
LLM-Finetune-Guide
Arrange methods and example on finetune LLMs
Stars: 60
This project provides a comprehensive guide to fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) with efficient methods like LoRA and P-tuning V2. It includes detailed instructions, code examples, and performance benchmarks for various LLMs and fine-tuning techniques. The guide also covers data preparation, evaluation, prediction, and running inference on CPU environments. By leveraging this guide, users can effectively fine-tune LLMs for specific tasks and applications.
README:
This project compiles important concepts and programming frameworks for fine-tuning large language models, providing executable examples for training and inference of LLMs.
👋 Welcome to join our Line community Open Chat: fine-tuning large language models and OpenAI applications
Switch language version: [ English | 繁體中文 | 简体中文 ]
If you want to reduce trial and error, you are welcome to enroll in my personally recorded step-by-step tutorial course:
- Fill out the survey to receive a discount voucher: https://www.surveycake.com/s/kn0bL
Currently, the following efficient fine-tuning methods are supported:
- LoRA
- P-tuning V2
Training Arguments:
| LLM | Fine-Tuning Method | Quantization Methods | Distributed Training Strategy | Batch Size | Required GPU memory (per card) | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bloom | LoRA | INT8 | None | 1 | 14GB | 86.71s/it |
| Bloom | LoRA | INT8 | Torch DDP on 2 GPUs | 1 | 13GB | 44.47s/it |
| Bloom | LoRA | INT8 | DeepSpeed ZeRO stage 3 on 2 GPUs | 1 | 13GB | 36.05s/it |
| ChatGLM-6B | P-Tuning | INT4 | DeepSpeed ZeRO stage 3 on 2 GPUs | 2 | 15GB | 14.7s/it |
You can choose to fine-tune with open-source or academic datasets, but if the open-source datasets do not fit your application scenario, you will need to use custom datasets for fine-tuning.
In this project, the format used for the dataset is .json. You will need to put the train, dev, and test files of the separated dataset in the instruction-datasets/ directory. You can also create a new folder to place the files, but the path should be specified accordingly in the commands.
Different fine-tuning methods have their required packages set up. To install them, simply navigate to the folder with requirements.txt and run:
git clone https://github.com/A-baoYang/LLM-FineTuning-Guide.git
conda create -n llm_ift python=3.8
conda activate llm_ift
cd LLM-Finetune-Guide/efficient-finetune/ptuning/v2
pip install -r requirements.txtAfter the data is prepared, you can start fine-tuning. The program has already been written and you can specify the data/model path and parameter replacement through the command.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python finetune.py \
--do_train \
--train_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/train.json \
--validation_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/dev.json \
--prompt_column input \
--response_column output \
--overwrite_cache \
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_PATH \
--output_dir finetuned/$DATATAG-$MODEL_TYPE-pt-$PRE_SEQ_LEN-$LRPlease refer to the complete parameter and command settings at: finetune.sh
- Start with
torchrun
torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=2 finetune.py --do_train \
--train_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/train.json \
--validation_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/dev.json \
--prompt_column input \
--response_column output \
--overwrite_cache \
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_PATH \
--output_dir finetuned/$DATATAG-$MODEL_TYPE-pt-$PRE_SEQ_LEN-$LR \Please refer to the complete parameter and command settings at: finetune-ddp.sh
- Start with
accelerate
accelerate launch finetune.py --do_train \
--train_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/train.json \
--validation_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/dev.json \
--prompt_column input \
--response_column output \
--overwrite_cache \
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_PATH \
--output_dir finetuned/$DATATAG-$MODEL_TYPE-pt-$PRE_SEQ_LEN-$LR \- Start with
accelerateandconfig_filearguments
accelerate launch --config_file ../../config/use_deepspeed.yaml finetune.py --do_train \
--train_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/train.json \
--validation_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/dev.json \
--prompt_column input \
