
Aiwnios
A HolyC Compiler/Runtime for 64bit ARM/X86
Stars: 89
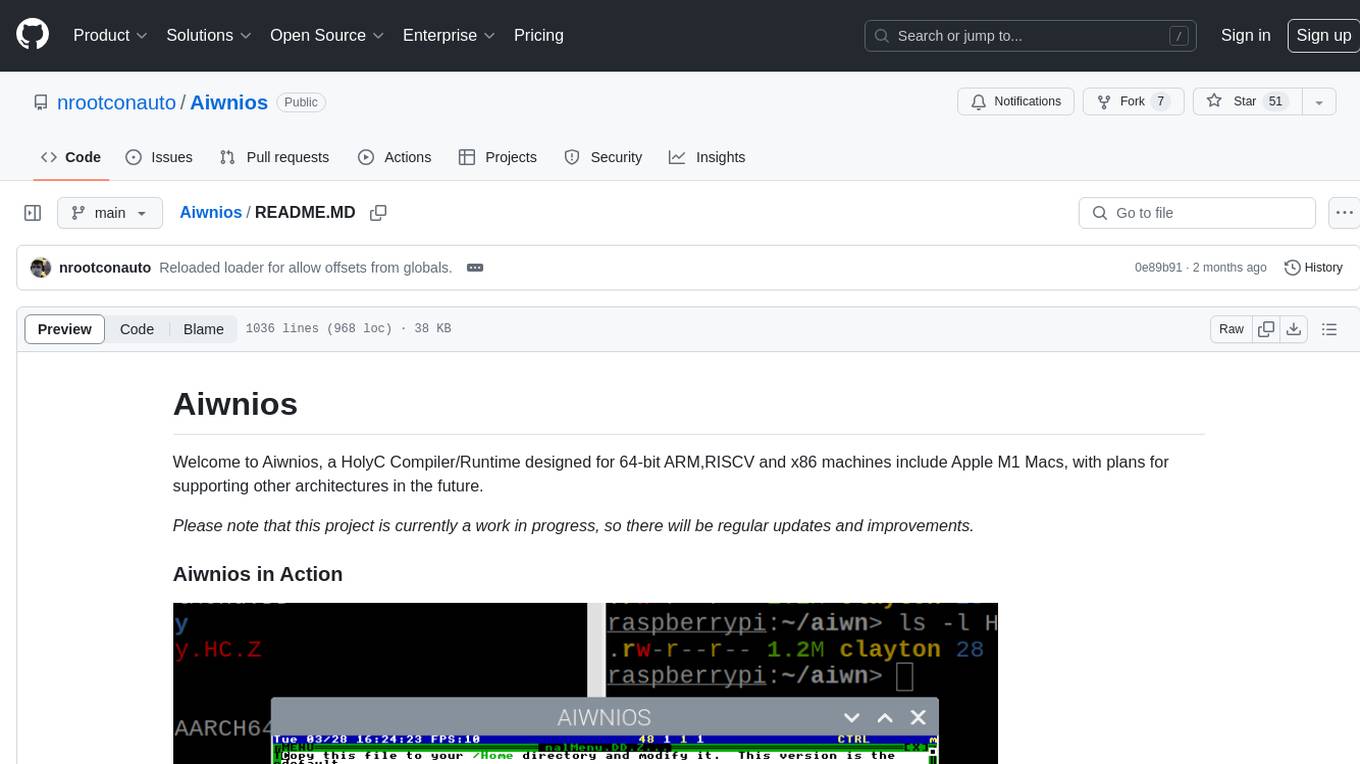
Aiwnios is a HolyC Compiler/Runtime designed for 64-bit ARM, RISCV, and x86 machines, including Apple M1 Macs, with plans for supporting other architectures in the future. The project is currently a work in progress, with regular updates and improvements planned. Aiwnios includes a sockets API (currently tested on FreeBSD) and a HolyC assembler accessible through AARCH64. The heart of Aiwnios lies in `arm_backend.c`, where the compiler is located, and a powerful AARCH64 assembler in `arm64_asm.c`. The compiler uses reverse Polish notation and statements are reversed. The developer manual is intended for developers working on the C side, providing detailed explanations of the source code.
