
r2ai
local language model for radare2
Stars: 245
r2ai is a tool designed to run a language model locally without internet access. It can be used to entertain users or assist in answering questions related to radare2 or reverse engineering. The tool allows users to prompt the language model, index large codebases, slurp file contents, embed the output of an r2 command, define different system-level assistant roles, set environment variables, and more. It is accessible as an r2lang-python plugin and can be scripted from various languages. Users can use different models, adjust query templates dynamically, load multiple models, and make them communicate with each other.
README:
,______ .______ .______ ,___
: __ \ \____ |: \ : __|
| \____|/ ____|| _,_ || : |
| : \ \ . || : || |
| |___\ \__:__||___| || |
|___| : |___||___|
*
Run a language model to entertain you or help answering questions about radare2 or reverse engineering in general. The language model may be local (running without Internet on your host) or remote (e.g if you have an API key). Note that models used by r2ai are pulled from external sources which may behave different or respond unreliable information. That's why there's an ongoing effort into improving the post-finetuning using memgpt-like techniques which can't get better without your help!
R2AI is structured into four independent components:
- r2ai (python cli tool)
- r2-like repl using r2pipe to comunicate with r2
- supports auto solving mode
- client and server openapi protocol
- download and manage models from huggingface
- decai (r2js plugin focus on decompilation)
- adds 'decai' command to the r2 shell
- talks to local or remote services with curl
- focus on decompilation
-
r2ai-plugin
- Native plugin written in C
- adds r2ai command inside r2
- r2ai-server
- favour ollama instead
- list and select models downloaded from r2ai
- simple cli tool to start local openapi webservers
- supports llamafile, llamacpp, r2ai-w and kobaldcpp
- Support Auto mode to solve tasks using function calling
- Use local and remote language models (llama, ollama, openai, anthropic, ..)
- Support OpenAI, Anthropic, Bedrock
- Index large codebases or markdown books using a vector database
- Slurp file and perform actions on that
- Embed the output of an r2 command and resolve questions on the given data
- Define different system-level assistant role
- Set environment variables to provide context to the language model
- Live with repl and batch mode from cli or r2 prompt
- Scriptable via r2pipe
- Use different models, dynamically adjust query template
- Load multiple models and make them talk between them
Install the various components via r2pm:
r2pm -ci r2air2pm -ci r2ai-pluginr2pm -ci decair2pm -ci r2ai-server
Running make will setup a python virtual environment in the current directory installing all the necessary dependencies and will get into a shell to run r2ai.
The installation is now splitted into two different targets:
-
make installwill place a symlink in$BINDIR/r2ai -
make install-decaiwill install the decai r2js decompiler plugin -
make install-serverwill install the r2ai-server
On Windows you may follow the same instructions, just ensure you have the right python environment ready and create the venv to use
git clone https://github.com/radareorg/r2ai
cd r2ai
set PATH=C:\Users\YOURUSERNAME\Local\Programs\Python\Python39\;%PATH%
python3 -m pip install .
python3 main.py- If you installed via r2pm, you can execute it like this:
r2pm -r r2ai - Otherwise,
./r2ai.sh [/absolute/path/to/binary]
If you have an API key, put it in the adequate file:
| AI | API key |
|---|---|
| OpenAI | $HOME/.r2ai.openai-key |
| Gemini | $HOME/.r2ai.gemini-key |
| Anthropic | $HOME/.r2ai.anthropic-key |
| Mistral | $HOME/.r2ai.mistral-key |
Example using an Anthropic API key:
$ cat ~/.r2ai.anthropic-key
sk-ant-api03-CENSORED
- List all downloaded models:
-m - Get a short list of models:
-MM - Help:
-h
Example selecting a remote models:
[r2ai:0x00006aa0]> -m anthropic:claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219
[r2ai:0x00006aa0]> -m openai:gpt-4
Example downloading a free local AI: Mistral 7B v0.2:
Launch r2ai, select the model and ask a question. If the model isn't downloaded yet, r2ai will ask you which precise version to download.
