aika
AIKA (Artificial Intelligence for Knowledge Acquisition) is an innovative approach to neural network design, diverging from traditional architectures that rely heavily on rigid matrix and vector operations. The AIKA Project introduces a flexible, sparse, and non-layered network representation, derived from a type hierarchy.
Stars: 75
AIKA (Artificial Intelligence for Knowledge Acquisition) is a new type of artificial neural network designed to mimic the behavior of a biological brain more closely and bridge the gap to classical AI. The network conceptually separates activations from neurons, creating two separate graphs to represent acquired knowledge and inferred information. It uses different types of neurons and synapses to propagate activation values, binding signals, causal relations, and training gradients. The network structure allows for flexible topology and supports the gradual population of neurons and synapses during training.
README:
AIKA (Artificial Intelligence for Knowledge Acquisition) is an innovative approach to neural network design, diverging from traditional architectures that rely heavily on rigid matrix and vector operations.
The AIKA Project introduces a flexible, sparse, and non-layered network representation, derived from a type hierarchy. Furthermore, it separates the primary neural network from its activation network. During the processing of a document, only those neurons and synapses in the activation network that are truly relevant are activated. The global neural network can encompass millions of neurons, yet the activation remains highly sparse. This sparsity is designed to enable efficient processing by focusing on the relevant subsections of the model.
A central element is the so-called "Linker," which transfers the structure of the neural network to the activation network. Here, not only activations but also so-called binding signals propagate through the network. Binding signals are inspired by two concepts:
- Individual constants from predicate logic.
- Temporally synchronized spiking activity in biological neural networks.
The Aika algorithm processes all changes in the network asynchronously as time-ordered events. Whenever a neuron exceeds its activation threshold, this is recorded as an event in a queue. The algorithm then processes these events sequentially. This creates a clear temporal order in which activations and binding signals are propagated. This event-based approach allows the system to flexibly respond to dynamic changes in the network while ensuring the correctness of the computation sequence at all times.
Unlike classical neural networks, which rely heavily on vector and matrix operations, Aika uses a hierarchy of different neuron types (e.g., excitatory, inhibitory) to define the architecture and behavior of the network. The mathematical models associated with these neuron types are organized as graphs of mathematical functions. This structure allows for flexible responses to dynamic changes in the activation network.
This module contains the mathematical core of AIKA, featuring:
- Graph-Based Representation: Declarative graph structures to represent the mathematical models.
- Type Hierarchy: Representing network elements such as neurons, synapses, and activations.
- Event-Driven Updates: Asynchronous state changes propagated via an event queue to maintain processing order.
The Fields Module acts as the foundation for building and instantiating the neural network. It ensures that state changes
in the mathematical model are asynchronously propagated through the network.
The Neural Network Module introduces a conceptual separation between:
- Neurons and Synapses: Representing the static knowledge acquired by the network.
- Activations and Links: Representing the dynamic information inferred from input data.
- Dual Graph Structure: Separate graphs for neurons (knowledge representation) and activations (input-specific inference).
- Dynamic Activation: Multiple activations for a single neuron, each tied to specific occurrences in the input data.
- Flexible Topology: Abandoning fixed-layered architectures, the sequence of activations adapts dynamically to the input data.
- Linker Component: Translates the neural network's structure into the activation network while propagating binding signals.
- Java 23 or higher
- Maven for dependency management
Clone the repository and build the project using Maven:
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/aika-algorithm/aika.git
# Navigate to the project directory
cd aika
# Build the project using Maven
mvn clean install- Instantiate the neural network using the
Fields Module. - Use the
Core Moduleto process input data and generate activations. - The project is currently being heavily restructured. A good starting point for getting
familiar with the project are the test-cases within the
Core Module.
We welcome contributions from the open-source community! To contribute:
- Fork the repository.
- Create a new branch (
feature/your-feature-name). - Commit your changes.
- Submit a pull request.
This project is licensed under the Apache License Version 2.0. See the LICENSE file for details.
Start exploring AIKA and join us in advancing the future of neural network design!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aika
Similar Open Source Tools

