pipelex
Declarative language for composable Al workflows. Devtool for agents and mere humans.
Stars: 614
Pipelex is an open-source devtool designed to transform how users build repeatable AI workflows. It acts as a Docker or SQL for AI operations, allowing users to create modular 'pipes' using different LLMs for structured outputs. These pipes can be connected sequentially, in parallel, or conditionally to build complex knowledge transformations from reusable components. With Pipelex, users can share and scale proven methods instantly, saving time and effort in AI workflow development.
README:

Pipelex is developing the open standard for repeatable AI workflows.
Write business logic, not API calls.
pip install pipelex
pipelex initTo use AI models, you need an API key:
- Free Pipelex API Key: Join our Discord community and request your free API key (no credit card required) in the 🔑・free-api-key channel.
- Bring your own API keys: OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Mistral
- Local AI: Ollama, vLLM, LM Studio, llama.cpp... any endpoint based on the OpenAI API or not, as you can plug-in your own non-standard APIs.
See Configure AI Providers for details.
Create a complete AI workflow with a single command:
pipelex build pipe "Take a CV and Job offer in PDF, analyze if they match and generate 5 questions for the interview" --output results/cv_match.plxThis command generates a production-ready .plx file with domain definitions, concepts, and multiple processing steps that analyzes CV-job fit and prepares interview questions.
cv_match.plx
domain = "cv_match"
description = "Matching CVs with job offers and generating interview questions"
main_pipe = "analyze_cv_job_match_and_generate_questions"
[concept.MatchAnalysis]
description = """
Analysis of alignment between a candidate and a position, including strengths, gaps, and areas requiring further exploration.
"""
[concept.MatchAnalysis.structure]
strengths = { type = "text", description = "Areas where the candidate's profile aligns well with the requirements", required = true }
gaps = { type = "text", description = "Areas where the candidate's profile does not meet the requirements or lacks evidence", required = true }
areas_to_probe = { type = "text", description = "Topics or competencies that need clarification or deeper assessment during the interview", required = true }
[concept.Question]
description = "A single interview question designed to assess a candidate."
refines = "Text"
[pipe.analyze_cv_job_match_and_generate_questions]
type = "PipeSequence"
description = """
Main pipeline that orchestrates the complete CV-job matching and interview question generation workflow. Takes a candidate's CV and a job offer as PDF documents, extracts their content, performs a comprehensive match analysis identifying strengths, gaps, and areas to probe, and generates exactly 5 targeted interview questions based on the analysis results.
"""
inputs = { cv_pdf = "PDF", job_offer_pdf = "PDF" }
output = "Question[5]"
steps = [
{ pipe = "extract_documents_parallel", result = "extracted_documents" },
{ pipe = "analyze_match", result = "match_analysis" },
{ pipe = "generate_interview_questions", result = "interview_questions" },
]📄 Click to view the supporting pipes implementation
[pipe.extract_documents_parallel]
type = "PipeParallel"
description = """
Executes parallel extraction of text content from both the CV PDF and job offer PDF simultaneously to optimize processing time.
"""
inputs = { cv_pdf = "PDF", job_offer_pdf = "PDF" }
output = "Dynamic"
parallels = [
{ pipe = "extract_cv_text", result = "cv_pages" },
{ pipe = "extract_job_offer_text", result = "job_offer_pages" },
]
add_each_output = true
[pipe.extract_cv_text]
type = "PipeExtract"
description = """
Extracts text content from the candidate's CV PDF document using OCR technology, converting all pages into machine-readable text format for subsequent analysis.
"""
inputs = { cv_pdf = "PDF" }
output = "Page[]"
model = "extract_text_from_pdf"
[pipe.extract_job_offer_text]
type = "PipeExtract"
description = """
Extracts text content from the job offer PDF document using OCR technology, converting all pages into machine-readable text format for subsequent analysis.
"""
inputs = { job_offer_pdf = "PDF" }
output = "Page[]"
model = "extract_text_from_pdf"
[pipe.analyze_match]
type = "PipeLLM"
description = """
Performs comprehensive analysis comparing the candidate's CV against the job offer requirements. Identifies and structures: (1) strengths where the candidate's profile aligns well with requirements, (2) gaps where the profile lacks evidence or doesn't meet requirements, and (3) specific areas requiring deeper exploration or clarification during the interview process.
