
llm.nvim
LLM powered development for Neovim
Stars: 812
llm.nvim is a plugin for Neovim that enables code completion using LLM models. It supports 'ghost-text' code completion similar to Copilot and allows users to choose their model for code generation via HTTP requests. The plugin interfaces with multiple backends like Hugging Face, Ollama, Open AI, and TGI, providing flexibility in model selection and configuration. Users can customize the behavior of suggestions, tokenization, and model parameters to enhance their coding experience. llm.nvim also includes commands for toggling auto-suggestions and manually requesting suggestions, making it a versatile tool for developers using Neovim.
README:
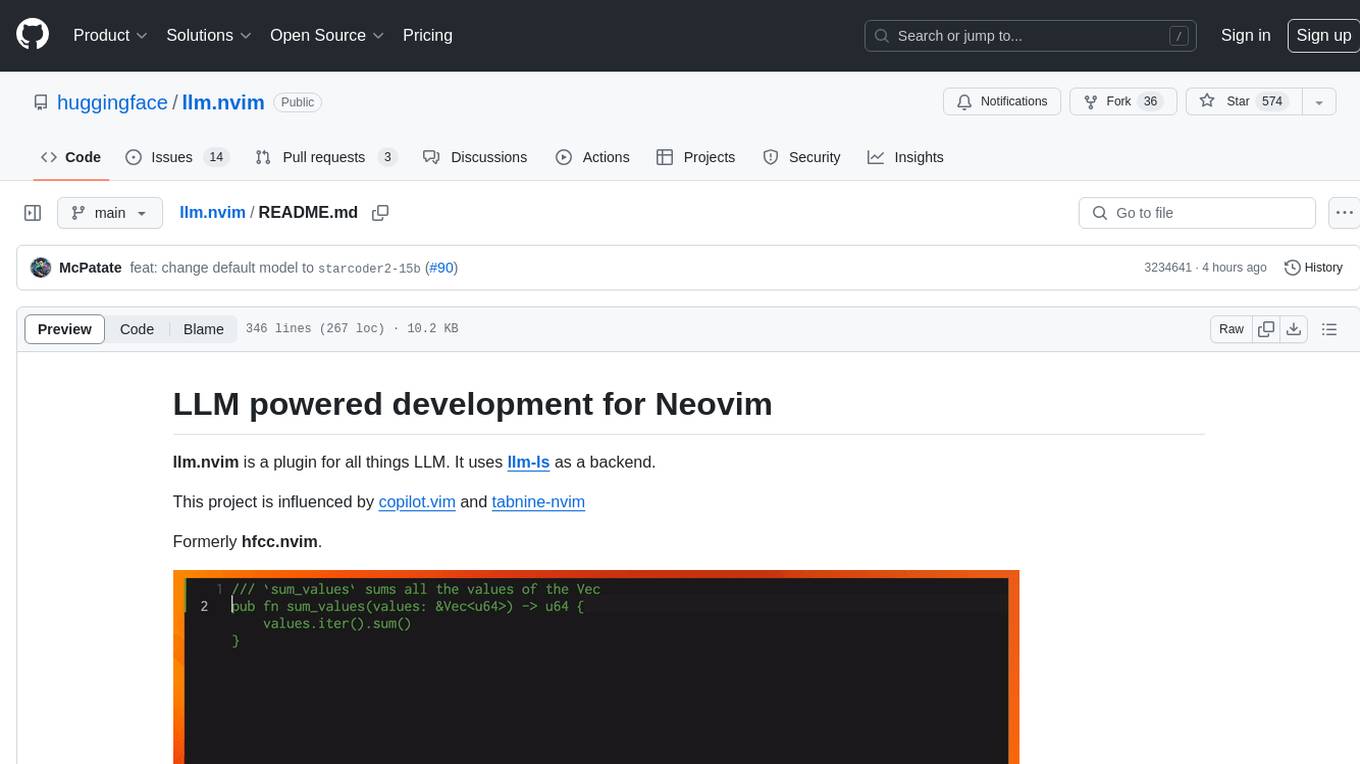
llm.nvim is a plugin for all things LLM. It uses llm-ls as a backend.