[r2ai:0x00006aa0]> -m TheBloke/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2-GGUF
Then ask your question, and r2ai will automatically download if needed:
[r2ai:0x00006aa0]> give me a short algorithm to test prime numbers
Select TheBloke/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2-GGUF model. See -M and -m flags
[?] Quality (smaller is faster):
> Small | Size: 2.9 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 5.4 GB
Medium | Size: 3.9 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 6.4 GB
Large | Size: 7.2 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 9.7 GB
See More
[?] Quality (smaller is faster):
> mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q2_K.gguf | Size: 2.9 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 5.4 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q3_K_L.gguf | Size: 3.6 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 6.1 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q3_K_M.gguf | Size: 3.3 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 5.8 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q3_K_S.gguf | Size: 2.9 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 5.4 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q4_0.gguf | Size: 3.8 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 6.3 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q4_K_M.gguf | Size: 4.1 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 6.6 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q4_K_S.gguf | Size: 3.9 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 6.4 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q5_0.gguf | Size: 4.7 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 7.2 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q5_K_M.gguf | Size: 4.8 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 7.3 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q5_K_S.gguf | Size: 4.7 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 7.2 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q6_K.gguf | Size: 5.5 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 8.0 GB
mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q8_0.gguf | Size: 7.2 GB, Estimated RAM usage: 9.7 GB
[?] Use this model by default? ~/.r2ai.model:
> Yes
No
[?] Download to ~/.local/share/r2ai/models? (Y/n): Y
Example selecting a local model served by Ollama
Download a model and make it available through Ollama:
$ ollama ls
NAME ID SIZE MODIFIED
codegeex4:latest 867b8e81d038 5.5 GB 23 hours ago
Use it from r2ai by prefixing its name with ollama/
[r2ai:0x00002d30]> -m ollama/codegeex4:latest
[r2ai:0x00002d30]> hi
Hello! How can I assist you today?
The standard mode is invoked by directly asking the question.
For the Auto mode, the question must be prefixed by ' (quote + space). The AI may instruct r2ai to run various commands. Those commands are run on your host, so you will be asked to review them before they run.
Example in "standard" mode:
[r2ai:0x00006aa0]> compute 4+5
4 + 5 = 9
[r2ai:0x00006aa0]> draw me a pancake in ASCII art
Sure, here's a simple ASCII pancake:
_____
( )
( )
-----
Example in auto mode:
[r2ai:0x00006aa0]>' Decompile the main
[..]
r2ai is going to execute the following command on the host
Want to edit? (ENTER to validate) pdf @ fcn.000015d0
This command will execute on this host: pdf @ fcn.000015d0. Agree? (y/N) y
If you wish to edit the command, you can do it inline for short one line commands, or an editor will pop up.
List all settings with -e
| Key | Explanation |
|---|---|
| debug_level | All verbose messages for level 1. Default is 2 |
| auto.max_runs | Maximum number of questions the AI is allowed to ask r2 in auto mode. |
| auto.hide_tool_output | By default false, consequently output of r2cmd, run_python etc is shown. Set to true to hide those internal messages. |
| chat.show_cost | Show the cost of each request to the AI if true |
- Get usage:
r2pm -r r2ai-server - List available servers:
r2pm -r r2ai-server -l - List available models:
r2pm -r r2ai-server -m
On Linux, models are stored in ~/.r2ai.models/. File ~/.r2ai.model lists the default model and other models.
Example launching a local Mistral AI server:
$ r2pm -r r2ai-server -l r2ai -m mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q2_K
[12/13/24 10:35:22] INFO r2ai.server - INFO - [R2AI] Serving at port 8080 web.py:336
Decai is used from r2 (e.g r2 ./mybinary). Get help with decai -h:
[0x00406cac]> decai -h
Usage: decai (-h) ...
decai -H - help setting up r2ai
decai -a [query] - solve query with auto mode
decai -d [f1 ..] - decompile given functions
decai -dr - decompile function and its called ones (recursive)
decai -dd [..] - same as above, but ignoring cache
decai -dD [query]- decompile current function with given extra query
...
List configuration variables with decai -e:
[0x00406cac]> decai -e
decai -e api=ollama
decai -e host=http://localhost
decai -e port=11434
decai -e prompt=Rewrite this function and respond ONLY with code, NO explanations, NO markdown, Change 'goto' into if/else/for/while, Simplify as much as possible, use better variable names, take function arguments and strings from comments like 'string:'
decai -e ctxfile=
...
