watch as factors are automatically mined, evolved, and validated through self-evolving trajectories.
💬 Research Direction → 🧩 Diversified Planning → 🔄 Trajectory → ✅ Validated Alpha Factors
Demo: Below is a short demo of the full flow from research direction to factor mining and backtesting UI.
▶ Click to play the QuantaAlpha end-to-end workflow demo.
| Dimension | Metric | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Predictive Power | Information Coefficient (IC) | 0.1501 |
| Rank IC | 0.1465 | |
| Strategy Return | Annualized Excess Return (ARR) | 27.75% |
| Max Drawdown (MDD) | 7.98% | |
| Calmar Ratio (CR) | 3.4774 |
🔬 Experiments: paper reproduction settings & metric definitions — English · 中文
git clone https://github.com/QuantaAlpha/QuantaAlpha.git
cd QuantaAlpha
conda create -n quantaalpha python=3.10
conda activate quantaalpha
# Install the package in development mode
SETUPTOOLS_SCM_PRETEND_VERSION=0.1.0 pip install -e .
# Install additional dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txtcp configs/.env.example .envEdit .env with your settings:
# === Required: Data Paths ===
QLIB_DATA_DIR=/path/to/your/qlib/cn_data # Qlib data directory
DATA_RESULTS_DIR=/path/to/your/results # Output directory
# === Required: LLM API ===
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-api-key
OPENAI_BASE_URL=https://your-llm-provider/v1 # e.g. DashScope, OpenAI
CHAT_MODEL=deepseek-v3 # or gpt-4, qwen-max, etc.
REASONING_MODEL=deepseek-v3QuantaAlpha requires two types of data: Qlib market data (for backtesting) and pre-computed price-volume HDF5 files (for factor mining). We provide all of them on HuggingFace for convenience.
Dataset: https://huggingface.co/datasets/QuantaAlpha/qlib_csi300
| File | Description | Size | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
cn_data.zip |
Qlib raw market data (A-share, 2016–2025) | 493 MB | Required for Qlib initialization & backtesting |
daily_pv.h5 |
Pre-computed full price-volume data | 398 MB | Required for factor mining |
daily_pv_debug.h5 |
Pre-computed debug subset (smaller) | 1.41 MB | Required for factor mining (debug/validation) |
Why provide HDF5 files? The system can auto-generate
daily_pv.h5from Qlib data on first run, but this process is very slow. Downloading pre-built HDF5 files saves significant time.
# Option A: Using huggingface-cli (recommended)
pip install huggingface_hub
huggingface-cli download QuantaAlpha/qlib_csi300 --repo-type dataset --local-dir ./hf_data
# Option B: Using wget
mkdir -p hf_data
wget -P hf_data https://huggingface.co/datasets/QuantaAlpha/qlib_csi300/resolve/main/cn_data.zip
wget -P hf_data https://huggingface.co/datasets/QuantaAlpha/qlib_csi300/resolve/main/daily_pv.h5
wget -P hf_data https://huggingface.co/datasets/QuantaAlpha/qlib_csi300/resolve/main/daily_pv_debug.h5# 1. Extract Qlib data
unzip hf_data/cn_data.zip -d ./data/qlib
# 2. Place HDF5 files into the default data directories
mkdir -p git_ignore_folder/factor_implementation_source_data
mkdir -p git_ignore_folder/factor_implementation_source_data_debug
cp hf_data/daily_pv.h5 git_ignore_folder/factor_implementation_source_data/daily_pv.h5
cp hf_data/daily_pv_debug.h5 git_ignore_folder/factor_implementation_source_data_debug/daily_pv.h5Note:
daily_pv_debug.h5must be renamed todaily_pv.h5when placed in the debug directory.
# Point to the extracted Qlib data directory (must contain calendars/, features/, instruments/)
QLIB_DATA_DIR=./data/qlib/cn_data
# Output directory for experiment results
DATA_RESULTS_DIR=./data/resultsThe HDF5 data directories can also be customized via environment variables if you prefer a different location:
# Optional: override default HDF5 data paths
FACTOR_CoSTEER_DATA_FOLDER=/your/custom/path/factor_source_data
FACTOR_CoSTEER_DATA_FOLDER_DEBUG=/your/custom/path/factor_source_data_debug./run.sh "<your input>"
# Example: Run with a research direction
./run.sh "Price-Volume Factor Mining"
# Example: Run with custom factor library suffix
./run.sh "Microstructure Factors" "exp_micro"The experiment will automatically mine, evolve, and validate alpha factors, and save all discovered factors to all_factors_library*.json.
