
eval-assist
EvalAssist is an open-source project that simplifies using large language models as evaluators (LLM-as-a-Judge) of the output of other large language models by supporting users in iteratively refining evaluation criteria in a web-based user experience.
Stars: 80
EvalAssist is an LLM-as-a-Judge framework built on top of the Unitxt open source evaluation library for large language models. It provides users with a convenient way of iteratively testing and refining LLM-as-a-judge criteria, supporting both direct (rubric-based) and pairwise assessment paradigms. EvalAssist is model-agnostic, supporting a rich set of off-the-shelf judge models that can be extended. Users can auto-generate a Notebook with Unitxt code to run bulk evaluations and save their own test cases. The tool is designed for evaluating text data using language models.
README:
Project Website • Documentation • Video demo
EvalAssist is an LLM-as-a-Judge framework built on top of the Unitxt open source evaluation library for large language models. The EvalAssist application provides users with a convenient way of iteratively testing and refining LLM-as-a-judge criteria, and supports both direct (rubric-based) and pairwise assessment paradigms (relation-based), the two most prevalent forms of LLM-as-a-judge evaluations available. EvalAssist is designed to be model-agnostic, i.e. the content to be evaluated can come from any model. EvalAssist supports a rich set of off-the-shelf judge models that can easily be extended. An API key is required to use the pre-defined judge models. Once users are satisfied with their criteria, they can auto-generate a Notebook with Unitxt code to run bulk evaluations with larger data sets based on their criteria definition. EvalAssist also includes a catalog of example test cases, exhibiting the use of LLM-as-a-judge across a variety of scenarios. Users can save their own test cases.
EvalAssist can be installed using various package managers. Before proceeding, ensure you're using Python >= 3.10, <3.14 to avoid compatibility issues. Make sure to set DATA_DIR to avoid data loss (e.g. export DATA_DIR="~/.eval_assist").
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # or venv\Scripts\activate.bat in Windows
pip install 'evalassist[webapp]'
eval-assist serveuvx --python 3.11 --from 'evalassist[webapp]' eval-assist serveconda create -n evalassist python=3.11
conda activate evalassist
pip install 'evalassist[webapp]'
eval-assist serveIn all cases, after running the command, you can access the EvalAssist server at http://localhost:8000.
EvalAssist can be configured through environment variables and command parameters. Take a look at the configuration documentation.
Check out the tutorials to see how to run evaluations and generate synthetic data.
You can run LLM as a Judge evaluations using Python only. For example:
from evalassist.judges import DirectJudge
from evalassist.judges.const import DEFAULT_JUDGE_INFERENCE_PARAMS
from unitxt.inference import CrossProviderInferenceEngine
judge = DirectJudge(
inference_engine=CrossProviderInferenceEngine(
model="llama-3-3-70b-instruct",
provider="watsonx",
**DEFAULT_JUDGE_INFERENCE_PARAMS,
),
)
results = judge(
instances=[
"Use the API client to fetch data from the server and the cache to store frequently accessed results for faster performance."
],
criteria="Is the text self-explanatory and self-contained?", # Create yes/no direct assessment criteria",
)Look at the documentation of the judges sub-package.
You can contribute to EvalAssist or to Unitxt. Look at the Contribution Guidelines for more details.
Look at the Local Development Guide for instructions on setting up a local development environment.
You can find extesive documentation of the system in the Documentation page.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for eval-assist
Similar Open Source Tools

eval-assist
EvalAssist is an LLM-as-a-Judge framework built on top of the Unitxt open source evaluation library for large language models. It provides users with a convenient way of iteratively testing and refining LLM-as-a-judge criteria, supporting both direct (rubric-based) and pairwise assessment paradigms. EvalAssist is model-agnostic, supporting a rich set of off-the-shelf judge models that can be extended. Users can auto-generate a Notebook with Unitxt code to run bulk evaluations and save their own test cases. The tool is designed for evaluating text data using language models.
