
noether
Deep-learning framework for Engineering AI. Built on transformer building blocks, it delivers the full engineering stack, allowing teams to build, train, and operate industrial simulation models across engineering verticals.
Stars: 101

Noether is Emmi AI's open software framework for Engineering AI. It is built on transformer building blocks, delivering the full engineering stack for building, training, and operating industrial simulation models across engineering verticals. The framework eliminates the need for component re-engineering or an in-house deep learning team. Noether features a modular transformer architecture optimized for physical systems, hardware agnostic execution across CPU, MPS, and NVIDIA GPUs, industrial-grade design for high-fidelity simulations, and built-in support for Multi-GPU and SLURM cluster environments.
README:
- Modular Transformer Architecture: Built on building blocks optimized for physical systems.
- Hardware Agnostic: Seamless execution across CPU, MPS (Apple Silicon), and NVIDIA GPUs.
- Industrial Grade: Designed for high-fidelity industrial simulations and engineering verticals.
- Ready for Scale: Built-in support for Multi-GPU and SLURM cluster environments.
- Installation
- Quickstart
- Performance Benchmarks
- Contributing
- Supported systems
- Licensing
- Endorsements
- Citing
It is possible to use the framework either from source or from the pre-built packages.
- install uv as the package manager on your system
- clone the repo into your desired folder:
git clone https://github.com/Emmi-AI/noether.git - follow the next steps 🚀
Installable package is available via pip and can be installed as:
pip install emmiai-noetherTo work with the prebuilt PyPi package you have to install relevant PyTorch version beforehand as it is a dependency
to build torch-cluster. Install emmiai-noether as follows:
uv pip install torch==2.8.0
uv pip install emmiai-noether==1.0.0 --no-build-isolation torch-clusterIf you prefer to work with the source code directly without installing a prebuilt package.
[!IMPORTANT] If you are running on NVIDIA GPUs or need custom CUDA paths, you must configure your environment variables first. Please follow our Advanced Linux Setup Guide before running the command below.
Create a fresh virtual environment and synchronize the core dependencies:
uv venv && source .venv/bin/activate
uv syncNote: Initial installation may take several minutes as third-party dependencies are compiled. Duration depends on your hardware and network speed.
Validate your installation by simply running the tests (if something fails with module import errors it means that the installation was incomplete):
pytest -q tests/if the tests are passed (warnings are okay to be logged) then you're all set and ready to go!
You might be in a situation when your venv won't be configured as intended anymore, to fix this:
- Deactivate existing environment in your terminal by running:
deactivate - Remove existing
.venv(optionally adduv.lock):rm -rf .venv uv.lock - [Optional] Clean uv cache:
uv cache clean - Create a new venv and activate it:
uv venv && source .venv/bin/activate - [Optional] If deleted, generate a new
uv.lockfile:uv lock - [Optional] If contributor:
pre-commit install
You can run a training job immediately using the tutorial configuration. For local development (Mac/CPU), use:
uv run noether-train --hp tutorial/configs/train_shapenet.yaml \
+experiment/shapenet=upt \
dataset_root=./data \
+accelerator=mps \Learn more about different hardware support here.
The following benchmarks demonstrate Noether's acceleration compatibility over different hardware using
the ShapeNet-Car dataset and the AB-UPT model.
[!NOTE] All benchmarks were conducted using FP32 precision to establish a baseline for raw computational performance.
| Hardware | Config | Precision | Time | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MacBook Pro M3 Max | 1x MPS | FP32 | 135m | 1.0x |
| RTX Pro 4500 (Blackwell) | 1x GPU | FP32 | 26m | 5.2x |
| RTX Pro 4500 (Blackwell) | 2x GPU | FP32 | 8m | 16.8x |
| NVIDIA H100 | 1x GPU | FP32 | 5.7m | 23.6x |
We follow these standards:
- Use typed coding in Python.
- Write documentation to new features and modules:
- In case of larger modules make sure to update the documentation that is not autogenerated under the
docs/. - For smaller features writing a clear API documentation is enough and required.
- In case of larger modules make sure to update the documentation that is not autogenerated under the
- Before committing your changes:
- Run tests via
pytest -q tests/. - Ensure that pre-commit hooks are not disabled and are runnable at every commit.
We are using
ruffas a linter and formatter as well asmypyfor type checking. Their configuration is defined in the project's root pyproject.toml.
- Run tests via
- Creating pull requests (PRs) is a mandatory step for any incoming changes that will end up on the
mainbranch.- For a PR to be merged at least one core maintainer must give their approval.
- All test must be green
To install pre-commit execute:
pre-commit installTo run the pre-commit configuration on all files, you can use:
pre-commit run --all-filesTo run the pre-commit configuration on specific files use:
pre-commit run --files /your/file/path1.py /your/file/path2.pyIn case of bugs use a corresponding template to create an issue.
In case of feature requests you can submit a PR with clear description of the proposed feature. In that case it must follow the guidelines, or file a feature request as an issue. In that case, we will consider adding it to our backlog.
- Mark
src/directory asSources Root(right mouse button click on the folder ->Mark Directory as) - Settings -> Editor -> Code Style -> Python -> Tabs and Indents -> change
Continuation indentfrom 8 to 4. - Settings -> Editor -> Code Style -> Python -> Spaces -> Around Operators ->
Power operator (**)
With available GitHub Actions we automate several workflows relevant to our development ranging from buildings the docs to building our modules as wheel files.
To test the desired workflow locally it is recommended to use act.
[!NOTE] Make sure to install Docker Desktop as requested by the official documentation.
Install it on a Mac with: brew install act
For example, to check the package release pipeline:
act workflow_dispatch --input version_type=patch -W .github/workflows/release.ymlor to see if tests are runnable:
act pull_request -W .github/workflows/run-tests.ymlWorth noting that we work with macOS and Linux environments thus in case of any issues on Windows, at this time, you have to find workarounds yourself.
[!NOTE] TL;DR: Research & development ✅| Production deployment ❌ (without commercial license)
The Noether Framework is licensed under a Non-Production License (based on Mistral AI's MNPL). This means you're free to use, modify, and research with the framework, but commercial/production use requires a separate commercial license from Emmi AI.
We're committed to open AI innovation while sustainably growing our business. For commercial licensing, contact us at [email protected] .
Read the full license here.