aika
AIKA (Artificial Intelligence for Knowledge Acquisition) is a new type of artificial neural network designed to mimic the behavior of a biological brain more closely and bridge the gap to classical AI. The network conceptually separates activations from neurons, creating two separate graphs to represent acquired knowledge and inferred information. It uses different types of neurons and synapses to propagate activation values, binding signals, causal relations, and training gradients. The network structure allows for flexible topology and supports the gradual population of neurons and synapses during training.
ai-algorithms
This repository is a work in progress that contains first-principle implementations of groundbreaking AI algorithms using various deep learning frameworks. Each implementation is accompanied by supporting research papers, aiming to provide comprehensive educational resources for understanding and implementing foundational AI algorithms from scratch.
MemoryBear
MemoryBear is a next-generation AI memory system developed by RedBear AI, focusing on overcoming limitations in knowledge storage and multi-agent collaboration. It empowers AI with human-like memory capabilities, enabling deep knowledge understanding and cognitive collaboration. The system addresses challenges such as knowledge forgetting, memory gaps in multi-agent collaboration, and semantic ambiguity during reasoning. MemoryBear's core features include memory extraction engine, graph storage, hybrid search, memory forgetting engine, self-reflection engine, and FastAPI services. It offers a standardized service architecture for efficient integration and invocation across applications.
PINNACLE
PINNACLE is a flexible geometric deep learning approach that trains on contextualized protein interaction networks to generate context-aware protein representations. It provides protein representations split across various cell-type contexts from different tissues and organs. The tool can be fine-tuned to study the genomic effects of drugs and nominate promising protein targets and cell-type contexts for further investigation. PINNACLE exemplifies the paradigm of incorporating context-specific effects for studying biological systems, especially the impact of disease and therapeutics.
Nucleoid
Nucleoid is a declarative (logic) runtime environment that manages both data and logic under the same runtime. It uses a declarative programming paradigm, which allows developers to focus on the business logic of the application, while the runtime manages the technical details. This allows for faster development and reduces the amount of code that needs to be written. Additionally, the sharding feature can help to distribute the load across multiple instances, which can further improve the performance of the system.
algebraic-nnhw
This repository contains the source code for a GEMM & deep learning hardware accelerator system used to validate proposed systolic array hardware architectures implementing efficient matrix multiplication algorithms to increase performance-per-area limits of GEMM & AI accelerators. Achieved results include up to 3× faster CNN inference, >2× higher mults/multiplier/clock cycle, and low area with high clock frequency. The system is specialized for inference of non-sparse DNN models with fixed-point/quantized inputs, fully accelerating all DNN layers in hardware, and highly optimizing GEMM acceleration.
EScAIP
EScAIP is an Efficiently Scaled Attention Interatomic Potential that leverages a novel multi-head self-attention formulation within graph neural networks to predict energy and forces between atoms in molecules and materials. It achieves substantial gains in efficiency, at least 10x speed up in inference time and 5x less memory usage compared to existing models. EScAIP represents a philosophy towards developing general-purpose Neural Network Interatomic Potentials that achieve better expressivity through scaling and continue to scale efficiently with increased computational resources and training data.
llama3_interpretability_sae