--response_column output \
--overwrite_cache \
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_PATH \
--output_dir finetuned/$DATATAG-$MODEL_TYPE-pt-$PRE_SEQ_LEN-$LR \- Start with
deepspeed
deepspeed --num_nodes 1 --num_gpus 2 finetune.py \
--deepspeed ../../config/zero_stage3_offload_config.json \
--do_train \
--train_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/train.json \
--validation_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/dev.json \
--prompt_column input \
--response_column output \
--overwrite_cache \
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_PATH \
--output_dir finetuned/$DATATAG-$MODEL_TYPE-pt-$PRE_SEQ_LEN-$LR \- For more fine-tuning examples, see: efficient-finetune/README.md
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python finetune.py \
--do_predict \
--validation_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/dev.json \
--test_file ../../../instruction-datasets/$DATATAG/test.json \
--overwrite_cache \
--prompt_column input \
--response_column output \
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_PATH \
--ptuning_checkpoint finetuned/$DATATAG-$MODEL_TYPE-pt-$PRE_SEQ_LEN-$LR/checkpoint-$STEP \
--output_dir finetuned/$DATATAG-$MODEL_TYPE-pt-$PRE_SEQ_LEN-$LR- Terminal
cd LLM-Finetune-Guide/efficient-finetune/ptuning/v2/serve/
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python cli_demo.py \
--pretrained_model_path THUDM/chatglm-6b \
--ptuning_checkpoint ../finetuned/chatglm-6b-pt-512-2e-2/checkpoint-3000 \
--is_cuda True- Web demo
cd LLM-Finetune-Guide/efficient-finetune/lora/serve/
python ui.py- Model API
cd LLM-Finetune-Guide/efficient-finetune/lora/serve/
python api.pyThe ability to run fine-tuned large language models in a CPU environment would greatly reduce the application threshold of LLMs.
- Use INT4 to run in CPU environment
cd LLM-Finetune-Guide/efficient-finetune/ptuning/v2/serve/
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python cli_demo.py \
--pretrained_model_path THUDM/chatglm-6b \
--ptuning_checkpoint ../finetuned/chatglm-6b-pt-512-2e-2/checkpoint-3000 \
--quantization_bit 4 \
--is_cuda True- Repository License: Apache-2.0 License
- Model License: Please refer to the license provided by each language model for details.
If this project is helpful to your work or research, please star & cite it as follows:
@Misc{LLM-Finetune-Guide,
title = {LLM Finetune Guide},
author = {A-baoYang},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/A-baoYang/LLM-Finetune-Guide}},
year = {2023}
}
This project was inspired by some amazing projects, which are listed below. Thanks for their great work.
- [THUDM/ChatGLM-6B]
- [ymcui/Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca]
- [tloen/alpaca-lora]
If you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to email us for inquiries: [email protected]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-Finetune-Guide
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-Finetune-Guide
This project provides a comprehensive guide to fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) with efficient methods like LoRA and P-tuning V2. It includes detailed instructions, code examples, and performance benchmarks for various LLMs and fine-tuning techniques. The guide also covers data preparation, evaluation, prediction, and running inference on CPU environments. By leveraging this guide, users can effectively fine-tune LLMs for specific tasks and applications.
rank_llm
RankLLM is a suite of prompt-decoders compatible with open source LLMs like Vicuna and Zephyr. It allows users to create custom ranking models for various NLP tasks, such as document reranking, question answering, and summarization. The tool offers a variety of features, including the ability to fine-tune models on custom datasets, use different retrieval methods, and control the context size and variable passages. RankLLM is easy to use and can be integrated into existing NLP pipelines.
GraphGen
GraphGen is a framework for synthetic data generation guided by knowledge graphs. It enhances supervised fine-tuning for large language models (LLMs) by generating synthetic data based on a fine-grained knowledge graph. The tool identifies knowledge gaps in LLMs, prioritizes generating QA pairs targeting high-value knowledge, incorporates multi-hop neighborhood sampling, and employs style-controlled generation to diversify QA data. Users can use LLaMA-Factory and xtuner for fine-tuning LLMs after data generation.
