
AILZ80ASM
Z80アセンブラ
Stars: 52
AILZ80ASM is a Z80 assembler that runs in a .NET 8 environment written in C#. It can be used to assemble Z80 assembly code and generate output files in various formats. The tool supports various command-line options for customization and provides features like macros, conditional assembly, and error checking. AILZ80ASM offers good performance metrics with fast assembly times and efficient output file sizes. It also includes support for handling different file encodings and provides a range of built-in functions for working with labels, expressions, and data types.
README:
AILZ80ASMは、C#で書かれた.NET 8の環境で動作するZ80アセンブラです。
- 「あいるぜっとはちまるあせむ」
- ご利用は自己責任でお願いします。利用により損害等が発生したとき、作者は責任をおいかねます。
- 本ソースコードを、Visual Studio 2022でビルドする。
- 実行形式をダウンロードして利用する。 ダウンロード
- 実行形式: win-x64版、osx-x64版、linux-x64版
※ 実行形式は、「自己完結型の実行可能ファイル」になっています。.NETの環境を用意する必要はありません。
- アセンブル時間
- 処理時間: 1.608 sec
- 出力結果: 47,735 bytes
- 処理行数: 約20,000行
- ベンチマーク・プロジェクト
AILZ80ASM [<オプション>] <オプション指定文字列:ファイル名等> [ <オプション指定文字列:ファイル名等>]
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80
コンソールアプリですので、コンソールより起動してください。
- UTF-8、SHIFT_JIS
- ファイルの形式は自動的に判断されます。
- 誤認識する場合には、コマンドラインオプション(--input-encode)をお使いください。
| コマンドライン | 説明 |
|---|---|
| -i, --input | アセンブリ対象のファイルをスペース区切りで指定します。 (オプション名の省略が可能) |
| -ie, --input-encode | 入力ファイルのエンコードを選択します。 [auto, utf-8, shift_jis] デフォルト値:auto |
| -o, --output | 出力ファイルを指定します。 |
| -om, --output-mode | 出力ファイルのモードを選択します。 [bin, hex, t88, cmt, sym, equ, lst, err, tag] デフォルト値:bin |
| -oe, --output-encode | 出力ファイルのエンコードを選択します。 [auto, utf-8, shift_jis] デフォルト値:auto |
| -lm, --list-mode | リストの出力形式を選択します。 [simple, middle, full] デフォルト値:full |
| -lob, --list-omit-binary | リストの出力でバイナリーインクルードを省略出力をします。 |
| -ep, --entry-point | エントリーポイントを指定します。 |
| -ts, --tab-size | TABのサイズを指定します。 デフォルト値:4 |
| -dw, --disable-warning | Warning、Informationをオフにするコードをスペース区切りで指定します。 |
| -ul, --unused-label | 未使用ラベルを確認します。 |
| -cd, --change-dir | アセンブル実行時のカレントディレクトリを変更します。終了時に元に戻ります。 |
| -gap, --gap-default | アセンブラのギャップのデフォルト値を指定します。 デフォルト値:$FF |
| -df, --diff-file | アセンブル出力結果のDIFFを取ります。アセンブル結果は出力されません。 |
| -dl, --define-label | ラベルをスペース区切りで指定します。値を設定するときは=で代入します。 |
| -nsa, --no-super-asm | スーパーアセンブルモードを無効にします。 |
| -sa, --start-address | スタートアドレス(出力)を指定します。ORGで指定したアドレスまで -gap で埋めます |
| -ips, --include-paths | インクルードするファイルの検索パスを指定します。 |
| -f, --force | 出力ファイルを上書きします。 |
| -v, --version | バージョンを表示します。 |
| -?, -h, --help | ヘルプを表示します。各オプションの詳細ヘルプを表示します。例: -h --input-mode |
| -??, --readme | Readme.mdを表示します。 |
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、出力はBIN形式
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、出力はBIN形式、上書き確認プロンプトを表示しないで上書きをする
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -f
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、出力はBIN形式、ログファイルを出力
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -bin -err
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、出力はBIN形式、LST形式、SYM形式、ログファイルを出力
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -bin -lst -sym -err
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、出力はCMT形式
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -cmt
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -om cmt
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、出力はBIN形式、CMT形式、リストの出力(形式:シンプル、タブサイズ8)
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -bin -cmt -lst -lm simple -ts 8
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、出力はBIN形式、ファイル名は、output.bin
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -bin output.bin
> AILZ80ASM -i sample.z80 -o output.bin -om bin
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、出力はBIN形式、指定(W0001,W9001,W9002)のワーニング表示をOFFにする
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -bin output.bin -dw W0001 W9001 W9002
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、ラベルを指定する
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -bin -dl TEST1=10 TEST2=20 TEST3
■ sample.z80をアセンブル、ラベルを指定する
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -bin -ips .\lib1
■ -omオプションのヘルプを表示
> AILZ80ASM -h -om