"""
inputs = { cv_pages = "Page[]", job_offer_pages = "Page[]" }
output = "MatchAnalysis"
model = "llm_to_answer_questions"
system_prompt = """
You are an expert HR analyst and recruiter specializing in candidate-job fit assessment. Your task is to generate a structured MatchAnalysis comparing a candidate's CV against job requirements.
"""
prompt = """
Analyze the match between the candidate's CV and the job offer requirements.
Candidate CV:
@cv_pages
Job Offer:
@job_offer_pages
Perform a comprehensive comparison and provide a structured analysis.
"""
[pipe.generate_interview_questions]
type = "PipeLLM"
description = """
Generates exactly 5 targeted, relevant interview questions based on the match analysis results. Questions are designed to probe identified gaps, clarify areas of uncertainty, validate strengths, and assess competencies that require deeper evaluation to determine candidate-position fit.
"""
inputs = { match_analysis = "MatchAnalysis" }
output = "Question[5]"
model = "llm_for_writing_cheap"
system_prompt = """
You are an expert HR interviewer and talent assessment specialist. Your task is to generate structured interview questions based on candidate-position match analysis.
"""
prompt = """
Based on the following match analysis between a candidate and a position, generate exactly 5 targeted interview questions.
@match_analysis
The questions should:
- Probe the identified gaps to assess if they are deal-breakers or can be mitigated
- Clarify areas that require deeper exploration
- Validate the candidate's strengths with concrete examples
- Be open-ended and behavioral when appropriate
- Help determine overall candidate-position fit
Generate exactly 5 interview questions.
"""View the pipeline flowchart:
flowchart TD
subgraph PAR["extract_documents_parallel (PipeParallel)"]
direction LR
EXTRACT_CV["extract_cv_text (PipeExtract)"]
EXTRACT_JOB["extract_job_offer_text (PipeExtract)"]
end
subgraph MAIN["analyze_cv_job_match_and_generate_questions (PipeSequence)"]
direction TB
PAR
CV_PAGES[["cv_pages: Page"]]
JOB_PAGES[["job_offer_pages: Page"]]
ANALYZE["analyze_match (PipeLLM)"]
MATCH[["MatchAnalysis"]]
GENERATE["generate_interview_questions (PipeLLM)"]
OUT[["Question"]]
end
CV_IN[["cv_pdf: PDF"]] --> EXTRACT_CV
JOB_IN[["job_offer_pdf: PDF"]] --> EXTRACT_JOB
EXTRACT_CV --> CV_PAGES
EXTRACT_JOB --> JOB_PAGES
CV_PAGES --> ANALYZE
JOB_PAGES --> ANALYZE
ANALYZE --> MATCH
MATCH --> GENERATE
GENERATE --> OUT
classDef default stroke:#1976D2,stroke-width:2px,fill:#E3F2FD,color:#0D47A1
style EXTRACT_CV stroke:#1565C0,fill:#BBDEFB,color:#0D47A1
style EXTRACT_JOB stroke:#1565C0,fill:#BBDEFB,color:#0D47A1
style PAR fill:#FFF9C4,stroke:#F57C00,stroke-width:2px
style CV_PAGES stroke:#2E7D32,fill:#C8E6C9,color:#1B5E20
style JOB_PAGES stroke:#2E7D32,fill:#C8E6C9,color:#1B5E20
style ANALYZE stroke:#1565C0,fill:#BBDEFB,color:#0D47A1
style MATCH stroke:#2E7D32,fill:#C8E6C9,color:#1B5E20
style GENERATE stroke:#1565C0,fill:#BBDEFB,color:#0D47A1
style OUT stroke:#2E7D32,fill:#C8E6C9,color:#1B5E20
style CV_IN stroke:#2E7D32,fill:#C8E6C9,color:#1B5E20
style JOB_IN stroke:#2E7D32,fill:#C8E6C9,color:#1B5E20
style MAIN fill:#F3E5F5,stroke:#7B1FA2,stroke-width:2pxVia CLI:
# Run with input file
pipelex run results/cv_match.plx --inputs inputs.jsonCreate an inputs.json file with your PDF URLs:
{
"cv_pdf": {
"concept": "PDF",
"content": {
"url": "https://pipelex-web.s3.amazonaws.com/demo/John-Doe-CV.pdf"
}
},
"job_offer_pdf": {
"concept": "PDF",
"content": {
"url": "https://pipelex-web.s3.amazonaws.com/demo/Job-Offer.pdf"
}
}
}Via Python:
import asyncio
import json
from pipelex.pipeline.execute import execute_pipeline
from pipelex.pipelex import Pipelex
async def run_pipeline():
with open("inputs.json", encoding="utf-8") as f:
inputs = json.load(f)
pipe_output = await execute_pipeline(
pipe_code="cv_match",
inputs=inputs
)
print(pipe_output.main_stuff_as_str)
Pipelex.make()
asyncio.run(run_pipeline())Install AI assistant rules to easily modify your pipelines:
pipelex kit rulesThis installs rules for Cursor, Claude, OpenAI Codex, GitHub Copilot, Windsurf, and Blackbox AI. Now you can refine pipelines with natural language:
- "Include confidence scores between 0 and 100 in the match analysis"
- "Write a recap email at the end"
Pipelex is an open-source language that enables you to build and run repeatable AI workflows. Instead of cramming everything into one complex prompt, you break tasks into focused steps, each pipe handling one clear transformation.