After mining, combine factors from the library for a full-period backtest:
# Backtest with custom factors only
python -m quantaalpha.backtest.run_backtest \
-c configs/backtest.yaml \
--factor-source custom \
--factor-json all_factors_library.json
# Combine with Alpha158(20) baseline factors
python -m quantaalpha.backtest.run_backtest \
-c configs/backtest.yaml \
--factor-source combined \
--factor-json all_factors_library.json
# Dry run (load factors only, skip backtest)
python -m quantaalpha.backtest.run_backtest \
-c configs/backtest.yaml \
--factor-source custom \
--factor-json all_factors_library.json \
--dry-run -vResults are saved to the directory specified in configs/backtest.yaml (experiment.output_dir).
📘 Need help? Check our comprehensive User Guide for advanced configuration, experiment reproduction, and detailed usage examples.
QuantaAlpha provides a web-based dashboard where you can complete the entire workflow through a visual interface — no command line needed.
conda activate quantaalpha
cd frontend-v2
bash start.sh
# Visit http://localhost:3000- ⚙️ Settings: Configure LLM API, data paths, and experiment parameters directly in the UI
- ⛏️ Factor Mining: Start experiments with natural language input and monitor progress in real-time
- 📚 Factor Library: Browse, search, and filter all discovered factors with quality classifications
- 📈 Independent Backtest: Select a factor library and run full-period backtests with visual results
QuantaAlpha is natively developed for Linux. Below is a guide to run it on Windows 10/11.
For technical details, see
docs/WINDOWS_COMPAT.md.
| Feature | Linux | Windows |
|---|---|---|
| Start mining | ./run.sh "direction" |
python launcher.py mine --direction "direction" |
| Start frontend | bash start.sh |
Start backend & frontend separately (see below) |
.env path format |
/home/user/data |
C:/Users/user/data (use forward slashes) |
| Extra config | None | Must set CONDA_DEFAULT_ENV (see below) |
| rdagent patches | None | Auto-applied (quantaalpha/compat/rdagent_patches.py) |
# 1. Install Miniconda (check "Add to PATH" during setup)
# 2. Create conda environment
conda create -n quantaalpha python=3.11 -y
conda activate quantaalpha
# 3. Clone and install
git clone https://github.com/QuantaAlpha/QuantaAlpha.git
cd QuantaAlpha
set SETUPTOOLS_SCM_PRETEND_VERSION=0.1.0
pip install -e .copy configs\.env.example .envEdit .env — use forward slashes for paths:
QLIB_DATA_DIR=C:/Users/yourname/path/to/cn_data
DATA_RESULTS_DIR=C:/Users/yourname/path/to/results
CONDA_ENV_NAME=quantaalpha
CONDA_DEFAULT_ENV=quantaalpha # ← Required on Windows# Factor mining
python launcher.py mine --direction "price-volume factor mining"
# Standalone backtest
python -m quantaalpha.backtest.run_backtest -c configs/backtest.yaml --factor-source custom --factor-json data/factorlib/all_factors_library.json -vRequires Node.js (v18+). Start in two terminals:
# Terminal 1 — Backend API
cd frontend-v2 && python backend/app.py
# Terminal 2 — Frontend
cd frontend-v2 && npm install && npm run devVisit http://localhost:3000.
| Error | Fix |
|---|---|
CondaConf conda_env_name: Input should be a valid string |
Add CONDA_DEFAULT_ENV=quantaalpha to .env
|
UnicodeEncodeError: 'gbk' |
Run chcp 65001 or set PYTHONIOENCODING=utf-8
|
Failed to resolve import "@radix-ui/react-hover-card" |
cd frontend-v2 && npm install |
We welcome all forms of contributions to make QuantaAlpha better! Here's how you can get involved:
- 🐛 Bug Reports: Found a bug? Open an issue to help us fix it.
- 💡 Feature Requests: Have a great idea? Start a discussion to suggest new features.
- 📝 Docs & Tutorials: Improve documentation, add usage examples, or write tutorials.
- 🔧 Code Contributions: Submit PRs for bug fixes, performance improvements, or new functionality.
- 🧬 New Factors: Share high-quality factors discovered in your own runs to benefit the community.