コマンドラインからラベルを指定することができます。代入式で指定すると値を設定できます。ラベル単体で記述した場合は#TRUEが設定されます。ネームスペースを指定して出力するには「.」で区切って指定します。
> AILZ80ASM sample.z80 -bin -equ -dl TEST1=10 TEST2=20 TEST3 NSTEST.TEST4=40
file: sample.equ
[NAME_SPACE_DEFAULT]
TEST1 equ 10
TEST2 equ 20
TEST3 equ #TRUE
[NSTEST]
TEST4 equ 40
- 0: アセンブルが正常に終了
- 1: アセンブルにエラーがあり、処理途中で終了、--diff-file オプションで出力ファイルの不一致あり
- 2: コマンドライン引数に間違いがあり、終了
- 3: 内部エラーが発生、アセンブルの強制終了
EXEと同じフォルダに以下の形式で「AILZ80ASM.json」を保存
{
"default-options": [
"-err"
],
"disable-warnings": [
"W0001",
"W9001",
"W9002"
]
}
特定のエラーがアセンブル時に発生した場合、再アセンブルを行ってエラーを解決するためのモードです。このモードを適用する前に、アセンブル解析の結果を確認し、再アセンブルによってエラーが解決できる可能性がある場合に限り、このモードが実行されます。このモードは、以下のエラーに対して有効です。
- E0010: 出力アドレスに影響する場所では$$は使えません。
- E0010: 参照したラベルのプログラムアドレスが確定できませんでした。
※ スーパーアセンブルモードを無効にする場合には、コマンドラインオプションに '-nsa' を付けてください
CMT形式の読み込みアドレスに利用されるエントリーポイントは、以下の優先順位で利用されます。
- コマンドラインオプション (-ep) で指定した値
- END で指定した値
- アセンブル結果が出力される最初のプログラムアドレス
- 新バージョンを入手
- インストール済みのAILZ80ASMでアセンブルを行う
- インストール済みのAILZ80ASMを退避
- 新バージョンでAILZ80ASMを置き換える
- 新バージョンでコマンドラインオプションに「-df」を付け、差分確認アセンブルを行う
- アセンブル結果が一致しているかが表示される
- アセンブル結果が一致していたら置き換え可能、一致していなければ置き換え不可なので退避したプログラムを元に戻す
- ザイログ・ニーモニックの表記
- 大文字、小文字の区別はしない
- 本アセンブラで利用できるニーモニック一覧
ラベルは、ネームスペース、標準ラベル、ローカルラベルで指定します。ネームスペースを指定しない場合には、 'NAME_SPACE_DEFAULT' が割り当てられています。必要に応じて変更をしてください。ラベルは指定した行以降は、下位のラベルを利用するときには上位のラベル名を省略することが出来ます。テンポラリーラベルは、.@に数字で宣言します。匿名ラベルは、.@@で宣言します。
- ラベルに使用できる文字
- 英文字: a-zA-Z
- 数字: 0-9
- 記号: _
- ラベルに使用できない文字列
- 先頭が数字の文字列
- 数値に変換できる文字列
- 予約文字列(命令名、レジスタ名、フラグ名)
- テンポラリーラベルに使用できる文字
- 数字: 0-9
- 大文字と小文字は区別しません
テンポラリーラベルは、.@に数字をつけて宣言します。テンポラリーラベルの制約として、ラベル名が一意である必要があります。例えば、ローカルラベル内では.@1 を一度しか宣言できません。匿名ラベルの場合は、ローカルラベル内に、.@@を複数記述することが出来ます。
- 匿名ラベルの制約
- ネームスペースを跨いで参照することは出来ません
- ORGを跨いで参照することは出来ません
- [<ネームスペース名>]
- デフォルト:
NAME_SPACE_DEFAULT
- デフォルト:
[NAME_SPACE_DEFAULT] ; ネームスペース指定
- <ラベル名[:]>
- 標準ラベル
LABLE: ; ラベル指定
- <[.]ローカルラベル名>
- ローカルラベル
LABLE: ; ラベル指定
.A ; ローカルラベル
.B ; ローカルラベル
- <[.]@テンポラリラベル番号>
- テンポラリー
LABLE: ; ラベル指定
.A ; ローカルラベル
.@1 ; テンポラリーラベル
.B ; ローカルラベル
.@1 ; テンポラリーラベル
- <[.]@@>
- 匿名ラベル
LABLE: ; ラベル指定
.A ; ローカルラベル
.@@ ; 匿名ラベル
.@@ ; 匿名ラベル
.B ; ローカルラベル
.@@ ; 匿名ラベル
.@@ ; 匿名ラベル
- <ネームスペース>.<ラベル名>.<ローカルラベル名>
- <ラベル名>.<ローカルラベル名>
- <ローカルラベル名>
ローカルラベルが存在する場合
- <ネームスペース>.<ラベル名>.<ローカルラベル名>.<テンポラリーラベル名>
- <ラベル名>.<ローカルラベル名>.<テンポラリーラベル名>
- <ローカルラベル名>.<テンポラリーラベル名>
- <テンポラリーラベル名> ローカルラベルが存在しない場合
- <ネームスペース>.<ラベル名>..<テンポラリーラベル名>
- <ラベル名>..<テンポラリーラベル名>
- <テンポラリーラベル名>
- .@H をラベルに追加すると、上位1バイトを取得 (.@HIGH でも可能)
- .@L をラベルに追加すると、下位1バイトを取得 (.@LOW でも可能)
- .@T をラベルに追加すると、ラベルに指定した名前を文字列として取得 (.@TEXT でも可能)
- .@E をラベルに追加すると、ラベルが存在すると#TRUE、存在しないと#FALSE (.@EXISTS でも可能)
- .@B をラベルに追加すると、後方(アドレスが小さい方)のラベルを選択できます (.@BACKWARD でも可能)
- .@F をラベルに追加すると、前方(アドレスが大きい方)のラベルを選択できます (.@FORWARD でも可能)
- .@NEAR をラベルに追加すると、アドレスが近いラベルを選択できます
- .@FAR をラベルに追加すると、アドレスが遠いラベルを選択できます
- @H@Lサンプル
- @Tサンプル
- @Eサンプル
- .@@B は、.@@.@Bの代わりに使うことが出来ます
- .@@F は、.@@.@Fの代わりに使うことができます
org $8000
ld a, 0
addr:
ld a, (addr)
ld hl, addr
.test
ld a, (addr.test)
ld hl, addr.test
ld hl, (addr.test)
org $8000
ld a, 0
addr:
ld a, (addr)
.@1 ; (1) addr..@1
ld hl, addr
.test
ld a,(.@1) ; 参照先 (2) 【注意:(1)は参照されない】
.@1 ; (2) addr.text.@1
ld hl, addr.test
.@2 ; (3) addr.text.@2
ld hl, (addr.test)
; 参照
ld hl, (addr..@1) ; 参照先 (1)
ld hl, (.text.@1) ; 参照先 (2)
ld hl, (.@1) ; 参照先 (2)
ld hl, (.@2) ; 参照先 (3)
; 特殊アクセス
EQT:
.@1 equ %00001100 ; (4) EQT..@1
.@2 equ %00001101 ; (5) EQT..@2
.@3 equ %00001110 ; (6) EQT..@3
;【マジック実装】本来ならEQT.AL.@1 を参照するが、存在しないとき EQT..@1を参照する
.AL equ (.@1 | .@2 | .@3) ; 参照先 (4) | (5) | (6)
- 2進数:先頭に0b or %、もしくは末尾にbを付けます。また _ を含める事が出来ます。
- 8進数:先頭に0o、もしくは末尾にoを付けます。
- 10進数:数値だけ、もしくは末尾にdを付けます。
- 16進数:先頭に0x or $、もしくは末尾にHを付けます。
- 文字列:先頭と末尾に ' を付けます。値が要求される場所では、最大2バイトの数値として扱えます。
- 文字列:先頭と末尾に " を付けます。値が要求される場所では、最大2バイトの数値として扱えます。
- BOOL型:真:#TRUE、偽:#FALSE
- 文字列を扱うときには、 ' で囲んでください。
- 文字列を扱うときには、 " で囲んでください。
- 文字列は、SJISとして扱います。
- SJIS以外を扱うには
- 文字列に@<CHARMAP名>:"あいうえお" と記述するとCHARMAPの情報で変換を行います。
- アセンブラに内蔵されているCHARMAPは、シフトJIS、JIS第1水準、JIS第1水準・第2水準です。
- CHARMAPを使うと、独自の変換テーブルを使う事が可能です。
DB "テスト" ; SJISで変換、アセンブラのデフォルト値
DB @JIS12:"テスト" ; JIS第一・二水準で変換
DB @SJIS:"テスト" ; SJISで変換
| エスケープ シーケンス | 表現 | Unicode エンコーディング |