Each pipe processes information using Concepts (typing with meaning) to ensure your pipelines make sense. The Pipelex language (.plx files) is simple and human-readable, even for non-technical users. Each step can be structured and validated, giving you the reliability of software with the intelligence of AI.
Learn More:
- Writing Workflows Tutorial - Complete guide with examples
- Build Reliable AI Workflows - Deep dive into Pipelex
- Configuration Guide - Set up AI providers and models
We highly recommend installing our extension for .plx files into your IDE. You can find it in the Open VSX Registry. It's coming soon to VS Code marketplace too. If you're using Cursor, Windsurf or another VS Code fork, you can search for it directly in your extensions tab.
Explore real-world examples in our Cookbook repository:
Clone it, fork it, and experiment with production-ready pipelines for various use cases.
The package supports the following additional features:
-
anthropic: Anthropic/Claude support for text generation -
google: Google models (Vertex) support for text generation -
mistralai: Mistral AI support for text generation and OCR -
bedrock: Amazon Bedrock support for text generation -
fal: Image generation with Black Forest Labs "FAL" service
Install all extras:
Using pip:
pip install "pipelex[anthropic,google,google-genai,mistralai,bedrock,fal]"Pipelex collects optional, anonymous usage data to help improve the product. On first run, you'll be prompted to choose your telemetry preference:
- Off: No telemetry data collected
- Anonymous: Anonymous usage data only (command usage, performance metrics, feature usage)
- Identified: Usage data with user identification (helps us provide better support)
Your prompts, LLM responses, file paths, and URLs are automatically redacted and never transmitted. You can change your preference at any time or disable telemetry completely by setting the DO_NOT_TRACK environment variable.
For more details, see the Telemetry Documentation or read our Privacy Policy.
We welcome contributions! Please see our Contributing Guidelines for details on how to get started, including development setup and testing information.
Join our vibrant Discord community to connect with other developers, share your experiences, and get help with your Pipelex projects!
- GitHub Issues: For bug reports and feature requests
- Discussions: For questions and community discussions
- Documentation
If you find Pipelex helpful, please consider giving us a star! It helps us reach more developers and continue improving the tool.
This project is licensed under the MIT license. Runtime dependencies are distributed under their own licenses via PyPI.
"Pipelex" is a trademark of Evotis S.A.S.
© 2025 Evotis S.A.S.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for pipelex
Similar Open Source Tools

pipelex
Pipelex is an open-source devtool designed to transform how users build repeatable AI workflows. It acts as a Docker or SQL for AI operations, allowing users to create modular 'pipes' using different LLMs for structured outputs. These pipes can be connected sequentially, in parallel, or conditionally to build complex knowledge transformations from reusable components. With Pipelex, users can share and scale proven methods instantly, saving time and effort in AI workflow development.
FlashLearn
FlashLearn is a tool that provides a simple interface and orchestration for incorporating Agent LLMs into workflows and ETL pipelines. It allows data transformations, classifications, summarizations, rewriting, and custom multi-step tasks using LLMs. Each step and task has a compact JSON definition, making pipelines easy to understand and maintain. FlashLearn supports LiteLLM, Ollama, OpenAI, DeepSeek, and other OpenAI-compatible clients.
npi
NPi is an open-source platform providing Tool-use APIs to empower AI agents with the ability to take action in the virtual world. It is currently under active development, and the APIs are subject to change in future releases. NPi offers a command line tool for installation and setup, along with a GitHub app for easy access to repositories. The platform also includes a Python SDK and examples like Calendar Negotiator and Twitter Crawler. Join the NPi community on Discord to contribute to the development and explore the roadmap for future enhancements.