This project focuses on implementing Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) for mechanistic interpretability in Large Language Models (LLMs) like Llama 3.2-3B. The SAEs aim to untangle superimposed representations in LLMs into separate, interpretable features for each neuron activation. The project provides an end-to-end pipeline for capturing training data, training the SAEs, analyzing learned features, and verifying results experimentally. It includes comprehensive logging, visualization, and checkpointing of SAE training, interpretability analysis tools, and a pure PyTorch implementation of Llama 3.1/3.2 chat and text completion. The project is designed for scalability, efficiency, and maintainability.
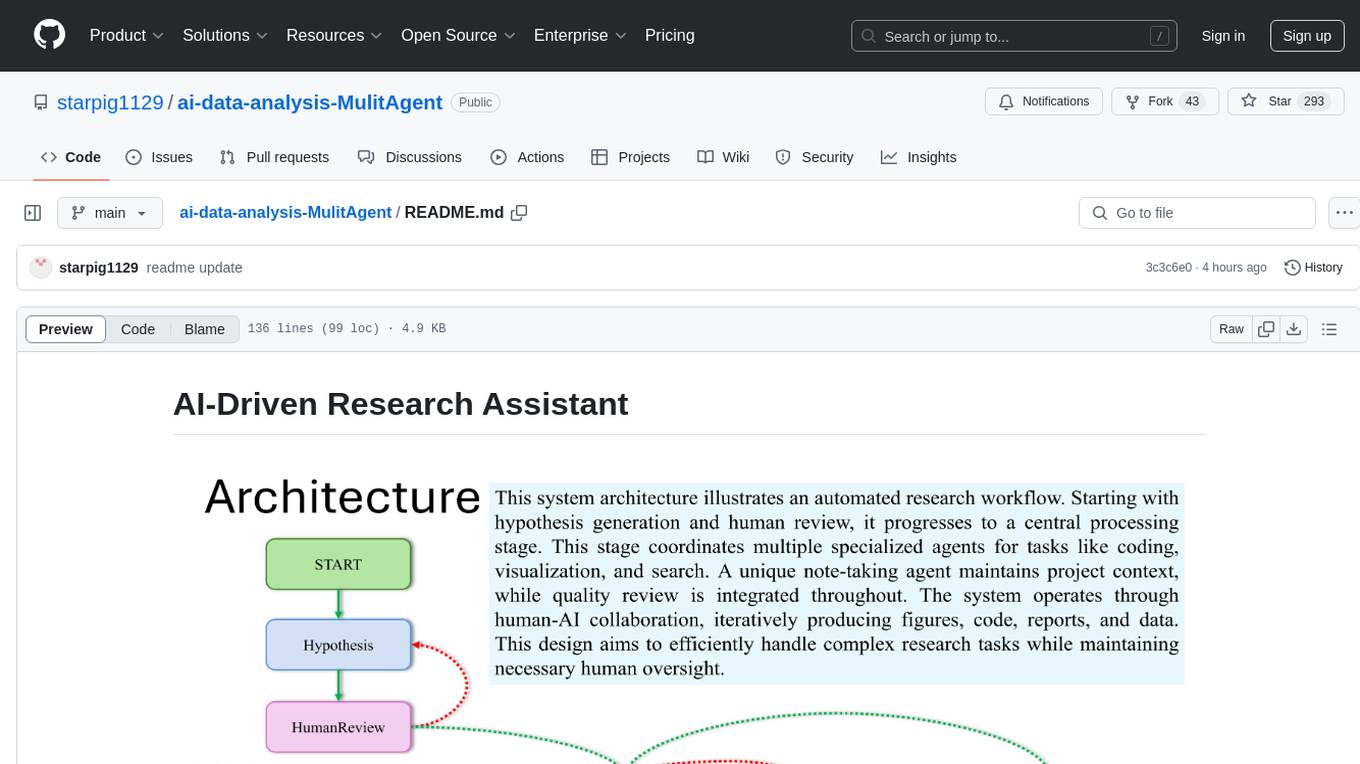
ai-data-analysis-MulitAgent
AI-Driven Research Assistant is an advanced AI-powered system utilizing specialized agents for data analysis, visualization, and report generation. It integrates LangChain, OpenAI's GPT models, and LangGraph for complex research processes. Key features include hypothesis generation, data processing, web search, code generation, and report writing. The system's unique Note Taker agent maintains project state, reducing overhead and improving context retention. System requirements include Python 3.10+ and Jupyter Notebook environment. Installation involves cloning the repository, setting up a Conda virtual environment, installing dependencies, and configuring environment variables. Usage instructions include setting data, running Jupyter Notebook, customizing research tasks, and viewing results. Main components include agents for hypothesis generation, process supervision, visualization, code writing, search, report writing, quality review, and note-taking. Workflow involves hypothesis generation, processing, quality review, and revision. Customization is possible by modifying agent creation and workflow definition. Current issues include OpenAI errors, NoteTaker efficiency, runtime optimization, and refiner improvement. Contributions via pull requests are welcome under the MIT License.
blades
Blades is a multimodal AI Agent framework in Go, supporting custom models, tools, memory, middleware, and more. It is well-suited for multi-turn conversations, chain reasoning, and structured output. The framework provides core components like Agent, Prompt, Chain, ModelProvider, Tool, Memory, and Middleware, enabling developers to build intelligent applications with flexible configuration and high extensibility. Blades leverages the characteristics of Go to achieve high decoupling and efficiency, making it easy to integrate different language model services and external tools. The project is in its early stages, inviting Go developers and AI enthusiasts to contribute and explore the possibilities of building AI applications in Go.
LongRoPE
LongRoPE is a method to extend the context window of large language models (LLMs) beyond 2 million tokens. It identifies and exploits non-uniformities in positional embeddings to enable 8x context extension without fine-tuning. The method utilizes a progressive extension strategy with 256k fine-tuning to reach a 2048k context. It adjusts embeddings for shorter contexts to maintain performance within the original window size. LongRoPE has been shown to be effective in maintaining performance across various tasks from 4k to 2048k context lengths.
Electronic-Component-Sorter
The Electronic Component Classifier is a project that uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to automate the identification and classification of electrical and electronic components. It features component classification into seven classes, user-friendly design, and integration with Flask for a user-friendly interface. The project aims to reduce human error in component identification, make the process safer and more reliable, and potentially help visually impaired individuals in identifying electronic components.
ManipVQA