README:
This is a HolyC Compiler/Runtime written for 64bit x86, aarch64 (includes MacOS) and RISC-V machines,although other architectures are planned for the future. This project is largely complete (aside from adding support for other architectures) so stay tuned.
| Architecture | OS |
|---|---|
| x86_64 | Windows, Linux and FreeBSD |
| aarch64 | Linux, FreeBSD and MacOS |
| rv64 (RISC-V 64) | Linux |
I develop on a lot of computers. For ARM I use an Apple M1 MacBook(MacOS x Asahi Linux). For RISC-V I use a LicheePi4. Make sure you buy one Trump imposes tariffs on sexy RISCV machines(I also test on a StarFive VisionFive 2). For X86_64 I use alot of old and new machines.
To build Aiwnios, you will need a C compiler, SDL2 development libraries and headers, and cmake. LTO with Clang/lld is supported if you like something saucy.
Build with the following after cloning:
# Build aiwnios
mkdir build;cd build;
cmake ..;
make -j$(nproc);
cd ..;
#Bootstrap the HCRT2.BIN to run it
./aiwnios -b;
#Run the HCRT2.BIN
./aiwnios; # Use -g or --grab-focus to grab the keyboard, -h for more optionsIf you want to create a cool package for your system, you can use CPack. Ill probably do this for you. The cpack is tested on Windows(NSIS). If you want to generate a FreeBSD .pkg,you'll need build cmake from source of FreeBSD because cpack has experimental support for FreeBSD. Make sure you enable it.
- Install msys2
- Run "MSYS2 MINGW64" (MUST BE MINGW64)
pacman -Sy git mingw-w64-x86_64-{gcc,SDL2,cmake}- Clone this repository
- Run the following after navigating to the directory
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
ninja
cd ..
- You will see the
aiwniosbinary in the directory
- Download WinLibs and add to PATH: Make sure the mingw32/bin or mingw64/bin folder from the extracted download is in your PATH and its location doesn't contain any spaces
- Download and extract devel mingw SDL2
- Clone this repository and navigate to it
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DSDL2_DIR=C:\Path\To\SDL2-devel-2.32.0-mingw\SDL2-2.32.0\x86_64-w64-mingw32\lib\cmake\SDL2 ..
ninja
cd ..
- You will see the
aiwniosbinary in the directory
Your on your own. Use homebrew to install packages, rest is same as FreeBSD
You can use the --tui to run a DolDoc enviroment in the terminal. Use ExitAiwnios; to leave.
You can make a standalone exe with an application(on MingW64(not msys unless you want all the libraries)).
It works by appending an HCRT2.BIN and RamDisk at the end of the executable. SDL on windows is statically linked by default.
You will need to include the Src and Doc(For /Doc/StandBy.DD and friends.) directories in your Aiwnios packages.
Do something like this:
DelTree("Root");
DirMk("Root");
CopyTree("Doc","Root/Doc");
CopyTree("Src","Root/Src");
AiwniosPack("a2.exe","Beep;\n","Root");I plan on adding something lit like an arm assembler from HolyC.
In aiwnios,the secret sauce is in mainly in *_backend.c. There you will find the compiler.
I have gutted out the TempleOS expression parsing code and replaced it with calls to __HC_ICAdd_XXXXX
which will be used in *_backend.c. There is a super assembler in *_asm.c
which you can use. Look at ffi.c to see how its used.
THIS COMPILER USES REVERSE POLISH NOTATION. And statements are reversed too so
the last statement is at head->base.next and the first one ends at head->base.last.
Email [email protected] for more info(I hear my code is unreadable so I will stop
explaining here).
Aiwnios comes with a sockets API.