ScaleLLM
ScaleLLM is a cutting-edge inference system engineered for large language models (LLMs), meticulously designed to meet the demands of production environments. It extends its support to a wide range of popular open-source models, including Llama3, Gemma, Bloom, GPT-NeoX, and more. ScaleLLM is currently undergoing active development. We are fully committed to consistently enhancing its efficiency while also incorporating additional features. Feel free to explore our **_Roadmap_** for more details. ## Key Features * High Efficiency: Excels in high-performance LLM inference, leveraging state-of-the-art techniques and technologies like Flash Attention, Paged Attention, Continuous batching, and more. * Tensor Parallelism: Utilizes tensor parallelism for efficient model execution. * OpenAI-compatible API: An efficient golang rest api server that compatible with OpenAI. * Huggingface models: Seamless integration with most popular HF models, supporting safetensors. * Customizable: Offers flexibility for customization to meet your specific needs, and provides an easy way to add new models. * Production Ready: Engineered with production environments in mind, ScaleLLM is equipped with robust system monitoring and management features to ensure a seamless deployment experience.
amd-shark-ai
The amdshark-ai repository contains the amdshark Modeling and Serving Libraries, which include sub-projects like shortfin for high performance inference, amdsharktank for model recipes and conversion tools, and amdsharktuner for tuning program performance. Developers can find API documentation, programming guides, and support matrix for various models within the repository.
Online-RLHF
This repository, Online RLHF, focuses on aligning large language models (LLMs) through online iterative Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It aims to bridge the gap in existing open-source RLHF projects by providing a detailed recipe for online iterative RLHF. The workflow presented here has shown to outperform offline counterparts in recent LLM literature, achieving comparable or better results than LLaMA3-8B-instruct using only open-source data. The repository includes model releases for SFT, Reward model, and RLHF model, along with installation instructions for both inference and training environments. Users can follow step-by-step guidance for supervised fine-tuning, reward modeling, data generation, data annotation, and training, ultimately enabling iterative training to run automatically.
LongLoRA
LongLoRA is a tool for efficient fine-tuning of long-context large language models. It includes LongAlpaca data with long QA data collected and short QA sampled, models from 7B to 70B with context length from 8k to 100k, and support for GPTNeoX models. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning, context extension, and improved LoRA fine-tuning. It provides pre-trained weights, fine-tuning instructions, evaluation methods, local and online demos, streaming inference, and data generation via Pdf2text. LongLoRA is licensed under Apache License 2.0, while data and weights are under CC-BY-NC 4.0 License for research use only.
star-vector
StarVector is a multimodal vision-language model for Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) generation. It can be used to perform image2SVG and text2SVG generation. StarVector works directly in the SVG code space, leveraging visual understanding to apply accurate SVG primitives. It achieves state-of-the-art performance in producing compact and semantically rich SVGs. The tool provides Hugging Face model checkpoints for image2SVG vectorization, with models like StarVector-8B and StarVector-1B. It also offers datasets like SVG-Stack, SVG-Fonts, SVG-Icons, SVG-Emoji, and SVG-Diagrams for evaluation. StarVector can be trained using Deepspeed or FSDP for tasks like Image2SVG and Text2SVG generation. The tool provides a demo with options for HuggingFace generation or VLLM backend for faster generation speed.
agentscope
AgentScope is a multi-agent platform designed to empower developers to build multi-agent applications with large-scale models. It features three high-level capabilities: Easy-to-Use, High Robustness, and Actor-Based Distribution. AgentScope provides a list of `ModelWrapper` to support both local model services and third-party model APIs, including OpenAI API, DashScope API, Gemini API, and ollama. It also enables developers to rapidly deploy local model services using libraries such as ollama (CPU inference), Flask + Transformers, Flask + ModelScope, FastChat, and vllm. AgentScope supports various services, including Web Search, Data Query, Retrieval, Code Execution, File Operation, and Text Processing. Example applications include Conversation, Game, and Distribution. AgentScope is released under Apache License 2.0 and welcomes contributions.
dora
Dataflow-oriented robotic application (dora-rs) is a framework that makes creation of robotic applications fast and simple. Building a robotic application can be summed up as bringing together hardwares, algorithms, and AI models, and make them communicate with each others. At dora-rs, we try to: make integration of hardware and software easy by supporting Python, C, C++, and also ROS2. make communication low latency by using zero-copy Arrow messages. dora-rs is still experimental and you might experience bugs, but we're working very hard to make it stable as possible.
