
celeste-python
Open source, type-safe primitives for multi-modal AI. All modelities, all providers, one interface 🌟
Stars: 204
Celeste AI is a type-safe, modality/provider-agnostic tool that offers unified interface for various providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Mistral, and more. It supports multiple modalities including text, image, audio, video, and embeddings, with full Pydantic validation and IDE autocomplete. Users can switch providers instantly, ensuring zero lock-in and a lightweight architecture. The tool provides primitives, not frameworks, for clean I/O operations.
README:
The primitive layer for multi-modal AI
All modalities. All providers. One interface.
Primitives, not frameworks.



🚀 This is the v1 Beta release. We're validating the new architecture before the stable v1.0 release. Feedback welcome!
Type-safe, modality/provider-agnostic primitives.
- Unified Interface: One API for OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Mistral, and 14+ others.
- True Multi-Modal: Text, Image, Audio, Video, Embeddings, Search —all first-class citizens.
- Type-Safe by Design: Full Pydantic validation and IDE autocomplete.
- Zero Lock-In: Switch providers instantly by changing a single config string.
- Primitives, Not Frameworks: No agents, no chains, no magic. Just clean I/O.
- Lightweight Architecture: No vendor SDKs. Pure, fast HTTP.
import celeste
# One SDK. Every modality. Any provider.
text = await celeste.text.generate("Explain quantum computing", model="claude-opus-4-5")
image = await celeste.images.generate("A serene mountain lake at dawn", model="flux-2-pro")
speech = await celeste.audio.speak("Welcome to the future", model="eleven_v3")
video = await celeste.videos.analyze(video_file, prompt="Summarize this clip", model="gemini-3-pro")
embeddings = await celeste.text.embed(["lorep ipsum", "dolor sit amet"], model="gemini-embedding-001")| Action | Text | Images | Audio | Video |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generate | ✓ | ✓ | ○ | ✓ |
| Edit | — | ✓ | — | — |
| Analyze | — | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Upscale | — | ○ | — | ○ |
| Speak | — | — | ✓ | — |
| Transcribe | — | — | ✓ | — |
| Embed | ✓ | ○ | — | ○ |
✓ Available · ○ Planned
from pydantic import BaseModel
class User(BaseModel):
name: str
age: int
# Model IDs
anthropic_model_id = "claude-4-5-sonnet"
google_model_id = "gemini-2.5-flash"# ❌ Anthropic Way
from anthropic import Anthropic
import json
client = Anthropic()
response = client.messages.create(
model=anthropic_model_id,
messages=[
{"role": "user",
"content": "Extract user info: John is 30"}
],
output_format={
"type": "json_schema",
"schema": User.model_json_schema()
}
)
user_data = json.loads(response.content[0].text)# ❌ Google Gemini Way
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
response = await client.aio.models.generate_content(
model=gemini_model_id,
contents="Extract user info: John is 30",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
response_mime_type="application/json",
response_schema=User
)
)
user = response.parsed# ✅ Celeste Way
import celeste
response = await celeste.text.generate(
"Extract user info: John is 30",
model=google_model_id, # <--- Choose any model from any provider
output_schema=User, # <--- Unified parameter working across all providers
)
user = response.content # Already parsed as User instanceFor explicit configuration or client reuse, use create_client with modality + operation. This is modality-first: you choose the output type and operation explicitly.
from celeste import create_client, Modality, Operation, Provider
client = create_client(
modality=Modality.TEXT,
operation=Operation.GENERATE,
provider=Provider.OLLAMA,
model="llama3.2",
)
response = await client.generate("Extract user info: John is 30", output_schema=User)
capabilityis still supported but deprecated. Prefermodality+operation.
uv add celeste-ai
# or
pip install celeste-ai# Full IDE autocomplete
import celeste
response = await celeste.text.generate(
"Explain AI",
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0.7, # ✅ Validated (0.0-2.0)
max_tokens=100, # ✅ Validated (int)
)
# Typed response
print(response.content) # str (IDE knows the type)
print(response.usage.input_tokens) # int
print(response.metadata["model"]) # strCatch errors before production.