Here is a simple server for you to play with until Nroot documents the Sockets API
U0 Main () {
U8 buf[STR_LEN];
I64 fd;
I64 s=NetSocketNew;
CNetAddr *addr;
addr=NetAddrNew("127.0.0.1",8000);
NetBindIn(s,addr);
NetListen(s,4);
while(TRUE) {
if(-1==NetPollForRead(1,&s)) {
Sleep(10);
} else {
fd=NetAccept(s,NULL);
while(-1==NetPollForRead(1,&fd))
Sleep(10);
buf[NetRead(fd,buf,STR_LEN)]=0;
"GOT:%s\n",buf;
NetClose(fd);
}
if(ScanKey)
break;
}
NetClose(s);
NetAddrDel(addr);
}
Main;_intern IC_SQR F64 Sqr(F64);aiwn_lexparser.h
enum {
/*Insert new IR code here */
IC_GOTO,
//...
};
//Later
HC_IC_BINDINGH(HC_ICAdd_Sqr)parser.c
//Add this
HC_IC_BINDING(HC_ICAdd_Sqr, IC_SQR);Add entires in these functions
parser.c
CRPN *ICFwd(CRPN *rpn) {
//...
case IC_SQR:
goto unop;
//...
}
CRPN *ParserDumpIR(CRPN *rpn, int64_t indent) {
//...
case IC_SQR:
printf("`2");
//...
}
int64_t DolDocDumpIR(char *to, int64_t len, CRPN *rpn) ;
int64_t AssignRawTypeToNode(CCmpCtrl *ccmp, CRPN *rpn) {
//...
case IC_SQR:
AssignRawTypeToNode(ccmp, rpn->base.next);
//Is a F64,use HashFind
rpn->ic_class = HashFind("F64", Fs->hash_table, HTT_CLASS, 1);
return rpn->raw_type = rpn->ic_class->raw_type;
break;
//...
}x86_64_backend.c
static int64_t SpillsTmpRegs(CRPN *rpn) {
//...
case IC_POS:
case IC_SQR:
//....
}
static int64_t PushTmpDepthFirst(CCmpCtrl *cctrl, CRPN *r, int64_t spilled) {
//...
case IC_SQR:
goto unop;
//...
}
static void SetKeepTmps(CRPN *rpn) {
//...
case IC_POS:
case IC_SQR: //Is a unop
//...
}
static int64_t __OptPassFinal(...) {
case IC_SQR:
next = ICArgN(rpn, 0);
code_off = __OptPassFinal(cctrl, next, bin, code_off);
code_off=PutICArgIntoReg(cctrl,&next->arg,RT_F64,0,bin,code_off); //Fallback to reg 0
if(rpn->res.mode==MD_REG) {
AIWNIOS_ADD_CODE(ARM_fmulReg(rpn->res.reg,next->arg.reg,next->arg.reg));
} else {
tmp.mode=MD_REG;
tmp.raw_type=RT_F64;
tmp.reg=MFR(cctrl,0); //MAKE SURE TO MARK THE VARIABLE AS modified
AIWNIOS_ADD_CODE(ARM_fmulReg(tmp.reg,rpn->res.reg,next->arg.reg,next->arg.reg));
code_off=ICMov(cctrl,&rpn->res,&tmp,bin,code_off);//Move tmp into result.
}
break;
}Src/AIWNIOS_CodeGen.HC
//At Start of file
#ifdef IMPORT_AIWNIOS_SYMS
import U8 *__HC_ICAdd_Sqr(U8 *);
#else
extern U8 *__HC_ICAdd_Sqr(U8 *);
#endif
U8 *AiwniosCompile(CCmpCtrl *cc,I64 *res_sz=NULL,CDbgInfo **info) {
//...
case IC_SQR:
new=__HC_ICAdd_Sqr(cc2);
break;
//...