TempCompass
TempCompass is a benchmark designed to evaluate the temporal perception ability of Video LLMs. It encompasses a diverse set of temporal aspects and task formats to comprehensively assess the capability of Video LLMs in understanding videos. The benchmark includes conflicting videos to prevent models from relying on single-frame bias and language priors. Users can clone the repository, install required packages, prepare data, run inference using examples like Video-LLaVA and Gemini, and evaluate the performance of their models across different tasks such as Multi-Choice QA, Yes/No QA, Caption Matching, and Caption Generation.
TTS-WebUI
TTS WebUI is a comprehensive tool for text-to-speech synthesis, audio/music generation, and audio conversion. It offers a user-friendly interface for various AI projects related to voice and audio processing. The tool provides a range of models and extensions for different tasks, along with integrations like Silly Tavern and OpenWebUI. With support for Docker setup and compatibility with Linux and Windows, TTS WebUI aims to facilitate creative and responsible use of AI technologies in a user-friendly manner.
everything-claude-code
The 'Everything Claude Code' repository is a comprehensive collection of production-ready agents, skills, hooks, commands, rules, and MCP configurations developed over 10+ months. It includes guides for setup, foundations, and philosophy, as well as detailed explanations of various topics such as token optimization, memory persistence, continuous learning, verification loops, parallelization, and subagent orchestration. The repository also provides updates on bug fixes, multi-language rules, installation wizard, PM2 support, OpenCode plugin integration, unified commands and skills, and cross-platform support. It offers a quick start guide for installation, ecosystem tools like Skill Creator and Continuous Learning v2, requirements for CLI version compatibility, key concepts like agents, skills, hooks, and rules, running tests, contributing guidelines, OpenCode support, background information, important notes on context window management and customization, star history chart, and relevant links.