This project is influenced by copilot.vim and tabnine-nvim
Formerly hfcc.nvim.
[!NOTE] When using the Inference API, you will probably encounter some limitations. Subscribe to the PRO plan to avoid getting rate limited in the free tier.
This plugin supports "ghost-text" code completion, à la Copilot.
Requests for code generation are made via an HTTP request.
You can use the Hugging Face Inference API or your own HTTP endpoint, provided it adheres to the APIs listed in backend.
The prompt sent to the model will always be sized to fit within the context window, with the number of tokens determined using tokenizers.
llm.nvim can interface with multiple backends hosting models.
You can override the url of the backend with the LLM_NVIM_URL environment variable. If url is nil, it will default to the Inference API's default url
When api_token is set, it will be passed as a header: Authorization: Bearer <api_token>.
llm-ls will try to add the correct path to the url to get completions if it does not already end with said path. You can disable this behavior by setting disable_url_path_completion to true.
-
Create and get your API token from here https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens.
-
Define how the plugin will read your token. For this you have multiple options, in order of precedence:
- Pass
api_token = <your token>in plugin opts - this is not recommended if you use a versioning tool for your configuration files - Set the
LLM_NVIM_HF_API_TOKENenvironment variable - You can define your
HF_HOMEenvironment variable and create a file containing your token at$HF_HOME/token - Install the huggingface-cli and run
huggingface-cli login- this will prompt you to enter your token and set it at the right path
- Pass
-
Choose your model on the Hugging Face Hub, and, in order of precedence, you can either:
- Set the
LLM_NVIM_MODELenvironment variable - Pass
model = <model identifier>in plugin opts
- Set the
Note: the model's value will be appended to the url like so : {url}/model/{model} as this is how we route requests to the right model.
Refer to Ollama's documentation on how to run ollama. Here is an example configuration:
{
model = "codellama:7b",
url = "http://localhost:11434", -- llm-ls uses "/api/generate"
-- cf https://github.com/ollama/ollama/blob/main/docs/api.md#parameters
request_body = {
-- Modelfile options for the model you use
options = {
temperature = 0.2,
top_p = 0.95,
}
}
}Note: model's value will be added to the request body.
Refer to Ollama's documentation on how to run ollama. Here is an example configuration:
{
model = "codellama",
url = "http://localhost:8000", -- llm-ls uses "/v1/completions"
-- cf https://github.com/abetlen/llama-cpp-python?tab=readme-ov-file#openai-compatible-web-server
request_body = {
temperature = 0.2,
top_p = 0.95,
}
}Note: model's value will be added to the request body.
Refer to TGI's documentation on how to run TGI. Here is an example configuration:
{
model = "bigcode/starcoder",
url = "http://localhost:8080", -- llm-ls uses "/generate"
-- cf https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference/#/Text%20Generation%20Inference/generate
request_body = {
parameters = {
temperature = 0.2,
top_p = 0.95,
}
}
}{
tokens_to_clear = { "<|endoftext|>" },
fim = {
enabled = true,
prefix = "<fim_prefix>",
middle = "<fim_middle>",
suffix = "<fim_suffix>",
},
model = "bigcode/starcoder",
context_window = 8192,
tokenizer = {
repository = "bigcode/starcoder",
}
}[!NOTE] These are the default config values
{
tokens_to_clear = { "<EOT>" },
fim = {
enabled = true,
prefix = "<PRE> ",
middle = " <MID>",
suffix = " <SUF>",
},
model = "codellama/CodeLlama-13b-hf",
context_window = 4096,
tokenizer = {
repository = "codellama/CodeLlama-13b-hf",
}
}[!NOTE] Spaces are important here
By default, llm-ls is installed by llm.nvim the first time it is loaded. The binary is downloaded from the release page and stored in:
vim.api.nvim_call_function("stdpath", { "data" }) .. "/llm_nvim/bin"When developing locally, when using mason or if you built your own binary because your platform is not supported, you can set the lsp.bin_path setting to the path of the binary. You can also start llm-ls via tcp using the --port [PORT] option, which is useful when using a debugger.
lsp.version is used only when llm.nvim downloads llm-ls from the release page.
lsp.cmd_env can be used to set environment variables for the llm-ls process.
