
RepairAgent
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for software repair.
Stars: 82
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair targeting the Defects4J benchmark. It uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs. The tool requires Docker, VS Code with Dev Containers extension, OpenAI API key, disk space of ~40 GB, and internet access. Users can get started with RepairAgent using either VS Code Dev Container or Docker Image. Running RepairAgent involves checking out the buggy project version, autonomous bug analysis, fix candidate generation, and testing against the project's test suite. Users can configure hyperparameters for budget control, repetition handling, commands limit, and external fix strategy. The tool provides output structure, experiment overview, individual analysis scripts, and data on fixed bugs from the Defects4J dataset.
README:
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair. It targets the Defects4J benchmark and uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs.
For details on the approach and evaluation, see the research paper.
- Requirements
- Getting Started
- Running RepairAgent
- Configuration
- Analyzing Results
- Replicating Experiments
- Our Data
- Contributing
- Docker >= 20.04 (install)
- VS Code with the Dev Containers extension (recommended, not required)
- OpenAI API key with credits (get one here)
- Disk space: ~40 GB (dependencies ~8 GB; experiment artifacts grow over time)
- Internet access for OpenAI API calls during execution
This is the easiest method. It builds a lightweight container locally and avoids pulling the full Docker image (~22 GB).
-
Clone and prepare the repository:
git clone https://github.com/sola-st/RepairAgent.git cd RepairAgent/repair_agent rm -rf defects4j git clone https://github.com/rjust/defects4j.git cp -r ../data/buggy-lines defects4j cp -r ../data/buggy-methods defects4j cd ..
-
Open in VS Code, then click "Reopen in Container" when prompted (or use the Command Palette:
Dev Containers: Reopen in Container). -
In the VS Code terminal:
cd repair_agent -
Mark generated files as assume-unchanged to keep your git status clean:
git update-index --assume-unchanged .env autogpt/.env run.sh git update-index --assume-unchanged ai_settings.yaml git update-index --assume-unchanged experimental_setups/experiments_list.txt git update-index --assume-unchanged experimental_setups/fixed_so_far
-
Set the OpenAI API key:
python3 set_api_key.py
This writes your key into the
.envfiles andrun.sh. Alternatively, export it directly:export OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-...
You are now ready to run RepairAgent (see Running RepairAgent).
-
Pull and start the container:
docker pull islemdockerdev/repair-agent:v1 docker run -itd --name apr-agent islemdockerdev/repair-agent:v1 docker start -i apr-agent
-
Attach to VS Code (optional): Open VS Code, go to the Containers panel (requires the Remote Explorer extension), find
apr-agent, and attach. The working directory is/app/AutoGPT. See this 1-minute tutorial for a walkthrough. -
Set the OpenAI API key:
python3 set_api_key.py
./run_on_defects4j.sh <bugs_file> <hyperparams_file> [model]Arguments:
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
bugs_file |
Text file with one Project BugIndex per line |
experimental_setups/bugs_list |
hyperparams_file |
JSON file with agent hyperparameters | hyperparams.json |
model |
OpenAI model name (optional, default: gpt-4o-mini) |
gpt-4o, gpt-4.1
|
Example:
./run_on_defects4j.sh experimental_setups/bugs_list hyperparams.json gpt-4o-miniThe bugs file format is one bug per line:
Chart 1
Math 5
Closure 10
Lang 22
- RepairAgent checks out the buggy project version from Defects4J.
- The agent autonomously analyzes the bug, explores the code, and generates fix candidates.
- Each candidate is applied and tested against the project's test suite.
- Logs and results are saved to
experimental_setups/experiment_N/(auto-incremented).