List possible APIs to discuss with AI: decai -e api=?:
[0x00406cac]> decai -e api=?
r2ai
claude
openapi
...
For example, if Ollama serves model codegeex4:latest (ollama ls), set decai API as ollama and model codegeex4:latest.
[0x00002d30]> decai -e api=ollama
[0x00002d30]> decai -e model=codegeex4:latest
[0x00002d30]> decai -q Explain what forkpty does in 2 lines
The `forkpty` function creates a new process with a pseudo-terminal, allowing the parent to interact with the child via standard input/output/err and controlling its terminal.
For example, assuming we have a local Mistral AI server running on port 8080 with r2ai-server, we can decompile a given function with decai -d.
The server shows it received the question:
GET
CUSTOM
RUNLINE: -R
127.0.0.1 - - [13/Dec/2024 10:40:49] "GET /cmd/-R HTTP/1.1" 200 -
GET
CUSTOM
RUNLINE: -i /tmp/.pdc.txt Rewrite this function and respond ONLY with code, NO explanations, NO markdown, Change goto into if/else/for/while, Simplify as much as possible, use better variable names, take function arguments and and strings from comments like string:. Transform this pseudocode into C
Put the API key in ~/.r2ai.mistral-key.
[0x000010d0]> decai -e api=mistral
[0x000010d0]> decai -d main
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv, char **envp) {
char password[40];
char input[40];
...
[0x00406cac]> decai -e api=openai
[0x00406cac]> decai -d
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void daemonize() {
daemon(1, 0);
}
...
Just run make
- add "undo" command to drop the last message
- dump / restore conversational states (see -L command)
- Implement
~,|and>and other r2shell features
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for r2ai
Similar Open Source Tools

r2ai
r2ai is a tool designed to run a language model locally without internet access. It can be used to entertain users or assist in answering questions related to radare2 or reverse engineering. The tool allows users to prompt the language model, index large codebases, slurp file contents, embed the output of an r2 command, define different system-level assistant roles, set environment variables, and more. It is accessible as an r2lang-python plugin and can be scripted from various languages. Users can use different models, adjust query templates dynamically, load multiple models, and make them communicate with each other.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
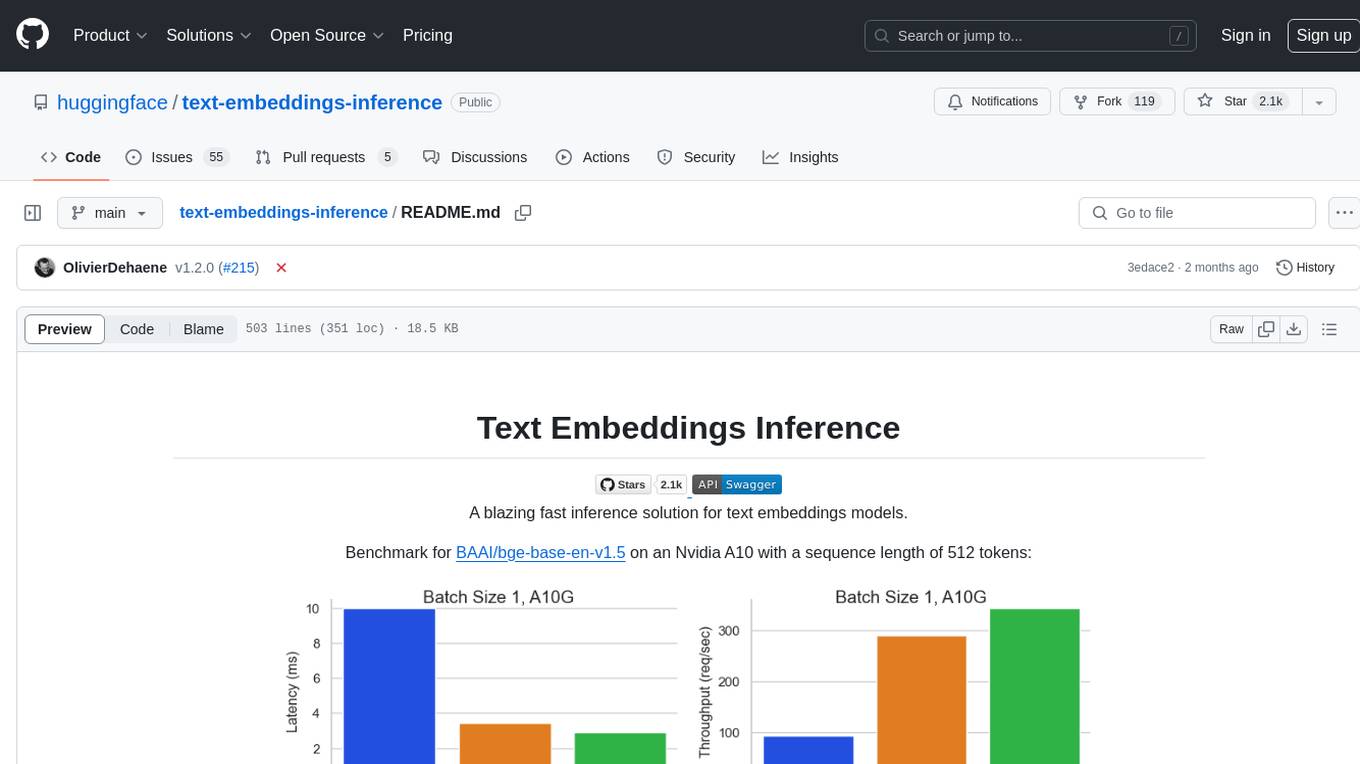
text-embeddings-inference
Text Embeddings Inference (TEI) is a toolkit for deploying and serving open source text embeddings and sequence classification models. TEI enables high-performance extraction for popular models like FlagEmbedding, Ember, GTE, and E5. It implements features such as no model graph compilation step, Metal support for local execution on Macs, small docker images with fast boot times, token-based dynamic batching, optimized transformers code for inference using Flash Attention, Candle, and cuBLASLt, Safetensors weight loading, and production-ready features like distributed tracing with Open Telemetry and Prometheus metrics.