}main.c
static int64_t STK___HC_ICAdd_Sqr(int64_t *stk) {
return (int64_t)__HC_ICAdd_Sqr((CCodeCtrl *)stk[0]);
}
// main()
PrsAddSymbol("__HC_ICAdd_Sqr", STK___HC_ICAdd_Sqr, 1);
- argtable3
- Cmake architecture detector by axr
- Xbyak Arm assembler
- sdl2-cmake-modules
- AArch64-Encodung
If you want something saucier and want to understand the sauce, look at the developer manual
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Aiwnios
Similar Open Source Tools

Aiwnios
Aiwnios is a HolyC Compiler/Runtime designed for 64-bit ARM, RISCV, and x86 machines, including Apple M1 Macs, with plans for supporting other architectures in the future. The project is currently a work in progress, with regular updates and improvements planned. Aiwnios includes a sockets API (currently tested on FreeBSD) and a HolyC assembler accessible through AARCH64. The heart of Aiwnios lies in `arm_backend.c`, where the compiler is located, and a powerful AARCH64 assembler in `arm64_asm.c`. The compiler uses reverse Polish notation and statements are reversed. The developer manual is intended for developers working on the C side, providing detailed explanations of the source code.
react-native-fast-tflite
A high-performance TensorFlow Lite library for React Native that utilizes JSI for power, zero-copy ArrayBuffers for efficiency, and low-level C/C++ TensorFlow Lite core API for direct memory access. It supports swapping out TensorFlow Models at runtime and GPU-accelerated delegates like CoreML/Metal/OpenGL. Easy VisionCamera integration allows for seamless usage. Users can load TensorFlow Lite models, interpret input and output data, and utilize GPU Delegates for faster computation. The library is suitable for real-time object detection, image classification, and other machine learning tasks in React Native applications.
deepgram-js-sdk
Deepgram JavaScript SDK. Power your apps with world-class speech and Language AI models.
gambit
Gambit is an open-source developer-first framework for building reliable LLM workflows. It helps compose small, typed 'decks' with clear inputs/outputs and guardrails. Users can run decks locally, stream traces, and debug with a built-in UI. The framework aims to improve orchestration by treating each step as a small deck, mixing LLM and compute tasks effortlessly, feeding models only necessary information, and providing built-in observability for debugging.
minja
Minja is a minimalistic C++ Jinja templating engine designed specifically for integration with C++ LLM projects, such as llama.cpp or gemma.cpp. It is not a general-purpose tool but focuses on providing a limited set of filters, tests, and language features tailored for chat templates. The library is header-only, requires C++17, and depends only on nlohmann::json. Minja aims to keep the codebase small, easy to understand, and offers decent performance compared to Python. Users should be cautious when using Minja due to potential security risks, and it is not intended for producing HTML or JavaScript output.
OpenAI-DotNet
OpenAI-DotNet is a simple C# .NET client library for OpenAI to use through their RESTful API. It is independently developed and not an official library affiliated with OpenAI. Users need an OpenAI API account to utilize this library. The library targets .NET 6.0 and above, working across various platforms like console apps, winforms, wpf, asp.net, etc., and on Windows, Linux, and Mac. It provides functionalities for authentication, interacting with models, assistants, threads, chat, audio, images, files, fine-tuning, embeddings, and moderations.
client-python
The Mistral Python Client is a tool inspired by cohere-python that allows users to interact with the Mistral AI API. It provides functionalities to access and utilize the AI capabilities offered by Mistral. Users can easily install the client using pip and manage dependencies using poetry. The client includes examples demonstrating how to use the API for various tasks, such as chat interactions. To get started, users need to obtain a Mistral API Key and set it as an environment variable. Overall, the Mistral Python Client simplifies the integration of Mistral AI services into Python applications.
com.openai.unity
com.openai.unity is an OpenAI package for Unity that allows users to interact with OpenAI's API through RESTful requests. It is independently developed and not an official library affiliated with OpenAI. Users can fine-tune models, create assistants, chat completions, and more. The package requires Unity 2021.3 LTS or higher and can be installed via Unity Package Manager or Git URL. Various features like authentication, Azure OpenAI integration, model management, thread creation, chat completions, audio processing, image generation, file management, fine-tuning, batch processing, embeddings, and content moderation are available.