You can install llm-ls via mason.nvim. To do so, run the following command:
:MasonInstall llm-lsThen reference llm-ls's path in your configuration:
{
-- ...
lsp = {
bin_path = vim.api.nvim_call_function("stdpath", { "data" }) .. "/mason/bin/llm-ls",
},
-- ...
}llm-ls uses tokenizers to make sure the prompt fits the context_window.
To configure it, you have a few options:
- No tokenization, llm-ls will count the number of characters instead:
{
tokenizer = nil,
}- from a local file on your disk:
{
tokenizer = {
path = "/path/to/my/tokenizer.json"
}
}- from a Hugging Face repository, llm-ls will attempt to download
tokenizer.jsonat the root of the repository:
{
tokenizer = {
repository = "myusername/myrepo"
api_token = nil -- optional, in case the API token used for the backend is not the same
}
}- from an HTTP endpoint, llm-ls will attempt to download a file via an HTTP GET request:
{
tokenizer = {
url = "https://my-endpoint.example.com/mytokenizer.json",
to = "/download/path/of/mytokenizer.json"
}
}You can tune the way the suggestions behave:
-
enable_suggestions_on_startuplets you choose to enable or disable "suggest-as-you-type" suggestions on neovim startup. You can then toggle auto suggest withLLMToggleAutoSuggest(see Commands) -
enable_suggestions_on_fileslets you enable suggestions only on specific files that match the pattern matching syntax you will provide. It can either be a string or a list of strings, for example:- to match on all types of buffers:
enable_suggestions_on_files: "*" - to match on all files in
my_project/:enable_suggestions_on_files: "/path/to/my_project/*" - to match on all python and rust files:
enable_suggestions_on_files: { "*.py", "*.rs" }
- to match on all types of buffers:
llm.nvim provides the following commands:
-
LLMToggleAutoSuggestenables/disables automatic "suggest-as-you-type" suggestions -
LLMSuggestionis used to manually request a suggestion
Using packer
require("packer").startup(function(use)
use {
'huggingface/llm.nvim',
config = function()
require('llm').setup({
-- cf Setup
})
end
}
end)Using lazy.nvim
require("lazy").setup({
{
'huggingface/llm.nvim',
opts = {
-- cf Setup
}
},
})Using vim-plug
Plug 'huggingface/llm.nvim'require('llm').setup({
-- cf Setup
})local llm = require('llm')
llm.setup({
api_token = nil, -- cf Install paragraph
model = "bigcode/starcoder2-15b", -- the model ID, behavior depends on backend
backend = "huggingface", -- backend ID, "huggingface" | "ollama" | "openai" | "tgi"
url = nil, -- the http url of the backend
tokens_to_clear = { "<|endoftext|>" }, -- tokens to remove from the model's output
-- parameters that are added to the request body, values are arbitrary, you can set any field:value pair here it will be passed as is to the backend
request_body = {
parameters = {
max_new_tokens = 60,
temperature = 0.2,
top_p = 0.95,
},
},
-- set this if the model supports fill in the middle
fim = {
enabled = true,
prefix = "<fim_prefix>",
middle = "<fim_middle>",
suffix = "<fim_suffix>",
},
debounce_ms = 150,
accept_keymap = "<Tab>",
dismiss_keymap = "<S-Tab>",
tls_skip_verify_insecure = false,
-- llm-ls configuration, cf llm-ls section
lsp = {
bin_path = nil,
host = nil,
port = nil,
cmd_env = nil, -- or { LLM_LOG_LEVEL = "DEBUG" } to set the log level of llm-ls
version = "0.5.3",
},
tokenizer = nil, -- cf Tokenizer paragraph
context_window = 1024, -- max number of tokens for the context window
enable_suggestions_on_startup = true,
enable_suggestions_on_files = "*", -- pattern matching syntax to enable suggestions on specific files, either a string or a list of strings
disable_url_path_completion = false, -- cf Backend
})
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm.nvim
Similar Open Source Tools

llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a plugin for Neovim that enables code completion using LLM models. It supports 'ghost-text' code completion similar to Copilot and allows users to choose their model for code generation via HTTP requests. The plugin interfaces with multiple backends like Hugging Face, Ollama, Open AI, and TGI, providing flexibility in model selection and configuration. Users can customize the behavior of suggestions, tokenization, and model parameters to enhance their coding experience. llm.nvim also includes commands for toggling auto-suggestions and manually requesting suggestions, making it a versatile tool for developers using Neovim.