mLoRA
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.

HuixiangDou
HuixiangDou is a **group chat** assistant based on LLM (Large Language Model). Advantages: 1. Design a two-stage pipeline of rejection and response to cope with group chat scenario, answer user questions without message flooding, see arxiv2401.08772 2. Low cost, requiring only 1.5GB memory and no need for training 3. Offers a complete suite of Web, Android, and pipeline source code, which is industrial-grade and commercially viable Check out the scenes in which HuixiangDou are running and join WeChat Group to try AI assistant inside. If this helps you, please give it a star ⭐
MockingBird
MockingBird is a toolbox designed for Mandarin speech synthesis using PyTorch. It supports multiple datasets such as aidatatang_200zh, magicdata, aishell3, and data_aishell. The toolbox can run on Windows, Linux, and M1 MacOS, providing easy and effective speech synthesis with pretrained encoder/vocoder models. It is webserver ready for remote calling. Users can train their own models or use existing ones for the encoder, synthesizer, and vocoder. The toolbox offers a demo video and detailed setup instructions for installation and model training.
metis
Metis is an open-source, AI-driven tool for deep security code review, created by Arm's Product Security Team. It helps engineers detect subtle vulnerabilities, improve secure coding practices, and reduce review fatigue. Metis uses LLMs for semantic understanding and reasoning, RAG for context-aware reviews, and supports multiple languages and vector store backends. It provides a plugin-friendly and extensible architecture, named after the Greek goddess of wisdom, Metis. The tool is designed for large, complex, or legacy codebases where traditional tooling falls short.
agenticSeek
AgenticSeek is a voice-enabled AI assistant powered by DeepSeek R1 agents, offering a fully local alternative to cloud-based AI services. It allows users to interact with their filesystem, code in multiple languages, and perform various tasks autonomously. The tool is equipped with memory to remember user preferences and past conversations, and it can divide tasks among multiple agents for efficient execution. AgenticSeek prioritizes privacy by running entirely on the user's hardware without sending data to the cloud.
consult-llm-mcp
Consult LLM MCP is an MCP server that enables users to consult powerful AI models like GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and DeepSeek Reasoner for complex problem-solving. It supports multi-turn conversations, direct queries with optional file context, git changes inclusion for code review, comprehensive logging with cost estimation, and various CLI modes for Gemini and Codex. The tool is designed to simplify the process of querying AI models for assistance in resolving coding issues and improving code quality.