|

|

|

|

|

|
If you use Noether in your research or industrial applications, please cite this repository. A formal BibTeX entry for our forthcoming ArXiv publication will be provided here shortly.
@misc{noether2026,
author = { Bleeker, Maurits AND Hennerbichler, Markus AND Kuksa, Pavel },
title = {Noether: A PyTorch-based Framework for Engineering AI},
year = {2026},
publisher = {GitHub},
note = {Equal contribution},
url = {https://github.com/Emmi-AI/noether}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for noether
Similar Open Source Tools

noether
Noether is Emmi AI's open software framework for Engineering AI. It is built on transformer building blocks, delivering the full engineering stack for building, training, and operating industrial simulation models across engineering verticals. The framework eliminates the need for component re-engineering or an in-house deep learning team. Noether features a modular transformer architecture optimized for physical systems, hardware agnostic execution across CPU, MPS, and NVIDIA GPUs, industrial-grade design for high-fidelity simulations, and built-in support for Multi-GPU and SLURM cluster environments.
aegis-stack
Aegis Stack is a system for creating and evolving modular Python applications quickly, without the need for extensive testing or clean architecture. It allows users to go from idea to working prototype rapidly, using familiar tools. The stack includes a CLI, a built-in system dashboard called Overseer, and an optional conversational interface named Illiana. Users can start with basic components and add or remove features as needed, without being locked into initial choices. Aegis Stack aims to provide a flexible and efficient development environment for Python applications.