memobase
Memobase is a user profile-based memory system designed to enhance Generative AI applications by enabling them to remember, understand, and evolve with users. It provides structured user profiles, scalable profiling, easy integration with existing LLM stacks, batch processing for speed, and is production-ready. Users can manage users, insert data, get memory profiles, and track user preferences and behaviors. Memobase is ideal for applications that require user analysis, tracking, and personalized interactions.
agentlang
AgentLang is an open-source programming language and framework designed for solving complex tasks with the help of AI agents. It allows users to build business applications rapidly from high-level specifications, making it more efficient than traditional programming languages. The language is data-oriented and declarative, with a syntax that is intuitive and closer to natural languages. AgentLang introduces innovative concepts such as first-class AI agents, graph-based hierarchical data model, zero-trust programming, declarative dataflow, resolvers, interceptors, and entity-graph-database mapping.
LightRAG
LightRAG is a repository hosting the code for LightRAG, a system that supports seamless integration of custom knowledge graphs, Oracle Database 23ai, Neo4J for storage, and multiple file types. It includes features like entity deletion, batch insert, incremental insert, and graph visualization. LightRAG provides an API server implementation for RESTful API access to RAG operations, allowing users to interact with it through HTTP requests. The repository also includes evaluation scripts, code for reproducing results, and a comprehensive code structure.
deep-searcher
DeepSearcher is a tool that combines reasoning LLMs and Vector Databases to perform search, evaluation, and reasoning based on private data. It is suitable for enterprise knowledge management, intelligent Q&A systems, and information retrieval scenarios. The tool maximizes the utilization of enterprise internal data while ensuring data security, supports multiple embedding models, and provides support for multiple LLMs for intelligent Q&A and content generation. It also includes features like private data search, vector database management, and document loading with web crawling capabilities under development.
continuous-eval
Open-Source Evaluation for LLM Applications. `continuous-eval` is an open-source package created for granular and holistic evaluation of GenAI application pipelines. It offers modularized evaluation, a comprehensive metric library covering various LLM use cases, the ability to leverage user feedback in evaluation, and synthetic dataset generation for testing pipelines. Users can define their own metrics by extending the Metric class. The tool allows running evaluation on a pipeline defined with modules and corresponding metrics. Additionally, it provides synthetic data generation capabilities to create user interaction data for evaluation or training purposes.
parea-sdk-py
Parea AI provides a SDK to evaluate & monitor AI applications. It allows users to test, evaluate, and monitor their AI models by defining and running experiments. The SDK also enables logging and observability for AI applications, as well as deploying prompts to facilitate collaboration between engineers and subject-matter experts. Users can automatically log calls to OpenAI and Anthropic, create hierarchical traces of their applications, and deploy prompts for integration into their applications.
lionagi
LionAGI is a robust framework for orchestrating multi-step AI operations with precise control. It allows users to bring together multiple models, advanced reasoning, tool integrations, and custom validations in a single coherent pipeline. The framework is structured, expandable, controlled, and transparent, offering features like real-time logging, message introspection, and tool usage tracking. LionAGI supports advanced multi-step reasoning with ReAct, integrates with Anthropic's Model Context Protocol, and provides observability and debugging tools. Users can seamlessly orchestrate multiple models, integrate with Claude Code CLI SDK, and leverage a fan-out fan-in pattern for orchestration. The framework also offers optional dependencies for additional functionalities like reader tools, local inference support, rich output formatting, database support, and graph visualization.
llm-rag-workshop
The LLM RAG Workshop repository provides a workshop on using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to generate and understand text in a human-like manner. It includes instructions on setting up the environment, indexing Zoomcamp FAQ documents, creating a Q&A system, and using OpenAI for generation based on retrieved information. The repository focuses on enhancing language model responses with retrieved information from external sources, such as document databases or search engines, to improve factual accuracy and relevance of generated text.