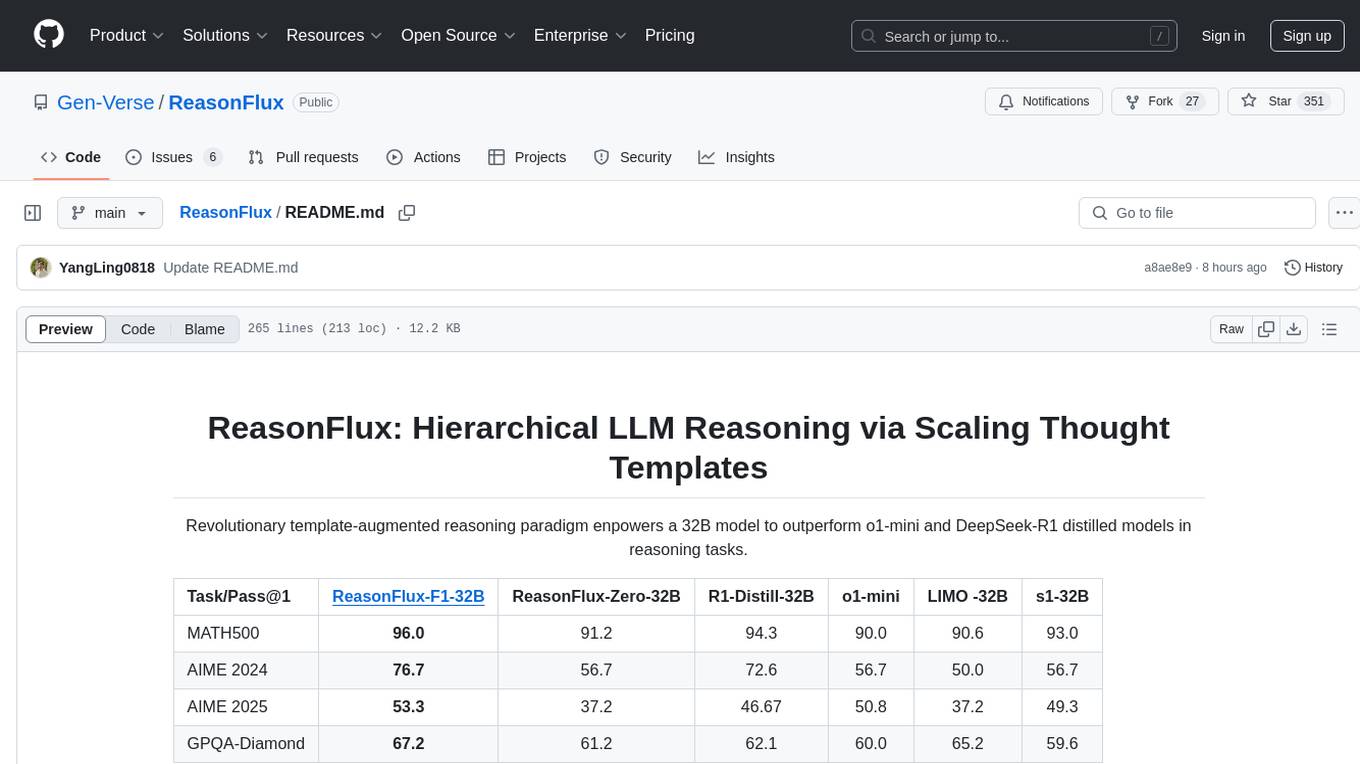
ReasonFlux
ReasonFlux is a revolutionary template-augmented reasoning paradigm that empowers a 32B model to outperform other models in reasoning tasks. The repository provides official resources for the paper 'ReasonFlux: Hierarchical LLM Reasoning via Scaling Thought Templates', including the latest released model ReasonFlux-F1-32B. It includes updates, dataset links, model zoo, getting started guide, training instructions, evaluation details, inference examples, performance comparisons, reasoning examples, preliminary work references, and citation information.
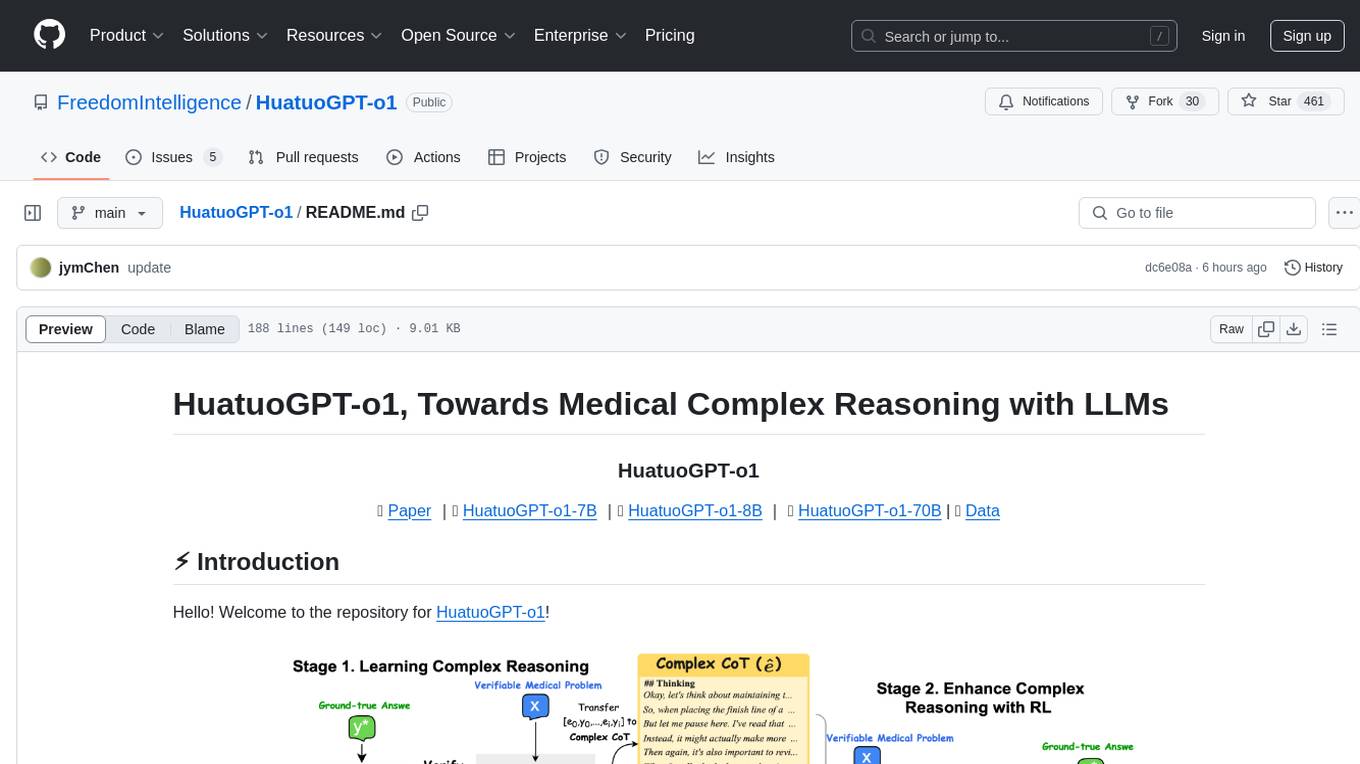
HuatuoGPT-o1
HuatuoGPT-o1 is a medical language model designed for advanced medical reasoning. It can identify mistakes, explore alternative strategies, and refine answers. The model leverages verifiable medical problems and a specialized medical verifier to guide complex reasoning trajectories and enhance reasoning through reinforcement learning. The repository provides access to models, data, and code for HuatuoGPT-o1, allowing users to deploy the model for medical reasoning tasks.
MooER
MooER (摩耳) is an LLM-based speech recognition and translation model developed by Moore Threads. It allows users to transcribe speech into text (ASR) and translate speech into other languages (AST) in an end-to-end manner. The model was trained using 5K hours of data and is now also available with an 80K hours version. MooER is the first LLM-based speech model trained and inferred using domestic GPUs. The repository includes pretrained models, inference code, and a Gradio demo for a better user experience.
For similar tasks

LLM-Finetune-Guide
This project provides a comprehensive guide to fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) with efficient methods like LoRA and P-tuning V2. It includes detailed instructions, code examples, and performance benchmarks for various LLMs and fine-tuning techniques. The guide also covers data preparation, evaluation, prediction, and running inference on CPU environments. By leveraging this guide, users can effectively fine-tune LLMs for specific tasks and applications.