nvim.ai
nvim.ai is a powerful Neovim plugin that enables AI-assisted coding and chat capabilities within the editor. Users can chat with buffers, insert code with an inline assistant, and utilize various LLM providers for context-aware AI assistance. The plugin supports features like interacting with AI about code and documents, receiving relevant help based on current work, code insertion, code rewriting (Work in Progress), and integration with multiple LLM providers. Users can configure the plugin, add API keys to dotfiles, and integrate with nvim-cmp for command autocompletion. Keymaps are available for chat and inline assist functionalities. The chat dialog allows parsing content with keywords and supports roles like /system, /you, and /assistant. Context-aware assistance can be accessed through inline assist by inserting code blocks anywhere in the file.
genaiscript
GenAIScript is a scripting environment designed to facilitate file ingestion, prompt development, and structured data extraction. Users can define metadata and model configurations, specify data sources, and define tasks to extract specific information. The tool provides a convenient way to analyze files and extract desired content in a structured format. It offers a user-friendly interface for working with data and automating data extraction processes, making it suitable for various data processing tasks.
parrot.nvim
Parrot.nvim is a Neovim plugin that prioritizes a seamless out-of-the-box experience for text generation. It simplifies functionality and focuses solely on text generation, excluding integration of DALLE and Whisper. It supports persistent conversations as markdown files, custom hooks for inline text editing, multiple providers like Anthropic API, perplexity.ai API, OpenAI API, Mistral API, and local/offline serving via ollama. It allows custom agent definitions, flexible API credential support, and repository-specific instructions with a `.parrot.md` file. It does not have autocompletion or hidden requests in the background to analyze files.
pipelex
Pipelex is an open-source devtool designed to transform how users build repeatable AI workflows. It acts as a Docker or SQL for AI operations, allowing users to create modular 'pipes' using different LLMs for structured outputs. These pipes can be connected sequentially, in parallel, or conditionally to build complex knowledge transformations from reusable components. With Pipelex, users can share and scale proven methods instantly, saving time and effort in AI workflow development.

memobase
Memobase is a user profile-based memory system designed to enhance Generative AI applications by enabling them to remember, understand, and evolve with users. It provides structured user profiles, scalable profiling, easy integration with existing LLM stacks, batch processing for speed, and is production-ready. Users can manage users, insert data, get memory profiles, and track user preferences and behaviors. Memobase is ideal for applications that require user analysis, tracking, and personalized interactions.
instructor
Instructor is a popular Python library for managing structured outputs from large language models (LLMs). It offers a user-friendly API for validation, retries, and streaming responses. With support for various LLM providers and multiple languages, Instructor simplifies working with LLM outputs. The library includes features like response models, retry management, validation, streaming support, and flexible backends. It also provides hooks for logging and monitoring LLM interactions, and supports integration with Anthropic, Cohere, Gemini, Litellm, and Google AI models. Instructor facilitates tasks such as extracting user data from natural language, creating fine-tuned models, managing uploaded files, and monitoring usage of OpenAI models.