Special thanks to:
- Qlib - Quantitative investment platform by Microsoft
- RD-Agent - An automated R&D framework by Microsoft (NeurIPS 2025)
- AlphaAgent - Multi-agent alpha factor mining framework (KDD 2025)
- QuantaAlpha was founded in April 2025 by a team of professors, postdocs, PhDs, and master's students from Tsinghua University, Peking University, CAS, CMU, HKUST, and more.
🌟 Our mission is to explore the "quantum" of intelligence and pioneer the "alpha" frontier of agent research — from CodeAgents to self-evolving intelligence, and further to financial and cross-domain specialized agents, we are committed to redefining the boundaries of AI.
✨ In 2026, we will continue to produce high-quality research in the following directions:
-
CodeAgent: End-to-end autonomous execution of real-world tasks
-
DeepResearch: Deep reasoning and retrieval-augmented intelligence
-
Agentic Reasoning / Agentic RL: Agent-based reasoning and reinforcement learning
-
Self-evolution and collaborative learning: Evolution and coordination of multi-agent systems
📢 We welcome students and researchers interested in these directions to join us!
🔗 Team Homepage: QuantaAlpha
📧 Email: [email protected]
Initiated by Professor Liwen Zhang from Shanghai University of Finance and Economics (SUFE), AIFin Lab is deeply rooted in the interdisciplinary fields of AI + Finance, Statistics, and Data Science. The team brings together cutting-edge scholars from top institutions such as SUFE, FDU, SEU, CMU, and CUHK. We are dedicated to building a comprehensive "full-link" system covering data, models, benchmarks, and intelligent prompting.
📢 We are actively looking for talented students (UG/Master/PhD) and researchers worldwide who are passionate about AI Agent security and financial intelligence to join AIFin Lab!
📧 Email: [email protected] (please CC to [email protected])
We look forward to hearing from you!
If you find QuantaAlpha useful in your research, please cite our work:
@misc{han2026quantaalphaevolutionaryframeworkllmdriven,
title={QuantaAlpha: An Evolutionary Framework for LLM-Driven Alpha Mining},
author={Jun Han and Shuo Zhang and Wei Li and Zhi Yang and Yifan Dong and Tu Hu and Jialuo Yuan and Xiaomin Yu and Yumo Zhu and Fangqi Lou and Xin Guo and Zhaowei Liu and Tianyi Jiang and Ruichuan An and Jingping Liu and Biao Wu and Rongze Chen and Kunyi Wang and Yifan Wang and Sen Hu and Xinbing Kong and Liwen Zhang and Ronghao Chen and Huacan Wang},
year={2026},
eprint={2602.07085},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={q-fin.ST},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2602.07085},
}⭐ If QuantaAlpha helps you, please give us a star!
Made with ❤️ by the QuantaAlpha Team
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for QuantaAlpha
Similar Open Source Tools

QuantaAlpha
QuantaAlpha is a framework designed for factor mining in quantitative alpha research. It combines LLM intelligence with evolutionary strategies to automatically mine, evolve, and validate alpha factors through self-evolving trajectories. The framework provides a trajectory-based approach with diversified planning initialization and structured hypothesis-code constraint. Users can describe their research direction and observe the automatic factor mining process. QuantaAlpha aims to transform how quantitative alpha factors are discovered by leveraging advanced technologies and self-evolving methodologies.
OpenResearcher
OpenResearcher is a fully open agentic large language model designed for long-horizon deep research scenarios. It achieves an impressive 54.8% accuracy on BrowseComp-Plus, surpassing performance of GPT-4.1, Claude-Opus-4, Gemini-2.5-Pro, DeepSeek-R1, and Tongyi-DeepResearch. The tool is fully open-source, providing the training and evaluation recipe—including data, model, training methodology, and evaluation framework for everyone to progress deep research. It offers features like a fully open-source recipe, highly scalable and low-cost generation of deep research trajectories, and remarkable performance on deep research benchmarks.
tokscale
Tokscale is a high-performance CLI tool and visualization dashboard for tracking token usage and costs across multiple AI coding agents. It helps monitor and analyze token consumption from various AI coding tools, providing real-time pricing calculations using LiteLLM's pricing data. Inspired by the Kardashev scale, Tokscale measures token consumption as users scale the ranks of AI-augmented development. It offers interactive TUI mode, multi-platform support, real-time pricing, detailed breakdowns, web visualization, flexible filtering, and social platform features.