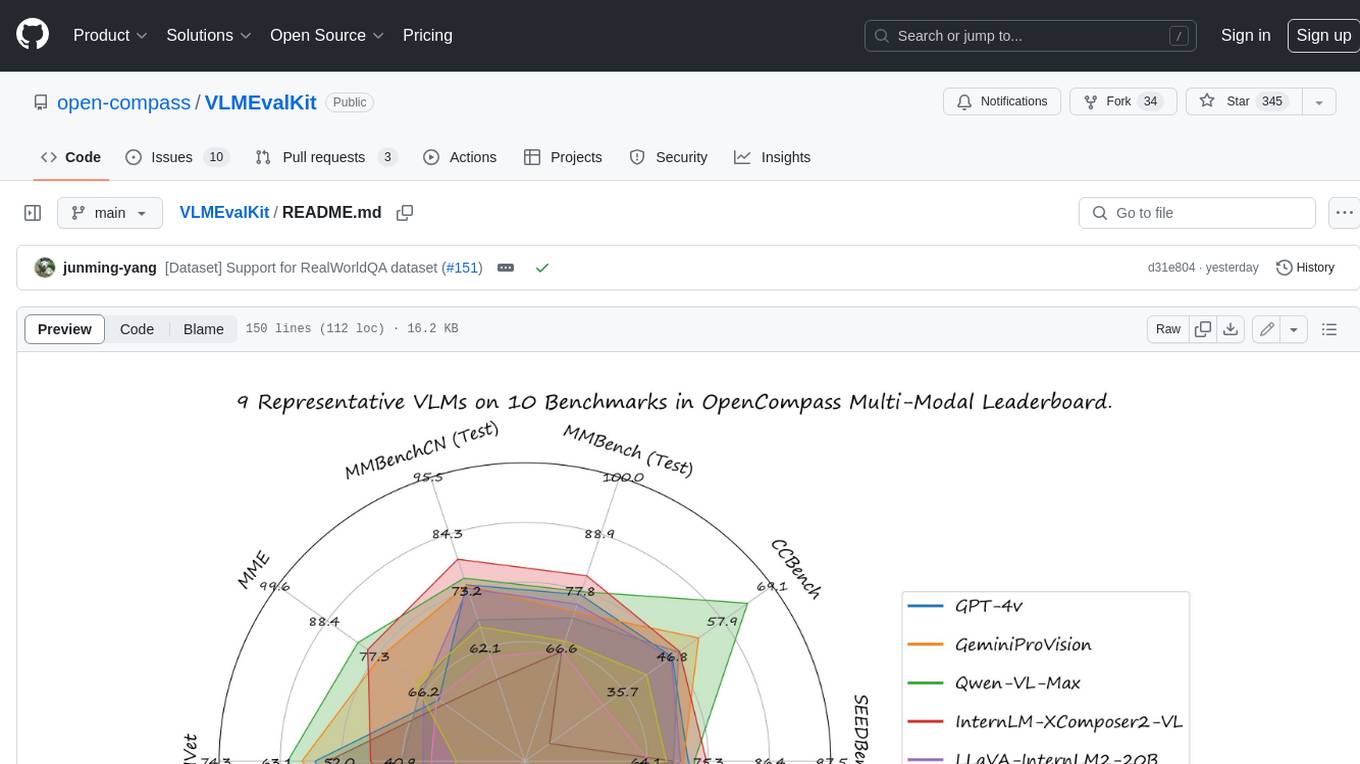
VLMEvalKit
VLMEvalKit is an open-source evaluation toolkit of large vision-language models (LVLMs). It enables one-command evaluation of LVLMs on various benchmarks, without the heavy workload of data preparation under multiple repositories. In VLMEvalKit, we adopt generation-based evaluation for all LVLMs, and provide the evaluation results obtained with both exact matching and LLM-based answer extraction.