We welcome contributions! See CONTRIBUTING.md.
Request a provider: GitHub Issues Report bugs: GitHub Issues
MIT license – see LICENSE for details.
Get Started • Documentation • GitHub
Made with ❤️ by developers tired of framework lock-in
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for celeste-python
Similar Open Source Tools

celeste-python
Celeste AI is a type-safe, modality/provider-agnostic tool that offers unified interface for various providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Mistral, and more. It supports multiple modalities including text, image, audio, video, and embeddings, with full Pydantic validation and IDE autocomplete. Users can switch providers instantly, ensuring zero lock-in and a lightweight architecture. The tool provides primitives, not frameworks, for clean I/O operations.
Conduit
Conduit is a unified Swift 6.2 SDK for local and cloud LLM inference, providing a single Swift-native API that can target Anthropic, OpenRouter, Ollama, MLX, HuggingFace, and Apple’s Foundation Models without rewriting your prompt pipeline. It allows switching between local, cloud, and system providers with minimal code changes, supports downloading models from HuggingFace Hub for local MLX inference, generates Swift types directly from LLM responses, offers privacy-first options for on-device running, and is built with Swift 6.2 concurrency features like actors, Sendable types, and AsyncSequence.
zeroclaw
ZeroClaw is a fast, small, and fully autonomous AI assistant infrastructure built with Rust. It features a lean runtime, cost-efficient deployment, fast cold starts, and a portable architecture. It is secure by design, fully swappable, and supports OpenAI-compatible provider support. The tool is designed for low-cost boards and small cloud instances, with a memory footprint of less than 5MB. It is suitable for tasks like deploying AI assistants, swapping providers/channels/tools, and pluggable everything.
GraphGen
GraphGen is a framework for synthetic data generation guided by knowledge graphs. It enhances supervised fine-tuning for large language models (LLMs) by generating synthetic data based on a fine-grained knowledge graph. The tool identifies knowledge gaps in LLMs, prioritizes generating QA pairs targeting high-value knowledge, incorporates multi-hop neighborhood sampling, and employs style-controlled generation to diversify QA data. Users can use LLaMA-Factory and xtuner for fine-tuning LLMs after data generation.
dexto
Dexto is a lightweight runtime for creating and running AI agents that turn natural language into real-world actions. It serves as the missing intelligence layer for building AI applications, standalone chatbots, or as the reasoning engine inside larger products. Dexto features a powerful CLI and Web UI for running AI agents, supports multiple interfaces, allows hot-swapping of LLMs from various providers, connects to remote tool servers via the Model Context Protocol, is config-driven with version-controlled YAML, offers production-ready core features, extensibility for custom services, and enables multi-agent collaboration via MCP and A2A.
llm_model_hub
Model Hub V2 is a one-stop platform for model fine-tuning, deployment, and debugging without code, providing users with a visual interface to quickly validate the effects of fine-tuning various open-source models, facilitating rapid experimentation and decision-making, and lowering the threshold for users to fine-tune large models. For detailed instructions, please refer to the Feishu documentation.
actor-core
Actor-core is a lightweight and flexible library for building actor-based concurrent applications in Java. It provides a simple API for creating and managing actors, as well as handling message passing between actors. With actor-core, developers can easily implement scalable and fault-tolerant systems using the actor model.
tokscale
Tokscale is a high-performance CLI tool and visualization dashboard for tracking token usage and costs across multiple AI coding agents. It helps monitor and analyze token consumption from various AI coding tools, providing real-time pricing calculations using LiteLLM's pricing data. Inspired by the Kardashev scale, Tokscale measures token consumption as users scale the ranks of AI-augmented development. It offers interactive TUI mode, multi-platform support, real-time pricing, detailed breakdowns, web visualization, flexible filtering, and social platform features.