ManipVQA is a framework that enhances Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with manipulation-centric knowledge through a Visual Question-Answering (VQA) format. It addresses the deficiency of conventional MLLMs in understanding affordances and physical concepts crucial for manipulation tasks. By infusing robotics-specific knowledge, including tool detection, affordance recognition, and physical concept comprehension, ManipVQA improves the performance of robots in manipulation tasks. The framework involves fine-tuning MLLMs with a curated dataset of interactive objects, enabling robots to understand and execute natural language instructions more effectively.
aihwkit
The IBM Analog Hardware Acceleration Kit is an open-source Python toolkit for exploring and using the capabilities of in-memory computing devices in the context of artificial intelligence. It consists of two main components: Pytorch integration and Analog devices simulator. The Pytorch integration provides a series of primitives and features that allow using the toolkit within PyTorch, including analog neural network modules, analog training using torch training workflow, and analog inference using torch inference workflow. The Analog devices simulator is a high-performant (CUDA-capable) C++ simulator that allows for simulating a wide range of analog devices and crossbar configurations by using abstract functional models of material characteristics with adjustable parameters. Along with the two main components, the toolkit includes other functionalities such as a library of device presets, a module for executing high-level use cases, a utility to automatically convert a downloaded model to its equivalent Analog model, and integration with the AIHW Composer platform. The toolkit is currently in beta and under active development, and users are advised to be mindful of potential issues and keep an eye for improvements, new features, and bug fixes in upcoming versions.
llmops-promptflow-template
LLMOps with Prompt flow is a template and guidance for building LLM-infused apps using Prompt flow. It provides centralized code hosting, lifecycle management, variant and hyperparameter experimentation, A/B deployment, many-to-many dataset/flow relationships, multiple deployment targets, comprehensive reporting, BYOF capabilities, configuration-based development, local prompt experimentation and evaluation, endpoint testing, and optional Human-in-loop validation. The tool is customizable to suit various application needs.
For similar tasks

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

sorrentum
Sorrentum is an open-source project that aims to combine open-source development, startups, and brilliant students to build machine learning, AI, and Web3 / DeFi protocols geared towards finance and economics. The project provides opportunities for internships, research assistantships, and development grants, as well as the chance to work on cutting-edge problems, learn about startups, write academic papers, and get internships and full-time positions at companies working on Sorrentum applications.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

zep-python
Zep is an open-source platform for building and deploying large language model (LLM) applications. It provides a suite of tools and services that make it easy to integrate LLMs into your applications, including chat history memory, embedding, vector search, and data enrichment. Zep is designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to use, making it a great choice for developers who want to build LLM-powered applications quickly and easily.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)

mojo
Mojo is a new programming language that bridges the gap between research and production by combining Python syntax and ecosystem with systems programming and metaprogramming features. Mojo is still young, but it is designed to become a superset of Python over time.

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.

databend
Databend is an open-source cloud data warehouse that serves as a cost-effective alternative to Snowflake. With its focus on fast query execution and data ingestion, it's designed for complex analysis of the world's largest datasets.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.