The --model flag (or third argument to run_on_defects4j.sh) sets all LLM models used by RepairAgent:
-
Main agent (
fast_llm/smart_llm): drives the agent's reasoning loop -
Static/auxiliary (
static_llm): used for mutation generation, fix queries, and auto-completion
For finer control, use environment variables:
export FAST_LLM=gpt-4o-mini # main agent fast model
export SMART_LLM=gpt-4o # main agent smart model
export STATIC_LLM=gpt-4o-mini # auxiliary LLM calls| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
budget_control.name |
Budget visibility: FULL-TRACK (show remaining cycles) or NO-TRACK (suppress) |
FULL-TRACK |
budget_control.params.#fixes |
Minimum patches the agent should suggest within the budget | 4 |
repetition_handling |
RESTRICT prevents the agent from repeating the same actions |
RESTRICT |
commands_limit |
Maximum number of agent cycles (iterations) | 40 |
external_fix_strategy |
How often to query an external LLM for fix suggestions (0 = disabled) | 0 |
Example:
{
"budget_control": {
"name": "FULL-TRACK",
"params": { "#fixes": 4 }
},
"repetition_handling": "RESTRICT",
"commands_limit": 40,
"external_fix_strategy": 0
}Each run creates an experiment folder under experimental_setups/:
experimental_setups/experiment_N/
logs/ # Full chat history and command outputs (one file per bug)
plausible_patches/ # Patches that pass all tests (one JSON file per bug)
mutations_history/ # Mutant patches generated from prior suggestions
responses/ # Raw LLM responses at each cycle
saved_contexts/ # Saved agent contexts
external_fixes/ # Fixes from external LLM queries (if enabled)
The experiment_overview.py script provides a single consolidated report across all experiments:
cd experimental_setups
# Analyze all experiments
python3 experiment_overview.py
# Analyze a specific range
python3 experiment_overview.py --start 1 --end 10
# JSON output for scripting
python3 experiment_overview.py --jsonThis produces:
- Grand totals (bugs tested, fixed, plausible patches, queries)
- Per-experiment summary table
- Per-project breakdown
- Per-bug detail with fix status, plausible status, iteration count
- Lists of fixed and plausible-only bugs
These older scripts are still available for specific tasks:
| Script | Purpose | Usage |
|---|---|---|
analyze_experiment_results.py |
Generate per-experiment text reports | python3 analyze_experiment_results.py |
collect_plausible_patches_files.py |
Consolidate plausible patches from multiple experiments | python3 collect_plausible_patches_files.py 1 10 |
get_list_of_fully_executed.py |
Find bugs that ran to completion (38+ cycles) | python3 get_list_of_fully_executed.py |
calculate_tokens.py |
Token usage statistics and cost analysis | python3 calculate_tokens.py |
-
Generate execution batches:
python3 get_defects4j_list.py
This creates bug lists under
experimental_setups/batches/. -
Run on each batch:
./run_on_defects4j.sh experimental_setups/batches/0 hyperparams.json gpt-4o-mini
Replace
0with the desired batch number. Batches can run in parallel. -
Analyze results using
experiment_overview.pyor the individual scripts above. -
Generate comparison tables (Table III in the paper):
cd experimental_setups python3 generate_main_table.py -
Draw Venn diagrams (Figure 6 in the paper):
python3 draw_venn_chatrepair_clean.py
- Prepare the GitBug-Java VM (~140 GB disk). See: https://github.com/gitbugactions/gitbug-java
- Copy RepairAgent into the VM.
- Run with
experimental_setups/gitbuglistas the bugs file. - Analyze results using the same scripts.
In our experiments, RepairAgent fixed 164 bugs on the Defects4J dataset.
| Resource | Location |
|---|---|
| List of fixed bugs | data/final_list_of_fixed_bugs |
| Patch implementation details | data/fixes_implementation |
| Root patches (main phase) | data/root_patches/ |
| Derived patches (mutations) | data/derivated_pathces/ |
| Defects4J 1.2 baseline comparison | repair_agent/experimental_setups/d4j12.csv |
Note: RepairAgent encountered middleware exceptions on 29 bugs, which were not re-run.