LLM-Blender
LLM-Blender is a framework for ensembling large language models (LLMs) to achieve superior performance. It consists of two modules: PairRanker and GenFuser. PairRanker uses pairwise comparisons to distinguish between candidate outputs, while GenFuser merges the top-ranked candidates to create an improved output. LLM-Blender has been shown to significantly surpass the best LLMs and baseline ensembling methods across various metrics on the MixInstruct benchmark dataset.
vinagent
Vinagent is a lightweight and flexible library designed for building smart agent assistants across various industries. It provides a simple yet powerful foundation for creating AI-powered customer service bots, data analysis assistants, or domain-specific automation agents. With its modular tool system, users can easily extend their agent's capabilities by integrating a wide range of tools that are self-contained, well-documented, and can be registered dynamically. Vinagent allows users to scale and adapt their agents to new tasks or environments effortlessly.
structured-logprobs
This Python library enhances OpenAI chat completion responses by providing detailed information about token log probabilities. It works with OpenAI Structured Outputs to ensure model-generated responses adhere to a JSON Schema. Developers can analyze and incorporate token-level log probabilities to understand the reliability of structured data extracted from OpenAI models.
promptic
Promptic is a tool designed for LLM app development, providing a productive and pythonic way to build LLM applications. It leverages LiteLLM, allowing flexibility to switch LLM providers easily. Promptic focuses on building features by providing type-safe structured outputs, easy-to-build agents, streaming support, automatic prompt caching, and built-in conversation memory.

LightRAG
LightRAG is a PyTorch library designed for building and optimizing Retriever-Agent-Generator (RAG) pipelines. It follows principles of simplicity, quality, and optimization, offering developers maximum customizability with minimal abstraction. The library includes components for model interaction, output parsing, and structured data generation. LightRAG facilitates tasks like providing explanations and examples for concepts through a question-answering pipeline.
For similar tasks

pipelex
Pipelex is an open-source devtool designed to transform how users build repeatable AI workflows. It acts as a Docker or SQL for AI operations, allowing users to create modular 'pipes' using different LLMs for structured outputs. These pipes can be connected sequentially, in parallel, or conditionally to build complex knowledge transformations from reusable components. With Pipelex, users can share and scale proven methods instantly, saving time and effort in AI workflow development.
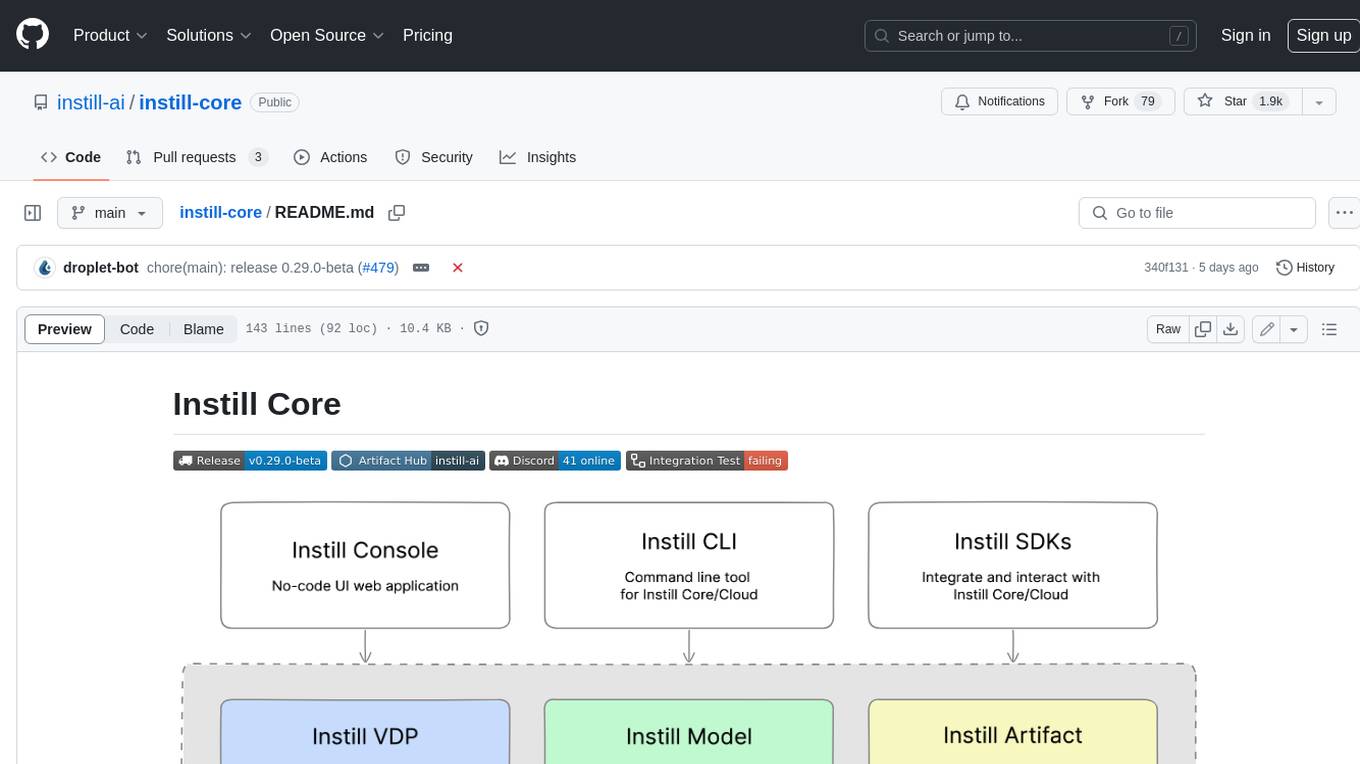
instill-core
Instill Core is an open-source orchestrator comprising a collection of source-available projects designed to streamline every aspect of building versatile AI features with unstructured data. It includes Instill VDP (Versatile Data Pipeline) for unstructured data, AI, and pipeline orchestration, Instill Model for scalable MLOps and LLMOps for open-source or custom AI models, and Instill Artifact for unified unstructured data management. Instill Core can be used for tasks such as building, testing, and sharing pipelines, importing, serving, fine-tuning, and monitoring ML models, and transforming documents, images, audio, and video into a unified AI-ready format.