ctinexus
CTINexus is a framework that leverages optimized in-context learning of large language models to automatically extract cyber threat intelligence from unstructured text and construct cybersecurity knowledge graphs. It processes threat intelligence reports to extract cybersecurity entities, identify relationships between security concepts, and construct knowledge graphs with interactive visualizations. The framework requires minimal configuration, with no extensive training data or parameter tuning needed.
llamafarm
LlamaFarm is a comprehensive AI framework that empowers users to build powerful AI applications locally, with full control over costs and deployment options. It provides modular components for RAG systems, vector databases, model management, prompt engineering, and fine-tuning. Users can create differentiated AI products without needing extensive ML expertise, using simple CLI commands and YAML configs. The framework supports local-first development, production-ready components, strategy-based configuration, and deployment anywhere from laptops to the cloud.
mindnlp
MindNLP is an open-source NLP library based on MindSpore. It provides a platform for solving natural language processing tasks, containing many common approaches in NLP. It can help researchers and developers to construct and train models more conveniently and rapidly. Key features of MindNLP include: * Comprehensive data processing: Several classical NLP datasets are packaged into a friendly module for easy use, such as Multi30k, SQuAD, CoNLL, etc. * Friendly NLP model toolset: MindNLP provides various configurable components. It is friendly to customize models using MindNLP. * Easy-to-use engine: MindNLP simplified complicated training process in MindSpore. It supports Trainer and Evaluator interfaces to train and evaluate models easily. MindNLP supports a wide range of NLP tasks, including: * Language modeling * Machine translation * Question answering * Sentiment analysis * Sequence labeling * Summarization MindNLP also supports industry-leading Large Language Models (LLMs), including Llama, GLM, RWKV, etc. For support related to large language models, including pre-training, fine-tuning, and inference demo examples, you can find them in the "llm" directory. To install MindNLP, you can either install it from Pypi, download the daily build wheel, or install it from source. The installation instructions are provided in the documentation. MindNLP is released under the Apache 2.0 license. If you find this project useful in your research, please consider citing the following paper: @misc{mindnlp2022, title={{MindNLP}: a MindSpore NLP library}, author={MindNLP Contributors}, howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/mindlab-ai/mindnlp}}, year={2022} }
agentfield
AgentField is an open-source control plane designed for autonomous AI agents, providing infrastructure for agents to make decisions beyond chatbots. It offers features like scaling infrastructure, routing & discovery, async execution, durable state, observability, trust infrastructure with cryptographic identity, verifiable credentials, and policy enforcement. Users can write agents in Python, Go, TypeScript, or interact via REST APIs. The tool enables the creation of AI backends that reason autonomously within defined boundaries, offering predictability and flexibility. AgentField aims to bridge the gap between AI frameworks and production-ready infrastructure for AI agents.
dexto
Dexto is a lightweight runtime for creating and running AI agents that turn natural language into real-world actions. It serves as the missing intelligence layer for building AI applications, standalone chatbots, or as the reasoning engine inside larger products. Dexto features a powerful CLI and Web UI for running AI agents, supports multiple interfaces, allows hot-swapping of LLMs from various providers, connects to remote tool servers via the Model Context Protocol, is config-driven with version-controlled YAML, offers production-ready core features, extensibility for custom services, and enables multi-agent collaboration via MCP and A2A.
RepairAgent
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair targeting the Defects4J benchmark. It uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs. The tool requires Docker, VS Code with Dev Containers extension, OpenAI API key, disk space of ~40 GB, and internet access. Users can get started with RepairAgent using either VS Code Dev Container or Docker Image. Running RepairAgent involves checking out the buggy project version, autonomous bug analysis, fix candidate generation, and testing against the project's test suite. Users can configure hyperparameters for budget control, repetition handling, commands limit, and external fix strategy. The tool provides output structure, experiment overview, individual analysis scripts, and data on fixed bugs from the Defects4J dataset.