kalavai-client
Kalavai is an open-source platform that transforms everyday devices into an AI supercomputer by aggregating resources from multiple machines. It facilitates matchmaking of resources for large AI projects, making AI hardware accessible and affordable. Users can create local and public pools, connect with the community's resources, and share computing power. The platform aims to be a management layer for research groups and organizations, enabling users to unlock the power of existing hardware without needing a devops team. Kalavai CLI tool helps manage both versions of the platform.
thinc
Thinc is a lightweight deep learning library that offers an elegant, type-checked, functional-programming API for composing models, with support for layers defined in other frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow and MXNet. You can use Thinc as an interface layer, a standalone toolkit or a flexible way to develop new models.
TaskingAI
TaskingAI brings Firebase's simplicity to **AI-native app development**. The platform enables the creation of GPTs-like multi-tenant applications using a wide range of LLMs from various providers. It features distinct, modular functions such as Inference, Retrieval, Assistant, and Tool, seamlessly integrated to enhance the development process. TaskingAI’s cohesive design ensures an efficient, intelligent, and user-friendly experience in AI application development.
DevoxxGenieIDEAPlugin
Devoxx Genie is a Java-based IntelliJ IDEA plugin that integrates with local and cloud-based LLM providers to aid in reviewing, testing, and explaining project code. It supports features like code highlighting, chat conversations, and adding files/code snippets to context. Users can modify REST endpoints and LLM parameters in settings, including support for cloud-based LLMs. The plugin requires IntelliJ version 2023.3.4 and JDK 17. Building and publishing the plugin is done using Gradle tasks. Users can select an LLM provider, choose code, and use commands like review, explain, or generate unit tests for code analysis.

mmore
MMORE is an open-source, end-to-end pipeline for ingesting, processing, indexing, and retrieving knowledge from various file types such as PDFs, Office docs, images, audio, video, and web pages. It standardizes content into a unified multimodal format, supports distributed CPU/GPU processing, and offers hybrid dense+sparse retrieval with an integrated RAG service through CLI and APIs.
gpt4all
GPT4All is an ecosystem to run powerful and customized large language models that work locally on consumer grade CPUs and any GPU. Note that your CPU needs to support AVX or AVX2 instructions. Learn more in the documentation. A GPT4All model is a 3GB - 8GB file that you can download and plug into the GPT4All open-source ecosystem software. Nomic AI supports and maintains this software ecosystem to enforce quality and security alongside spearheading the effort to allow any person or enterprise to easily train and deploy their own on-edge large language models.
plandex
Plandex is an open source, terminal-based AI coding engine designed for complex tasks. It uses long-running agents to break up large tasks into smaller subtasks, helping users work through backlogs, navigate unfamiliar technologies, and save time on repetitive tasks. Plandex supports various AI models, including OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, and more. It allows users to manage context efficiently in the terminal, experiment with different approaches using branches, and review changes before applying them. The tool is platform-independent and runs from a single binary with no dependencies.
anything-llm
AnythingLLM is a full-stack application that enables you to turn any document, resource, or piece of content into context that any LLM can use as references during chatting. This application allows you to pick and choose which LLM or Vector Database you want to use as well as supporting multi-user management and permissions.
Newelle
Newelle is an advanced virtual assistant application that offers a wide range of features, including advanced customization, flexible model support, terminal command execution, voice support, long-term memory, chat with documents, web search, website reading, profile manager, file manager, rich formatting, and chat editing. It also supports extensions to enhance its functionality, such as the Mini Window Mode. Users can install Newelle using various methods like install.sh, GNOME Builder, Nix, or Flathub. However, the Flathub version has restricted permissions to ensure security. Newelle's forks include Newelle Lite for aarch64 and Nyarch Assistant, a Waifu AI Assistant.