ChatDBG
ChatDBG is an AI-based debugging assistant for C/C++/Python/Rust code that integrates large language models into a standard debugger (`pdb`, `lldb`, `gdb`, and `windbg`) to help debug your code. With ChatDBG, you can engage in a dialog with your debugger, asking open-ended questions about your program, like `why is x null?`. ChatDBG will _take the wheel_ and steer the debugger to answer your queries. ChatDBG can provide error diagnoses and suggest fixes. As far as we are aware, ChatDBG is the _first_ debugger to automatically perform root cause analysis and to provide suggested fixes.
python-tgpt
Python-tgpt is a Python package that enables seamless interaction with over 45 free LLM providers without requiring an API key. It also provides image generation capabilities. The name _python-tgpt_ draws inspiration from its parent project tgpt, which operates on Golang. Through this Python adaptation, users can effortlessly engage with a number of free LLMs available, fostering a smoother AI interaction experience.
java-genai
Java idiomatic SDK for the Gemini Developer APIs and Vertex AI APIs. The SDK provides a Client class for interacting with both APIs, allowing seamless switching between the 2 backends without code rewriting. It supports features like generating content, embedding content, generating images, upscaling images, editing images, and generating videos. The SDK also includes options for setting API versions, HTTP request parameters, client behavior, and response schemas.
js-genai
The Google Gen AI JavaScript SDK is an experimental SDK for TypeScript and JavaScript developers to build applications powered by Gemini. It supports both the Gemini Developer API and Vertex AI. The SDK is designed to work with Gemini 2.0 features. Users can access API features through the GoogleGenAI classes, which provide submodules for querying models, managing caches, creating chats, uploading files, and starting live sessions. The SDK also allows for function calling to interact with external systems. Users can find more samples in the GitHub samples directory.
aixt
Aixt is a programming framework for microcontrollers using a modern language syntax based on V, with components including the Aixt programming language, Aixt to C Transpiler, and Aixt API. It is designed to be modular, allowing easy incorporation of new devices and boards through a TOML configuration file. The Aixt to C Transpiler translates Aixt source code to C for specific microcontroller compilers. The Aixt language implements a subset of V with differences in variables, strings, arrays, default integers size, structs, functions, and preprocessor commands. The Aixt API provides functions for digital I/O, analog inputs, PWM outputs, and serial ports.
genaiscript
GenAIScript is a scripting environment designed to facilitate file ingestion, prompt development, and structured data extraction. Users can define metadata and model configurations, specify data sources, and define tasks to extract specific information. The tool provides a convenient way to analyze files and extract desired content in a structured format. It offers a user-friendly interface for working with data and automating data extraction processes, making it suitable for various data processing tasks.
consult-llm-mcp
Consult LLM MCP is an MCP server that enables users to consult powerful AI models like GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and DeepSeek Reasoner for complex problem-solving. It supports multi-turn conversations, direct queries with optional file context, git changes inclusion for code review, comprehensive logging with cost estimation, and various CLI modes for Gemini and Codex. The tool is designed to simplify the process of querying AI models for assistance in resolving coding issues and improving code quality.
llm-chain
LLM Chain is a PHP library for building LLM-based features and applications. It provides abstractions for Language Models and Embeddings Models from platforms like OpenAI, Azure, Google, Replicate, and others. The core feature is to interact with language models via messages, supporting different message types and content. LLM Chain also supports tool calling, document embedding, vector stores, similarity search, structured output, response streaming, image processing, audio processing, embeddings, parallel platform calls, and input/output processing. Contributions are welcome, and the repository contains fixture licenses for testing multi-modal features.
For similar tasks

Aiwnios
Aiwnios is a HolyC Compiler/Runtime designed for 64-bit ARM, RISCV, and x86 machines, including Apple M1 Macs, with plans for supporting other architectures in the future. The project is currently a work in progress, with regular updates and improvements planned. Aiwnios includes a sockets API (currently tested on FreeBSD) and a HolyC assembler accessible through AARCH64. The heart of Aiwnios lies in `arm_backend.c`, where the compiler is located, and a powerful AARCH64 assembler in `arm64_asm.c`. The compiler uses reverse Polish notation and statements are reversed. The developer manual is intended for developers working on the C side, providing detailed explanations of the source code.

llm_processes
This repository contains code for LLM Processes, which focuses on generating numerical predictive distributions conditioned on natural language. It supports various LLMs through Hugging Face transformer APIs and includes experiments on prompt engineering, 1D synthetic data, comparison to LLMTime, Fashion MNIST, black-box optimization, weather regression, in-context learning, and text conditioning. The code requires Python 3.9+, PyTorch 2.3.0+, and other dependencies for running experiments and reproducing results.