FlashLearn
FlashLearn is a tool that provides a simple interface and orchestration for incorporating Agent LLMs into workflows and ETL pipelines. It allows data transformations, classifications, summarizations, rewriting, and custom multi-step tasks using LLMs. Each step and task has a compact JSON definition, making pipelines easy to understand and maintain. FlashLearn supports LiteLLM, Ollama, OpenAI, DeepSeek, and other OpenAI-compatible clients.
gitleaks
Gitleaks is a tool for detecting secrets like passwords, API keys, and tokens in git repos, files, and whatever else you wanna throw at it via stdin. It can be installed using Homebrew, Docker, or Go, and is available in binary form for many popular platforms and OS types. Gitleaks can be implemented as a pre-commit hook directly in your repo or as a GitHub action. It offers scanning modes for git repositories, directories, and stdin, and allows creating baselines for ignoring old findings. Gitleaks also provides configuration options for custom secret detection rules and supports features like decoding encoded text and generating reports in various formats.
CAG
Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG) is an alternative paradigm to Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that eliminates real-time retrieval delays and errors by preloading all relevant resources into the model's context. CAG leverages extended context windows of large language models (LLMs) to generate responses directly, providing reduced latency, improved reliability, and simplified design. While CAG has limitations in knowledge size and context length, advancements in LLMs are addressing these issues, making CAG a practical and scalable alternative for complex applications.
vim-ai
vim-ai is a plugin that adds Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities to Vim and Neovim. It allows users to generate code, edit text, and have interactive conversations with GPT models powered by OpenAI's API. The plugin uses OpenAI's API to generate responses, requiring users to set up an account and obtain an API key. It supports various commands for text generation, editing, and chat interactions, providing a seamless integration of AI features into the Vim text editor environment.
SimplerLLM
SimplerLLM is an open-source Python library that simplifies interactions with Large Language Models (LLMs) for researchers and beginners. It provides a unified interface for different LLM providers, tools for enhancing language model capabilities, and easy development of AI-powered tools and apps. The library offers features like unified LLM interface, generic text loader, RapidAPI connector, SERP integration, prompt template builder, and more. Users can easily set up environment variables, create LLM instances, use tools like SERP, generic text loader, calling RapidAPI APIs, and prompt template builder. Additionally, the library includes chunking functions to split texts into manageable chunks based on different criteria. Future updates will bring more tools, interactions with local LLMs, prompt optimization, response evaluation, GPT Trainer, document chunker, advanced document loader, integration with more providers, Simple RAG with SimplerVectors, integration with vector databases, agent builder, and LLM server.
deepgram-js-sdk
Deepgram JavaScript SDK. Power your apps with world-class speech and Language AI models.
lmstudio.js
lmstudio.js is a pre-release alpha client SDK for LM Studio, allowing users to use local LLMs in JS/TS/Node. It is currently undergoing rapid development with breaking changes expected. Users can follow LM Studio's announcements on Twitter and Discord. The SDK provides API usage for loading models, predicting text, setting up the local LLM server, and more. It supports features like custom loading progress tracking, model unloading, structured output prediction, and cancellation of predictions. Users can interact with LM Studio through the CLI tool 'lms' and perform tasks like text completion, conversation, and getting prediction statistics.
ogpt.nvim
OGPT.nvim is a Neovim plugin that enables users to interact with various language models (LLMs) such as Ollama, OpenAI, TextGenUI, and more. Users can engage in interactive question-and-answer sessions, have persona-based conversations, and execute customizable actions like grammar correction, translation, keyword generation, docstring creation, test addition, code optimization, summarization, bug fixing, code explanation, and code readability analysis. The plugin allows users to define custom actions using a JSON file or plugin configurations.
swarmzero
SwarmZero SDK is a library that simplifies the creation and execution of AI Agents and Swarms of Agents. It supports various LLM Providers such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Anthropic, MistralAI, Gemini, Nebius, and Ollama. Users can easily install the library using pip or poetry, set up the environment and configuration, create and run Agents, collaborate with Swarms, add tools for complex tasks, and utilize retriever tools for semantic information retrieval. Sample prompts are provided to help users explore the capabilities of the agents and swarms. The SDK also includes detailed examples and documentation for reference.