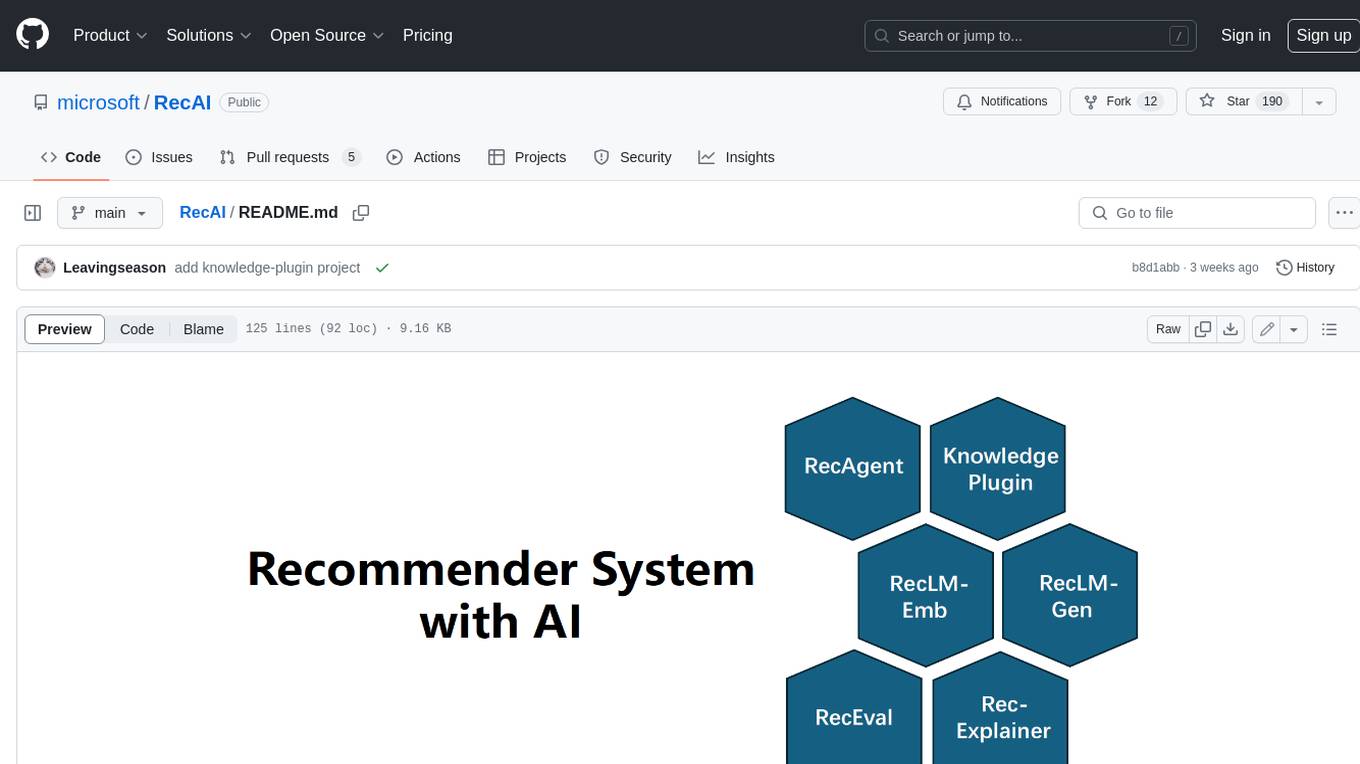
RecAI
RecAI is a project that explores the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into recommender systems, addressing the challenges of interactivity, explainability, and controllability. It aims to bridge the gap between general-purpose LLMs and domain-specific recommender systems, providing a holistic perspective on the practical requirements of LLM4Rec. The project investigates various techniques, including Recommender AI agents, selective knowledge injection, fine-tuning language models, evaluation, and LLMs as model explainers, to create more sophisticated, interactive, and user-centric recommender systems.
tods-arxiv-daily-paper
This repository provides a tool for fetching and summarizing daily papers from the arXiv repository. It allows users to stay updated with the latest research in various fields by automatically retrieving and summarizing papers on a daily basis. The tool simplifies the process of accessing and digesting academic papers, making it easier for researchers and enthusiasts to keep track of new developments in their areas of interest.

awesome-generative-ai-guide
This repository serves as a comprehensive hub for updates on generative AI research, interview materials, notebooks, and more. It includes monthly best GenAI papers list, interview resources, free courses, and code repositories/notebooks for developing generative AI applications. The repository is regularly updated with the latest additions to keep users informed and engaged in the field of generative AI.

llms-tools
The 'llms-tools' repository is a comprehensive collection of AI tools, open-source projects, and research related to Large Language Models (LLMs) and Chatbots. It covers a wide range of topics such as AI in various domains, open-source models, chats & assistants, visual language models, evaluation tools, libraries, devices, income models, text-to-image, computer vision, audio & speech, code & math, games, robotics, typography, bio & med, military, climate, finance, and presentation. The repository provides valuable resources for researchers, developers, and enthusiasts interested in exploring the capabilities of LLMs and related technologies.