LLMTSCS
LLMLight is a novel framework that employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for Traffic Signal Control (TSC). The framework leverages the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs to engage in a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. LLMLight has been demonstrated to be remarkably effective, generalizable, and interpretable against various transportation-based and RL-based baselines on nine real-world and synthetic datasets.
models
A fast CLI and TUI for browsing AI models, benchmarks, and coding agents. Browse 2000+ models across 85+ providers from models.dev. Track AI coding assistants with version detection and GitHub integration. Compare model performance across 15+ benchmarks from Artificial Analysis. Features CLI commands, interactive TUI, cross-provider search, copy to clipboard, JSON output. Includes curated catalog of AI coding assistants, auto-updating benchmark data, per-model open weights detection, and detail panel for benchmarks. Supports customization of tracked agents and quick sorting of benchmarks. Utilizes data from models.dev, Artificial Analysis, curated catalog in data/agents.json, and GitHub API.
automem
AutoMem is a production-grade long-term memory system for AI assistants, achieving 90.53% accuracy on the LoCoMo benchmark. It combines FalkorDB (Graph) and Qdrant (Vectors) storage systems to store, recall, connect, learn, and perform with memories. AutoMem enables AI assistants to remember, connect, and evolve their understanding over time, similar to human long-term memory. It implements techniques from peer-reviewed memory research and offers features like multi-hop bridge discovery, knowledge graphs that evolve, 9-component hybrid scoring, memory consolidation cycles, background intelligence, 11 relationship types, and more. AutoMem is benchmark-proven, research-validated, and production-ready, with features like sub-100ms recall, concurrent writes, automatic retries, health monitoring, dual storage redundancy, and automated backups.
sdk
The Kubeflow SDK is a set of unified Pythonic APIs that simplify running AI workloads at any scale without needing to learn Kubernetes. It offers consistent APIs across the Kubeflow ecosystem, enabling users to focus on building AI applications rather than managing complex infrastructure. The SDK provides a unified experience, simplifies AI workloads, is built for scale, allows rapid iteration, and supports local development without a Kubernetes cluster.
llm4s
LLM4S provides a simple, robust, and scalable framework for building Large Language Models (LLM) applications in Scala. It aims to leverage Scala's type safety, functional programming, JVM ecosystem, concurrency, and performance advantages to create reliable and maintainable AI-powered applications. The framework supports multi-provider integration, execution environments, error handling, Model Context Protocol (MCP) support, agent frameworks, multimodal generation, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) workflows. It also offers observability features like detailed trace logging, monitoring, and analytics for debugging and performance insights.
Edit-Banana
Edit Banana is a universal content re-editor that allows users to transform fixed content into fully manipulatable assets. Powered by SAM 3 and multimodal large models, it enables high-fidelity reconstruction while preserving original diagram details and logical relationships. The platform offers advanced segmentation, fixed multi-round VLM scanning, high-quality OCR, user system with credits, multi-user concurrency, and a web interface. Users can upload images or PDFs to get editable DrawIO (XML) or PPTX files in seconds. The project structure includes components for segmentation, text extraction, frontend, models, and scripts, with detailed installation and setup instructions provided. The tool is open-source under the Apache License 2.0, allowing commercial use and secondary development.

OSA
OSA (Open-Source-Advisor) is a tool designed to improve the quality of scientific open source projects by automating the generation of README files, documentation, CI/CD scripts, and providing advice and recommendations for repositories. It supports various LLMs accessible via API, local servers, or osa_bot hosted on ITMO servers. OSA is currently under development with features like README file generation, documentation generation, automatic implementation of changes, LLM integration, and GitHub Action Workflow generation. It requires Python 3.10 or higher and tokens for GitHub/GitLab/Gitverse and LLM API key. Users can install OSA using PyPi or build from source, and run it using CLI commands or Docker containers.
For similar tasks

QuantaAlpha
QuantaAlpha is a framework designed for factor mining in quantitative alpha research. It combines LLM intelligence with evolutionary strategies to automatically mine, evolve, and validate alpha factors through self-evolving trajectories. The framework provides a trajectory-based approach with diversified planning initialization and structured hypothesis-code constraint. Users can describe their research direction and observe the automatic factor mining process. QuantaAlpha aims to transform how quantitative alpha factors are discovered by leveraging advanced technologies and self-evolving methodologies.
For similar jobs
qlib
Qlib is an open-source, AI-oriented quantitative investment platform that supports diverse machine learning modeling paradigms, including supervised learning, market dynamics modeling, and reinforcement learning. It covers the entire chain of quantitative investment, from alpha seeking to order execution. The platform empowers researchers to explore ideas and implement productions using AI technologies in quantitative investment. Qlib collaboratively solves key challenges in quantitative investment by releasing state-of-the-art research works in various paradigms. It provides a full ML pipeline for data processing, model training, and back-testing, enabling users to perform tasks such as forecasting market patterns, adapting to market dynamics, and modeling continuous investment decisions.