|---|---|---|
| \' | 単一引用符「'」 | 0x0027 |
| \" | 単一引用符「"」 | 0x0022 |
| \\ | 円記号「\」 | 0x005C |
| \0 | Null | 0x0000 |
| \a | ベル (警告) | 0x0007 |
| \b | バックスペース | 0x0008 |
| \f | フォーム フィード | 0x000C |
| \n | 改行 | 0x000A |
| \r | キャリッジ リターン | 0x000D |
| \t | 水平タブ | 0x0009 |
| \v | 垂直タブ | 0x000B |
| 名前 | デフォルト | 詳細 |
|---|---|---|
| @SJIS | * | シフトJIS |
| @JIS1 | JIS第1水準 | |
| @JIS12 | JIS第1水準・第2水準 |
- $ は、現在のプログラム・ロケーションカウンタを参照することができます
- $$ は、現在のアウトプット・ロケーションカウンタを参照することができます
詳細は、ORG命令の章をご覧ください
値を指定するところに、式を使用することができます。使用できる演算子と優先順位は、下の表のとおりです。
| 優先順位 | 演算子 | コメント |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ( ) | 括弧 |
| 2 | low high exists text backward forward near far | 下位8ビット 上位8ビット ラベル存在 ラベル値文字列 後方ラベル 前方ラベル 近いラベル 遠いラベル |
| 3 | + - ! ~ | 正記号 負記号 論理NOT ビット反転 |
| 4 | * / % | 乗算 除算 剰余 |
| 5 | + - | 加算 減算 |
| 6 | << >> | 左シフト 右シフト |
| 7 | < > <= >= | 算術比較 |
| 8 | == != | 算術比較 |
| 9 | & | ビットAND |
| 10 | ^ | ビットXOR |
| 11 | | | ビットOR |
| 12 | && | 論理AND |
| 13 | || | 論理OR |
| 14 | : | 三項演算子 |
| 15 | ? | 三項演算子 |
| ※大文字と小文字は区別しません |
下位8ビットを取得します
ld a, low $1234 ; a = $34
上位8ビットを取得します
ld a, high $1234 ; a = $12
ラベルが存在する時には、 #TRUEを返します。ラベルが存在しない時には、#FALSE を返します。
LB1 equ $10
#IF exists LB1
;展開されます
#ENDIF
#IF exists LB2
;展開されません
#ENDIF
ラベルに設定された文字列を取得します。
LDEX a, 1
LDEX b, 1
LDEX MACRO arg1, arg2
#IF text arg1 == "a"
ld a, arg2
#ELSE
ld b, arg2
#ENDIF
ENDM
後方(アドレスが小さい方)のラベルを指定します。
LB:
.Sub1
.@1 ; ここが参照されています
.Sub2
JP backward .@1
.Sub3
.@1
前方(アドレスが大きい方)のラベルを指定します。
LB:
.Sub1
.@1
.Sub2
JP forward .@1
.Sub3
.@1 ; ここが参照されています
プログラムアドレスが近いラベルを参照します。距離が同じ場合には後方(アドレスが小さい方)のラベルが優先されます。
LB:
.Sub1
.@1 ; ここが参照されています
.Sub2
JP near .@1
.Sub3
LD HL, 0
LD DE, HL
.@1
プログラムアドレスが遠いラベルを参照します。距離が同じ場合には後方(アドレスが小さい方)のラベルが優先されます。
LB:
.Sub1
.@1
.Sub2
JP far .@1
.Sub3
LD HL, 0
LD DE, HL
.@1 ; ここが参照されています
式に()を利用することが出来ますが、命令には()が含まれるものがあります。式の全体を()で囲むとアドレス指定になります。
ld a,($1234 + 5) ;アドレス指定
ld a,($1234) + 5 ;値として指定されます。16bit値が指定されているので、ワーニングが表示されます。
- ; 以降はコメントとして処理されます
本アセンブラの特徴として、アセンブル時のアドレスとアウトプット時のアドレスを別で管理しています。通常モードで利用する場合には、第一引数だけで利用してください。アウトプットアドレスは自動的に制御されます。第二引数を利用した時には、アウトプットアドレスを制御できます。その時にはROM出力モードになり、ラベルに使われるアドレスと出力のアドレスを別々に制御することが出来ます。プログラム・ロケーションカウンターは、アセンブル内で重複可能になります。アウトプット時のアドレスは、アウトプット・ロケーションカウンターと呼び、バイナリデータの出力位置を指定します。出力用のアドレスになりますので、重複することは出来ません。
- <式>
- プログラム・ロケーションカウンターの値を変更します。
- 出力されるラベルの計算に影響を与えます。プログラム中で何度でも変更可能です。ROM出力モードでは、アドレスの重複も可能です。
- <式2>
- アウトプット・ロケーションカウンターの値を変更します。こちらを指定するとROM出力モードになります。
- 出力されるバイナリーに影響を与えます。プログラム中で何度でも変更可能です。アドレスの重複は不可能です。
- バイナリーの出力を制御したいときに使用します
- <式3>
- 先アドレスを指定した場合には、<ギャップ値>で埋めます。<式3>を設定するとその値で埋めます。
- メモリのアライメントを合わせるには、ALIGNをお勧めします。
- サンプル
ORG $1000
LB1000:
LD A, (LB1000)
ORG $1010
LB1010:
LD A, (LB1010)
ORG $2000, $0020
LB2000:
LD A, (LB2000)
出力結果
0000 3A 00 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
0010 3A 10 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
0020 3A 00 20 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
- ロケーションカウンタの値を、<式>で設定したアライメント境界まで移動します。
- <式>に設定できる値は、2のべき乗である必要があります。
- 移動により空いた領域には、<ギャップ値> または <式2> の値で埋められます。
- ALIGN以降のプログラム等の出力情報が無い場合には、出力結果は切り詰められます。
- サンプル
- ロケーションカウンタの値を、<式>で設定した値を加算した場所に移動します。
- <式>のバイト数、<ギャップ値>で埋めます。<式2>を設定するとその値で埋めます
- DS以降のプログラム等の出力情報が無い場合には、出力結果は切り詰められます。
- サンプル
- 指定したラベルに、<式> の値を持たせます。
- 即値、式、$、$$、(文字、文字列、#TRUE or #FALSE version:1.0.0以降)
- ローカルラベルで利用することも可能です。
- サンプル
PORT_A equ $CC
.WRITE equ $01
.READ equ $02
LD A, PORT_A.WRITE
OUT (PORT_A), A
LD A, PORT_A.READ
OUT (PORT_A), A
アセンブラ内で利用する、文字列の変換テーブルをロードします。
- <CHARMAP名>は、先頭に@を付ける形で命名します。例:@SJIS
- <ファイル名>は、変換テーブルをロードします。
- ファイル形式
- Json形式(UTF-8 with BOM)
- ファイル形式のサンプル
- ファイル形式のサンプル (文字列指定)
- 使い方のサンプル
ファイル名の内容を読み取り、その場所に展開します
- <ファイル名>は、ロードしたいファイル名を指定します。
- <ファイルタイプ>は、TEXT と BINARY が選択できます。省略するとTEXTになります。また短縮形 T, B が使えます。
- <開始位置>は、ファイルの読み出し開始位置が指定できます。(ファイルタイプがBINARYの時に有効)
- <長さ>は、ファイルの読み込み長さが指定できます。(ファイルタイプがBINARYの時に有効)
- サンプル
include "Test.inc" ; テキストファイルとして展開されます
include "Test.inc", B ; バイナリーファイルとして展開されます
include "Test.inc", B, $1000 ; バイナリーファイルとして展開されます。読み込み位置は、$1000からになります。
include "Test.inc", B, $1000, 200 ; バイナリーファイルとして展開されます。読み込み位置は、$1000からになります。読み込み長さは200バイトです。