LLM-Blender
LLM-Blender is a framework for ensembling large language models (LLMs) to achieve superior performance. It consists of two modules: PairRanker and GenFuser. PairRanker uses pairwise comparisons to distinguish between candidate outputs, while GenFuser merges the top-ranked candidates to create an improved output. LLM-Blender has been shown to significantly surpass the best LLMs and baseline ensembling methods across various metrics on the MixInstruct benchmark dataset.
MINI_LLM
This project is a personal implementation and reproduction of a small-parameter Chinese LLM. It mainly refers to these two open source projects: https://github.com/charent/Phi2-mini-Chinese and https://github.com/DLLXW/baby-llama2-chinese. It includes the complete process of pre-training, SFT instruction fine-tuning, DPO, and PPO (to be done). I hope to share it with everyone and hope that everyone can work together to improve it!
LLM-Tuning
LLM-Tuning is a collection of tools and resources for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs). It includes a library of pre-trained LoRA models, a set of tutorials and examples, and a community forum for discussion and support. LLM-Tuning makes it easy to fine-tune LLMs for a variety of tasks, including text classification, question answering, and dialogue generation. With LLM-Tuning, you can quickly and easily improve the performance of your LLMs on downstream tasks.
LLM-FineTuning-Large-Language-Models
This repository contains projects and notes on common practical techniques for fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs). It includes fine-tuning LLM notebooks, Colab links, LLM techniques and utils, and other smaller language models. The repository also provides links to YouTube videos explaining the concepts and techniques discussed in the notebooks.