kaapana
Kaapana is an open-source toolkit for state-of-the-art platform provisioning in the field of medical data analysis. The applications comprise AI-based workflows and federated learning scenarios with a focus on radiological and radiotherapeutic imaging. Obtaining large amounts of medical data necessary for developing and training modern machine learning methods is an extremely challenging effort that often fails in a multi-center setting, e.g. due to technical, organizational and legal hurdles. A federated approach where the data remains under the authority of the individual institutions and is only processed on-site is, in contrast, a promising approach ideally suited to overcome these difficulties. Following this federated concept, the goal of Kaapana is to provide a framework and a set of tools for sharing data processing algorithms, for standardized workflow design and execution as well as for performing distributed method development. This will facilitate data analysis in a compliant way enabling researchers and clinicians to perform large-scale multi-center studies. By adhering to established standards and by adopting widely used open technologies for private cloud development and containerized data processing, Kaapana integrates seamlessly with the existing clinical IT infrastructure, such as the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), and ensures modularity and easy extensibility.
awesome-RLAIF
Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) is a concept that describes a type of machine learning approach where **an AI agent learns by receiving feedback or guidance from another AI system**. This concept is closely related to the field of Reinforcement Learning (RL), which is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to make a sequence of decisions in an environment to maximize a cumulative reward. In traditional RL, an agent interacts with an environment and receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on the actions it takes. It learns to improve its decision-making over time to achieve its goals. In the context of Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback, the AI agent still aims to learn optimal behavior through interactions, but **the feedback comes from another AI system rather than from the environment or human evaluators**. This can be **particularly useful in situations where it may be challenging to define clear reward functions or when it is more efficient to use another AI system to provide guidance**. The feedback from the AI system can take various forms, such as: - **Demonstrations** : The AI system provides demonstrations of desired behavior, and the learning agent tries to imitate these demonstrations. - **Comparison Data** : The AI system ranks or compares different actions taken by the learning agent, helping it to understand which actions are better or worse. - **Reward Shaping** : The AI system provides additional reward signals to guide the learning agent's behavior, supplementing the rewards from the environment. This approach is often used in scenarios where the RL agent needs to learn from **limited human or expert feedback or when the reward signal from the environment is sparse or unclear**. It can also be used to **accelerate the learning process and make RL more sample-efficient**. Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback is an area of ongoing research and has applications in various domains, including robotics, autonomous vehicles, and game playing, among others.
ianvs
Ianvs is a distributed synergy AI benchmarking project incubated in KubeEdge SIG AI. It aims to test the performance of distributed synergy AI solutions following recognized standards, providing end-to-end benchmark toolkits, test environment management tools, test case control tools, and benchmark presentation tools. It also collaborates with other organizations to establish comprehensive benchmarks and related applications. The architecture includes critical components like Test Environment Manager, Test Case Controller, Generation Assistant, Simulation Controller, and Story Manager. Ianvs documentation covers quick start, guides, dataset descriptions, algorithms, user interfaces, stories, and roadmap.
awesome-llms-fine-tuning
This repository is a curated collection of resources for fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT, BERT, RoBERTa, and their variants. It includes tutorials, papers, tools, frameworks, and best practices to aid researchers, data scientists, and machine learning practitioners in adapting pre-trained models to specific tasks and domains. The resources cover a wide range of topics related to fine-tuning LLMs, providing valuable insights and guidelines to streamline the process and enhance model performance.
matchem-llm
A public repository collecting links to state-of-the-art training sets, QA, benchmarks and other evaluations for various ML and LLM applications in materials science and chemistry. It includes datasets related to chemistry, materials, multimodal data, and knowledge graphs in the field. The repository aims to provide resources for training and evaluating machine learning models in the materials science and chemistry domains.
PaddleNLP
PaddleNLP is an easy-to-use and high-performance NLP library. It aggregates high-quality pre-trained models in the industry and provides out-of-the-box development experience, covering a model library for multiple NLP scenarios with industry practice examples to meet developers' flexible customization needs.
Coding-Tutor
This repository explores the potential of LLMs as coding tutors through the proposed Traver agent workflow. It focuses on incorporating knowledge tracing and turn-by-turn verification to tackle challenges in coding tutoring. The method extends beyond coding to other task-tutoring scenarios, adapting content to users' varying levels of background knowledge. The repository introduces the DICT evaluation protocol for assessing tutor performance through student simulation and coding tests. It also discusses the inference-time scaling with verifiers and provides resources for training and evaluation.