jupyter-quant
Jupyter Quant is a dockerized environment tailored for quantitative research, equipped with essential tools like statsmodels, pymc, arch, py_vollib, zipline-reloaded, PyPortfolioOpt, numpy, pandas, sci-py, scikit-learn, yellowbricks, shap, optuna, ib_insync, Cython, Numba, bottleneck, numexpr, jedi language server, jupyterlab-lsp, black, isort, and more. It does not include conda/mamba and relies on pip for package installation. The image is optimized for size, includes common command line utilities, supports apt cache, and allows for the installation of additional packages. It is designed for ephemeral containers, ensuring data persistence, and offers volumes for data, configuration, and notebooks. Common tasks include setting up the server, managing configurations, setting passwords, listing installed packages, passing parameters to jupyter-lab, running commands in the container, building wheels outside the container, installing dotfiles and SSH keys, and creating SSH tunnels.
FinRobot
FinRobot is an open-source AI agent platform designed for financial applications using large language models. It transcends the scope of FinGPT, offering a comprehensive solution that integrates a diverse array of AI technologies. The platform's versatility and adaptability cater to the multifaceted needs of the financial industry. FinRobot's ecosystem is organized into four layers, including Financial AI Agents Layer, Financial LLMs Algorithms Layer, LLMOps and DataOps Layers, and Multi-source LLM Foundation Models Layer. The platform's agent workflow involves Perception, Brain, and Action modules to capture, process, and execute financial data and insights. The Smart Scheduler optimizes model diversity and selection for tasks, managed by components like Director Agent, Agent Registration, Agent Adaptor, and Task Manager. The tool provides a structured file organization with subfolders for agents, data sources, and functional modules, along with installation instructions and hands-on tutorials.
hands-on-lab-neo4j-and-vertex-ai
This repository provides a hands-on lab for learning about Neo4j and Google Cloud Vertex AI. It is intended for data scientists and data engineers to deploy Neo4j and Vertex AI in a Google Cloud account, work with real-world datasets, apply generative AI, build a chatbot over a knowledge graph, and use vector search and index functionality for semantic search. The lab focuses on analyzing quarterly filings of asset managers with $100m+ assets under management, exploring relationships using Neo4j Browser and Cypher query language, and discussing potential applications in capital markets such as algorithmic trading and securities master data management.
jupyter-quant
Jupyter Quant is a dockerized environment tailored for quantitative research, equipped with essential tools like statsmodels, pymc, arch, py_vollib, zipline-reloaded, PyPortfolioOpt, numpy, pandas, sci-py, scikit-learn, yellowbricks, shap, optuna, and more. It provides Interactive Broker connectivity via ib_async and includes major Python packages for statistical and time series analysis. The image is optimized for size, includes jedi language server, jupyterlab-lsp, and common command line utilities. Users can install new packages with sudo, leverage apt cache, and bring their own dot files and SSH keys. The tool is designed for ephemeral containers, ensuring data persistence and flexibility for quantitative analysis tasks.
Qbot
Qbot is an AI-oriented automated quantitative investment platform that supports diverse machine learning modeling paradigms, including supervised learning, market dynamics modeling, and reinforcement learning. It provides a full closed-loop process from data acquisition, strategy development, backtesting, simulation trading to live trading. The platform emphasizes AI strategies such as machine learning, reinforcement learning, and deep learning, combined with multi-factor models to enhance returns. Users with some Python knowledge and trading experience can easily utilize the platform to address trading pain points and gaps in the market.
FinMem-LLM-StockTrading
This repository contains the Python source code for FINMEM, a Performance-Enhanced Large Language Model Trading Agent with Layered Memory and Character Design. It introduces FinMem, a novel LLM-based agent framework devised for financial decision-making, encompassing three core modules: Profiling, Memory with layered processing, and Decision-making. FinMem's memory module aligns closely with the cognitive structure of human traders, offering robust interpretability and real-time tuning. The framework enables the agent to self-evolve its professional knowledge, react agilely to new investment cues, and continuously refine trading decisions in the volatile financial environment. It presents a cutting-edge LLM agent framework for automated trading, boosting cumulative investment returns.
LLMs-in-Finance
This repository focuses on the application of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of finance. It provides insights and knowledge about how LLMs can be utilized in various scenarios within the finance industry, particularly in generating AI agents. The repository aims to explore the potential of LLMs to enhance financial processes and decision-making through the use of advanced natural language processing techniques.