headroom
Headroom is a tool designed to optimize the context layer for Large Language Models (LLMs) applications by compressing redundant boilerplate outputs. It intercepts context from tool outputs, logs, search results, and intermediate agent steps, stabilizes dynamic content like timestamps and UUIDs, removes low-signal content, and preserves original data for retrieval only when needed by the LLM. It ensures provider caching works efficiently by aligning prompts for cache hits. The tool works as a transparent proxy with zero code changes, offering significant savings in token count and enabling reversible compression for various types of content like code, logs, JSON, and images. Headroom integrates seamlessly with frameworks like LangChain, Agno, and MCP, supporting features like memory, retrievers, agents, and more.
alphora
Alphora is a full-stack framework for building production AI agents, providing agent orchestration, prompt engineering, tool execution, memory management, streaming, and deployment with an async-first, OpenAI-compatible design. It offers features like agent derivation, reasoning-action loop, async streaming, visual debugger, OpenAI compatibility, multimodal support, tool system with zero-config tools and type safety, prompt engine with dynamic prompts, memory and storage management, sandbox for secure execution, deployment as API, and more. Alphora allows users to build sophisticated AI agents easily and efficiently.
Rankify
Rankify is a Python toolkit designed for unified retrieval, re-ranking, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) research. It integrates 40 pre-retrieved benchmark datasets and supports 7 retrieval techniques, 24 state-of-the-art re-ranking models, and multiple RAG methods. Rankify provides a modular and extensible framework, enabling seamless experimentation and benchmarking across retrieval pipelines. It offers comprehensive documentation, open-source implementation, and pre-built evaluation tools, making it a powerful resource for researchers and practitioners in the field.
evalplus
EvalPlus is a rigorous evaluation framework for LLM4Code, providing HumanEval+ and MBPP+ tests to evaluate large language models on code generation tasks. It offers precise evaluation and ranking, coding rigorousness analysis, and pre-generated code samples. Users can use EvalPlus to generate code solutions, post-process code, and evaluate code quality. The tool includes tools for code generation and test input generation using various backends.
exstruct
ExStruct is an Excel structured extraction engine that reads Excel workbooks and outputs structured data as JSON, including cells, table candidates, shapes, charts, smartart, merged cell ranges, print areas/views, auto page-break areas, and hyperlinks. It offers different output modes, formula map extraction, table detection tuning, CLI rendering options, and graceful fallback in case Excel COM is unavailable. The tool is designed to fit LLM/RAG pipelines and provides benchmark reports for accuracy and utility. It supports various formats like JSON, YAML, and TOON, with optional extras for rendering and full extraction targeting Windows + Excel environments.
llamafarm
LlamaFarm is a comprehensive AI framework that empowers users to build powerful AI applications locally, with full control over costs and deployment options. It provides modular components for RAG systems, vector databases, model management, prompt engineering, and fine-tuning. Users can create differentiated AI products without needing extensive ML expertise, using simple CLI commands and YAML configs. The framework supports local-first development, production-ready components, strategy-based configuration, and deployment anywhere from laptops to the cloud.
openlrc
Open-Lyrics is a Python library that transcribes voice files using faster-whisper and translates/polishes the resulting text into `.lrc` files in the desired language using LLM, e.g. OpenAI-GPT, Anthropic-Claude. It offers well preprocessed audio to reduce hallucination and context-aware translation to improve translation quality. Users can install the library from PyPI or GitHub and follow the installation steps to set up the environment. The tool supports GUI usage and provides Python code examples for transcription and translation tasks. It also includes features like utilizing context and glossary for translation enhancement, pricing information for different models, and a list of todo tasks for future improvements.
agentscope
AgentScope is a multi-agent platform designed to empower developers to build multi-agent applications with large-scale models. It features three high-level capabilities: Easy-to-Use, High Robustness, and Actor-Based Distribution. AgentScope provides a list of `ModelWrapper` to support both local model services and third-party model APIs, including OpenAI API, DashScope API, Gemini API, and ollama. It also enables developers to rapidly deploy local model services using libraries such as ollama (CPU inference), Flask + Transformers, Flask + ModelScope, FastChat, and vllm. AgentScope supports various services, including Web Search, Data Query, Retrieval, Code Execution, File Operation, and Text Processing. Example applications include Conversation, Game, and Distribution. AgentScope is released under Apache License 2.0 and welcomes contributions.