RAGElo
RAGElo is a streamlined toolkit for evaluating Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)-powered Large Language Models (LLMs) question answering agents using the Elo rating system. It simplifies the process of comparing different outputs from multiple prompt and pipeline variations to a 'gold standard' by allowing a powerful LLM to judge between pairs of answers and questions. RAGElo conducts tournament-style Elo ranking of LLM outputs, providing insights into the effectiveness of different settings.
openssa
OpenSSA is an open-source framework for creating efficient, domain-specific AI agents. It enables the development of Small Specialist Agents (SSAs) that solve complex problems in specific domains. SSAs tackle multi-step problems that require planning and reasoning beyond traditional language models. They apply OODA for deliberative reasoning (OODAR) and iterative, hierarchical task planning (HTP). This "System-2 Intelligence" breaks down complex tasks into manageable steps. SSAs make informed decisions based on domain-specific knowledge. With OpenSSA, users can create agents that process, generate, and reason about information, making them more effective and efficient in solving real-world challenges.
For similar tasks

eval-assist
EvalAssist is an LLM-as-a-Judge framework built on top of the Unitxt open source evaluation library for large language models. It provides users with a convenient way of iteratively testing and refining LLM-as-a-judge criteria, supporting both direct (rubric-based) and pairwise assessment paradigms. EvalAssist is model-agnostic, supporting a rich set of off-the-shelf judge models that can be extended. Users can auto-generate a Notebook with Unitxt code to run bulk evaluations and save their own test cases. The tool is designed for evaluating text data using language models.
qgate-model
QGate-Model is a machine learning meta-model with synthetic data, designed for MLOps and feature store. It is independent of machine learning solutions, with definitions in JSON and data in CSV/parquet formats. This meta-model is useful for comparing capabilities and functions of machine learning solutions, independently testing new versions of machine learning solutions, and conducting various types of tests (unit, sanity, smoke, system, regression, function, acceptance, performance, shadow, etc.). It can also be used for external test coverage when internal test coverage is not available or weak.
llm-datasets
LLM Datasets is a repository containing high-quality datasets, tools, and concepts for LLM fine-tuning. It provides datasets with characteristics like accuracy, diversity, and complexity to train large language models for various tasks. The repository includes datasets for general-purpose, math & logic, code, conversation & role-play, and agent & function calling domains. It also offers guidance on creating high-quality datasets through data deduplication, data quality assessment, data exploration, and data generation techniques.
LLM4IR-Survey
LLM4IR-Survey is a collection of papers related to large language models for information retrieval, organized according to the survey paper 'Large Language Models for Information Retrieval: A Survey'. It covers various aspects such as query rewriting, retrievers, rerankers, readers, search agents, and more, providing insights into the integration of large language models with information retrieval systems.
Main
This repository contains material related to the new book _Synthetic Data and Generative AI_ by the author, including code for NoGAN, DeepResampling, and NoGAN_Hellinger. NoGAN is a tabular data synthesizer that outperforms GenAI methods in terms of speed and results, utilizing state-of-the-art quality metrics. DeepResampling is a fast NoGAN based on resampling and Bayesian Models with hyperparameter auto-tuning. NoGAN_Hellinger combines NoGAN and DeepResampling with the Hellinger model evaluation metric.
continuous-eval
Open-Source Evaluation for LLM Applications. `continuous-eval` is an open-source package created for granular and holistic evaluation of GenAI application pipelines. It offers modularized evaluation, a comprehensive metric library covering various LLM use cases, the ability to leverage user feedback in evaluation, and synthetic dataset generation for testing pipelines. Users can define their own metrics by extending the Metric class. The tool allows running evaluation on a pipeline defined with modules and corresponding metrics. Additionally, it provides synthetic data generation capabilities to create user interaction data for evaluation or training purposes.
eShopSupport
eShopSupport is a sample .NET application showcasing common use cases and development practices for building AI solutions in .NET, specifically Generative AI. It demonstrates a customer support application for an e-commerce website using a services-based architecture with .NET Aspire. The application includes support for text classification, sentiment analysis, text summarization, synthetic data generation, and chat bot interactions. It also showcases development practices such as developing solutions locally, evaluating AI responses, leveraging Python projects, and deploying applications to the Cloud.
Awesome-Knowledge-Distillation-of-LLMs
A collection of papers related to knowledge distillation of large language models (LLMs). The repository focuses on techniques to transfer advanced capabilities from proprietary LLMs to smaller models, compress open-source LLMs, and refine their performance. It covers various aspects of knowledge distillation, including algorithms, skill distillation, verticalization distillation in fields like law, medical & healthcare, finance, science, and miscellaneous domains. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of the research in the area of knowledge distillation of LLMs.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.