aim
Aim is a command-line tool for downloading and uploading files with resume support. It supports various protocols including HTTP, FTP, SFTP, SSH, and S3. Aim features an interactive mode for easy navigation and selection of files, as well as the ability to share folders over HTTP for easy access from other devices. Additionally, it offers customizable progress indicators and output formats, and can be integrated with other commands through piping. Aim can be installed via pre-built binaries or by compiling from source, and is also available as a Docker image for platform-independent usage.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
evalchemy
Evalchemy is a unified and easy-to-use toolkit for evaluating language models, focusing on post-trained models. It integrates multiple existing benchmarks such as RepoBench, AlpacaEval, and ZeroEval. Key features include unified installation, parallel evaluation, simplified usage, and results management. Users can run various benchmarks with a consistent command-line interface and track results locally or integrate with a database for systematic tracking and leaderboard submission.
react-native-fast-tflite
A high-performance TensorFlow Lite library for React Native that utilizes JSI for power, zero-copy ArrayBuffers for efficiency, and low-level C/C++ TensorFlow Lite core API for direct memory access. It supports swapping out TensorFlow Models at runtime and GPU-accelerated delegates like CoreML/Metal/OpenGL. Easy VisionCamera integration allows for seamless usage. Users can load TensorFlow Lite models, interpret input and output data, and utilize GPU Delegates for faster computation. The library is suitable for real-time object detection, image classification, and other machine learning tasks in React Native applications.
screen-pipe
Screen-pipe is a Rust + WASM tool that allows users to turn their screen into actions using Large Language Models (LLMs). It enables users to record their screen 24/7, extract text from frames, and process text and images for tasks like analyzing sales conversations. The tool is still experimental and aims to simplify the process of recording screens, extracting text, and integrating with various APIs for tasks such as filling CRM data based on screen activities. The project is open-source and welcomes contributions to enhance its functionalities and usability.
runpod-worker-comfy
runpod-worker-comfy is a serverless API tool that allows users to run any ComfyUI workflow to generate an image. Users can provide input images as base64-encoded strings, and the generated image can be returned as a base64-encoded string or uploaded to AWS S3. The tool is built on Ubuntu + NVIDIA CUDA and provides features like built-in checkpoints and VAE models. Users can configure environment variables to upload images to AWS S3 and interact with the RunPod API to generate images. The tool also supports local testing and deployment to Docker hub using Github Actions.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern
For similar tasks

r2ai
r2ai is a tool designed to run a language model locally without internet access. It can be used to entertain users or assist in answering questions related to radare2 or reverse engineering. The tool allows users to prompt the language model, index large codebases, slurp file contents, embed the output of an r2 command, define different system-level assistant roles, set environment variables, and more. It is accessible as an r2lang-python plugin and can be scripted from various languages. Users can use different models, adjust query templates dynamically, load multiple models, and make them communicate with each other.

kodit
Kodit is a Code Indexing MCP Server that connects AI coding assistants to external codebases, providing accurate and up-to-date code snippets. It improves AI-assisted coding by offering canonical examples, indexing local and public codebases, integrating with AI coding assistants, enabling keyword and semantic search, and supporting OpenAI-compatible or custom APIs/models. Kodit helps engineers working with AI-powered coding assistants by providing relevant examples to reduce errors and hallucinations.
lmql
LMQL is a programming language designed for large language models (LLMs) that offers a unique way of integrating traditional programming with LLM interaction. It allows users to write programs that combine algorithmic logic with LLM calls, enabling model reasoning capabilities within the context of the program. LMQL provides features such as Python syntax integration, rich control-flow options, advanced decoding techniques, powerful constraints via logit masking, runtime optimization, sync and async API support, multi-model compatibility, and extensive applications like JSON decoding and interactive chat interfaces. The tool also offers library integration, flexible tooling, and output streaming options for easy model output handling.
LLM_Web_search
LLM_Web_search project gives local LLMs the ability to search the web by outputting a specific command. It uses regular expressions to extract search queries from model output and then utilizes duckduckgo-search to search the web. LangChain's Contextual compression and Okapi BM25 or SPLADE are used to extract relevant parts of web pages in search results. The extracted results are appended to the model's output.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