include "Test.inc", B, , 200 ; バイナリーファイルとして展開されます。読み込み位置は、$0000からになります。読み込み長さは200バイトです。
- <式>の1バイト値を設定します
- サンプル
- ループの条件で、式の内容を展開します
- ネストも可能
- 例:DB [Y=0..2:[X=0..4:Y*8+X]]
- サンプル
- <式>の2バイト値を設定します
- サンプル
- ループの条件で、式の内容を展開します
- ネストも可能
- 例:DW [Y=24..0:$8000 + Y * $140]
- サンプル
- <式>のバイト数、0で埋めます。<式2>を設定するとその値で埋めます
- サンプル
- <式>の2バイト数、0で埋めます。<式2>を設定するとその値で埋めます
- サンプル
- MACROからENDMまでがマクロとして定義されます
- 引数に付けた名前がマクロ内で利用できます
- マクロ名に()を含める事が出来ます。ただし先頭に付ける事は出来ません
- サンプル1
- サンプル2
- サンプル3
ARG1 equ 2
.Three equ 3
ALLLD
TestArg ARG1, ARG1.Three
INITLD B ; レジスター名を指定
ALLLD MACRO
ld a,1
ld b,2
ld c,3
ld d,4
ld e,5
ld h,6
ld l,7
ENDM
TestArg MACRO a1, a2
ld a, a1
ld b, a2
ENDM
INITLD MACRO REG
LD A, REG
LD REG, 0
ENDM
- 式1に設定した値の回数分をREPTの中に記述してある命令を展開します。
- 式2には、最終の展開時に削除したい命令数を負の値で設定します。ラベルだけの行や空行は削除対象外です。
- ネストに対応しています
- サンプル
REPT 3
xor a
ENDM
REPT 8 LAST -1
ld (hl), a
set 5, h
ld (hl), a
add hl, de
ENDM
※ LAST -1で消える行にラベルが設定されている場合にはエラーになります。2行に分ける等の工夫をしてください。
REPT 8 LAST -1
ld (hl), a
set 5, h
or a
jr z, .@1
add hl, de
.@1 add hl, de
ENDM
- ENUMは、名前とラベル名で組み合わされたEQUが定義されます。
- <ラベル名>は、<名前>.<ラベル名> 形式でアクセスが可能です。
- <長さ>は、次の要素の値を決める時の加算値になります。(デフォルトは1)
- <値>は、はその要素に設定される値を表します。(デフォルトは、前の要素の<値>+<長さ>)
Color ENUM
RED = 5 ; 5
GREEN ; 6
BLUE :2 ; 7, サイズ2バイト
YELLOW ; 9
ORANGE :2 = 12 ; 12, サイズ2バイト
CYAN ; 14
PURPLE = RED-1 ; 4
ENDM
INIT:
LD A, Color.RED ; 5
LD B, Color.GREEN ; 6
LD C, Color.BLUE ; 7
LD D, Color.YELLOW ; 9
LD E, Color.ORANGE ; 12
LD H, Color.CYAN ; 14
LD L, Color.PURPLE ; 4
式をまとめる事が出来ます
- 複数行にまたがる事は出来ません。
- サンプル
LD A, ABS(-1) ; LD A, 1
LD B, ABS(1) ; LD B, 1
Function ABS(value) => value < 0 ? value * -1 : value
アセンブルの実行を中断します。これ以降のソースコードはアセンブルされません。アセンブル結果は出力されます。
- 式1に設定した値は、エントリーポイントに使われます。利用個所: CMT出力
CHECKからENDCで囲まれた範囲のアセンブル結果がアライメント境界を超えるとアセンブルエラー(E6002)になります。
- 式2に設定した値は、アライメント境界のオフセット値になります。2バイトデータの先頭だけアライメント境界内に入っている事を保証したいときに、2と設定します。
org 0x100
CHECK ALIGN 256
DB 0, 1, 2, 3 ,4
ENDC
org 0x1FF
CHECK ALIGN 256 ; **** E6002 ****
DB 0, 1, 2, 3 ,4
ENDC
条件付きアセンブルを制御します
- #IF: 条件付きアセンブルを開始します。コードは、指定された条件がTRUEの時にアセンブル対象になります。
- #ELIF: 前の条件付きアセンブルを終了して、指定された条件がTRUEの時にアセンブル対象になります。
- #ELSE: 前の条件付きアセンブルを終了して、前条件がFALSEの時にアセンブル対象になります。
- #ENDIF: 条件付きアセンブルを終了します。
- #ERROR: 無条件にエラーを発生させます。
- #TRUE: 真(bool型)
- #FALSE: 偽(bool型)
- サンプル
#if mode == 1
ld a,1
#print "mode == 1の処理がされました"
#elif mode == 2
ld d,4
#else
#error "modeの値が範囲外です。"
#endif
アセンブルの情報をインフォメーション[I0001]として表示します。
- 引数1: 出力の文字列を設定します。{#}を指定すると、引数2以降の値を含めて出力出来ます。
- 引数2: 引数1で指定したフォーマットに表示する値を設定します。
TEST1 EQU 1
TEST2 EQU 2
#PRINT "TEST1:{0}, TEST2:{1}", TEST1, TEST2
ソースコードをアセンブルするときに、記述があるファイルを1回だけアセンブルすることを指定します
#pragma once
LABEL equ 00FFH
ラベルの再定義エラーを回避する方法 (#pragma onceの利用を推奨)
#if LABEL.@EXISTS
LABEL equ 00FFH
#endif
#if exists LABEL
LABEL equ 00FFH
#endif
LST形式のファイルの出力を停止します。
- 引数1: bool型をしています。TRUE: 出力あり, FALSE: 出力なし
on equ #TRUE
off equ #FALSE
ld a, 0
#LIST off
ld b, 1
#LIST on
ld c, 2
ret
- (IX) → (IX+0)
- (IY) → (IY+0)
- SUB A, → SUB
- EX HL,DE → EX DE,HL
- .local: → .local
- レベル分けされており、E:Error,W:Warning,I:Information があります。
- Errorに該当する行がある場合には、ソースコードは最後まで評価されますが、アセンブル結果は出力されません。
- エラーコード一覧
- AILZ80ASMでのENDMは、「END Macro」ではなく「End of Multi-Purpose Block」と言い張っていますので、色々な命令で使われています。
- 内藤時浩様(サンプルコード)プログラミング指南 - Code Knowledge
- 山本昌志様(Z80命令セット)Yamamoto's Laboratory
- 神楽坂朋様(Z80命令表)神楽坂製作所
- Thomas Scherrer様(Z80 Undocumented Instructions) Thomas Scherrer Z80-Family HomePage
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AILZ80ASM
Similar Open Source Tools

AILZ80ASM
AILZ80ASM is a Z80 assembler that runs in a .NET 8 environment written in C#. It can be used to assemble Z80 assembly code and generate output files in various formats. The tool supports various command-line options for customization and provides features like macros, conditional assembly, and error checking. AILZ80ASM offers good performance metrics with fast assembly times and efficient output file sizes. It also includes support for handling different file encodings and provides a range of built-in functions for working with labels, expressions, and data types.