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking
lunary
Lunary is an open-source observability and prompt platform for Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a suite of features to help AI developers take their applications into production, including analytics, monitoring, prompt templates, fine-tuning dataset creation, chat and feedback tracking, and evaluations. Lunary is designed to be usable with any model, not just OpenAI, and is easy to integrate and self-host.
langflow
Langflow is an open-source Python-powered visual framework designed for building multi-agent and RAG applications. It is fully customizable, language model agnostic, and vector store agnostic. Users can easily create flows by dragging components onto the canvas, connect them, and export the flow as a JSON file. Langflow also provides a command-line interface (CLI) for easy management and configuration, allowing users to customize the behavior of Langflow for development or specialized deployment scenarios. The tool can be deployed on various platforms such as Google Cloud Platform, Railway, and Render. Contributors are welcome to enhance the project on GitHub by following the contributing guidelines.
AIOS
AIOS, a Large Language Model (LLM) Agent operating system, embeds large language model into Operating Systems (OS) as the brain of the OS, enabling an operating system "with soul" -- an important step towards AGI. AIOS is designed to optimize resource allocation, facilitate context switch across agents, enable concurrent execution of agents, provide tool service for agents, maintain access control for agents, and provide a rich set of toolkits for LLM Agent developers.

lanarky
Lanarky is a Python web framework designed for building microservices using Large Language Models (LLMs). It is LLM-first, fast, modern, supports streaming over HTTP and WebSockets, and is open-source. The framework provides an abstraction layer for developers to easily create LLM microservices. Lanarky guarantees zero vendor lock-in and is free to use. It is built on top of FastAPI and offers features familiar to FastAPI users. The project is now in maintenance mode, with no active development planned, but community contributions are encouraged.
For similar tasks

noether
Noether is Emmi AI's open software framework for Engineering AI. It is built on transformer building blocks, delivering the full engineering stack for building, training, and operating industrial simulation models across engineering verticals. The framework eliminates the need for component re-engineering or an in-house deep learning team. Noether features a modular transformer architecture optimized for physical systems, hardware agnostic execution across CPU, MPS, and NVIDIA GPUs, industrial-grade design for high-fidelity simulations, and built-in support for Multi-GPU and SLURM cluster environments.
AIO
AIO is a comprehensive guide for setting up a home All-in-One server, enabling users to create an enterprise-level virtualized environment at home. It allows running multiple operating systems simultaneously, achieving public network access, optimizing hardware performance, and reducing IT costs. The guide includes detailed documentation for setting up from scratch and requires a computer with virtualization support, VMware ESXi installation media, and basic network configuration knowledge.
batteries-included
Batteries Included is an all-in-one platform for building and running modern applications, simplifying cloud infrastructure complexity. It offers production-ready capabilities through an intuitive interface, focusing on automation, security, and enterprise-grade features. The platform includes databases like PostgreSQL and Redis, AI/ML capabilities with Jupyter notebooks, web services deployment, security features like SSL/TLS management, and monitoring tools like Grafana dashboards. Batteries Included is designed to streamline infrastructure setup and management, allowing users to concentrate on application development without dealing with complex configurations.
For similar jobs
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
dl_model_infer
This project is a c++ version of the AI reasoning library that supports the reasoning of tensorrt models. It provides accelerated deployment cases of deep learning CV popular models and supports dynamic-batch image processing, inference, decode, and NMS. The project has been updated with various models and provides tutorials for model exports. It also includes a producer-consumer inference model for specific tasks. The project directory includes implementations for model inference applications, backend reasoning classes, post-processing, pre-processing, and target detection and tracking. Speed tests have been conducted on various models, and onnx downloads are available for different models.
joliGEN
JoliGEN is an integrated framework for training custom generative AI image-to-image models. It implements GAN, Diffusion, and Consistency models for various image translation tasks, including domain and style adaptation with conservation of semantics. The tool is designed for real-world applications such as Controlled Image Generation, Augmented Reality, Dataset Smart Augmentation, and Synthetic to Real transforms. JoliGEN allows for fast and stable training with a REST API server for simplified deployment. It offers a wide range of options and parameters with detailed documentation available for models, dataset formats, and data augmentation.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
awesome-RK3588
RK3588 is a flagship 8K SoC chip by Rockchip, integrating Cortex-A76 and Cortex-A55 cores with NEON coprocessor for 8K video codec. This repository curates resources for developing with RK3588, including official resources, RKNN models, projects, development boards, documentation, tools, and sample code.