For similar tasks

HPT
Hyper-Pretrained Transformers (HPT) is a novel multimodal LLM framework from HyperGAI, trained for vision-language models capable of understanding both textual and visual inputs. The repository contains the open-source implementation of inference code to reproduce the evaluation results of HPT Air on different benchmarks. HPT has achieved competitive results with state-of-the-art models on various multimodal LLM benchmarks. It offers models like HPT 1.5 Air and HPT 1.0 Air, providing efficient solutions for vision-and-language tasks.
learnopencv
LearnOpenCV is a repository containing code for Computer Vision, Deep learning, and AI research articles shared on the blog LearnOpenCV.com. It serves as a resource for individuals looking to enhance their expertise in AI through various courses offered by OpenCV. The repository includes a wide range of topics such as image inpainting, instance segmentation, robotics, deep learning models, and more, providing practical implementations and code examples for readers to explore and learn from.
spark-free-api
Spark AI Free 服务 provides high-speed streaming output, multi-turn dialogue support, AI drawing support, long document interpretation, and image parsing. It offers zero-configuration deployment, multi-token support, and automatic session trace cleaning. It is fully compatible with the ChatGPT interface. The repository includes multiple free-api projects for various AI services. Users can access the API for tasks such as chat completions, AI drawing, document interpretation, image analysis, and ssoSessionId live checking. The project also provides guidelines for deployment using Docker, Docker-compose, Render, Vercel, and native deployment methods. It recommends using custom clients for faster and simpler access to the free-api series projects.
mlx-vlm
MLX-VLM is a package designed for running Vision LLMs on Mac systems using MLX. It provides a convenient way to install and utilize the package for processing large language models related to vision tasks. The tool simplifies the process of running LLMs on Mac computers, offering a seamless experience for users interested in leveraging MLX for vision-related projects.
clarifai-python-grpc
This is the official Clarifai gRPC Python client for interacting with their recognition API. Clarifai offers a platform for data scientists, developers, researchers, and enterprises to utilize artificial intelligence for image, video, and text analysis through computer vision and natural language processing. The client allows users to authenticate, predict concepts in images, and access various functionalities provided by the Clarifai API. It follows a versioning scheme that aligns with the backend API updates and includes specific instructions for installation and troubleshooting. Users can explore the Clarifai demo, sign up for an account, and refer to the documentation for detailed information.
horde-worker-reGen
This repository provides the latest implementation for the AI Horde Worker, allowing users to utilize their graphics card(s) to generate, post-process, or analyze images for others. It offers a platform where users can create images and earn 'kudos' in return, granting priority for their own image generations. The repository includes important details for setup, recommendations for system configurations, instructions for installation on Windows and Linux, basic usage guidelines, and information on updating the AI Horde Worker. Users can also run the worker with multiple GPUs and receive notifications for updates through Discord. Additionally, the repository contains models that are licensed under the CreativeML OpenRAIL License.