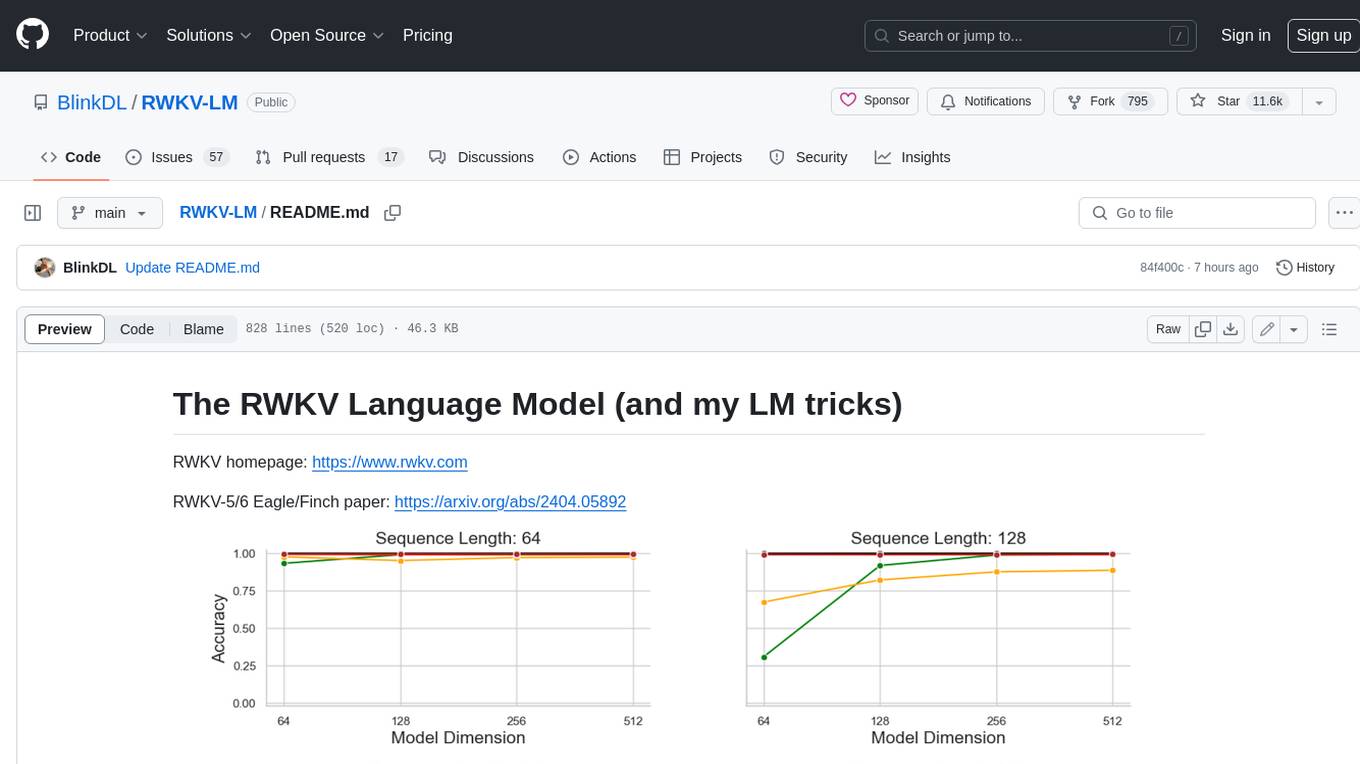
RWKV-LM
RWKV is an RNN with Transformer-level LLM performance, which can also be directly trained like a GPT transformer (parallelizable). And it's 100% attention-free. You only need the hidden state at position t to compute the state at position t+1. You can use the "GPT" mode to quickly compute the hidden state for the "RNN" mode. So it's combining the best of RNN and transformer - **great performance, fast inference, saves VRAM, fast training, "infinite" ctx_len, and free sentence embedding** (using the final hidden state).
awesome-transformer-nlp
This repository contains a hand-curated list of great machine (deep) learning resources for Natural Language Processing (NLP) with a focus on Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), attention mechanism, Transformer architectures/networks, Chatbot, and transfer learning in NLP.
self-llm
This project is a Chinese tutorial for domestic beginners based on the AutoDL platform, providing full-process guidance for various open-source large models, including environment configuration, local deployment, and efficient fine-tuning. It simplifies the deployment, use, and application process of open-source large models, enabling more ordinary students and researchers to better use open-source large models and helping open and free large models integrate into the lives of ordinary learners faster.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.