For similar tasks
LLMUnity
LLM for Unity enables seamless integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) within the Unity engine, allowing users to create intelligent characters for immersive player interactions. The tool supports major LLM models, runs locally without internet access, offers fast inference on CPU and GPU, and is easy to set up with a single line of code. It is free for both personal and commercial use, tested on Unity 2021 LTS, 2022 LTS, and 2023. Users can build multiple AI characters efficiently, use remote servers for processing, and customize model settings for text generation.

llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a plugin for Neovim that enables code completion using LLM models. It supports 'ghost-text' code completion similar to Copilot and allows users to choose their model for code generation via HTTP requests. The plugin interfaces with multiple backends like Hugging Face, Ollama, Open AI, and TGI, providing flexibility in model selection and configuration. Users can customize the behavior of suggestions, tokenization, and model parameters to enhance their coding experience. llm.nvim also includes commands for toggling auto-suggestions and manually requesting suggestions, making it a versatile tool for developers using Neovim.
sparkle
Sparkle is a tool that streamlines the process of building AI-driven features in applications using Large Language Models (LLMs). It guides users through creating and managing agents, defining tools, and interacting with LLM providers like OpenAI. Sparkle allows customization of LLM provider settings, model configurations, and provides a seamless integration with Sparkle Server for exposing agents via an OpenAI-compatible chat API endpoint.
code-review-gpt
Code Review GPT uses Large Language Models to review code in your CI/CD pipeline. It helps streamline the code review process by providing feedback on code that may have issues or areas for improvement. It should pick up on common issues such as exposed secrets, slow or inefficient code, and unreadable code. It can also be run locally in your command line to review staged files. Code Review GPT is in alpha and should be used for fun only. It may provide useful feedback but please check any suggestions thoroughly.
shell_gpt
ShellGPT is a command-line productivity tool powered by AI large language models (LLMs). This command-line tool offers streamlined generation of shell commands, code snippets, documentation, eliminating the need for external resources (like Google search). Supports Linux, macOS, Windows and compatible with all major Shells like PowerShell, CMD, Bash, Zsh, etc.

syncode
SynCode is a novel framework for the grammar-guided generation of Large Language Models (LLMs) that ensures syntactically valid output with respect to defined Context-Free Grammar (CFG) rules. It supports general-purpose programming languages like Python, Go, SQL, JSON, and more, allowing users to define custom grammars using EBNF syntax. The tool compares favorably to other constrained decoders and offers features like fast grammar-guided generation, compatibility with HuggingFace Language Models, and the ability to work with various decoding strategies.
DemoGPT
DemoGPT is an all-in-one agent library that provides tools, prompts, frameworks, and LLM models for streamlined agent development. It leverages GPT-3.5-turbo to generate LangChain code, creating interactive Streamlit applications. The tool is designed for creating intelligent, interactive, and inclusive solutions in LLM-based application development. It offers model flexibility, iterative development, and a commitment to user engagement. Future enhancements include integrating Gorilla for autonomous API usage and adding a publicly available database for refining the generation process.
CodeGen
CodeGen is an official release of models for Program Synthesis by Salesforce AI Research. It includes CodeGen1 and CodeGen2 models with varying parameters. The latest version, CodeGen2.5, outperforms previous models. The tool is designed for code generation tasks using large language models trained on programming and natural languages. Users can access the models through the Hugging Face Hub and utilize them for program synthesis and infill sampling. The accompanying Jaxformer library provides support for data pre-processing, training, and fine-tuning of the CodeGen models.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