If you find issues, bugs, or documentation gaps, please open an issue or email the author.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for RepairAgent
Similar Open Source Tools

RepairAgent
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair targeting the Defects4J benchmark. It uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs. The tool requires Docker, VS Code with Dev Containers extension, OpenAI API key, disk space of ~40 GB, and internet access. Users can get started with RepairAgent using either VS Code Dev Container or Docker Image. Running RepairAgent involves checking out the buggy project version, autonomous bug analysis, fix candidate generation, and testing against the project's test suite. Users can configure hyperparameters for budget control, repetition handling, commands limit, and external fix strategy. The tool provides output structure, experiment overview, individual analysis scripts, and data on fixed bugs from the Defects4J dataset.
evalchemy
Evalchemy is a unified and easy-to-use toolkit for evaluating language models, focusing on post-trained models. It integrates multiple existing benchmarks such as RepoBench, AlpacaEval, and ZeroEval. Key features include unified installation, parallel evaluation, simplified usage, and results management. Users can run various benchmarks with a consistent command-line interface and track results locally or integrate with a database for systematic tracking and leaderboard submission.
factorio-learning-environment
Factorio Learning Environment is an open source framework designed for developing and evaluating LLM agents in the game of Factorio. It provides two settings: Lab-play with structured tasks and Open-play for building large factories. Results show limitations in spatial reasoning and automation strategies. Agents interact with the environment through code synthesis, observation, action, and feedback. Tools are provided for game actions and state representation. Agents operate in episodes with observation, planning, and action execution. Tasks specify agent goals and are implemented in JSON files. The project structure includes directories for agents, environment, cluster, data, docs, eval, and more. A database is used for checkpointing agent steps. Benchmarks show performance metrics for different configurations.
FDAbench
FDABench is a benchmark tool designed for evaluating data agents' reasoning ability over heterogeneous data in analytical scenarios. It offers 2,007 tasks across various data sources, domains, difficulty levels, and task types. The tool provides ready-to-use data agent implementations, a DAG-based evaluation system, and a framework for agent-expert collaboration in dataset generation. Key features include data agent implementations, comprehensive evaluation metrics, multi-database support, different task types, extensible framework for custom agent integration, and cost tracking. Users can set up the environment using Python 3.10+ on Linux, macOS, or Windows. FDABench can be installed with a one-command setup or manually. The tool supports API configuration for LLM access and offers quick start guides for database download, dataset loading, and running examples. It also includes features like dataset generation using the PUDDING framework, custom agent integration, evaluation metrics like accuracy and rubric score, and a directory structure for easy navigation.
mcp-ts-template
The MCP TypeScript Server Template is a production-grade framework for building powerful and scalable Model Context Protocol servers with TypeScript. It features built-in observability, declarative tooling, robust error handling, and a modular, DI-driven architecture. The template is designed to be AI-agent-friendly, providing detailed rules and guidance for developers to adhere to best practices. It enforces architectural principles like 'Logic Throws, Handler Catches' pattern, full-stack observability, declarative components, and dependency injection for decoupling. The project structure includes directories for configuration, container setup, server resources, services, storage, utilities, tests, and more. Configuration is done via environment variables, and key scripts are available for development, testing, and publishing to the MCP Registry.
paperless-gpt
paperless-gpt is a tool designed to generate accurate and meaningful document titles and tags for paperless-ngx using Large Language Models (LLMs). It supports multiple LLM providers, including OpenAI and Ollama. With paperless-gpt, you can streamline your document management by automatically suggesting appropriate titles and tags based on the content of your scanned documents. The tool offers features like multiple LLM support, customizable prompts, easy integration with paperless-ngx, user-friendly interface for reviewing and applying suggestions, dockerized deployment, automatic document processing, and an experimental OCR feature.
r2ai
r2ai is a tool designed to run a language model locally without internet access. It can be used to entertain users or assist in answering questions related to radare2 or reverse engineering. The tool allows users to prompt the language model, index large codebases, slurp file contents, embed the output of an r2 command, define different system-level assistant roles, set environment variables, and more. It is accessible as an r2lang-python plugin and can be scripted from various languages. Users can use different models, adjust query templates dynamically, load multiple models, and make them communicate with each other.
paperbanana
PaperBanana is an automated academic illustration tool designed for AI scientists. It implements an agentic framework for generating publication-quality academic diagrams and statistical plots from text descriptions. The tool utilizes a two-phase multi-agent pipeline with iterative refinement, Gemini-based VLM planning, and image generation. It offers a CLI, Python API, and MCP server for IDE integration, along with Claude Code skills for generating diagrams, plots, and evaluating diagrams. PaperBanana is not affiliated with or endorsed by the original authors or Google Research, and it may differ from the original system described in the paper.