For similar jobs

Aiwnios
Aiwnios is a HolyC Compiler/Runtime designed for 64-bit ARM, RISCV, and x86 machines, including Apple M1 Macs, with plans for supporting other architectures in the future. The project is currently a work in progress, with regular updates and improvements planned. Aiwnios includes a sockets API (currently tested on FreeBSD) and a HolyC assembler accessible through AARCH64. The heart of Aiwnios lies in `arm_backend.c`, where the compiler is located, and a powerful AARCH64 assembler in `arm64_asm.c`. The compiler uses reverse Polish notation and statements are reversed. The developer manual is intended for developers working on the C side, providing detailed explanations of the source code.
byteir
The ByteIR Project is a ByteDance model compilation solution. ByteIR includes compiler, runtime, and frontends, and provides an end-to-end model compilation solution. Although all ByteIR components (compiler/runtime/frontends) are together to provide an end-to-end solution, and all under the same umbrella of this repository, each component technically can perform independently. The name, ByteIR, comes from a legacy purpose internally. The ByteIR project is NOT an IR spec definition project. Instead, in most scenarios, ByteIR directly uses several upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo. Most of ByteIR compiler passes are compatible with the selected upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo.
mlir-air
This repository contains tools and libraries for building AIR platforms, runtimes and compilers.
husky
Husky is a research-focused programming language designed for next-generation computing. It aims to provide a powerful and ergonomic development experience for various tasks, including system level programming, web/native frontend development, parser/compiler tasks, game development, formal verification, machine learning, and more. With a strong type system and support for human-in-the-loop programming, Husky enables users to tackle complex tasks such as explainable image classification, natural language processing, and reinforcement learning. The language prioritizes debugging, visualization, and human-computer interaction, offering agile compilation and evaluation, multiparadigm support, and a commitment to a good ecosystem.
llama3.java
Llama3.java is a practical Llama 3 inference tool implemented in a single Java file. It serves as the successor of llama2.java and is designed for testing and tuning compiler optimizations and features on the JVM, especially for the Graal compiler. The tool features a GGUF format parser, Llama 3 tokenizer, Grouped-Query Attention inference, support for Q8_0 and Q4_0 quantizations, fast matrix-vector multiplication routines using Java's Vector API, and a simple CLI with 'chat' and 'instruct' modes. Users can download quantized .gguf files from huggingface.co for model usage and can also manually quantize to pure 'Q4_0'. The tool requires Java 21+ and supports running from source or building a JAR file for execution. Performance benchmarks show varying tokens/s rates for different models and implementations on different hardware setups.
llvm-aie
This repository extends the LLVM framework to generate code for use with AMD/Xilinx AI Engine processors. AI Engine processors are in-order, exposed-pipeline VLIW processors focused on application acceleration for AI, Machine Learning, and DSP applications. The repository adds LLVM support for specific features like non-power of 2 pointers, operand latencies, resource conflicts, negative operand latencies, slot assignment, relocations, code alignment restrictions, and register allocation. It includes support for Clang, LLD, binutils, Compiler-RT, and LLVM-LIBC.
iree-amd-aie
This repository contains an early-phase IREE compiler and runtime plugin for interfacing the AMD AIE accelerator to IREE. It provides architectural overview, developer setup instructions, building guidelines, and runtime driver setup details. The repository focuses on enabling the integration of the AMD AIE accelerator with IREE, offering developers the tools and resources needed to build and run applications leveraging this technology.
AILZ80ASM
AILZ80ASM is a Z80 assembler that runs in a .NET 8 environment written in C#. It can be used to assemble Z80 assembly code and generate output files in various formats. The tool supports various command-line options for customization and provides features like macros, conditional assembly, and error checking. AILZ80ASM offers good performance metrics with fast assembly times and efficient output file sizes. It also includes support for handling different file encodings and provides a range of built-in functions for working with labels, expressions, and data types.