cl-waffe2
cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
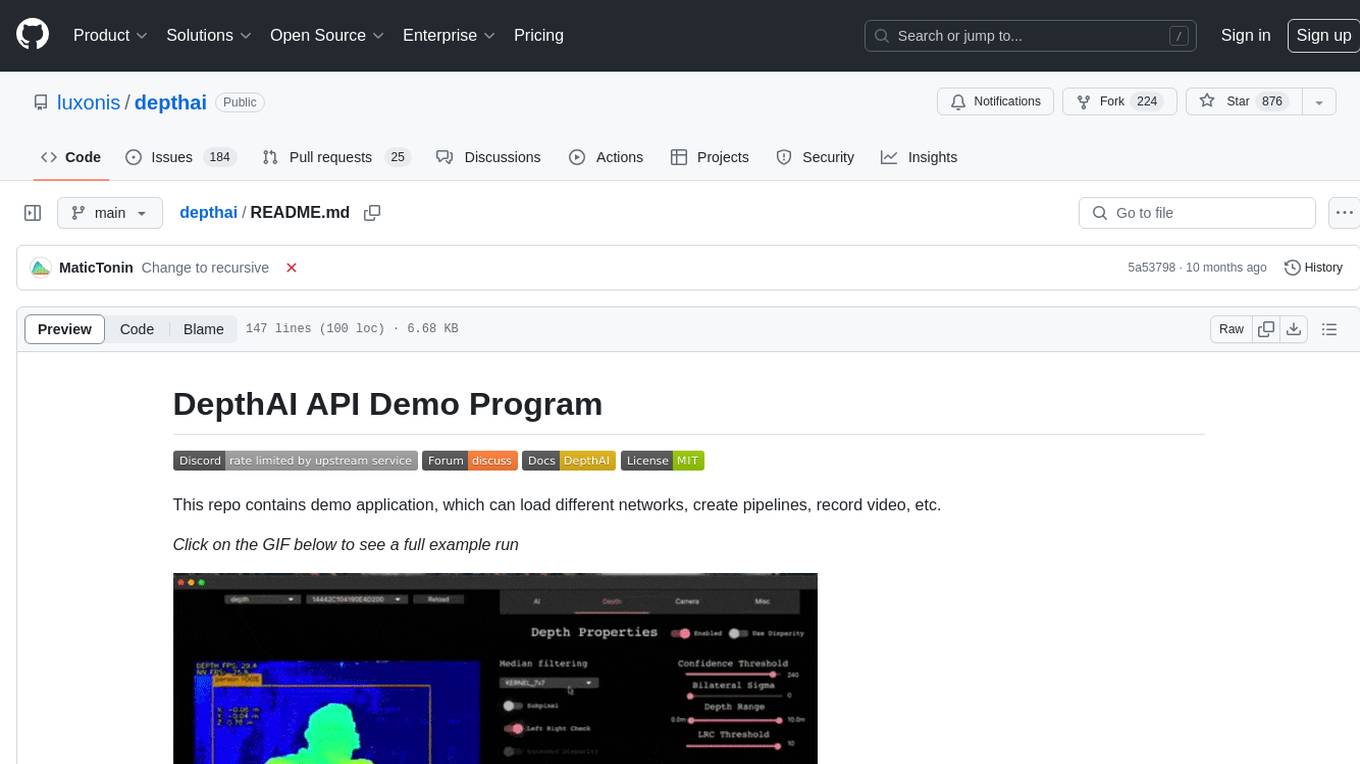
depthai
This repository contains a demo application for DepthAI, a tool that can load different networks, create pipelines, record video, and more. It provides documentation for installation and usage, including running programs through Docker. Users can explore DepthAI features via command line arguments or a clickable QT interface. Supported models include various AI models for tasks like face detection, human pose estimation, and object detection. The tool collects anonymous usage statistics by default, which can be disabled. Users can report issues to the development team for support and troubleshooting.