OSA
OSA (Open-Source-Advisor) is a tool designed to improve the quality of scientific open source projects by automating the generation of README files, documentation, CI/CD scripts, and providing advice and recommendations for repositories. It supports various LLMs accessible via API, local servers, or osa_bot hosted on ITMO servers. OSA is currently under development with features like README file generation, documentation generation, automatic implementation of changes, LLM integration, and GitHub Action Workflow generation. It requires Python 3.10 or higher and tokens for GitHub/GitLab/Gitverse and LLM API key. Users can install OSA using PyPi or build from source, and run it using CLI commands or Docker containers.
quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
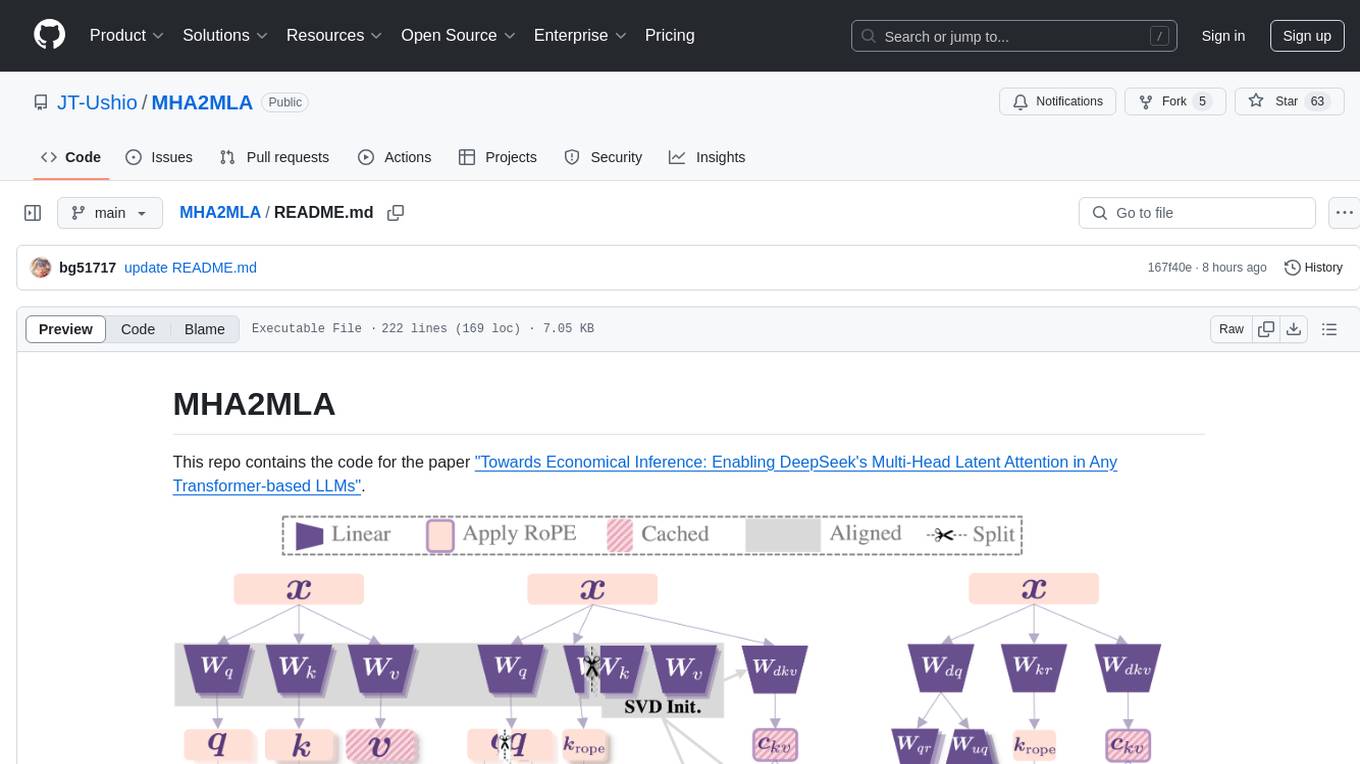
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.