fastRAG
fastRAG is a research framework designed to build and explore efficient retrieval-augmented generative models. It incorporates state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) and Information Retrieval to empower researchers and developers with a comprehensive tool-set for advancing retrieval augmented generation. The framework is optimized for Intel hardware, customizable, and includes key features such as optimized RAG pipelines, efficient components, and RAG-efficient components like ColBERT and Fusion-in-Decoder (FiD). fastRAG supports various unique components and backends for running LLMs, making it a versatile tool for research and development in the field of retrieval-augmented generation.
ai-on-openshift
AI on OpenShift is a site providing installation recipes, patterns, and demos for AI/ML tools and applications used in Data Science and Data Engineering projects running on OpenShift. It serves as a comprehensive resource for developers looking to deploy AI solutions on the OpenShift platform.

sematic
Sematic is an open-source ML development platform that allows ML Engineers and Data Scientists to write complex end-to-end pipelines with Python. It can be executed locally, on a cloud VM, or on a Kubernetes cluster. Sematic enables chaining data processing jobs with model training into reproducible pipelines that can be monitored and visualized in a web dashboard. It offers features like easy onboarding, local-to-cloud parity, end-to-end traceability, access to heterogeneous compute resources, and reproducibility.
SuperKnowa
SuperKnowa is a fast framework to build Enterprise RAG (Retriever Augmented Generation) Pipelines at Scale, powered by watsonx. It accelerates Enterprise Generative AI applications to get prod-ready solutions quickly on private data. The framework provides pluggable components for tackling various Generative AI use cases using Large Language Models (LLMs), allowing users to assemble building blocks to address challenges in AI-driven text generation. SuperKnowa is battle-tested from 1M to 200M private knowledge base & scaled to billions of retriever tokens.

ZetaForge
ZetaForge is an open-source AI platform designed for rapid development of advanced AI and AGI pipelines. It allows users to assemble reusable, customizable, and containerized Blocks into highly visual AI Pipelines, enabling rapid experimentation and collaboration. With ZetaForge, users can work with AI technologies in any programming language, easily modify and update AI pipelines, dive into the code whenever needed, utilize community-driven blocks and pipelines, and share their own creations. The platform aims to accelerate the development and deployment of advanced AI solutions through its user-friendly interface and community support.

AdalFlow
AdalFlow is a library designed to help developers build and optimize Large Language Model (LLM) task pipelines. It follows a design pattern similar to PyTorch, offering a light, modular, and robust codebase. Named in honor of Ada Lovelace, AdalFlow aims to inspire more women to enter the AI field. The library is tailored for various GenAI applications like chatbots, translation, summarization, code generation, and autonomous agents, as well as classical NLP tasks such as text classification and named entity recognition. AdalFlow emphasizes modularity, robustness, and readability to support users in customizing and iterating code for their specific use cases.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.