TelegramForwarder
Telegram Forwarder is a message forwarding tool that allows you to forward messages from specified chats to other chats without the need for a bot to enter the corresponding channels/groups to listen. It can be used for information stream integration filtering, message reminders, content archiving, and more. The tool supports multiple sources forwarding, keyword filtering in whitelist and blacklist modes, regular expression matching, message content modification, AI processing using major vendors' AI interfaces, media file filtering, and synchronization with a universal forum blocking plugin to achieve three-end blocking.
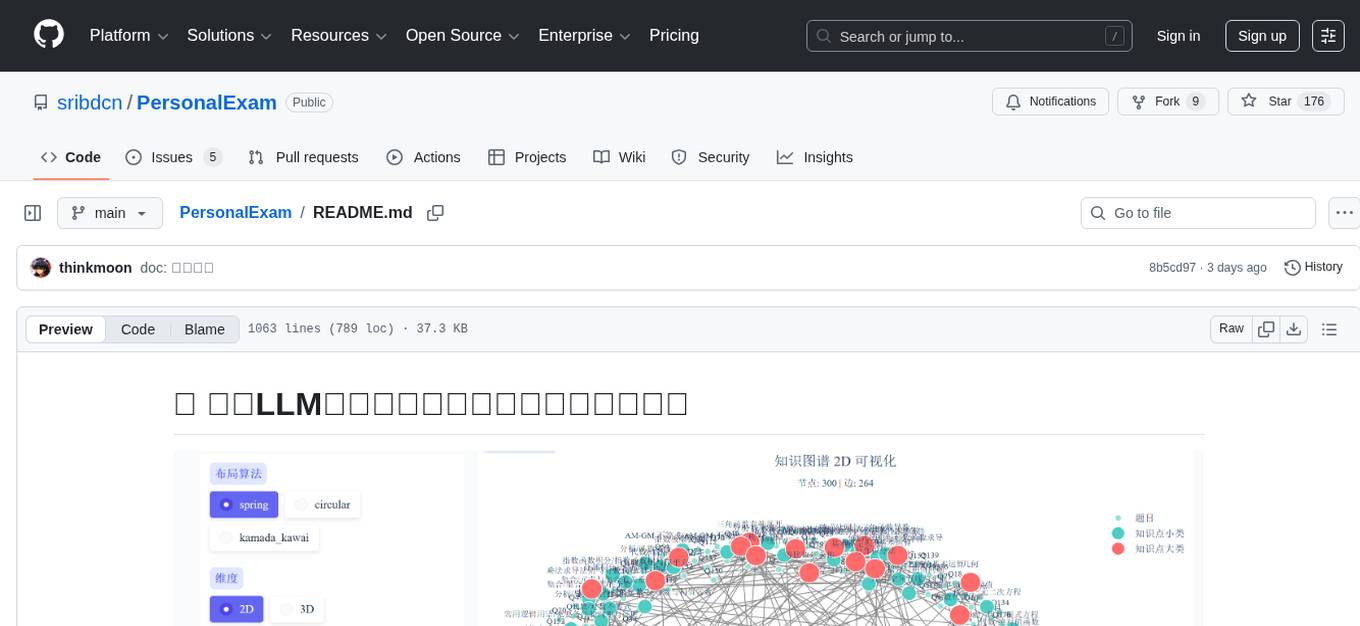
PersonalExam
PersonalExam is a personalized question generation system based on LLM and knowledge graph collaboration. It utilizes the BKT algorithm, RAG engine, and OpenPangu model to achieve personalized intelligent question generation and recommendation. The system features adaptive question recommendation, fine-grained knowledge tracking, AI answer evaluation, student profiling, visual reports, interactive knowledge graph, user management, and system monitoring.
LangChain-SearXNG
LangChain-SearXNG is an open-source AI search engine built on LangChain and SearXNG. It supports faster and more accurate search and question-answering functionalities. Users can deploy SearXNG and set up Python environment to run LangChain-SearXNG. The tool integrates AI models like OpenAI and ZhipuAI for search queries. It offers two search modes: Searxng and ZhipuWebSearch, allowing users to control the search workflow based on input parameters. LangChain-SearXNG v2 version enhances response speed and content quality compared to the previous version, providing a detailed configuration guide and showcasing the effectiveness of different search modes through comparisons.
astrbot_plugin_qq_group_daily_analysis
AstrBot Plugin QQ Group Daily Analysis is an intelligent chat analysis plugin based on AstrBot. It provides comprehensive statistics on group chat activity and participation, extracts hot topics and discussion points, analyzes user behavior to assign personalized titles, and identifies notable messages in the chat. The plugin generates visually appealing daily chat analysis reports in various formats including images and PDFs. Users can customize analysis parameters, manage specific groups, and schedule automatic daily analysis. The plugin requires configuration of an LLM provider for intelligent analysis and adaptation to the QQ platform adapter.
VideoCaptioner
VideoCaptioner is a video subtitle processing assistant based on a large language model (LLM), supporting speech recognition, subtitle segmentation, optimization, translation, and full-process handling. It is user-friendly and does not require high configuration, supporting both network calls and local offline (GPU-enabled) speech recognition. It utilizes a large language model for intelligent subtitle segmentation, correction, and translation, providing stunning subtitles for videos. The tool offers features such as accurate subtitle generation without GPU, intelligent segmentation and sentence splitting based on LLM, AI subtitle optimization and translation, batch video subtitle synthesis, intuitive subtitle editing interface with real-time preview and quick editing, and low model token consumption with built-in basic LLM model for easy use.
torch-rechub
Torch-RecHub is a lightweight, efficient, and user-friendly PyTorch recommendation system framework. It provides easy-to-use solutions for industrial-level recommendation systems, with features such as generative recommendation models, modular design for adding new models and datasets, PyTorch-based implementation for GPU acceleration, a rich library of 30+ classic and cutting-edge recommendation algorithms, standardized data loading, training, and evaluation processes, easy configuration through files or command-line parameters, reproducibility of experimental results, ONNX model export for production deployment, cross-engine data processing with PySpark support, and experiment visualization and tracking with integrated tools like WandB, SwanLab, and TensorBoardX.
OpenClawChineseTranslation
OpenClaw Chinese Translation is a localization project that provides a fully Chinese interface for the OpenClaw open-source personal AI assistant platform. It allows users to interact with their AI assistant through chat applications like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Discord to manage daily tasks such as emails, calendars, and files. The project includes both CLI command-line and dashboard web interface fully translated into Chinese.
Con-Nav-Item
Con-Nav-Item is a modern personal navigation system designed for digital workers. It is not just a link bookmark but also an all-in-one workspace integrated with AI smart generation, multi-device synchronization, card-based management, and deep browser integration.