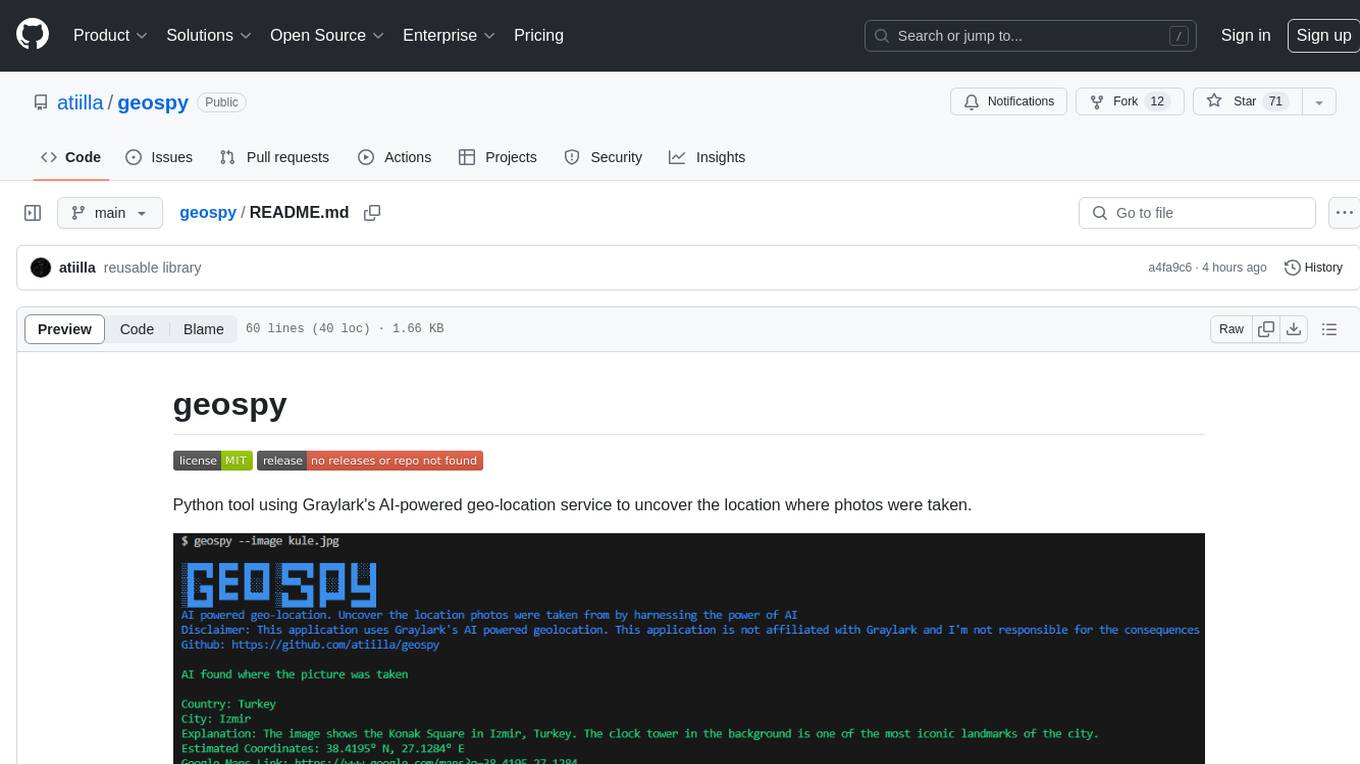
geospy
Geospy is a Python tool that utilizes Graylark's AI-powered geolocation service to determine the location where photos were taken. It allows users to analyze images and retrieve information such as country, city, explanation, coordinates, and Google Maps links. The tool provides a seamless way to integrate geolocation services into various projects and applications.
Awesome-Colorful-LLM
Awesome-Colorful-LLM is a meticulously assembled anthology of vibrant multimodal research focusing on advancements propelled by large language models (LLMs) in domains such as Vision, Audio, Agent, Robotics, and Fundamental Sciences like Mathematics. The repository contains curated collections of works, datasets, benchmarks, projects, and tools related to LLMs and multimodal learning. It serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in exploring the intersection of language models and various modalities for tasks like image understanding, video pretraining, 3D modeling, document understanding, audio analysis, agent learning, robotic applications, and mathematical research.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.