HuixiangDou
HuixiangDou is a **group chat** assistant based on LLM (Large Language Model). Advantages: 1. Design a two-stage pipeline of rejection and response to cope with group chat scenario, answer user questions without message flooding, see arxiv2401.08772 2. Low cost, requiring only 1.5GB memory and no need for training 3. Offers a complete suite of Web, Android, and pipeline source code, which is industrial-grade and commercially viable Check out the scenes in which HuixiangDou are running and join WeChat Group to try AI assistant inside. If this helps you, please give it a star ⭐
TPI-LLM
TPI-LLM (Tensor Parallelism Inference for Large Language Models) is a system designed to bring LLM functions to low-resource edge devices, addressing privacy concerns by enabling LLM inference on edge devices with limited resources. It leverages multiple edge devices for inference through tensor parallelism and a sliding window memory scheduler to minimize memory usage. TPI-LLM demonstrates significant improvements in TTFT and token latency compared to other models, and plans to support infinitely large models with low token latency in the future.
auto-engineer
Auto Engineer is a tool designed to automate the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) by building production-grade applications with a combination of human and AI agents. It offers a plugin-based architecture that allows users to install only the necessary functionality for their projects. The tool guides users through key stages including Flow Modeling, IA Generation, Deterministic Scaffolding, AI Coding & Testing Loop, and Comprehensive Quality Checks. Auto Engineer follows a command/event-driven architecture and provides a modular plugin system for specific functionalities. It supports TypeScript with strict typing throughout and includes a built-in message bus server with a web dashboard for monitoring commands and events.
rwkv.cpp
rwkv.cpp is a port of BlinkDL/RWKV-LM to ggerganov/ggml, supporting FP32, FP16, and quantized INT4, INT5, and INT8 inference. It focuses on CPU but also supports cuBLAS. The project provides a C library rwkv.h and a Python wrapper. RWKV is a large language model architecture with models like RWKV v5 and v6. It requires only state from the previous step for calculations, making it CPU-friendly on large context lengths. Users are advised to test all available formats for perplexity and latency on a representative dataset before serious use.
LLMTSCS
LLMLight is a novel framework that employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for Traffic Signal Control (TSC). The framework leverages the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs to engage in a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. LLMLight has been demonstrated to be remarkably effective, generalizable, and interpretable against various transportation-based and RL-based baselines on nine real-world and synthetic datasets.
For similar tasks

RepairAgent
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair targeting the Defects4J benchmark. It uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs. The tool requires Docker, VS Code with Dev Containers extension, OpenAI API key, disk space of ~40 GB, and internet access. Users can get started with RepairAgent using either VS Code Dev Container or Docker Image. Running RepairAgent involves checking out the buggy project version, autonomous bug analysis, fix candidate generation, and testing against the project's test suite. Users can configure hyperparameters for budget control, repetition handling, commands limit, and external fix strategy. The tool provides output structure, experiment overview, individual analysis scripts, and data on fixed bugs from the Defects4J dataset.

cosdata
Cosdata is a cutting-edge AI data platform designed to power the next generation search pipelines. It features immutability, version control, and excels in semantic search, structured knowledge graphs, hybrid search capabilities, real-time search at scale, and ML pipeline integration. The platform is customizable, scalable, efficient, enterprise-grade, easy to use, and can manage multi-modal data. It offers high performance, indexing, low latency, and high requests per second. Cosdata is designed to meet the demands of modern search applications, empowering businesses to harness the full potential of their data.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.