HuaTuoAI
HuaTuoAI is an artificial intelligence image classification system specifically designed for traditional Chinese medicine. It utilizes deep learning techniques, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), to accurately classify Chinese herbs and ingredients based on input images. The project aims to unlock the secrets of plants, depict the unknown realm of Chinese medicine using technology and intelligence, and perpetuate ancient cultural heritage.
ZcChat
ZcChat is an AI desktop pet suitable for Galgame characters, featuring long-term memory, expressive actions, control over the computer, and voice functions. It utilizes Letta for AI long-term memory, Galgame-style character illustrations for more actions and expressions, and voice interaction with support for various voice synthesis tools like Vits. Users can configure characters, install Letta, set up voice synthesis and input, and control the pet to interact with the computer. The tool enhances visual and auditory experiences for users interested in AI desktop pets.
rime_wanxiang_pro
Rime Wanxiang Pro is an enhanced version of Wanxiang, supporting the 9, 14, and 18-key layouts. It features a pinyin library with optimized word and language models, supporting accurate sentence output with tones. The tool also allows for mixed Chinese and English input, offering various usage scenarios. Users can customize their input method by selecting different decoding and auxiliary code rules, enabling flexible combinations of pinyin and auxiliary codes. The tool simplifies the complex configuration of Rime and provides a unified word library for multiple input methods, enhancing input efficiency and user experience.
prompt-optimizer
Prompt Optimizer is a powerful AI prompt optimization tool that helps you write better AI prompts, improving AI output quality. It supports both web application and Chrome extension usage. The tool features intelligent optimization for prompt words, real-time testing to compare before and after optimization, integration with multiple mainstream AI models, client-side processing for security, encrypted local storage for data privacy, responsive design for user experience, and more.
ai-trend-publish
AI TrendPublish is an AI-based trend discovery and content publishing system that supports multi-source data collection, intelligent summarization, and automatic publishing to WeChat official accounts. It features data collection from various sources, AI-powered content processing using DeepseekAI Together, key information extraction, intelligent title generation, automatic article publishing to WeChat official accounts with custom templates and scheduled tasks, notification system integration with Bark for task status updates and error alerts. The tool offers multiple templates for content customization and is built using Node.js + TypeScript with AI services from DeepseekAI Together, data sources including Twitter/X API and FireCrawl, and uses node-cron for scheduling tasks and EJS as the template engine.
tradecat
TradeCat is a comprehensive data analysis and trading platform designed for cryptocurrency, stock, and macroeconomic data. It offers a wide range of features including multi-market data collection, technical indicator modules, AI analysis, signal detection engine, Telegram bot integration, and more. The platform utilizes technologies like Python, TimescaleDB, TA-Lib, Pandas, NumPy, and various APIs to provide users with valuable insights and tools for trading decisions. With a modular architecture and detailed documentation, TradeCat aims to empower users in making informed trading decisions across different markets.
For similar tasks

AILZ80ASM
AILZ80ASM is a Z80 assembler that runs in a .NET 8 environment written in C#. It can be used to assemble Z80 assembly code and generate output files in various formats. The tool supports various command-line options for customization and provides features like macros, conditional assembly, and error checking. AILZ80ASM offers good performance metrics with fast assembly times and efficient output file sizes. It also includes support for handling different file encodings and provides a range of built-in functions for working with labels, expressions, and data types.
tt-metal
TT-NN is a python & C++ Neural Network OP library. It provides a low-level programming model, TT-Metalium, enabling kernel development for Tenstorrent hardware.
mscclpp
MSCCL++ is a GPU-driven communication stack for scalable AI applications. It provides a highly efficient and customizable communication stack for distributed GPU applications. MSCCL++ redefines inter-GPU communication interfaces, delivering a highly efficient and customizable communication stack for distributed GPU applications. Its design is specifically tailored to accommodate diverse performance optimization scenarios often encountered in state-of-the-art AI applications. MSCCL++ provides communication abstractions at the lowest level close to hardware and at the highest level close to application API. The lowest level of abstraction is ultra light weight which enables a user to implement logics of data movement for a collective operation such as AllReduce inside a GPU kernel extremely efficiently without worrying about memory ordering of different ops. The modularity of MSCCL++ enables a user to construct the building blocks of MSCCL++ in a high level abstraction in Python and feed them to a CUDA kernel in order to facilitate the user's productivity. MSCCL++ provides fine-grained synchronous and asynchronous 0-copy 1-sided abstracts for communication primitives such as `put()`, `get()`, `signal()`, `flush()`, and `wait()`. The 1-sided abstractions allows a user to asynchronously `put()` their data on the remote GPU as soon as it is ready without requiring the remote side to issue any receive instruction. This enables users to easily implement flexible communication logics, such as overlapping communication with computation, or implementing customized collective communication algorithms without worrying about potential deadlocks. Additionally, the 0-copy capability enables MSCCL++ to directly transfer data between user's buffers without using intermediate internal buffers which saves GPU bandwidth and memory capacity. MSCCL++ provides consistent abstractions regardless of the location of the remote GPU (either on the local node or on a remote node) or the underlying link (either NVLink/xGMI or InfiniBand). This simplifies the code for inter-GPU communication, which is often complex due to memory ordering of GPU/CPU read/writes and therefore, is error-prone.
mlir-air
This repository contains tools and libraries for building AIR platforms, runtimes and compilers.

free-for-life
A massive list including a huge amount of products and services that are completely free! ⭐ Star on GitHub • 🤝 Contribute # Table of Contents * APIs, Data & ML * Artificial Intelligence * BaaS * Code Editors * Code Generation * DNS * Databases * Design & UI * Domains * Email * Font * For Students * Forms * Linux Distributions * Messaging & Streaming * PaaS * Payments & Billing * SSL
AIMr
AIMr is an AI aimbot tool written in Python that leverages modern technologies to achieve an undetected system with a pleasing appearance. It works on any game that uses human-shaped models. To optimize its performance, users should build OpenCV with CUDA. For Valorant, additional perks in the Discord and an Arduino Leonardo R3 are required.
aika
AIKA (Artificial Intelligence for Knowledge Acquisition) is a new type of artificial neural network designed to mimic the behavior of a biological brain more closely and bridge the gap to classical AI. The network conceptually separates activations from neurons, creating two separate graphs to represent acquired knowledge and inferred information. It uses different types of neurons and synapses to propagate activation values, binding signals, causal relations, and training gradients. The network structure allows for flexible topology and supports the gradual population of neurons and synapses during training.
nextpy
Nextpy is a cutting-edge software development framework optimized for AI-based code generation. It provides guardrails for defining AI system boundaries, structured outputs for prompt engineering, a powerful prompt engine for efficient processing, better AI generations with precise output control, modularity for multiplatform and extensible usage, developer-first approach for transferable knowledge, and containerized & scalable deployment options. It offers 4-10x faster performance compared to Streamlit apps, with a focus on cooperation within the open-source community and integration of key components from various projects.
For similar jobs
byteir
The ByteIR Project is a ByteDance model compilation solution. ByteIR includes compiler, runtime, and frontends, and provides an end-to-end model compilation solution. Although all ByteIR components (compiler/runtime/frontends) are together to provide an end-to-end solution, and all under the same umbrella of this repository, each component technically can perform independently. The name, ByteIR, comes from a legacy purpose internally. The ByteIR project is NOT an IR spec definition project. Instead, in most scenarios, ByteIR directly uses several upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo. Most of ByteIR compiler passes are compatible with the selected upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo.

mlir-air
This repository contains tools and libraries for building AIR platforms, runtimes and compilers.
husky
Husky is a research-focused programming language designed for next-generation computing. It aims to provide a powerful and ergonomic development experience for various tasks, including system level programming, web/native frontend development, parser/compiler tasks, game development, formal verification, machine learning, and more. With a strong type system and support for human-in-the-loop programming, Husky enables users to tackle complex tasks such as explainable image classification, natural language processing, and reinforcement learning. The language prioritizes debugging, visualization, and human-computer interaction, offering agile compilation and evaluation, multiparadigm support, and a commitment to a good ecosystem.
Aiwnios
Aiwnios is a HolyC Compiler/Runtime designed for 64-bit ARM, RISCV, and x86 machines, including Apple M1 Macs, with plans for supporting other architectures in the future. The project is currently a work in progress, with regular updates and improvements planned. Aiwnios includes a sockets API (currently tested on FreeBSD) and a HolyC assembler accessible through AARCH64. The heart of Aiwnios lies in `arm_backend.c`, where the compiler is located, and a powerful AARCH64 assembler in `arm64_asm.c`. The compiler uses reverse Polish notation and statements are reversed. The developer manual is intended for developers working on the C side, providing detailed explanations of the source code.
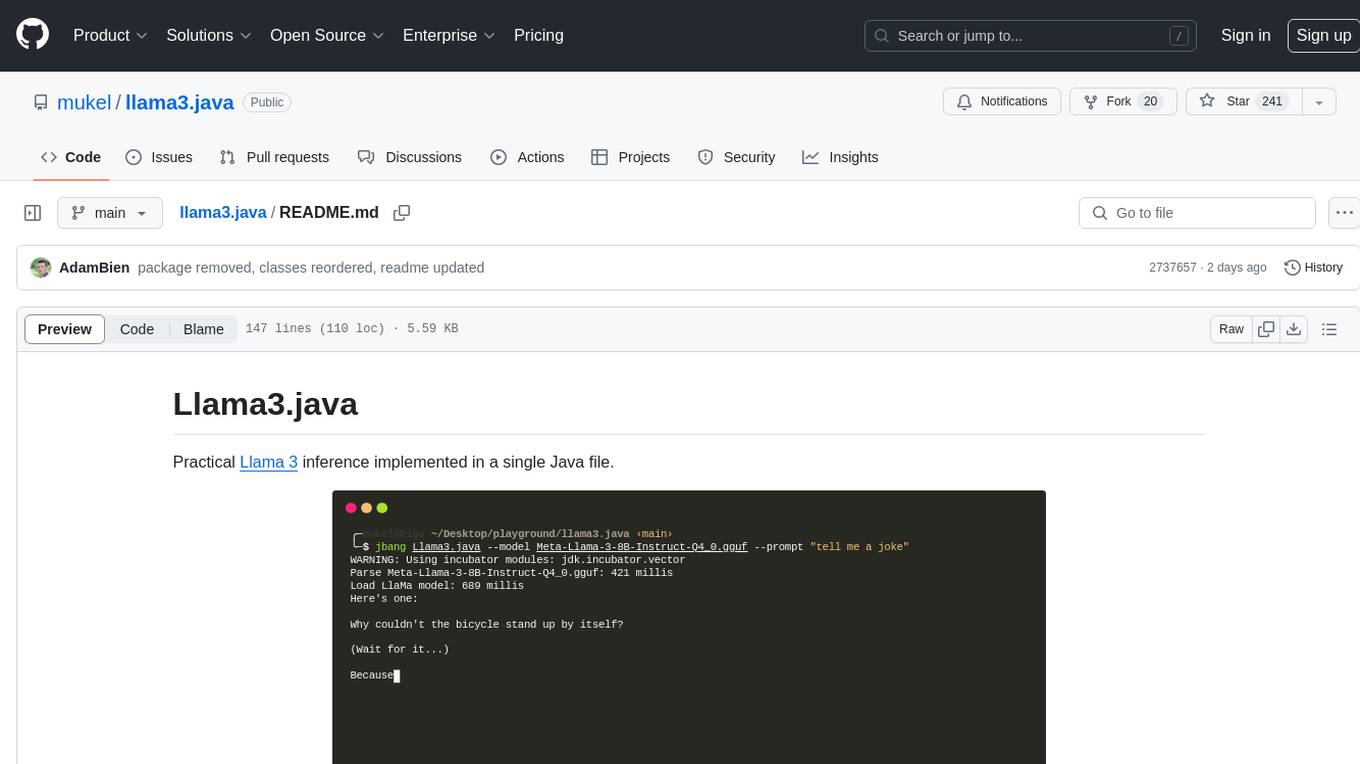
llama3.java
Llama3.java is a practical Llama 3 inference tool implemented in a single Java file. It serves as the successor of llama2.java and is designed for testing and tuning compiler optimizations and features on the JVM, especially for the Graal compiler. The tool features a GGUF format parser, Llama 3 tokenizer, Grouped-Query Attention inference, support for Q8_0 and Q4_0 quantizations, fast matrix-vector multiplication routines using Java's Vector API, and a simple CLI with 'chat' and 'instruct' modes. Users can download quantized .gguf files from huggingface.co for model usage and can also manually quantize to pure 'Q4_0'. The tool requires Java 21+ and supports running from source or building a JAR file for execution. Performance benchmarks show varying tokens/s rates for different models and implementations on different hardware setups.
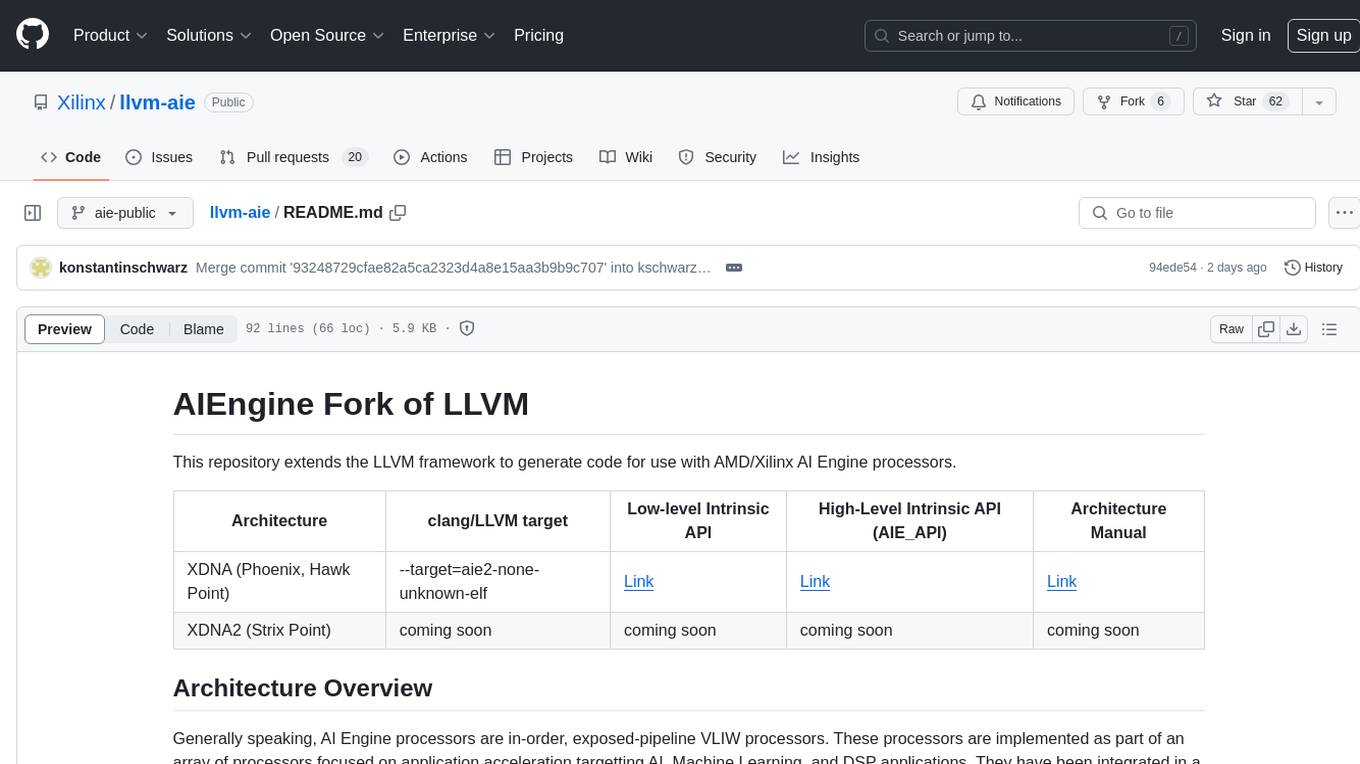
llvm-aie
This repository extends the LLVM framework to generate code for use with AMD/Xilinx AI Engine processors. AI Engine processors are in-order, exposed-pipeline VLIW processors focused on application acceleration for AI, Machine Learning, and DSP applications. The repository adds LLVM support for specific features like non-power of 2 pointers, operand latencies, resource conflicts, negative operand latencies, slot assignment, relocations, code alignment restrictions, and register allocation. It includes support for Clang, LLD, binutils, Compiler-RT, and LLVM-LIBC.
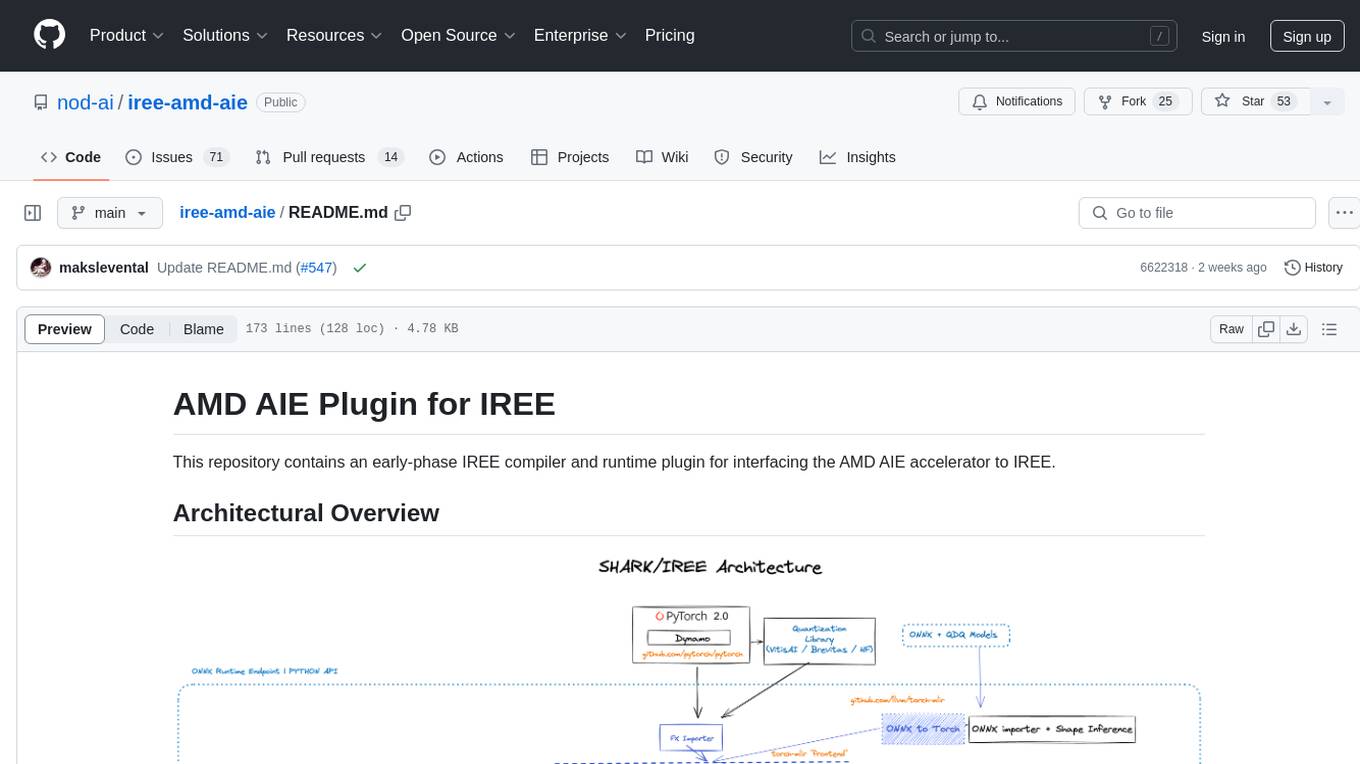
iree-amd-aie
This repository contains an early-phase IREE compiler and runtime plugin for interfacing the AMD AIE accelerator to IREE. It provides architectural overview, developer setup instructions, building guidelines, and runtime driver setup details. The repository focuses on enabling the integration of the AMD AIE accelerator with IREE, offering developers the tools and resources needed to build and run applications leveraging this technology.

AILZ80ASM
AILZ80ASM is a Z80 assembler that runs in a .NET 8 environment written in C#. It can be used to assemble Z80 assembly code and generate output files in various formats. The tool supports various command-line options for customization and provides features like macros, conditional assembly, and error checking. AILZ80ASM offers good performance metrics with fast assembly times and efficient output file sizes. It also includes support for handling different file encodings and provides a range of built-in functions for working with labels, expressions, and data types.
